The DDMAP TLV provides with exactly the same features as the existing DSMAP TLV, plus the enhancements to trace the details of LSP stitching and LSP hierarchy. The latter is achieved using a new sub-TLV of the DDMAP TLV called the FEC stack change sub-TLV. The following figures show the structures of these two objects as defined in RFC 6424.
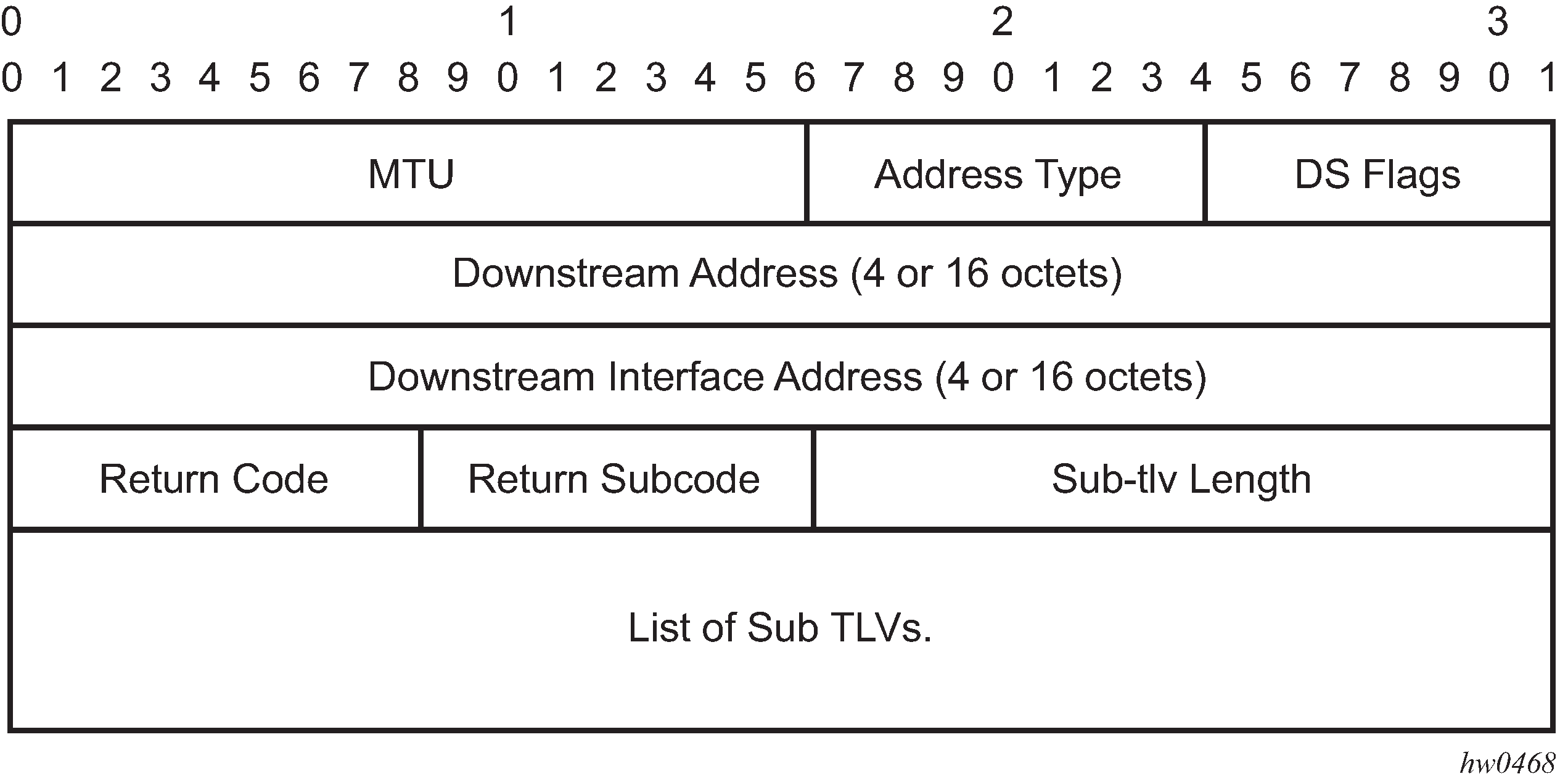
The DDMAP TLV format is derived from the DSMAP TLV format. The key change is that variable length and optional fields have been converted into sub-TLVs. The fields have the same use and meaning as in RFC 4379.
