A Continuity Check Message (CCM) is a multicast frame that is generated by a MEP and multicast to all other MEPs in the same MA. The CCM does not require a reply message. To identify faults, the receiving MEP maintains an internal list of remote MEPs it should be receiving CCM messages from.
This list is based on the remote MEP ID configuration within the association the MEP is created in. When the local MEP does not receive a CCM from one of the configured remote MEPs within a preconfigured period, the local MEP raises an alarm.
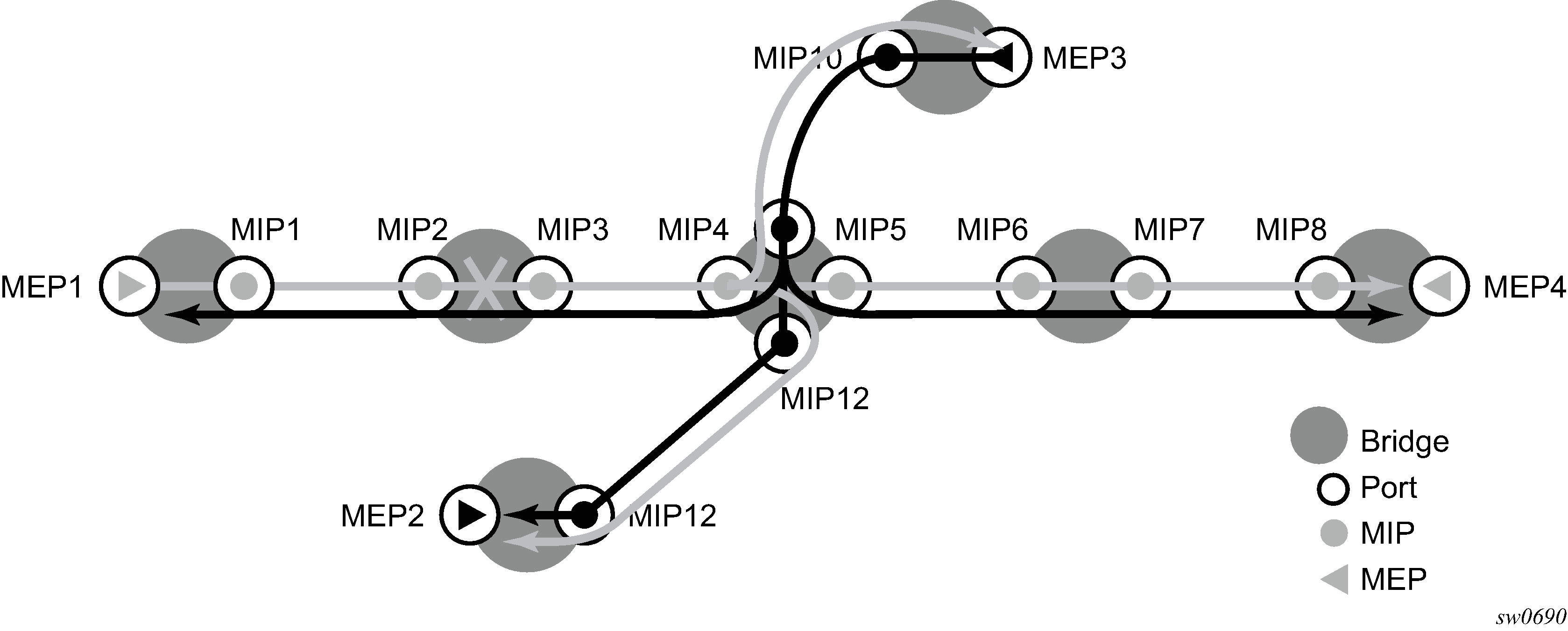
The following figure shows a CFM continuity check.
