VRRP for IPv4 is supported on all 7210 SAS platforms as described in this document, except those operating in access-uplink mode.
VRRP for IPv6 is supported only for VPRN interfaces on 7210 SAS-Mxp.
VRRP for IPv6 does not support authentication. See IETF RFC 5798 for more information.
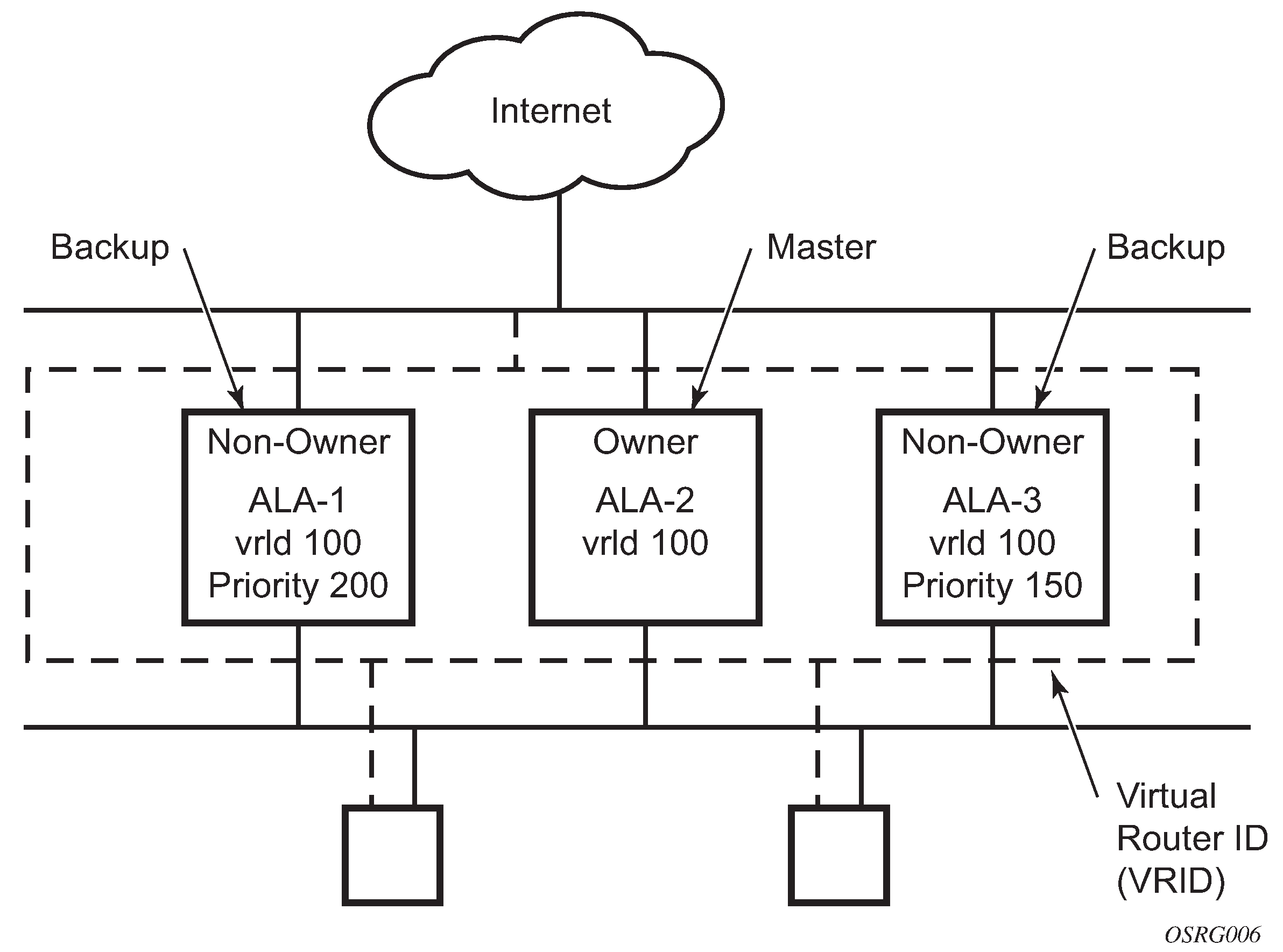
VRRP describes a method of implementing a redundant IP interface shared between two or more routers on a common LAN segment, allowing a group of routers to function as one virtual router. When this IP interface is specified as a default gateway on hosts directly attached to this LAN, the routers sharing the IP interface prevent a single point of failure by limiting access to this gateway address. VRRP can be implemented on IES service interfaces, VPRN interfaces, and on core network IP interfaces.
The VRRP standards RFC 3768 use the term ‟master” state to denote the virtual router that is currently acting as the active forwarding router for the VRRP instance.
If the virtual router in the master state fails, the backup router configured with the highest acceptable priority becomes the active virtual router. The new active router assumes the normal packet forwarding for the local hosts.
The following figure shows an example of a VRRP configuration.