The 7210 SAS operates as a PCE Client (PCC) only, supporting PCC capabilities for RSVP-TE LSPs. References to PCE router operation apply to the Network Services Platform (NSP) or to a virtualized Service Router (VSR) operating in the control and management domain of the NSP, and are included for informational purposes only.
PCEP is one of several protocols used for communication between a wide area network (WAN) software-defined network (SDN) controller and network elements.
The Nokia WAN SDN Controller is known as the NSP. The NSP is a set of applications built on a common framework that hosts and integrates them by providing common functions. The applications are developed in a Java environment.
The NSP provides two major functions:
programmable multi-vendor service provisioning
network resource control, including resource management at Layer 0 (optical path), Layer 1 (ODU path), Layer 2 (MPLS tunnel), and at the IP flow level
The network discovery and control function implements a common set of standards-based southbound interfaces to the network elements for both topology discovery and tunnel and flow programming. A virtual SR OS (vSROS) applies the southbound interfaces to the network elements and the adaptation layer to the applications. The southbound interfaces include IGP and the Network Functions Manager - Packet (NFM-P) for topology discovery, PCEP for handling path computation requests and LSP state updates with the network elements, and forwarding plane programming protocols such as Openflow, BGP flowspec, and I2RS.
The above NSP functions are provided in a number of modules that can be used together or separately as shown in the following figure.
