The following figure shows the main MACsec concepts used in the static CAK scenario.
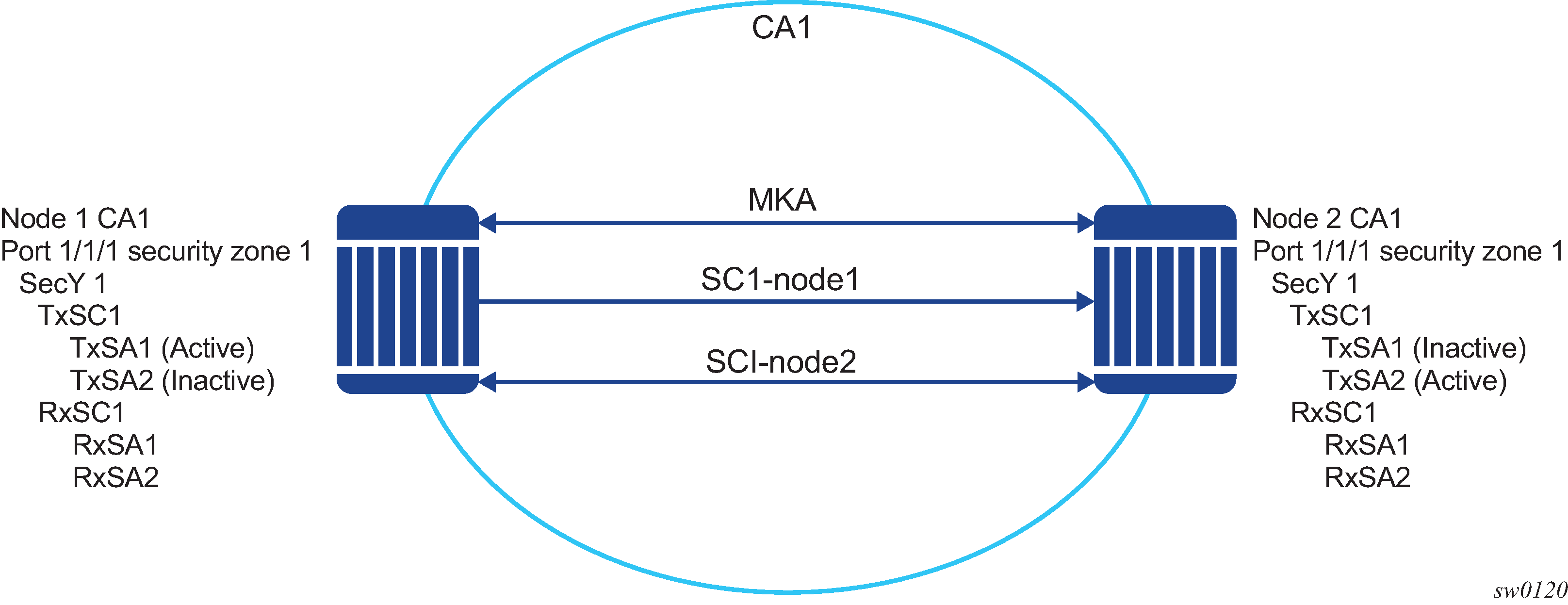
MACsec uses SAs to encrypt packets. Each SA has a single SAK that contains the cryptographic operations used to encrypt the datapath PDUs.
The SAK is the secret key used by an SA to encrypt the channel.
When enabled, MACsec uses a static CAK security mode, which has two security keys: a CAK that secures control plane traffic and a randomly generated SAK that secures data plane traffic. Both keys are used to secure the point-to-point or point-to-multipoint Ethernet link and are regularly exchanged between devices on each end of the Ethernet link.
The following figure shows MACsec generating the CAK.
