3. Filter policies
This chapter provides information about filter policies and management.
3.1. Filter policy configuration overview
Filter policies, also referred to as Access Control Lists (ACLs), are templates applied to services or access uplink ports to control network traffic into (ingress) or out of (egress) a service access port (SAP) or access uplink based on IP and MAC matching criteria. Filters are applied to services to look at packets entering or leaving a SAP. Filters can be used on several interfaces. The same filter can be applied to ingress traffic, egress traffic, or both. Ingress filters affect only inbound traffic destined for the routing complex, and egress filters affect only outbound traffic sent from the routing complex.
Configuring an entity with a filter policy is optional. If an entity such as a service is not configured with filter policies, then all traffic is allowed on the ingress and egress interfaces. By default, there are no filters associated with services or interfaces. They must be explicitly created and associated. When you create a new filter, default values are provided although you must specify a unique filter ID value to each new filter policy as well as each new filter entry and associated actions. The filter entries specify the filter matching criteria and also an action to be taken upon a match.
In 7210 SAS platforms, the available ingress and egress (egress CAM resources allocation is supported only on 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp) CAM hardware resources can be allocated as per user needs for use with different filter criteria. By default on the 7210 SAS-D, the system allocates resources to maintain backward compatibility with release 4.0.
Users can modify the resource allocation based on their need to scale the number of entries or number of associations (that is, number of SAP/IP interfaces using a filter policy that defines particular match criteria). If no CAM resources are allocated to particular match criteria defined in a filter policy, then the association of that filter policy to a SAP will fail. This is true for both ingress and egress filter policy. Please read the following configuration notes section for more information.
Only one ingress IP or MAC filter policy and one egress IP or MAC filter policy can be applied to a Layer 2 SAP. For the 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C, both IPv4 and IPv6 ingress and egress filter policy can be used simultaneously with a Layer 2 SAP. For the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp, both IPv4 and IPv6 filter policies can be used simultaneously on ingress only; either IPv4 or IPv6 filter policies can be used on egress.
Only one ingress IP filter policy and one egress IP filter policy can be applied to a network IP interface. Both IPv4 and IPv6 ingress and egress filter policy can be used simultaneously with an IP interface (For example: IES IP interface in access-uplink mode in 7210 SAS-D) for which IPv6 addressing is supported. Network filter policies control the forwarding and dropping of packets based on IP match criteria.
| Note: Non-IP packets are not hitting the IP filter policy, so the default action in the filter policy will not apply to these packets. |
3.1.1. Service-based filtering
IP and MAC filter policies specify either a forward or a drop action for packets based on information specified in the match criteria.
Filter entry matching criteria can be as general or specific as you require, but all conditions in the entry must be met in order for the packet to be considered a match and the specified entry action performed. The process stops when the first complete match is found and executes the action defined in the entry, either to drop or forward packets that match the criteria.
3.1.2. Filter policy entities
A filter policy compares the match criteria specified within a filter entry to packets coming through the system, in the order the entries are numbered in the policy. When a packet matches all the parameters specified in the entry, the system takes the specified action to either drop or forward the packet. If a packet does not match the entry parameters, the packet continues through the filter process and is compared to the next filter entry, and so on. If the packet does not match any of the entries, then system executes the default action specified in the filter policy. Each filter policy is assigned a unique filter ID. Each filter policy is defined with the following:
- scope
- default action
- description
Each filter entry contains the following:
- match criteria
- an action
3.1.2.1. Applying filter policies
Filter policies can be applied to specific service types:
- EpipeBoth MAC and IP filters are supported on an Epipe SAP.
- IESOnly IP filters are supported on IES SAP
- VPLSBoth MAC and IP filters are supported on a VPLS SAP.
- VPRNOnly IP filters are supported on VPRN SAP.
The following tables describe the support of filter policies on 7210 SAS platforms.
