Linear 1-for-1 protection of MPLS-TP LSPs is supported, as defined in RFC 6378. This applies only to LSPs (not PWs).
This is supported edge-to-edge on an LSP, between two LERs, where normal traffic is transported either on the working LSP or on the protection LSP using a logical selector bridge at the source of the protected LSP.
At the sink LER of the protected LSP, the LSP that carries the normal traffic is selected, and that LSP becomes the working LSP. A protection switching coordination (PSC) protocol coordinates between the source and sink bridge, which LSP will be used, as working path and protection path. The PSC protocol is always carried on a G-ACh on the protection LSP.
The 7210 SAS supports single-phased coordination between the LSP endpoints, in which the initiating LER performs the protection switch over to the alternate path and informs the far-end LER of the switch.
Bidirectional protection switching is achieved by the PSC protocol coordinating between the two end points to determine which of the two possible paths (that is, the working or protect path), transmits user traffic at any given time.
It is possible to configure non-revertive or revertive behavior. For non-revertive, the LSP will not switch back to the working path when the PSC switch over requests end, while for revertive configurations, the LSP always returns back to the working path when the switch over requests end.
The following figures show the behavior of linear protection in more detail.
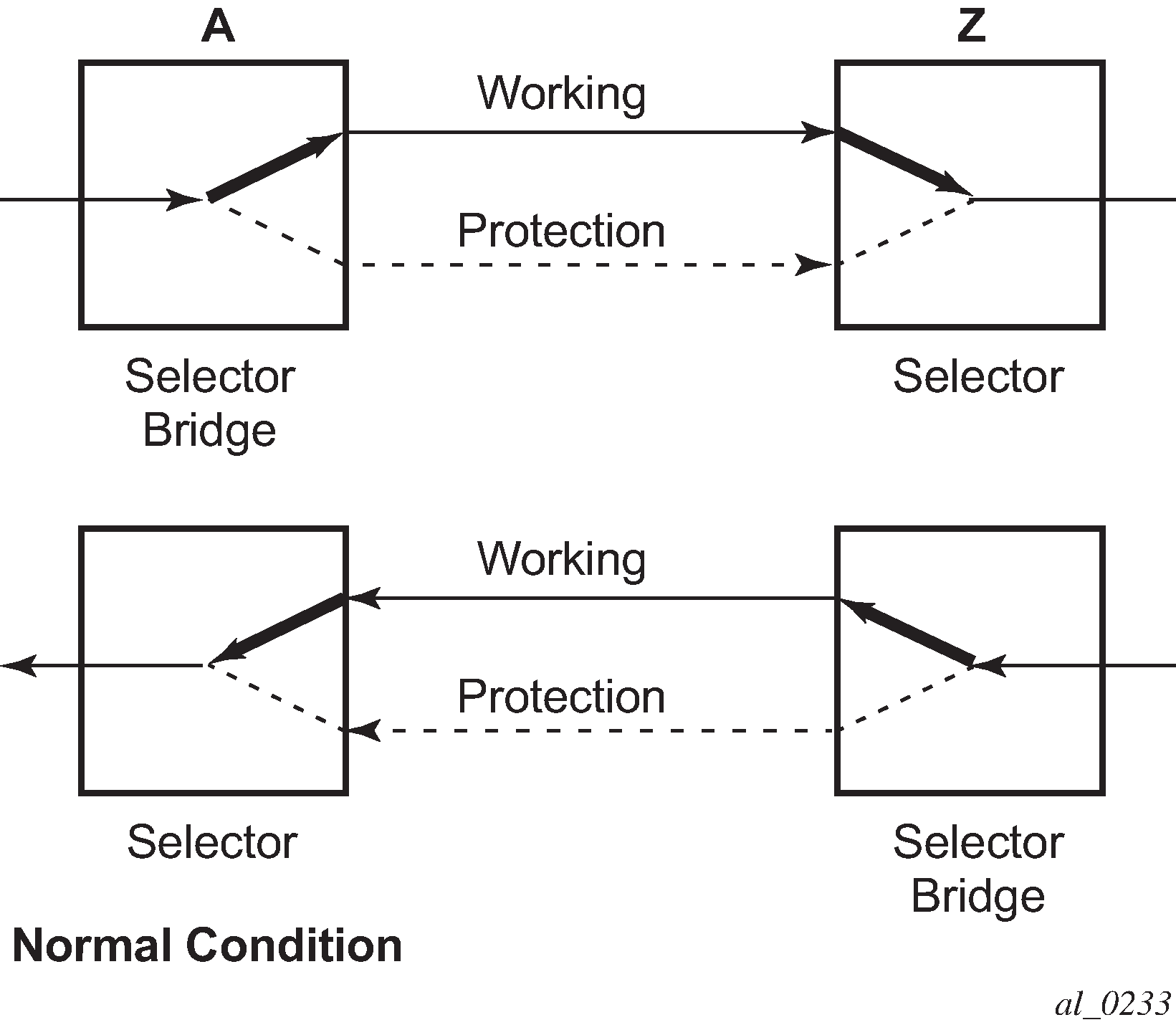
In normal condition, user data packets are sent on the working path on both directions, from A to Z and Z to A.