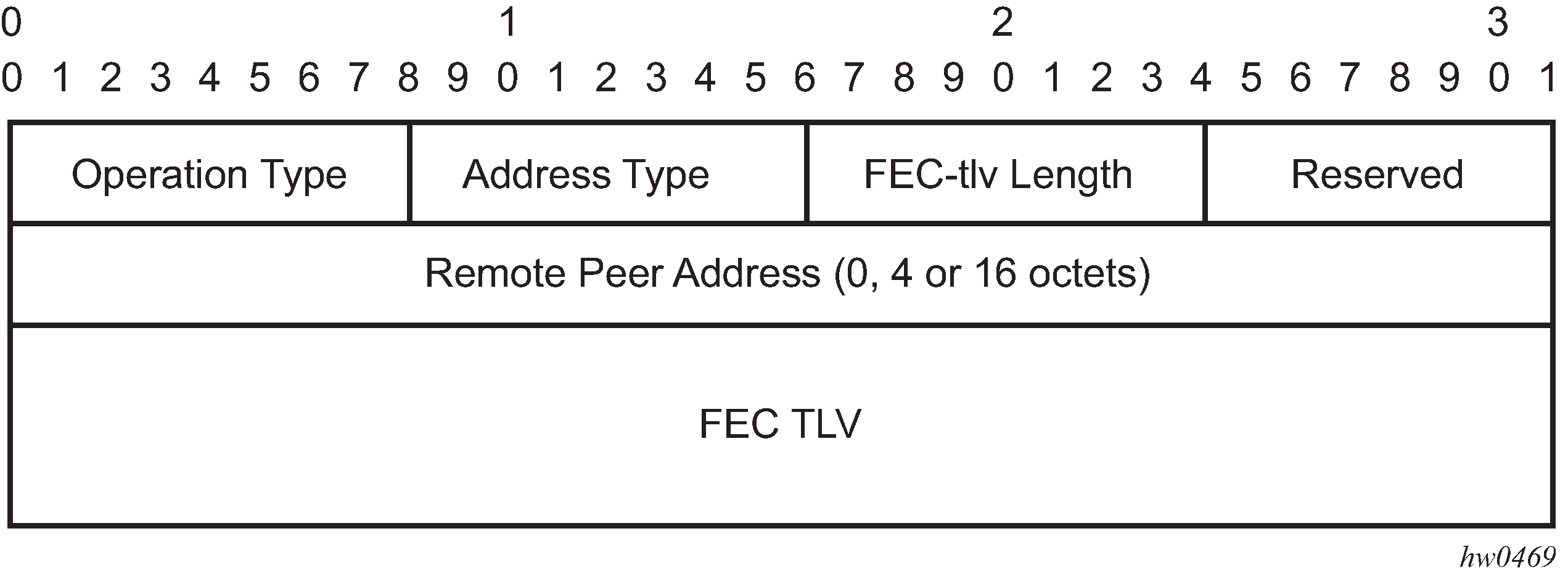
The operation type specifies the action associated with the FEC stack change. The following operation types are defined.
Type # Operation
------ ---------
1 Push
2 Pop
More details on the processing of the fields of the FEC stack change sub-TLV are provided later in this section.
The user can configure which downstream mapping TLV to use globally on a system by using the following command:
configure test-oam mpls-echo-request-downstream-map {dsmap | ddmap}
This command specifies which format of the downstream mapping TLV to use in all LSP trace packets and LDP tree trace packets originated on this node. The Downstream Mapping (DSMAP) TLV is the original format in RFC 4379 and is the default value. The Downstream Detailed Mapping (DDMAP) TLV is the new enhanced format specified in RFC 6424.
This command applies to LSP trace of an RSVP P2P LSP, a MPLS-TP LSP, a BGP IPv4 Label Route, or LDP unicast FEC, and to LDP tree trace of a unicast LDP FEC. It does not apply to LSP trace of an RSVP P2MP LSP which always uses the DDMAP TLV.
The global DSMAP/DDMAP setting impacts the behavior of both OAM LSP trace packets and SAA test packets of type lsp-trace and is used by the sender node when one of the following events occurs:
An SAA test of type lsp-trace is created (not modified) and no value is specified for the per-test downstream-map-tlv {dsmap | ddmap | none} option. In this case the SAA test downstream-map-tlv value defaults to the global mpls-echo-request-downstream-map value.
An OAM test of type lsp-trace test is executed and no value is specified for the per-test downstream-map-tlv {dsmap | ddmap | none} option. In this case, the OAM test downstream-map-tlv value defaults to the global mpls-echo-request-downstream-map value.
A consequence of the preceding rules is that a change to the value of mpls-echo-request-downstream-map option does not affect the value inserted in the downstream mapping TLV of existing tests.
The following are the details of the processing of the new DDMAP TLV:
When either the DSMAP TLV or the DDMAP TLV is received in an echo request message, the responder node will include the same type of TLV in the echo reply message with the correct downstream interface information and label stack information.
If an echo request message without a Downstream Mapping TLV (DSMAP or DDMAP) expires at a node which is not the egress for the target FEC stack, the responder node always includes the DSMAP TLV in the echo reply message. This can occur in the following cases:
The user issues a LSP trace from a sender node with a min-ttl value higher than 1 and a max-ttl value lower than the number of hops to reach the egress of the target FEC stack. This is the sender node behavior when the global configuration or the per-test setting of the DSMAP/DDMAP is set to DSMAP.
The user issues a LSP ping from a sender node with a ttl value lower than the number of hops to reach the egress of the target FEC stack. This is the sender node behavior when the global configuration of the DSMAP/DDMAP is set to DSMAP.
The behavior in 2.a is changed when the global configuration or the per-test setting of the Downstream Mapping TLV is set to DDMAP. The sender node will include in this case the DDMAP TLV with the Downstream IP address field set to the all-routers multicast address as per Section 3.3 of RFC 4379. The responder node then bypasses the interface and label stack validation and replies with a DDMAP TLV with the correct downstream information for the target FEC stack.
A sender node never includes the DSMAP or DDMAP TLV in an LSP ping message.