Table 35: Applying filter policies for 7210 SAS-D, 7210 SAS-Dxp, and 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T
Service | IPv4 filter | IPv6 filter | MAC filter |
Epipe | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) |
VPLS | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) |
RVPLS (VPLS SAPs) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Not supported | Not supported |
RVPLS (RVPLS IES IP Interface) | Ingress Override filters (ingress) | Not supported | Not supported |
IES | IES access SAP (ingress and egress), IES access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | IES access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Not supported |
Table 36: Applying filter policies for 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C
Service | IPv4 filter | IPv6 filter | MAC filter |
Epipe | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Epipe access SAP (ingress and egress), Epipe access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) |
VPLS | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) |
RVPLS (VPLS SAPs) | VPLS access SAP (ingress and egress), VPLS access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Not supported | Not supported |
RVPLS (RVPLS IES IP Interface) | Ingress Override filters (ingress) | Not supported | Not supported |
IES | IES access SAP (ingress and egress), IES access-uplink SAP (ingress and egress) | Not supported | Not supported |
VPRN | VPRN interface SAP (ingress and egress) | Not supported | Not supported |
Network port IP interface | Network port IP interface (ingress and egress) | Not supported | Not supported |
3.1.2.2. ACL on range SAPs
The ACLs on VLAN range SAPs are supported only on ingress (for Epipe and VPLS services). The following table lists ACL support on Epipe and VPLAS services.
Table 37: Applying ACLs support on Epipe and VPLS services on 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C variants when using range SAPs
Types of filters | Epipe | VPLS |
Ingress IP or IPv6 | Yes | Yes |
Ingress MAC | Yes | Yes |
Egress IP | Yes | Yes |
Egress MAC | Yes | Yes |
Filter policies are applied to the following service entities:
- SAP ingressIP and MAC filter policies applied on the SAP ingress define the Service Level Agreement (SLA) enforcement of service packets as they ingress a SAP according to the filter policy match criteria. SAP ingress policies can be applied on SAP created on access ports or access uplink ports.
- SAP egressFilter policies applied on SAP egress define the Service Level Agreement (SLA) enforcement for service packets as they egress on the SAP according to the filter policy match criteria. SAP egress policies can be applied on both access ports and access uplink ports.
- IES IP interfacesIP filter policies are applied to IES SAPs.
- network ingressIP filter policies are applied to network ingress IP interfaces. This is supported only on 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C.
- network egressIP filter policies are applied to network egress IP interfaces. This is supported only on 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C.
The following table lists the Packet Fields available for match in QoS classification policy and ACL policy for different SAPs.
Table 38: Packet fields for match in QoS classification policy and ACL policy
Ingress SAP type | Packet contents (only Ethernet–II frames) | MAC address match | Inner VLAN ID and Dot1p match 1 | Outer VLAN ID and Dot1p match 1 | Etype match | IPv4/IPv6 criteria match |
NULL SAP | Null tag | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
Dot1q SAP (includes Dot1q explicit null SAP and Dot1q Default SAP) | Null tag | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
Dot1q SAP (includes Dot1q SAP, Dot1q range SAP) | Null tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
QinQ SAP - 0.* SAP (matches only null and priority tag packets) | Null tag | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Single tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Two tags | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Three or more tags | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
QinQ SAP (*.* Default QinQ SAP) | Null tag | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
QinQ SAP (includes Q1.* SAP) | Null tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
QinQ SAP (includes Q1.0 SAP) | Null tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Single tag | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags (inner tag is a priority tag) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Two tags (inner tag is not a priority tag) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
QinQ SAP (includes Q1.Q2 SAP) | Null tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid |
Priority tag (both VID and Dot1p) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Single tag | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Two tags (inner tag is a priority tag) | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | Invalid | |
Two tags (inner tag is not a priority tag) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Three or more tags | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
- VLAN tag matching is supported only on 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C.
Note:
3.2. Creating and applying filter policies
The following figure shows the steps for creating and applying filter policies.
Figure 4: Creating and applying filter policies

3.2.1. Packet matching criteria
As few or as many match parameters can be specified as required, but all conditions must be met in order for the packet to be considered a match and the specified action performed. The process stops when the first complete match is found and then executes the action defined in the entry, either to drop or forward packets that match the criteria.
IP filter policies match criteria that associate traffic with an ingress or egress SAP. Matching criteria to drop or forward IP traffic include:
- Source IP address and maskSource IP address and mask values can be entered as search criteria. The IPv4 addressing scheme consists of 32 bits expressed in dotted decimal notation (X.X.X.X).Address ranges are configured by specifying mask values, the 32-bit combination used to describe the address portion which refers to the subnet and which portion refers to the host. The mask length is expressed as an integer (range 1 to 32).The IPv6 addressing scheme consists of 128 bits expressed in compressed representation of IPv6 addresses (RFC 1924, A Compact Representation of IPv6 Addresses).
- 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C, 7210 SAS-D, and 7210 SAS-Dxp support the use of either IPv6 64-bit address match or IPv6 128-bit address match. Use of IPv6 64-bit address in the match criteria provides better scale but provides lesser IPv6 header fields for match criteria. Use of a IPv6 128-bit address in the match criteria provides lesser scale but more IPv6 header fields for match criteria.
