2.10. Configuring MPLS and RSVP with CLI
This section provides information to configure MPLS and RSVP using the command line interface.
2.11. MPLS Configuration Overview
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) enables routers to forward traffic based on a simple label embedded into the packet header. A router examines the label to determine the next hop for the packet, saving time for router address lookups to the next node when forwarding packets. MPLS is not enabled by default and must be explicitly enabled.
2.11.1. LSPs
To configure MPLS-signaled label-switched paths (LSPs), an LSP must run from an ingress router to an egress router. Configure only the ingress router and configure LSPs to allow the software to make the forwarding decisions or statically configure some or all routers in the path. The LSP is set up by Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP), through RSVP signaling messages. The 7210 SAS automatically manages label values. Labels that are automatically assigned have values ranging from 1,024 through 1,048,575 (see Label Values).
A static LSP is a manually set up LSP where the next-hop IP address and the outgoing label are explicitly specified.
2.11.2. Paths
To configure signaled LSPs, you must first create one or more named paths on the ingress router. For each path, the transit routers (hops) in the path are specified.
2.11.3. Router Interface
At least one router interface and one system interface must be defined in the config>router>interface context in order to configure MPLS on an interface.
2.11.4. Choosing the Signaling Protocol
If only static label switched paths are used in your configurations, then you must manually define the paths through the MPLS network. Label mappings and actions configured at each hop must be specified. You do not need to enable RSVP if you are configuring static LSPs.
If dynamic LSP signaling is implemented in your network, then RSVP must be specified. Enable signaling protocols only on the links where the functionality is required.
In order to implement MPLS, the following entities must be enabled:
- MPLS must be enabled on all routers that are part of an LSP.
- RSVP must be enabled on the same routers.
When MPLS is enabled and either RSVP is also enabled, MPLS uses RSVP to set up the configured LSPs. For example, when you configure an LSP with both MPLS and RSVP running, RSVP initiates a session for the LSP. RSVP uses the local router as the RSVP session sender and the LSP destination as the RSVP session receiver. When the RSVP session is created, the LSP is set up on the path created by the session. If the session is not successfully created, RSVP notifies MPLS, MPLS can then either initiate backup paths or retry the initial path.
2.12. Basic MPLS Configuration
This section provides information to configure MPLS and provides configuration examples of common configuration tasks. To enable MPLS on the 7210 SAS, you must configure at least one MPLS interface. The other MPLS configuration parameters are optional. The following is an example of an MPLS configuration.
The admin-group is configured in the config>router>if-attribute context and associated with the MPLS interface in the config>router>mpls>interface context.
2.13. Common Configuration Tasks
This section provides a brief overview of the tasks to configure MPLS and provides the CLI commands.
The following protocols must be enabled on each participating router.
- MPLS
- RSVP (for RSVP-signaled MPLS only)
- LDP
In order for MPLS to run, you must configure at least one MPLS interface in the config>router>mpls context.
- An interface must be created in the config>router>interface context before it can be applied to MPLS.
- In the config>router>mpls context, configure path parameters for configuring LSP parameters. A path specifies some or all hops from ingress to egress. A path can be used by multiple LSPs.
- When an LSP is created, the egress router must be specified in the to command and at least one primary or secondary path must be specified. All other statements under the LSP hierarchy are optional.
2.13.1. Configuring Global MPLS Parameters
Admin groups signify link colors, such as red, yellow, or green. MPLS interfaces advertise the link colors that they support. CSPF uses the information when paths are computed for constraint-based LSPs. CSPF must be enabled in order for admin groups to be relevant.
Use the following syntax to configure MPLS admin-group parameters.
The following is a sample admin group configuration output.
2.13.2. Configuring an MPLS Interface
Configure the label-map parameters if the interface is used in a static LSP. Use the following syntax to configure an MPLS interface on a router.
The following is a sample interface configuration output.
2.13.3. Configuring MPLS Paths
Configure an LSP path to use in MPLS. When configuring an LSP, the IP address of the hops that the LSP should traverse on its way to the egress router must be specified. The intermediate hops must be configured as either strict or loose meaning that the LSP must take either a direct path from the previous hop router to this router (strict) or can traverse through other routers (loose).
Use the following syntax to configure a path.
The following is a sample path configuration output.
2.13.4. Configuring an MPLS LSP
Configure an LSP path for MPLS. When configuring an LSP, you must specify the IP address of the egress router in the to statement. Specify the primary path to be used. Secondary paths can be explicitly configured or signaled upon the failure of the primary path. All other statements are optional.
The following is a sample MPLS LSP configuration output.
2.13.4.1. Configuring a Static LSP
An LSP can be explicitly (statically) configured. Static LSPs are configured on every node along the path. The label’s forwarding information includes the address of the next hop router.
Use the following syntax to configure a static LSP.
The following is a sample static LSP configuration output.
2.13.5. Configuring Manual Bypass Tunnels
Consider the network setup in Figure 28 that shows nodes A through F.
