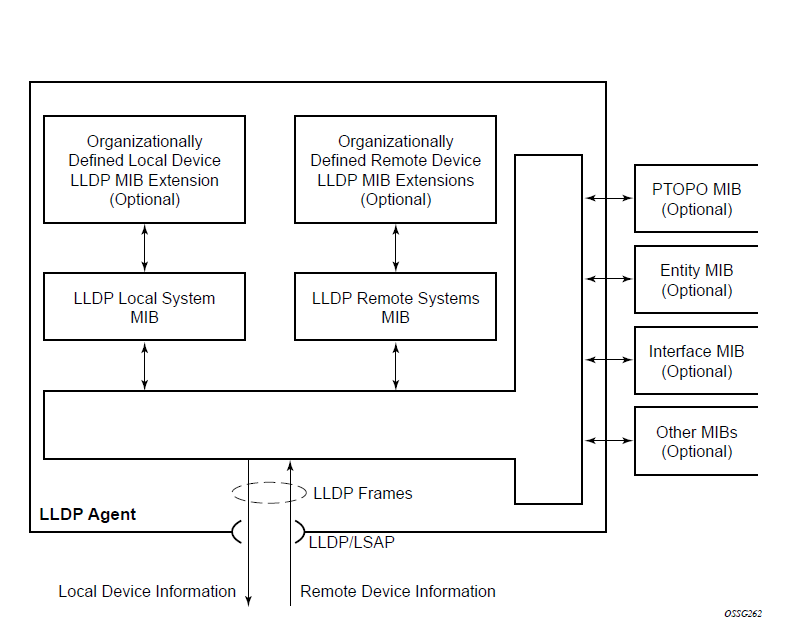
The IEEE 802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a unidirectional protocol that uses the MAC layer to transmit specific information about the capabilities and status of the local device. The LLDP can send as well as receive information from a remote device stored in the related MIB (or MIBs).
The LLDP does not contain a mechanism to solicit information received from other LLDP agents or to confirm the receipt of information. However, LLDP provides the flexibility to enable a transmitter and receiver separately, and the following LLDP agent configurations are allowed:
only transmit information
only receive information
transmit and receive information
The information fields in each LLDP frame are contained in an LLDP Data Unit (LLDPDU) as a sequence of variable length information elements. Each information element includes Type, Length, and Value fields (TLVs):
Type indicates the nature of information being transmitted.
Length indicates the length of the information string in octets.
Value is the actual information that is transmitted. (For example, a binary bit map or an alphanumeric string that can contain one or more fields).
Each LLDPDU contains four mandatory TLVs and optional TLVs selected by the Network Management. The following is the format of an LLDPDU:
Chassis ID TLV
Port ID TLV
Time To Live (TTL) TLV
zero or more optional TLVs, depending on the maximum size of the LLDPDU allowed
End of LLDPDU TLV
A concatenated string formed by the Chassis ID TLV and the Port ID TLV is used by a recipient to identify an LLDP port or agent. The combination of the Port ID and Chassis ID TLVs remains unchanged until the port or agent is operational.
The TTL field of a Time-To-Live TLV can be a zero or non-zero value. A zero TTL field value notifies the receiving LLDP agent to immediately discard all information related to sending LLDP agent. A non-zero TTL field value indicates the time duration for which the receiving LLDP agent should retain the information of the sending LLDP agent. The receiving LLDP agent discards all information related to the sending LLDP agent after the time interval indicated in the TTL field is complete.
A TTL zero value is used to signal that the sending LLDP port has initiated a port shutdown procedure.
The End Of LLDPDU TLV indicates the end of the LLDPDU.
The following information is included in the protocol as defined by the IEEE 802.1ab standard:
Connectivity and management information about the local station to adjacent stations on the same IEEE 802 LAN is advertised.
Network management information from adjacent stations on the same IEEE 802 LAN is received.
It operates with all IEEE 802 access protocols and network media.
Network management information schema and object definitions suitable for storing connection information about adjacent stations is established.
It supports compatibility with a number of MIBs.
The following figure shows the LLDP internal architecture for a network node.
To detect and address network problems and inconsistencies in the configuration, the network operators can discover the topology information using LLDP. The standard-based tools address the complex network scenarios where multiple devices from different vendors are interconnected using Ethernet interfaces.
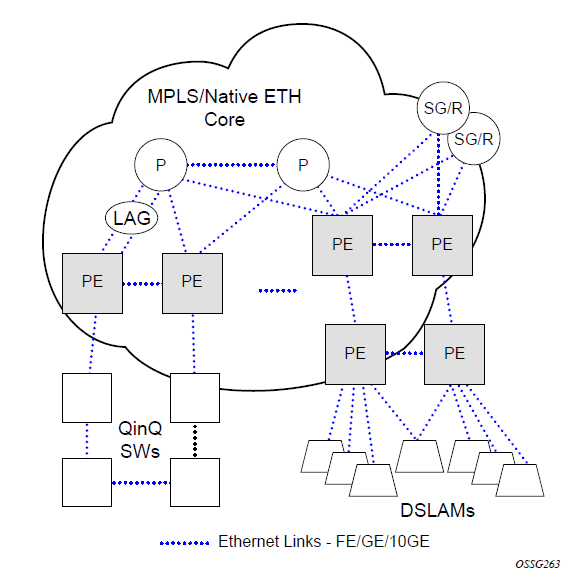
The following figure shows an MPLS network that uses Ethernet interfaces in the core, or as an access or handoff interface to connect to different kinds of Ethernet-enabled devices such as service gateway and routers, QinQ switches, DSLAMs, or customer equipment.
The topology information of the network in the following figure can be discovered if IEEE 802.1ab LLDP is running on each of the Ethernet interfaces in the network.