- Destination IP address and maskDestination IP address and mask values can be entered as search criteria. A choice similar to that available for source IPv6 addresses is also available for destination IPv6 addresses.
- ProtocolEntering a protocol ID (such as TCP, UDP, etc.) allows the filter to search for the protocol specified in this field.
- ProtocolFor IPv6: entering a next header allows the filter to match the first next header following the IPv6 header.
- Source portEntering the source port number allows the filter to search for matching TCP or UDP port values.
- Destination portEntering the destination port number allows the filter to search for matching TCP or UDP.
- DSCP markingEntering a DSCP marking enables the filter to search for the DSCP marking specified in this field. See DSCP name to DSCP value table.
- ICMP codeEntering an ICMP code allows the filter to search for matching ICMP codes in the ICMP header.
- ICMP typeEntering an ICMP type allows the filter to search for matching ICMP types in the ICMP header.
- Extension header presentEnabling this match criterion allows matching of IPv6 packets that have any of the well-known extension headers in the IPv6 header. This match criterion is not supported for IPv6 filters on 7210 SAS-Dxp.
- IPv4 filters created in the mode to use IPv6 resources cannot be applied at the egress SAP. Similarly, IPv4 filters created in the mode to use IPv6 resources will fail to match fragment options.
- FragmentationEnabling fragmentation allows matches to occurs if packets have either the more fragment (MF) bit set or have the Fragment Offset field of the IP header set to a non-zero value.
- Option presentEnabling the option presence allows the filter to search for presence or absence of IP options in the packet. Padding and EOOL are also considered as IP options.
- TCP-ACK/SYN flagsEntering a TCP-SYN/TCP-ACK flag allows the filter to search for the TCP flags specified in these fields.
MAC filter policies match criteria that associate traffic with an ingress or egress SAP. Matching criteria to drop or forward MAC traffic include:
- Source MAC address and maskEntering the source MAC address range allows the filter to search for matching a source MAC address and/or range. Enter the source MAC address and mask in the form of xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx; for example, 00:dc:98:1d:00:00.
- Destination MAC address and maskEntering the destination MAC address range allows the filter to search for matching a destination MAC address and/or range. Enter the destination MAC address and mask in the form of xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx; for example, 02:dc:98:1d:00:01.
- Dot1p and maskEntering an IEEE 802.1p value or range allows the filter to search for matching 802.1p frame. The Dot1p and mask accepts decimal, hex, or binary in the range of 0 to 7. This is not supported on 7210 SAS-K devices.
- EthertypeEntering an Ethernet type II Ethertype value to be used as a filter match criterion. The Ethernet type field is a two-byte field used to identify the protocol carried by the Ethernet frame. The Ethertype accepts decimal, hex, or binary in the range of 1536 to 65535.
- Outer Dot1p (Only on 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C)Entering the Outer Dot1p value or range (using the mask) allows the filter to search for frames whose outermost Dot1p (that is, the Dot1p in the outermost VLAN tag of the packet) matches the Dot1p value configured. The Dot1p value and mask accepts decimal values in the range 0 to 7.
- Inner Outer Dot1p (Only on 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C)Entering the Inner Dot1p value or range (using the mask) allows the filter to search for frames whose inner Dot1p (thats is, the Dot1p in the VLAN tag immediately following the outermost VLAN tag of the packet) matches the Dot1p value configured. The Dot1p value and mask accepts decimal values in the range 0 to 7.
3.2.1.1. DSCP values
The following table describes DSCP names and associated DSCP values.
