The ingress LER automatically selects the ABR when setting up an inter-area RSVP P2P LSP. The user does not need to include the ABR as a loose hop in the LSP path definition.
CSPF adds the capability to compute all segments of a multi-segment intra-area or inter-area LSP path in one operation.
The following figure shows the role of each node in the signaling of an inter-area LSP with automatic ABR node selection.
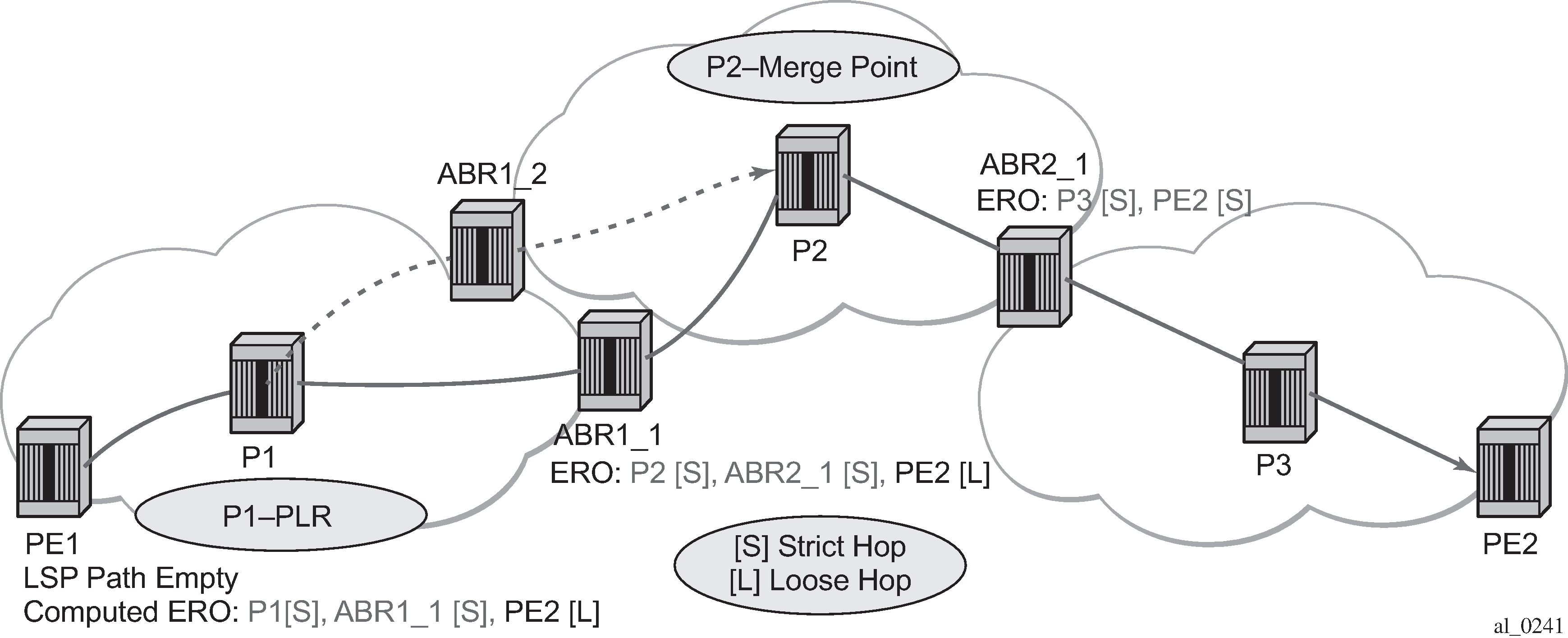
CSPF for an inter-area LSP operates as follows:
CSPF in the ingress LER node determines that an LSP is an inter-area LSP by doing a route lookup using the destination address of a P2P LSP (that is, the address in the to field of the LSP configuration). If there is no intra-area route to the destination address, the LSP is considered an inter-area LSP.
When the path of the LSP is empty, CSPF computes a single-segment intra-area path to an ABR node that advertised a prefix matching with the destination address of the LSP.
When the path of the LSP contains one or more hops, CSPF computes a multi-segment intra-area path that includes the hops that are in the area of the ingress LER node.
When all hops are in the area of the ingress LER node, the calculated path ends on an ABR node that advertised a prefix matching the destination address of the LSP.
