In order for the maximum length service frame to successfully travel from a local ingress SAP to a remote egress SAP, the MTU values configured on the port on which the local ingress SAP is provisioned and the port on which the egress SAP is provisioned must be coordinated to accept the maximum frame size the service can forward.
The following figure shows an example of the targeted MTU values to configure for an Epipe service (ALA-A and ALA-B).
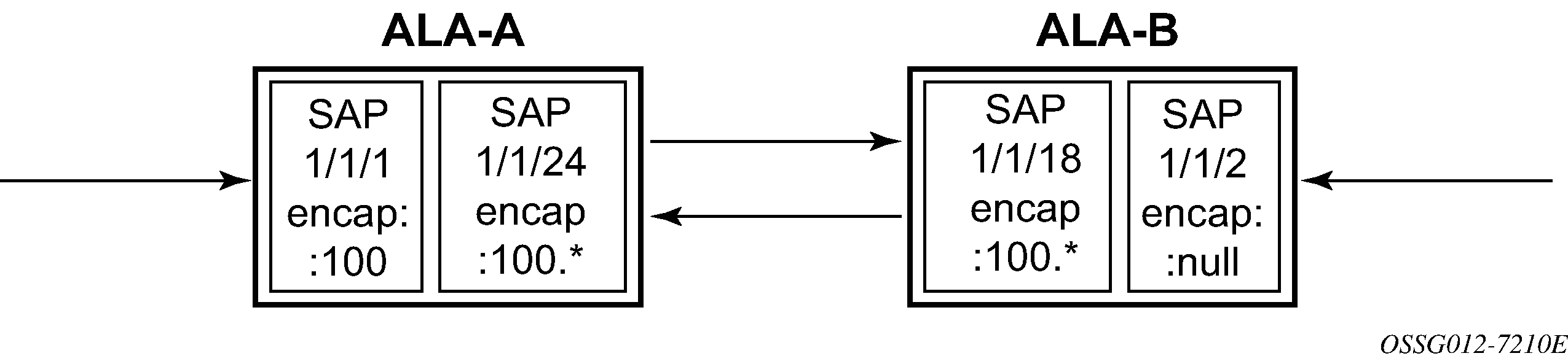
Because ALA-A uses Dot1q encapsulation, the port 1/1/1 MTU must be set to 1518 to be able to accept a 1514-byte service frame (see the following table for MTU default values). Each of the access uplink port MTU must be set to at least 1518 as well. Finally, the MTU of ALA-B SAP (access port 1/1/2) must be at least 1514, as it uses null encapsulation.
The following table describes sample MTU configuration values.
ALA-A |
ALA-B |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Access (SAP) |
Access Uplink (SAP) |
Access Uplink (SAP) |
Access (SAP) |
|
Port (slot/MDA/port) |
1/1/1 |
1/1/24 |
1/1/18 |
1/1/2 |
Mode type |
access (dot1q) |
access-uplink (QinQ) |
access-uplink (QinQ) |
access (null) |
MTU |
1518 |
1518 |
1518 |
1514 |
Instead, if ALA-A uses a dot1q-preserve SAP on port 1/1/1, then port 1/1/1 MTU must be set to 1518 to be able to accept a 1514-byte service frame (see the following table for MTU default values). Each of the access uplink port MTU must be set to at least 1522 as well. Finally, the MTU of ALA-B SAP (access port 1/1/2) must be at least 1518, as it uses Dot1q encapsulation.
The following table describes sample MTU configuration values.
ALA-A |
ALA-B |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Access (SAP) |
Access Uplink (SAP) |
Access Uplink (SAP) |
Access (SAP) |
|
Port (slot/MDA/port) |
1/1/1 |
1/1/24 |
1/1/18 |
1/1/2 |
Mode type |
access (dot1q-preserve) |
access-uplink (QinQ) |
access-uplink (QinQ) |
access (dot1q-preserve) |
MTU |
1518 |
1522 |
1522 |
1518 |