Proactive Continuity Check (CC) is used to detect a loss of continuity defect (LOC) between two MEPs in a MEG. Proactive Connectivity Verification (CV) is used to detect an unexpected connectivity defect between two MEPs (For example: mis-merging or disconnection), as well as unexpected connectivity within the MEG with an unexpected MEP. This feature implements both functions using proactive generation of OAM packets by the source MEP that are processed by the peer sink MEP. CC and CV packets are always sent in-band such that they fate share with user traffic, either on an LSP, PW or section and are used to trigger protection switching mechanisms.
Proactive CC/CV based on bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) for MPLS-TP is described in RFC 6428. BFD packets are sent using operator configurable timers and encapsulated without UDP/IP headers on a standardized G-ACh channel on an LSP or PW.
CC packets simply consist of a BFD control packet, while CV packets also include an identifier for the source MEP in order that the sink MEP can detect if it is receiving packets from an incorrect peer MEP, therefore indicating a mis-connectivity defect. Other defect types (including period mis-configuration defect) should be supported. When a supported defect is detected, an appropriate alarm is generated (for example: log, SNMP trap) at the receiving MEP and all traffic on the associated transport path (LSP or PW) is blocked. This is achieved using linear protection for CC defects, and by blocking the ingress datapath for CV defects.
7210 SAS-R6, 7210 SAS-R12, and 7210 SAS-T only support BFD-based CC mode. BFD-based CC-CV mode is not supported in the current release.
When an LSP with CV is first configured, the LSP will be held in the CV defect state for 3.5 seconds after the first valid CV packet is received.
The following figures show an example of linear protection switching of LSPs triggered based on a CC or CV defect detected by BFD CC/CV.
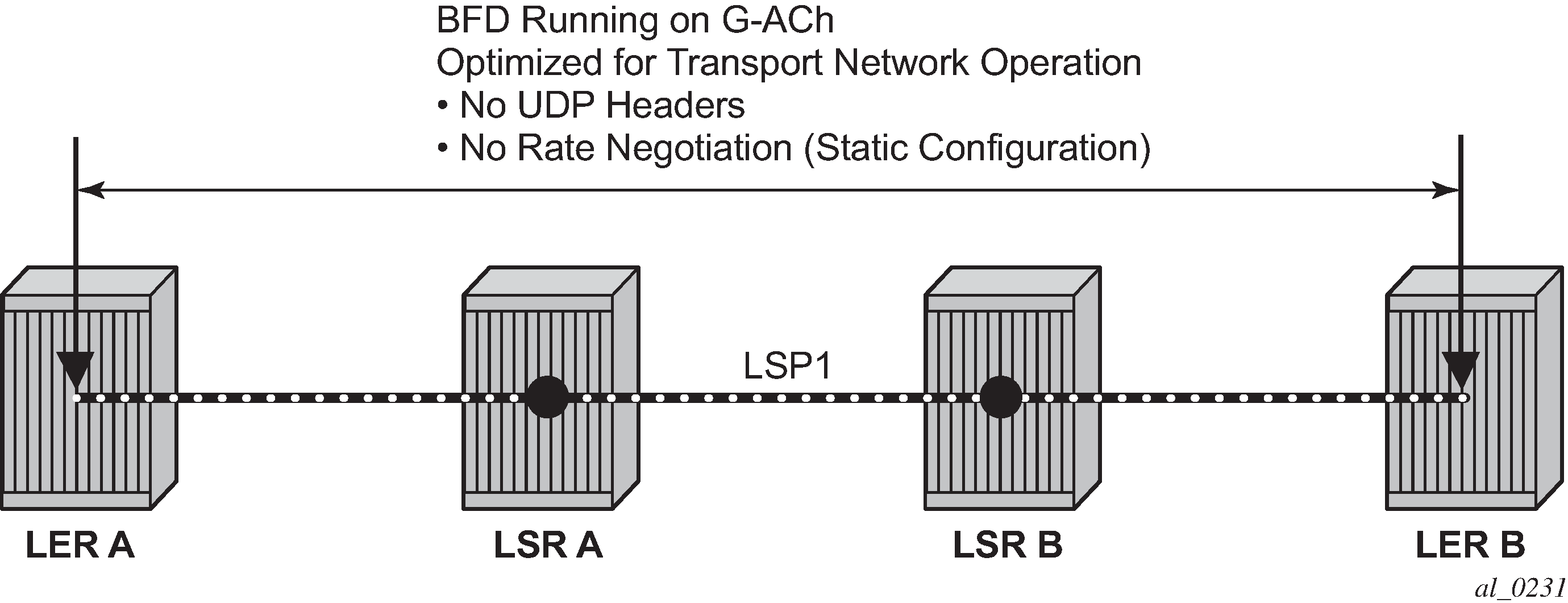
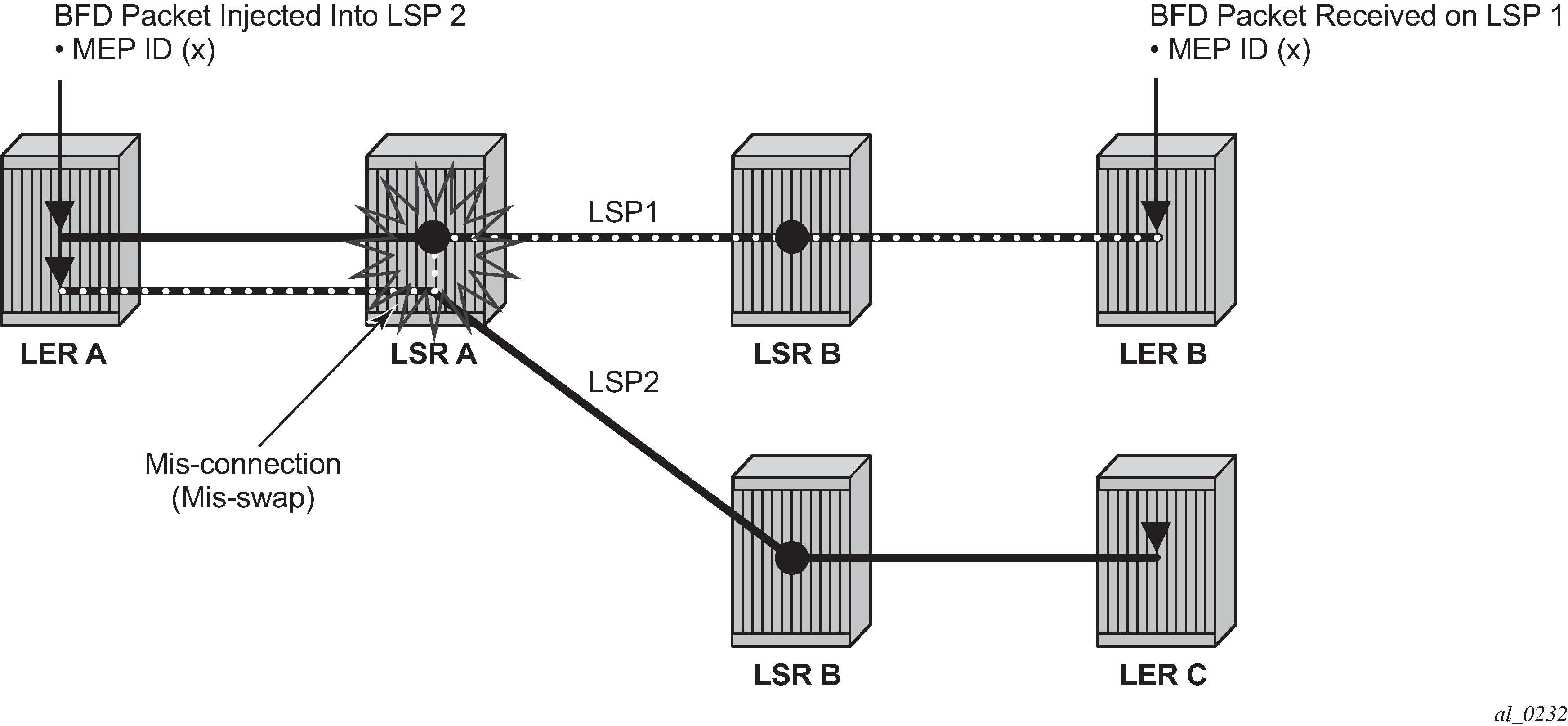
Note that RFC 6428 defines two BFD session modes: Coordinated mode, in which the session state on both directions of the LSP is coordinated and constructed from a single, bidirectional BFD session, and independent mode, in which two independent sessions are bound together at a MEP. Coordinated mode is supported.
BFD is supported on MPLS-TP LSPs. When BFD_CV detects a mis-connectivity on an LSP, the system will drop all incoming non-OAM traffic with the LSP label (at the LSP termination point) instead of forwarding it to the associated SAP or PW segment.
The following G-ACh channel types are supported for the combined CC/CV mode:
0x22 for BFD CC with no IP encapsulation
0x23 for BFD CV
The 0x07 G-ACh channel type is used for the CC-only mode.