Figure 28: Manual Bypass Tunnels
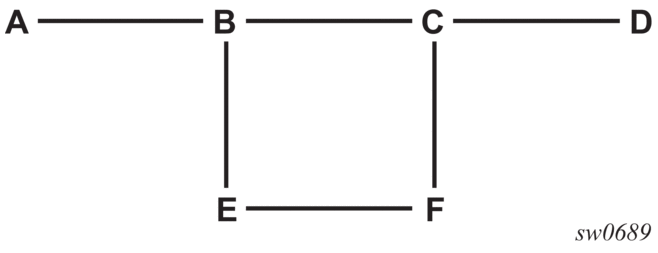
The user first configures the option to disable the dynamic bypass tunnels.
Listed below are the steps to configure the manual bypass tunnels:
- Configure the option to disable the dynamic bypass tunnels on the 7210 SAS node B (if required). The CLI for this configuration is: config>router>mpls>dynamic-bypass [disable | enable] The dynamic bypass tunnels are enabled by default.
- Configure an LSP on node B, such as B-E-F-C which is used only as bypass. The user specifies each hop in the path, for example, the bypass LSP has a strict path.
Including the bypass-only keyword disables the following options under the LSP configuration:
- bandwidth
- fast-reroute
- secondary
The following LSP configuration options are allowed:
- adaptive
- adspec
- cspf
- exclude
- hop-limit
- include
- metric
The following is a sample bypass tunnel configuration output.
- Configure an LSP from A to D and indicate fast-reroute bypass protection, select the facility as “FRR method”. (config>router>mpls>lsp>fast-reroute facility). Observe if the following criteria apply:
- If the LSP passes through B
- A bypass is requested
- The next hop is C
- A manually configured bypass-only tunnel exists from B to C (excluding link B to C)
Result: Node B uses the manually configured bypass-only tunnel from B to C.
2.14. Configuring RSVP Parameters
RSVP is used to set up LSPs. RSVP must be enabled on the router interfaces that are participating in signaled LSPs. The keep-multiplier and refresh-time default values can be modified in the RSVP context.
Initially, interfaces are configured in the config>router>mpls>interface context. Only these existing (MPLS) interfaces are available to modify in the config>router> rsvp context. Interfaces cannot be directly added in the RSVP context.
The following is a sample RSVP configuration output.
2.14.1. Configuring RSVP Message Pacing Parameters
RSVP message pacing maintains a count of the messages that were dropped because the output queue for the egress interface was full.
Use the following syntax to configure RSVP parameters.
The following is a sample RSVP message pacing configuration output.
2.14.2. Configuring Graceful Shutdown
Enable TE graceful shutdown on the maintenance interface using the config>router>rsvp>interface>graceful-shutdown command.
Disable graceful shutdown by executing the no form of the command at the RSVP interface level or at the RSVP level. This restores the user-configured TE parameters of the maintenance links, and the 7210 SAS maintenance node floods them.
2.15. MPLS Configuration Management Tasks
This section describes the MPLS configuration management tasks.
2.15.1. Modifying MPLS Parameters
| Note: You must shut down MPLS entities in order to modify parameters. Re-enable (no shutdown) the entity for the change to take effect. |
2.15.2. Modifying an MPLS LSP
Some MPLS LSP parameters such as primary and secondary, must be shut down before they can be edited or deleted from the configuration.
The following is a sample MPLS LSP configuration output.
2.15.3. Modifying MPLS Path Parameters
In order to modify path parameters, the config>router>mpls>path context must be shut down first.
The following is a sample path configuration output.
2.15.4. Modifying MPLS Static LSP Parameters
In order to modify static LSP parameters, the config>router>mpls>path context must be shut down first.
The following is a sample static LSP configuration output.
2.15.5. Deleting an MPLS Interface
In order to delete an interface from the MPLS configuration, the interface must be shut down first.
Use the following syntax to delete an interface from the MPLS configuration.
2.16. RSVP Configuration Management Tasks
This section describes the RSVP configuration management tasks.
2.16.1. Modifying RSVP Parameters
Only interfaces configured in the MPLS context can be modified in the RSVP context.
The no rsvp command deletes this RSVP protocol instance and removes all configuration parameters for this RSVP instance. The shutdown command suspends the execution and maintains the existing configuration.
The following example displays a modified RSVP configuration example:
2.16.2. Modifying RSVP Message Pacing Parameters
RSVP message pacing maintains a count of the messages that were dropped because the output queue for the egress interface was full.
The following is a sample modified RSVP message pacing configuration output.
2.16.3. Deleting an Interface from RSVP
Interfaces cannot be deleted directly from the RSVP configuration. An interface must have been configured in the MPLS context and then the RSVP context. The interface must first be deleted from the MPLS context. This removes the association from RSVP.
See Deleting an MPLS Interface for information on deleting an MPLS interface.