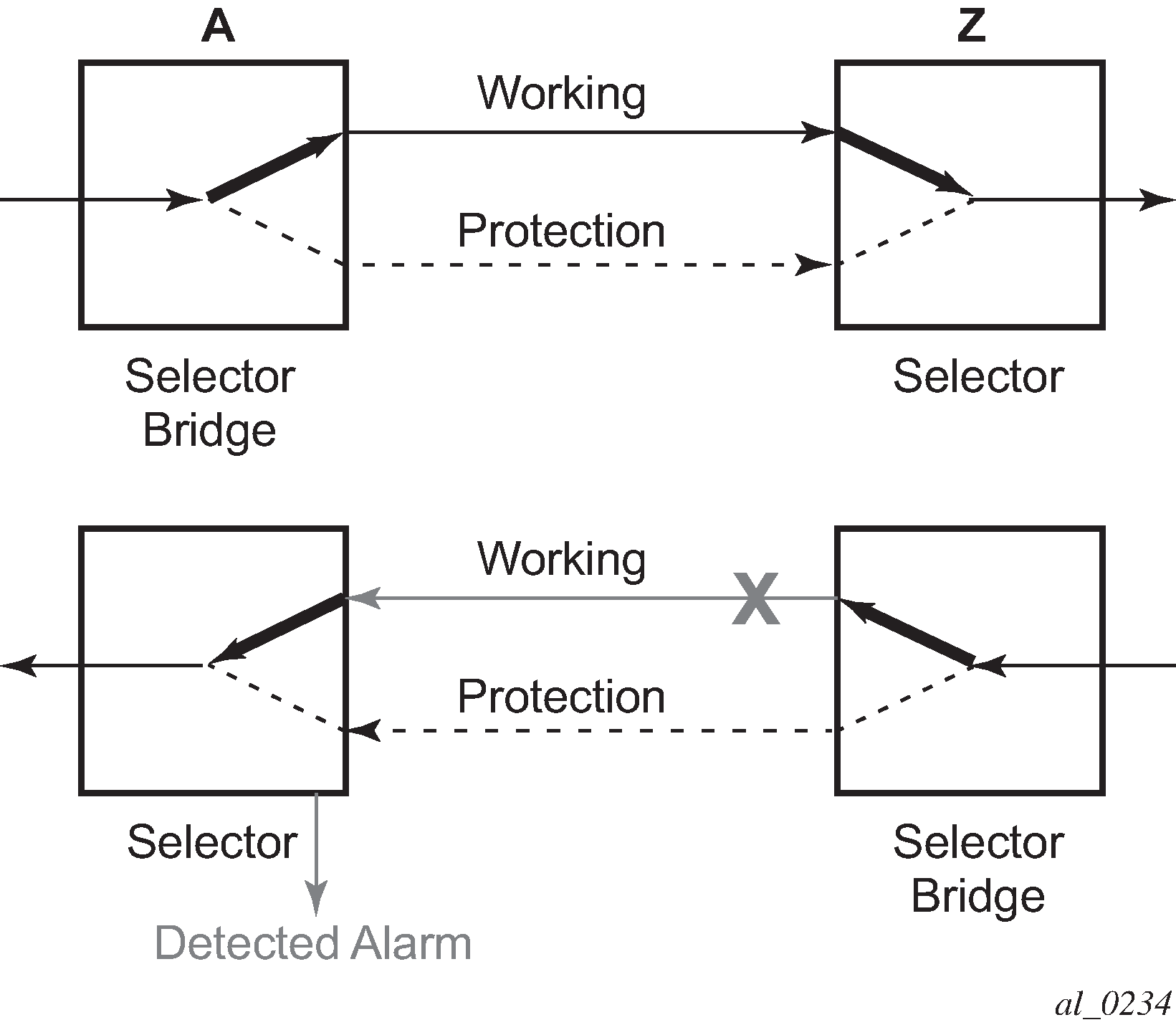
A defect in the direction of transmission from node Z to node A impacts the working connection Z-to-A, and initiates the detection of a defect at the node A.