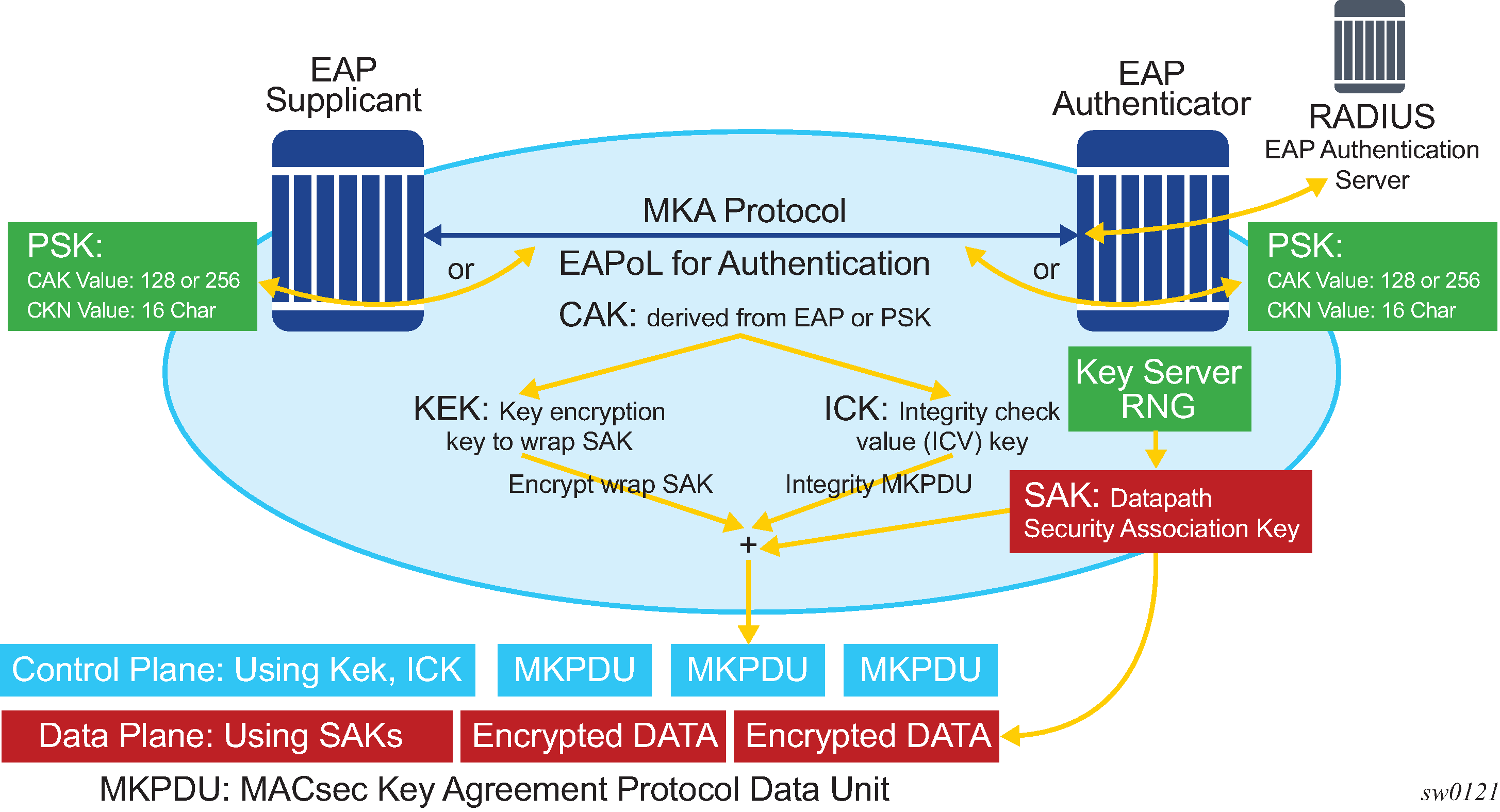
The node initially needs to secure the control plane communication to distribute the SAKs between two or more members of a CA domain.
The control plane is secured using a CAK, which is generated using one of the following methods:
EAPoL
preshared key
(CAK and CKN values are configured using the CLI). The following CAK and CKN rules apply.
CAK uses 32 hexadecimal characters for a 128-bit key, and 64 hexadecimal characters for a 256-bit key, depending on the algorithm used for control plane encryption; for example, aes-128-cmac or aes-256-cmac.
CKN is a 32-octet character (64 hex) and is the name that identifies the CAK. This allows each of the MKA participants to select which CAK to use to process a received MKPDU. MKA places the following restrictions on the format of the CKN:
it must comprise an integral number of octets, between 1 and 32 (inclusive)
all potential members of the CA must use the same CKN
CAK and CKN must match on peers to create a MACsec-secure CA.
The following figure shows MACsec control plane authentication and encryption.