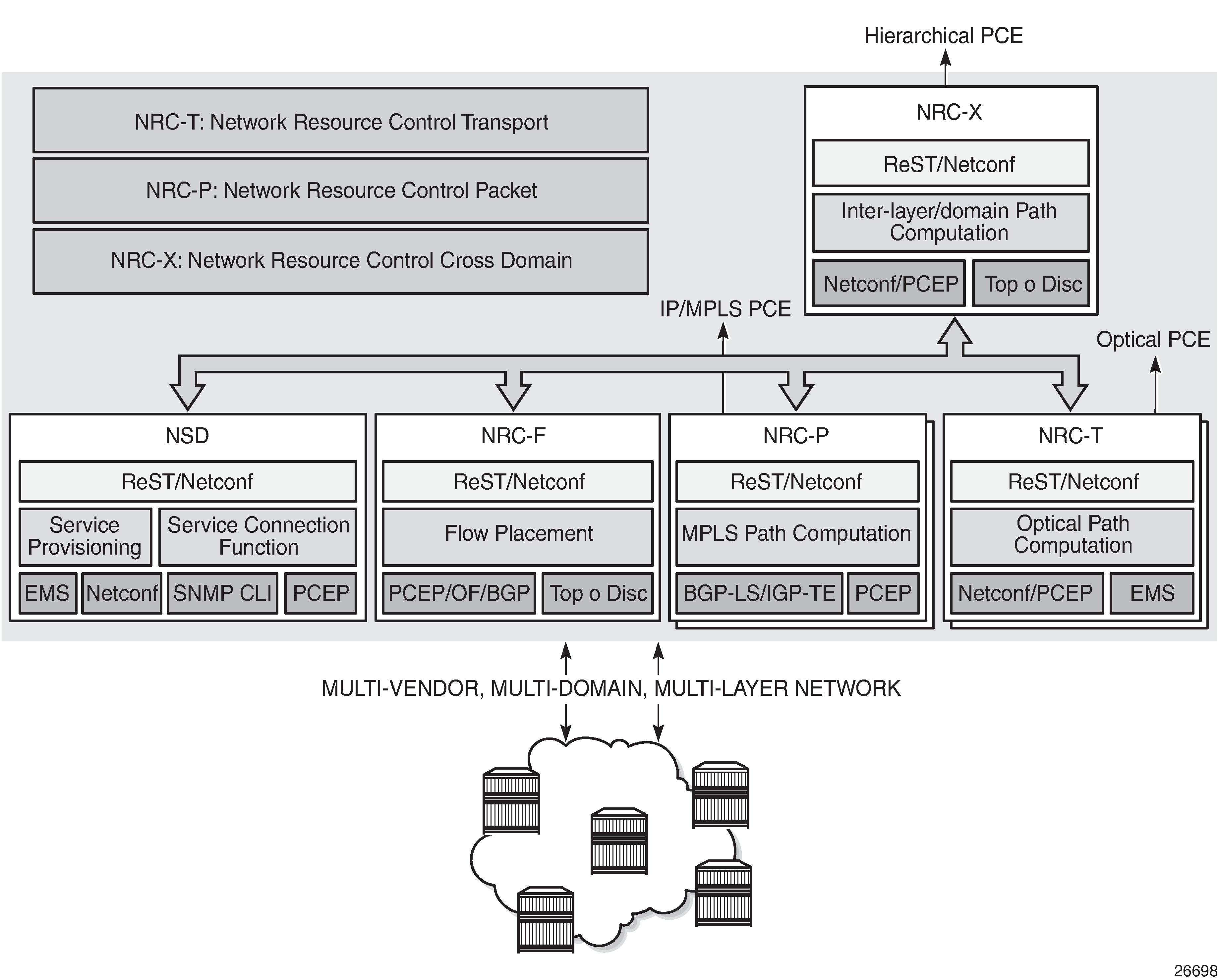
The two main components of the NSP are:
Network Services Director (NSD)
The NSD is a programmable and multi-vendor service provisioning tool that provides a single and simple API to the user and OSS. It implements a service model abstraction and adapts to each vendor-specific service model. It supports provisioning services such as E-Line, E-LAN, E-Tree, Layer 3 VPN, traffic steering, and service chaining.
Network Resource Controller (NRC)
The NRC implements separate modules for computing and managing optimal paths for optical tunnels (NRC-T) and MPLS tunnels (NRC-P), and for computing optimal routing and placement of IP flows (NRC-F). In addition, a resource controller for inter-layer IP and optical path computation and more complex inter-domain MPLS path computation is provided as part of the Network Resource Controller Cross Domain (NRC-X).
The Network Resource Controller - Packet (NRC-P) implements the stateful PCE for packet networks. The following figure shows the NRC-P architecture and its main components.
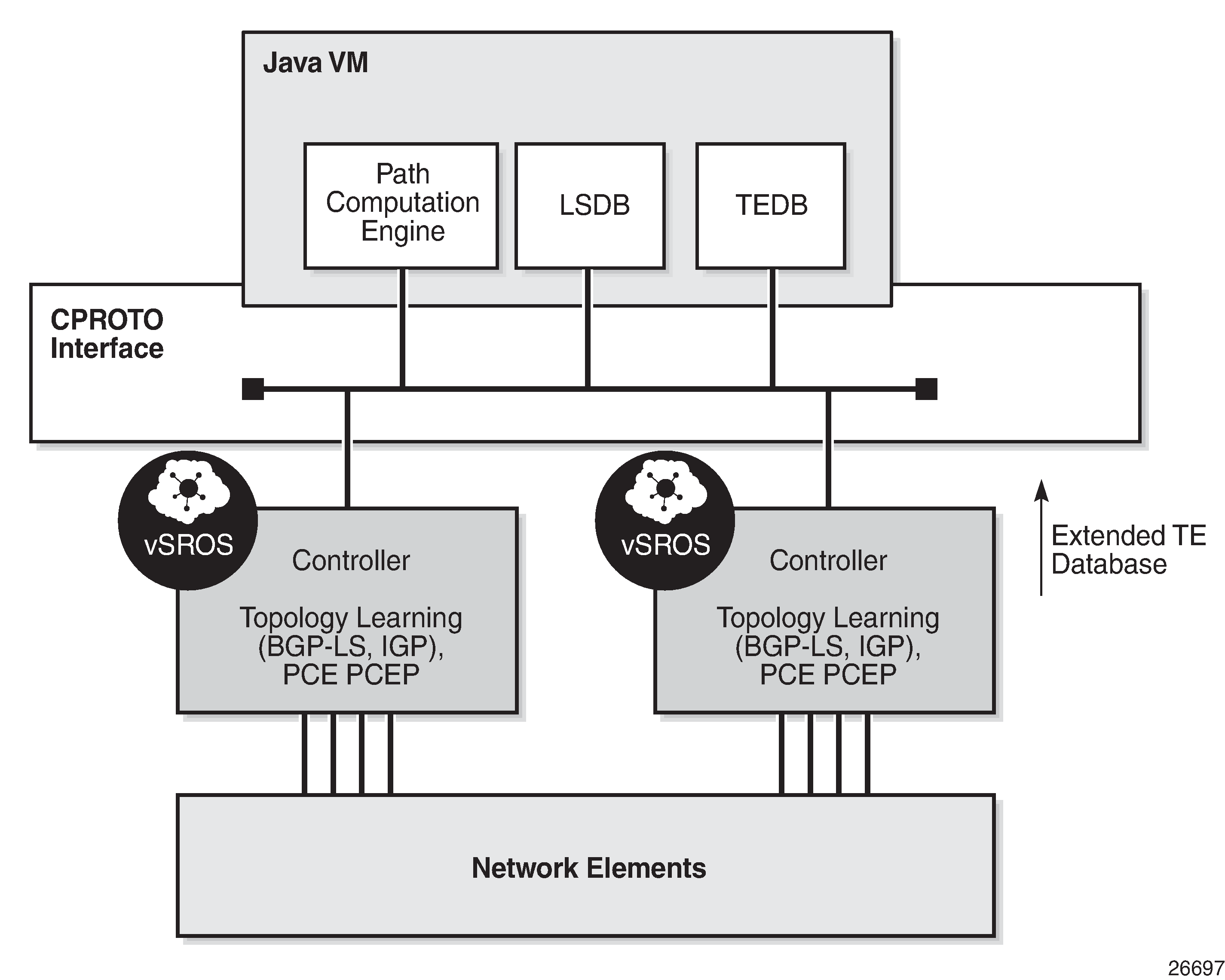
The NRC-P has the following architecture:
a single Virtual Machine (VM) handling the Java implementation of an MPLS path computation engine, a TE graph database, and an LSP database
a plug-in adapter with the Nokia CPROTO interface, providing reliable, TCP-based message delivery between vSROS and Java-VM. The plug-in adapter implements a compact encoding/decoding (codec) function for the message content using Google ProtoBuf. Google ProtoBuf also provides for automatic C++ (vSROS side) and Java (Java-VM side) code generation to process the exchanged message content.