Table 39: DSCP name to DSCP value table
DSCP name | Decimal DSCP value | Hexadecimal DSCP value | Binary DSCP value |
default | 0 | * | |
cp1 | 1 | ||
cp2 | 2 | ||
cp3 | 3 | ||
cp4 | 4 | ||
cp5 | 5 | ||
cp6 | 6 | ||
cp7 | 7 | * | |
cs1 | 8 | ||
cp9 | 9 | ||
af11 | 11 | * | |
af12 | 12 | * | |
cp13 | 13 | ||
cp15 | 15 | ||
cs2 | 16 | * | |
cp17 | 17 | ||
af21 | 18 | * | |
cp19 | 19 | ||
af22 | 20 | * | |
cp21 | 21 | ||
af23 | 22 | * | |
cp23 | 23 | ||
cs3 | 24 | * | |
cp25 | 25 | ||
af31 | 26 | * | |
cp27 | 27 | ||
af32 | 28 | * | |
cp29 | 29 | ||
af33 | 30 | * | |
cp21 | 31 | ||
cs4 | 32 | * | |
cp33 | 33 | ||
af41 | 34 | * | |
cp35 | 35 | ||
af42 | 36 | * | |
cp37 | 37 | ||
af43 | 38 | * | |
cp39 | 39 | ||
cs5 | 40 | * | |
cp41 | 41 | ||
cp42 | 42 | ||
cp43 | 43 | ||
cp44 | 44 | ||
cp45 | 45 | ||
ef | 46 | * | |
cp47 | 47 | ||
nc1 | 48 | * | (cs6) |
cp49 | 49 | ||
cp50 | 50 | ||
cp51 | 51 | ||
cp52 | 52 | ||
cp53 | 53 | ||
cp54 | 54 | ||
cp55 | 55 | ||
cp56 | 56 | ||
cp57 | 57 | ||
nc2 | 58 | * | (cs7) |
cp60 | 60 | ||
cp61 | 61 | ||
cp62 | 62 |
3.2.2. Ordering filter entries
When entries are created, they should be arranged sequentially from the most explicit entry to the least explicit. Filter matching ceases when a packet matches an entry. The entry action is performed on the packet. 7210 SAS supports either drop or forward action.To be considered a match, the packet must meet all the conditions defined in the entry.
Packets are compared to entries in a filter policy in an ascending entry ID order. To reorder entries in a filter policy, edit the entry ID value; for example, to reposition entry ID 6 to a more explicit location, change the entry ID 6 value to entry ID 2.
When a filter consists of a single entry, the filter executes actions as follows:
- If a packet matches all the entry criteria, the entry’s specified action is performed (drop or forward).
- If a packet does not match all of the entry criteria, the policy’s default action is performed.
If a filter policy contains two or more entries, packets are compared in ascending entry ID order (1, 2, 3 or 10, 20, 30, etc.):
- Packets are compared with the criteria in the first entry ID.
- If a packet matches all the properties defined in the entry, the entry’s specified action is executed.
- If a packet does not completely match, the packet continues to the next entry, and then subsequent entries.
- If a packet does not completely match any subsequent entries, then the default action is performed.
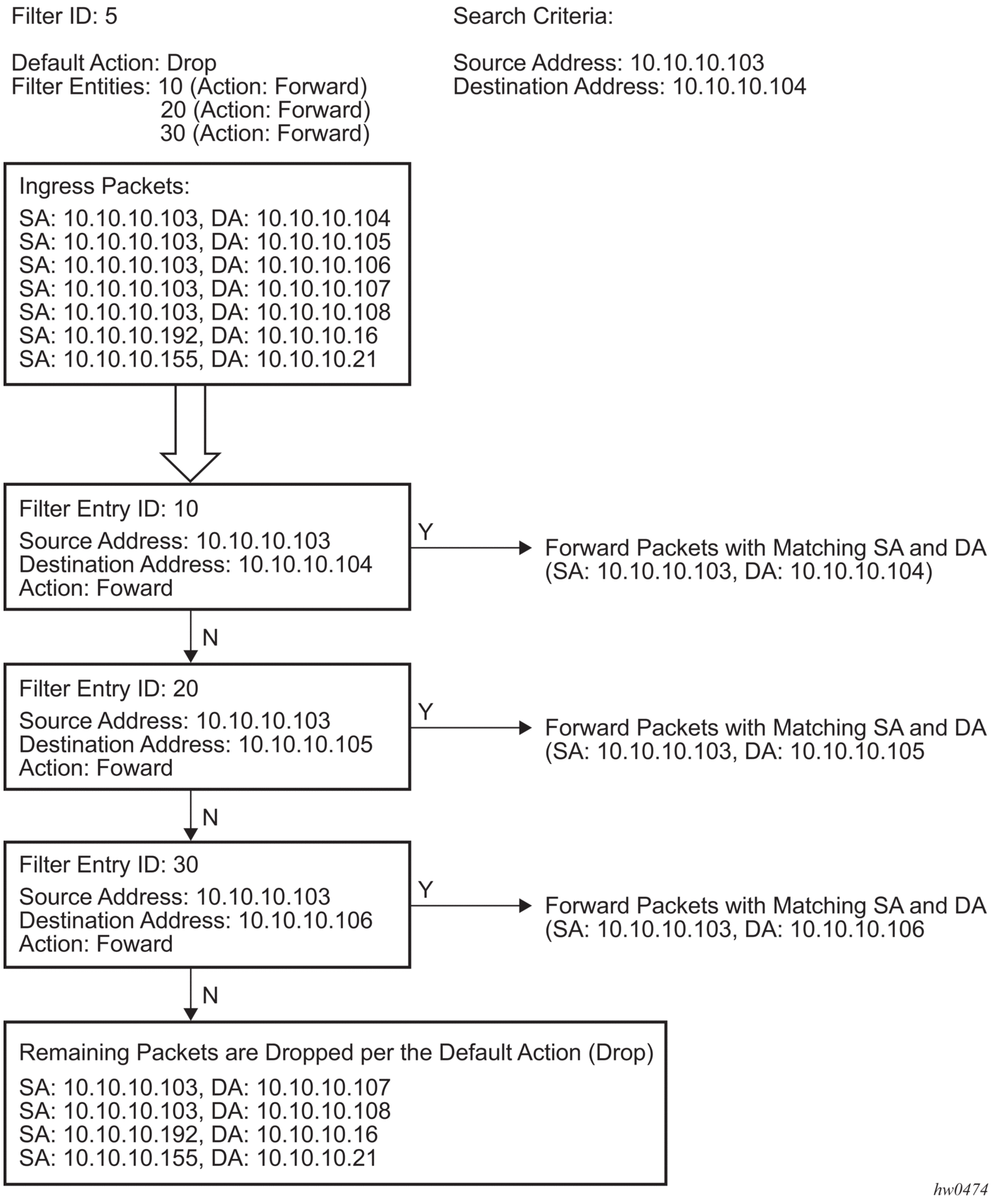
The following figure shows an example of several packets forwarded upon matching the filter criteria and several packets traversing through the filter entries and then dropped.
Figure 5: Filtering process example
3.2.3. Applying filters
This section provides information about applying filters.
3.2.3.1. Applying a filter to a SAP