When there are one or more hops that are not in the area of the ingress LER node, the calculated path ends on an ABR node that advertised a prefix matching with the first hop address that is not in the area of the ingress LER node.
In the case of a multi-segment inter-area LSP, if CSPF finds a hop that can be reached through an intra-area path but that resides on an ABR, CSPF calculates a path only up to that ABR. This is because there is a better chance to reach the destination of the LSP by first signaling the LSP up to that ABR and continuing the path calculation from there by having the ABR expand the remaining hops in the ERO.
The following figure shows this behavior. The TE link between ABR nodes D and E is in area 0. When node C computes the path for the LSP from C to B, in which the path specifies nodes D and E as loose hops, it fails the path computation if CSPF attempts a path all the way to the last hop in the local area, node E. Instead, CSPF stops the path at node D, which further expands the ERO by including link D to E as part of the path in area 0.
Figure: CSPF for an inter-area LSP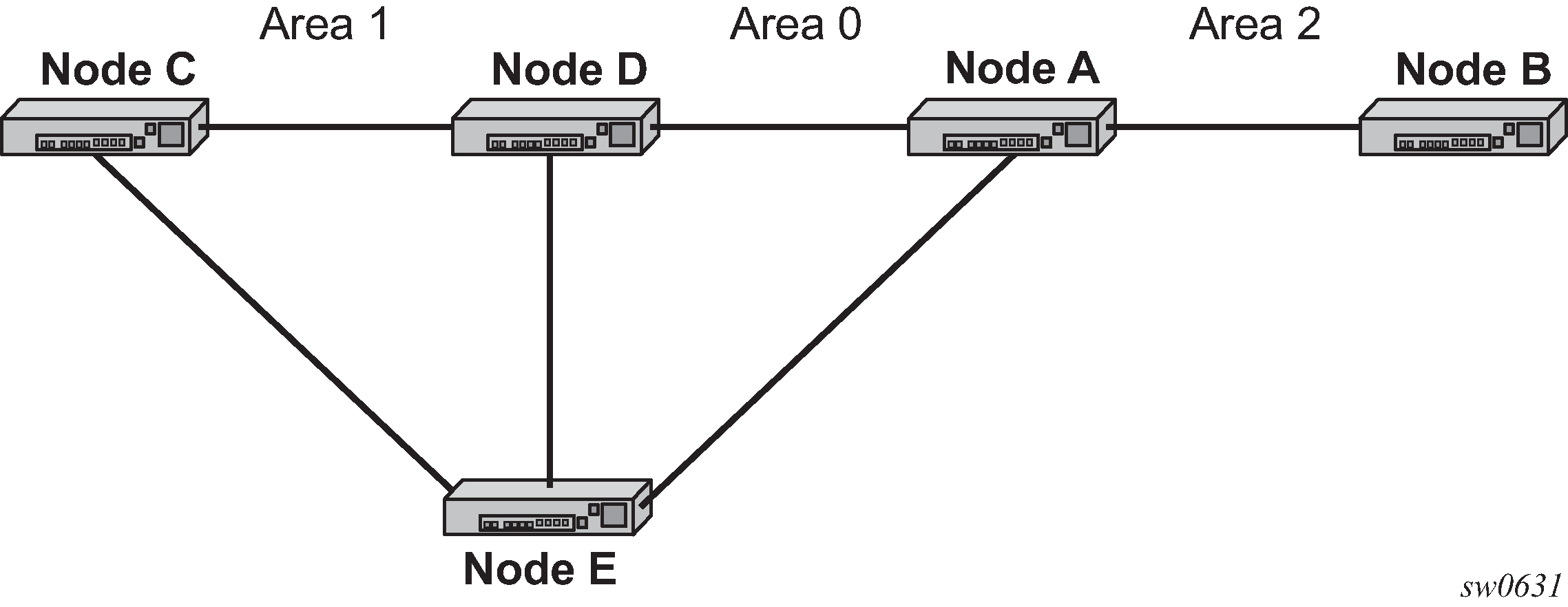
If there is more than one ABR that advertises a prefix, CSPF calculates a path for all ABRs. Only the shortest path is withheld. If more than one path has the shortest path, CSPF chooses a path randomly.
The path for an intra-area LSP cannot exit and re-enter the local area of the ingress LER.