a single VM running a vSROS image that handles the functions of topology discovery of multiple IGP instances and areas via IGP and NFM-P. For larger network domains, one VM running the vSROS image can be dedicated to a specific function.
The PCE module uses PCEP to communicate with its PCCs, and communicates with other PCEs to coordinate inter-domain path computation. Each router acting as a PCC initiates a PCEP session to the PCE in its domain.
When the user enables PCE control for one or more RSVP-TE LSPs, the PCE owns the path updating and periodic reoptimization of the LSPs. In this case, the PCE acts in an active stateful role. The PCE can also act in a passive stateful role for other LSPs on the router by discovering the LSPs and taking into account their resource consumption when computing the path for the LSPs it has control ownership of.
The following is a high-level description of the PCE and PCC capabilities:
base PCEP implementation, as defined in RFC 5440
active and passive stateful PCE LSP update, as defined in draft-ietf-pce-stateful-pce
delegation of LSP control to the PCE
synchronization of the LSP database with network elements for PCE-controlled LSPs and network element-controlled LSPs
support for PCC-initiated LSPs, as defined in draft-ietf-pce-stateful-pce
support for LSP path diversity across different LERs using extensions to the PCE path profile, as defined in draft-alvarez-pce-path-profiles
support for LSP path bidirectionality constraints using extensions to the PCE path profile, as defined in draft-alvarez-pce-path-profiles