During the SAP creation process, ingress and egress filters are selected from a list of qualifying IP and MAC filters. When ingress filters are applied to a SAP, packets received at the SAP are checked against the matching criteria in the filter entries. If the packet completely matches all criteria in an entry, the checking stops and an entry action is performed. If permitted, the traffic is forwarded according to the specification of the action. If the packets do not match, the default filter action is applied. If permitted, the traffic is forwarded.
When egress filters are applied to a SAP, packets received at the egress SAP are checked against the matching criteria in the filter entries. If the packet completely matches all criteria in an entry, the checking stops. If permitted, the traffic is transmitted. If denied, the traffic is dropped. If the packets do not match, the default filter action is applied.
Filters can be added or changed to an existing SAP configuration by modifying the SAP parameters. Filter policies are not operational until they are applied to a SAP and the service enabled.
3.2.3.2. Applying a filter to an IES interface
An IP filter can be applied to an IES SAP. Packets received on the interface are checked against the matching criteria in the filter entries. If the packet completely matches all criteria in an entry, the checking stops. If permitted, the traffic is forwarded. If the packets do not match, they are discarded or forwarded based on the default action specified in the policy.
3.2.3.3. Applying a filter to a network IP interface
An IP filter can be applied to a network port IP interface. Packets received on the interface are checked against the matching criteria in the filter entries. If the packet completely matches all criteria in an entry, the checking stops. If permitted, the traffic is forwarded. If the packets do not match, they are discarded or forwarded based on the default action specified in the policy.
3.3. Configuration notes
| Note: Refer to the 7210 SAS-D, Dxp, K 2F1C2T, K 2F6C4T, K 3SFP+ 8C Services Guide for service specific ACL support and restrictions. |
The following information describes filter implementation caveats:
- Creating a filter policy is optional.
- Associating a service with a filter policy is optional.
- When a filter policy is configured, it should be defined as having either an exclusive scope for one-time use, or a template scope meaning that the filter can be applied to multiple SAPs.
- A specific filter must be explicitly associated with a specific service in order for packets to be matched.
- A filter policy can consist of zero or more filter entry. Each entry represents a collection of filter match criteria. When packets enter the ingress or egress ports, packets are compared to the criteria specified within the entry or entries.
- When a large (complex) filter is configured, it may take a few seconds to load the filter policy configuration and be instantiated.
- On the 7210 SAS-D, 7210 SAS-Dxp, 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C, IP filters applied on an IES SAP cannot match against IP packets containing IP options.