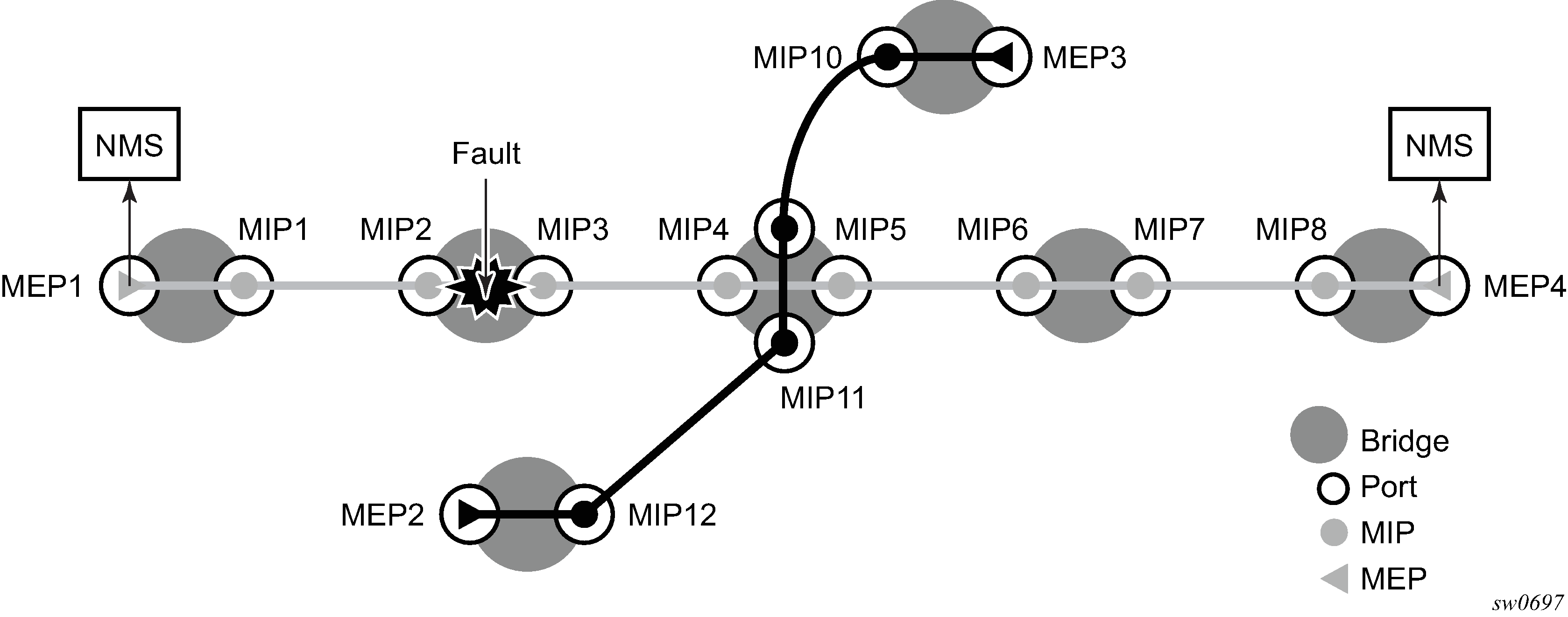
The following figure shows a CFM CC failure scenario.
The following functions are supported:
CC can be enabled or disabled for a MEP.
MEP entries can be configured and deleted in the CC MEP monitoring database manually. Only remote MEPs must be configured. Local MEPs are automatically added to the database when they are created.
The CCM transmit interval can be configured for 100 ms (only supported on the 7210 SAS-D).
When configuring MEPs with subsecond CCM intervals, bandwidth consumption must be taken into consideration. Each CCM PDU is 100 bytes (800 bits). Taken individually, this is a small value. However, the bandwidth consumption increases rapidly as multiple MEPs are configured with 10 ms timers, 100 packets per second. Subsecond CCM-enabled MEPs are supported on the following:
Down MEPs configured on Ethernet SAPs.
Lowest MD-level, when multiple MEPs exist on the same Ethernet SAP.
Individual Ethernet tunnel paths requiring EAPs but not on the Ethernet tunnel itself. This requires the MEPs to be part of the Y.1731 context because of the EAPS.
The CCM will declare a fault when:
the CCM stops hearing from one of the remote MEPs for 3.5 times the CC interval
the CCM hears from a MEP with a lower MD level
the CCM hears from a MEP that is not part of the local MEP MA
the CCM hears from a MEP that is in the same MA but not in the configured MEP list
the CCM hears from a MEP in the same MA with the same MEP ID as the receiving MEP
the CC interval of the remote MEP does not match the local configured CC interval
the remote MEP is declaring a fault
An alarm is raised and a trap is sent if the defect is greater than or equal to the configured low-priority-defect value.
Remote Defect Indication (RDI) is supported but by default is not recognized as a defect condition because the low-priority-defect setting default does not include RDI.
The Sender ID TLV may optionally be configured to carry the Chassis ID. When configured, the following information will be included in CCM messages:
Only the Chassis ID portion of the TLV will be included.
The Management Domain and Management Address fields are not supported on transmission.
The Sender ID TLV is not supported with subsecond CCM-enabled MEPs.
The Sender TLV is supported for service (id-permission) MEPs.