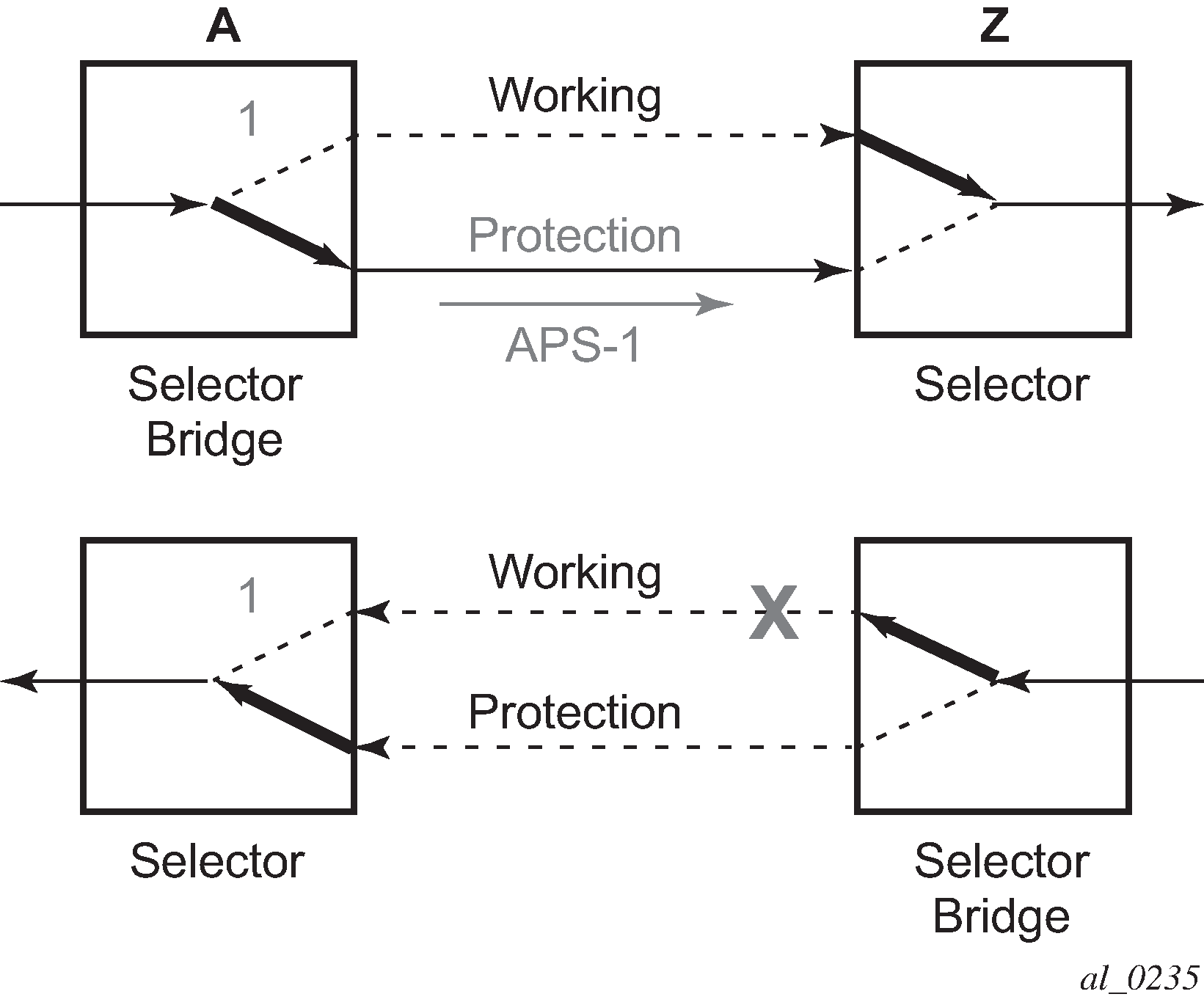
The unidirectional PSC protocol initiates protection switching: the selector bridge at node A is switched to protection connection A-to-Z and the selector at node A switches to protection connection Z to-A. The PSC packet, sent from node A to node Z, requests a protection switch to node Z.