- The action keyword must be entered for the entry to be active. Any filter entry without the action keyword will be considered incomplete and be inactive.
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp, ingress filter CAM resources used to match packet fields are shared with other features such as SAP ingress QoS, CFM UP MEP, and G8032. By default software assigns a fixed amount of resources for use by ingress ACLs. User has an option to either increase this by taking away resources from other features or decrease by taking away resources from ingress ACLs. The number of ACLs that can be supported is directly dependent on the amount of resources allocated toward ingress ACLs.
- On the 7210 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp when a filter policy is created with the option ipv6-64bit-address, the entries can only use only the IPv6 src-ip and IPv6 dst-ip fields in the match criteria.
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp when a filter policy is created with the option ipv6-128bit-address, the entries can use the IPv6 src-ip, IPv6 dst-ip, IPv6 DSCP, TCP/UDP port numbers (source and destination port), ICMP code and type, and TCP flags fields in the match criteria.
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp the resources must be allocated for use by ingress IPv6 filters, before associating an IPv6 filter policy to a SAP. By default, the software does not enable the use of IPv6 resources. Until resources are allocated for use by IPv6 filters, software fails all attempts to associate a IPv6 filter policy with a SAP.
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp, the available ingress CAM hardware resources can be allocated as per user needs for use with different filter criteria using the commands under the configure> system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress context. By default, the system allocates resources to maintain backward compatibility with release 4.0. Users can modify the resource allocation based on their need to scale the number of entries or number of associations (that is, number of SAP/IP interfaces using a filter policy that defines a particular match criterion).
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp, the available egress CAM hardware resources can be allocated as per user needs for use with different filter criteria using the commands under the configure> system>resource-profile> egress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-egress context. By default, the system allocates resources to maintain backward compatibility with release 4.0. Users can modify the resource allocation based on their needs to scale the number of entries or the number of associations (that is, number of SAP/IP interfaces using a filter policy that defines a particular match criterion).
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp IPv6 ACLs and MAC QoS policies cannot co-exist on the SAP.
- On the 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp if no CAM resources are allocated to a particular match criterion defined in a filter policy, then the association of that filter policy to a SAP will fail. This is true for both ingress and egress filter policy.
- Only the 7210 SAS-K allows for use of outer VLAN ID and inner VLAN ID for match in MAC criteria with both ingress and egress ACLs. Other 7210 SAS platforms do not support use of outer and inner VLAN ID field for match in the MAC criteria.
3.3.1. MAC filters
The following are configuration notes for MAC filters:
- If a MAC filter policy is created with an entry and entry action specified but the packet matching criteria is not defined, then all packets processed through this filter policy entry will pass and take the action specified. There are no default parameters defined for matching criteria.
- MAC filters cannot be applied to network interfaces, routable VPLS or IES services.
- Some of the MAC match criteria fields are exclusive to each other, based on the type of Ethernet frame. Use the following table to determine the exclusivity of fields.In the 7210 SAS, the default frame-format is “Ethernet-II”
Table 40: MAC match criteria exclusivity rules
Frame format | Etype |
Ethernet – II | Yes |
802.3 | No |
802.3 – snap | No |
802.3-llc | No |
3.3.2. IP filters
The following are configuration notes for IP filters:
- Define filter entry packet matching criteriaIf a filter policy is created with an entry and entry action specified but the packet matching criteria is not defined, then all packets processed through this filter policy entry will pass and take the action specified. There are no default parameters defined for matching criteria.
- ActionAn action parameter must be specified for the entry to be active. Any filter entry without an action parameter specified will be considered incomplete and be inactive.
3.3.3. IPv6 filters
The following are configuration notes for IPv6 filters:
- Define filter entry packet matching criteriaIf a filter policy is created with an entry and entry action specified, but the packet matching criteria is not defined, then all packets processed through this filter policy entry passes and takes the action specified. There are no default parameters defined for matching criteria.
- ActionAn action parameter must be specified for the entry to be active. Any filter entry without an action parameter specified is considered incomplete and inactive.
3.3.3.1. Resource usage for ingress filter policies for 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp
When the user allocates resources from the ingress CAM resource pool for use by filter policies using the configure>system>resource-profile CLI commands, the system allocates resources in chunks of fixed-size entries (for example, 256 entries per chunk on 7210 SAS-D).
| Note: The number of entries for each chunk or slice is different for both ingress-internal-tcam resource pool and egress-internal-tcam resource pool for different platforms. |
The usage of these entries by different type of match criteria follows. In the following examples, it is assumed that a chunk/slice has 256 entries considering 7210 SAS-D. The example and the computation needs to be modified suitably for other platforms with different number of entries per chunk/slice.