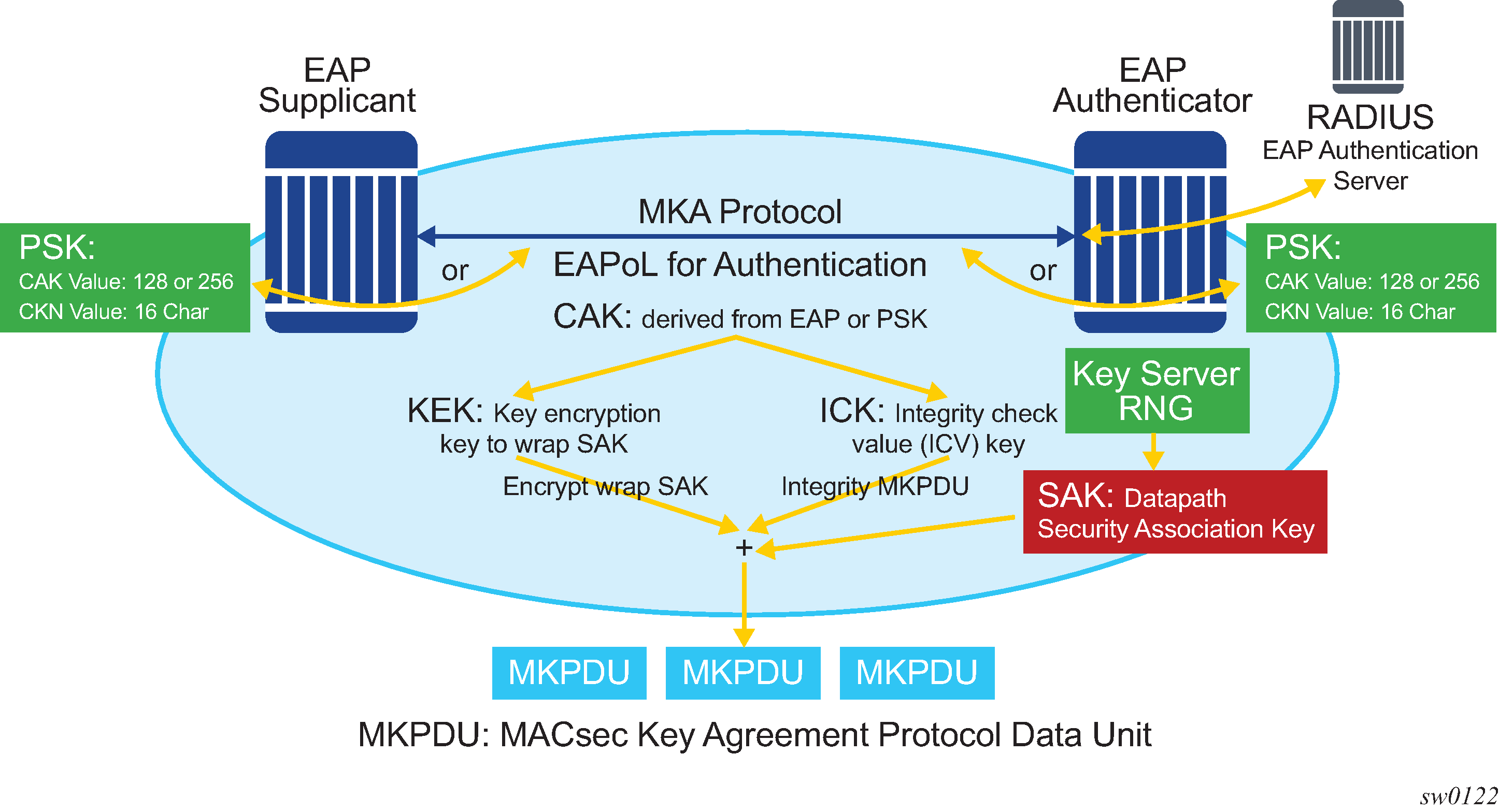
After the CAK is generated, it can obtain the following additional keys:
KEK (Key Encryption Key)
The KEK is used to wrap and encrypt the SAKs.
ICK (Integrity Connection Value (ICV) Key)
The ICK is used for an integrity check of each MKPDU send between two CAs.
The key server then creates a SAK and shares it with the CAs of the security domain, and that SAK secures all data traffic traversing the link. The key server periodically creates and shares a randomly created SAK over the point-to-point link for as long as MACsec is enabled.
The SAK is encrypted using the AES-CMAC, the KEK as the encryption key, and ICK as the integration key.