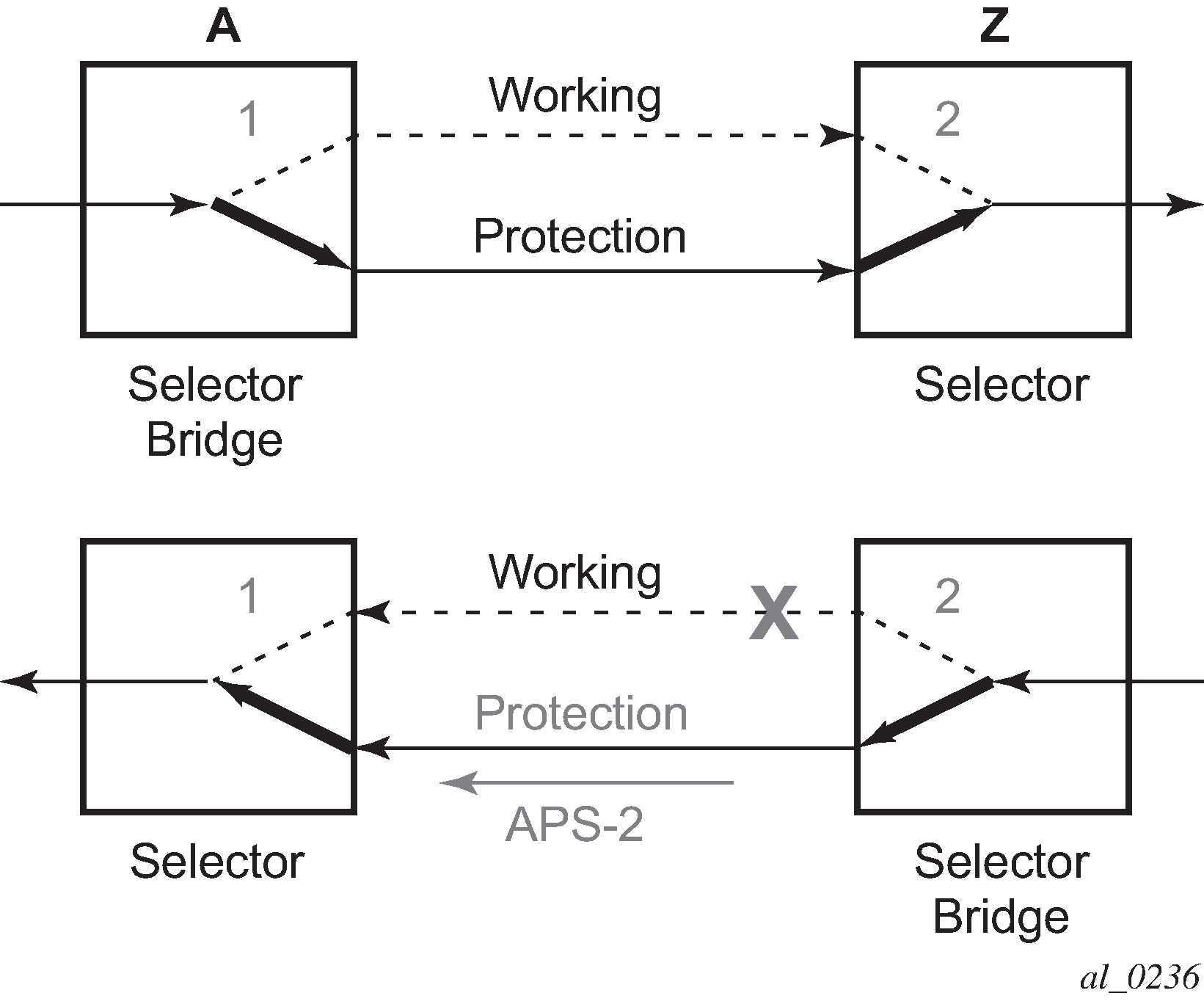
After node Z validates the priority of the protection switch request, the selector at node Z is switched to protection connection A-to-Z and the selector bridge at the node Z is switched to protection connection Z-to-A. The PSC packet, sent from node Z to node A, is used as acknowledge, informing node A about the switching.
If BFD CC or CC/CV OAM packets are used to detect defects on the working and protection path, they are inserted on both working and protection paths, and are sent regardless of whether the selected path is the currently active path.
The 7210 SAS supports the following operator commands:
Forced Switch
Manual Switch
Clear
Lockout of protection