- mac-criteriaUser needs to allocate resources for mac-criteria from the filter resource pool by using the command “configure> system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam>acl-sap-ingress> mac-match-enable" before using ingress ACLs with mac-criteria. Every entry configured in the filter policy using the mac-criteria uses one (1) entry from the chunks allocated for use by mac-criteria in the hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 50 entries and uses “configure>system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress> mac-match-enable 1”, the user configures one chunk for use by mac-criteria (allowing a total of 256 entries. one reserved for internal use entries for use by SAPs using filter policies that use mac-criteria). In this case, the user can have 5 SAPs using mac-criteria filter policy and consumes 250 entries.
- ipv4-criteriaUser needs to allocate resources for ip(v4)-criteria from the filter resource pool by using the command “configure> system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress> ipv4-match-enable" before using ingress ACLs with ipv4-criteria. The resource usage per IPv4 match entry is same as the mac-criteria. Please check the preceding example. When created with "use-ipv6-resource" the resource usage is the same as IPv6 filters using ipv6-128-bit-addresses.
- ipv6-criteria using ipv6-64-bit addressesUser needs to allocate resources for ipv6-criteria with 64-bit address match from the filter resource pool by using the command “configure> system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress> ipv6-64only-match-enable” before using ingress ACLs with ipv6-criteria that use only IPv6 64-bit address for source and destination IPv6 addresses.The IPv6 headers fields available for match is limited. Please see the following CLI description for filter for more information. The usage is same as the ipv4 and mac-criteria. An ipv6 128 bit address uses 2 entries from the chunk for every match entry configured in filter policy, whereas, an IP filter uses only one entry from the chunk for every entry configured.
- ipv6-criteria using ipv6-128-bit addressesUser needs to allocate resources for ipv6-criteria with 128-bit address match from the filter resource pool by using the command “configure> system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress> ipv4-ipv6-128-match-enable” before using ingress ACLs with ipv6-criteria that use only IPv6 128-bit address for source and destination IPv6 addresses. These resources can be shared by a policy that uses only IPv4 criteria entries. Every entry configured in the filter policy using the ipv6-criteria with 128-bit addresses uses two (2) entries from the chunks allocated for use by ipv6-criteria (128-bit) in the hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 50 entries and using “configure>system> resource-profile> ingress-internal-tcam> acl-sap-ingress> ipv4-ipv6-128-match-enable 1”, the user configures one chunk for use by ipv6-criteria with 128-bit addresses (allowing for a total of 128 entries for use by SAPs using filter policies that use this criteria). In this case, user can have five (5) SAPs using this filter policy and consumes 125 entries. When a chunk is allocated to IPv6 criteria, the software automatically adjusts the number of available entries in that chunk to 128, instead of 256, because 2 entries are needed to match IPv6 fields.
The users can use tools>dump> system-resources command to know the current usage and availability. For example: Though chunks are allocated in 256 entries, only 128 entries show up against filters using those of IPv6 128-bit addresses. One or more entries are reserved for system use and is not available for user.
3.3.3.2. Resource usage for egress filter policies (supported only for 7210 SAS-D and 7210 SAS-Dxp)
When the user allocates resources for use by filter policies using the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam CLI commands, the system allocates resources in chunks of 128 entries from the egress internal tcam pool in hardware. The usage of these entries by different type of match criteria is as follows:
- mac-criteriaThe user needs to allocate resources for using mac-criteria using the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-match-enable 2 or configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-ipv4-match-enable 2 command or the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-ipv6-64bit-match-enable 2 command. In the last two cases, the resources can be shared with SAPs that use IPv4 or IPv6 64-bit filter policies. The first case allocates resources for exclusive use by MAC filter policies. The resource usage varies based how resources have been allocated:
- If resources are allocated for use by mac-criteria only (using mac-match-enable), then every entry configured in the filter policy uses one (1) entry from the chunks allocated for use by mac-criteria in the hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 25 mac-criteria entries and uses the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-match-enable 2 command, the user configures two chunks for use by mac-criteria, allowing a total of 256 entries for use by SAPs using filter policies that use mac-criteria. Therefore, the user can have about 10 SAPs using mac-criteria filter policy and consumes 250 entries. With this, SAPs using ipv4 criteria or ipv6 criteria cannot share the resources along with SAPs using mac-criteria.
