For protection of the area border router, the upstream node of the area border router acts as a point-of-local-repair (PLR), and the next-hop node to the protected domain border routers is the merge-point (MP). Both manual and dynamic bypass are available to protect the area border node.
Manual bypass protection works only when a completely strict path is provisioned that avoids the area border node.
Dynamic bypass protection provides the automatic computation, signaling, and association with the primary path of an inter-area P2P LSP to provide ABR node protection. The following figure shows the role of each node in ABR node protection using a dynamic bypass LSP.
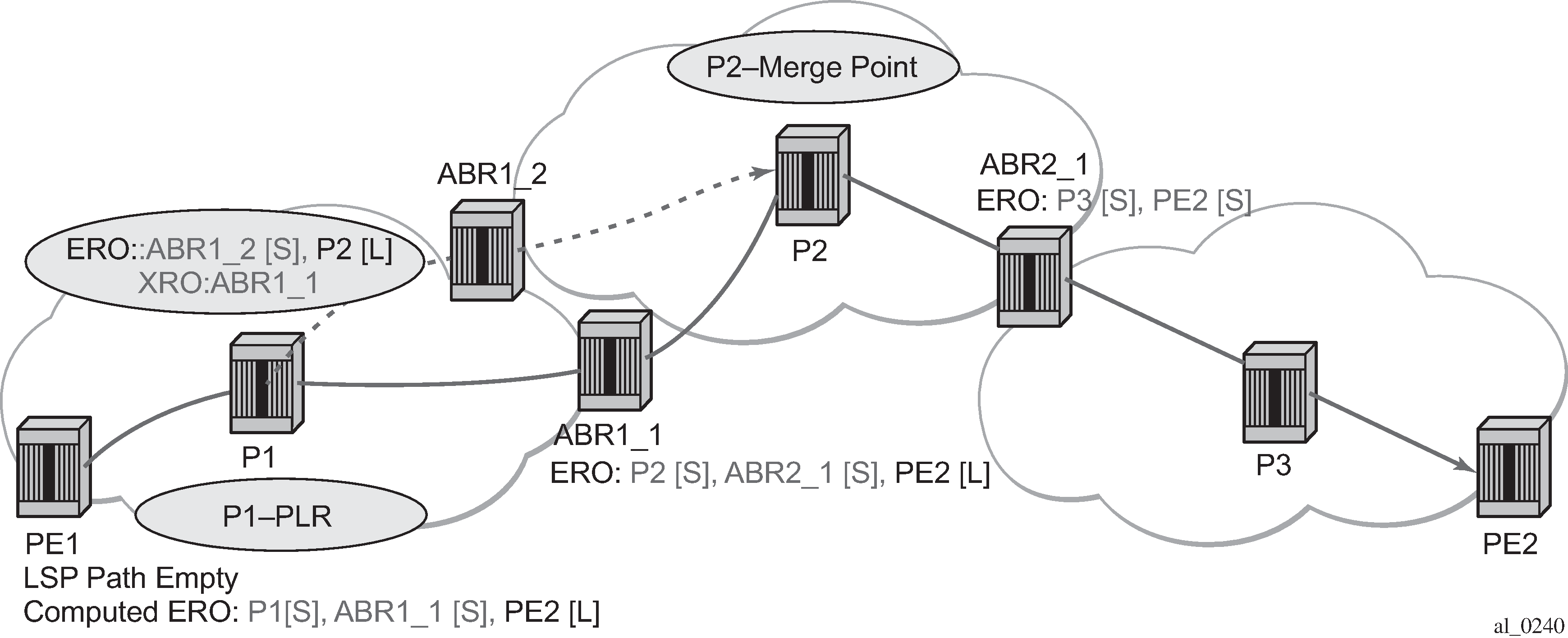
For a PLR node within the local area of the ingress LER to provide ABR node protection, the node must dynamically signal a bypass LSP and associate it with the primary path of the inter-area LSP using the following:
The PLR must inspect the record route object (RRO) node ID of the LSP primary path to determine the address of the node immediately downstream of the ABR in the other area.
The PLR signals an inter-area bypass LSP with a destination address set to the address downstream of the ABR and with the exclude router object (XRO) set to exclude the node ID of the protected ABR.
The request to CSPF is for a path to the merge-point (that is, the next-next-hop in the RRO received in the RESV for the primary path) along with the constraint to exclude the protected ABR. If CSPF returns a path that can only go to an intermediate hop, the PLR node signals the dynamic bypass and automatically includes the XRO with the address of the protected ABR. Otherwise, the PLR signals the dynamic bypass directly to the merge-point node with no XRO object in the Path message.
If a node-protect dynamic bypass cannot be found or signaled, the PLR node attempts a link-protect dynamic bypass LSP. As in existing implementation of dynamic bypass within the same area, the PLR attempts in the background to signal a node-protect bypass at the receipt of every third RESV refresh message for the primary path.
Refresh reduction over dynamic bypass works only if the RRO node ID also contains the interface address. Otherwise, the neighbor is not created when the bypass is activated by the PLR. The Path state times out after three refreshes following the activation of the bypass backup LSP.
A one-to-one detour backup LSP cannot be used at the PLR for the protection of the ABR. As a result, a PLR node does not signal a one-to-one detour LSP for ABR protection. In addition, an ABR rejects a Path message that is received from a third party implementation with a detour object and with the ERO having the next-hop loose. This is performed regardless of whether the cspf-on-loose-hop command is enabled on the node. That is, the router as a transit ABR for the detour path rejects the signaling of an inter-area detour backup LSP.