- If the resources are allocated for sharing between mac-criteria and ipv4-criteria, every entry configured in the filter policy uses 2 (two) entries from the chunks allocated in hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 25 mac-criteria entries and another filter policy configured with 25 IPv4 criteria entries and, with mac-ipv4-match-enable set to 2, that is, user configures two chunks for sharing between MAC and IPv4, allowing for a total of 128 entries for use by SAPs that use filter policies using ipv4-criteria or mac-criteria. Therefore, the user can have about 4 SAPs using filter policies, such that 2 SAPs uses mac-criteria and the other 2 SAPs use ipv4-criteria or any combination thereof.
- If the resources are allocated for sharing between mac-criteria and ipv6-64bit-criteria, then every entry configured in the filter policy uses 2 (two) entries from the chunks allocated in hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 50 mac-criteria entries and another filter policy configured with 50 IPv6 64-bit criteria entries and, with mac-ipv6-64bit-match-enable set to 2, that is, user configures two chunks for sharing between MAC and IPv6-64bit, allowing for a total of 128 entries for use by SAPs that use filter policies using ipv6-64bit-criteria or mac-criteria. Therefore, the user can have about 2 SAPs using filter policies, such that one SAP uses mac-criteria and the other one SAP uses ipv6-64bit-criteria or any combination thereof.
- ipv4-criteriaThe user need to allocate resources using the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-ipv4-match-enable command. The resource usage explanation precedes.
- ipv6-criteria using ipv6-64-bit addressesThe user need to allocate resources using the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress mac-ipv6-64bit-match-enable command. The resource usage explanation precedes.
- ipv6-criteria using ipv6-128-bit addressesThe user need to allocate resources using the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress ipv6-128bit-match-enable command. This command allocates resources for exclusive by IPv6-128bit criteria filter policies and cannot be shared by SAPs using any another criteria. If resources are allocated for use by ipv6-128bit-criteria only, then every entry configured in the filter policy uses two (2) entries from the chunks allocated for use in hardware. For example: Assume a filter policy is configured with 50 ipv6-128bit-criteria entries and user uses the configure system resource-profile egress-internal-tcam acl-sap-egress ipv6-128bit-match-enable 2 command, to configure two chunks for use by ipv6-128bit-criteria. This allows for a total of 128 for use by SAPs using filter policies that use ipv6-128bit-criteria. Therefore the user can have about 2 SAPs using ipv6-128bit-criteria filter policy and consumes 100 entries.
The user can use tools dump system-resources command to know the current usage and availability.
3.3.4. Ingress filter policy resource usage: 7210 SAS-K 2F1C2T, 7210 SAS-K 2F6C4T, and 7210 SAS-K 3SFP+ 8C
When the user allocates resources from the ingress CAM resource pool for use by filter policies using the configure system resource-profile ingress-internal-tcam acl-sap-ingress command, the system allocates resources in chunks of fixed-size entries (512 entries per chunk on 7210 SAS-K). Resources must be allocated using these commands before associating a filter policy with the SAP, otherwise the command returns an error. The usage of these entries by different types of match criteria follow:
- mac-criteria, ipv4-criteria and ipv6-criteria with 64-bit-addressUser needs to allocate resources, in terms of number of slices, for filter policies that use mac criteria, ipv4 criteria and ipv6 64-bit criteria from the ingress internal tcam resource pool using the configure system resource-profile ingress-internal-tcam acl-sap-ingress command. The entries allocated are shared by filter policies that use any of these criteria. Each filter entry configured in the policy takes away a single resource from the pool allocated for filter policies.
- ipv6-criteria with 128-bit addressUser needs to allocate resources, in terms of number of slices, for filter policies that use ipv6 128-bit criteria from the ingress internal tcam resource pool using the configure system resource-profile ingress-internal-tcam acl-sap-ingress mac-ipv4-ipv6-128-match-enable command. User can allocate all the slices allocated for the filter policies (using the configure system resource-profile ingress-internal-tcam acl-sap-ingress command) for use by ipv6 criteria with 128-bit addresses or allocation only a portion of it. The entries allocated are used by filter policies that use ipv6 criteria with 128-bit addresses. Each filter entry configured in the policy takes away two (2) resources from the pool. Software uses these resources also for mac criteria, ipv4 criteria, and ipv6 criteria with 64-bit address. Irrespective of the criteria, two (2) resources are taken for each entry configured on the filter policy.
Use the tools dump system-resources command to know the current usage and availability.