Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management (ETH-CFM) is defined in two similar standards: IEEE 802.1ag and ITU-T Y.1731. Both standards specify protocols, procedures, and managed objects to support transport fault management, including discovery and verification of the path, detection and isolation of a connectivity fault for each Ethernet service instance.
The configuration is split into multiple CLI contexts. The base ETH-CFM configuration defines the different management constructs and administrative elements. This configuration is performed in the eth-cfm context. The individual management points are configured within the specific service contexts in which they are applied (port, SAP, and so on).
See the 7210 SAS-R6, R12 Services Guide for detailed information about the basic service-applicable material to build the service-specific management points, MEPs, and MIPs. The different service types support a subset of the features from the complete ETH-CFM suite.
ETH-CC used for continuity is available to all MEPs configured within a service. The 7210 SAS devices support Down MEPs and Up MEPs, though the support is not available on all platforms. See the 7210 SAS-Mxp, R6, R12, S, Sx, T OAM and Diagnostics Guide for more information about platform support.
The troubleshooting tools ETH-LBM, ETH-LBR, LTM ETH-TST, and LTR ETH-TST, defined by the IEEE 802.1ag specification and the ITU-T Y.1731 recommendation, are applicable to all MEPs (and MIPs where appropriate). The advanced notification function, Alarm Indication Signal (AIS), defined by the ITU-T Y.1731, is supported on Epipe services.
The advanced performance functions, 1DM, DMM/DMR, and SLM/SLR, are supported on all service MEPs.
See the 7210 SAS-Mxp, R6, R12, S, Sx, T OAM and Diagnostics Guide for more information about the individual features and functions that are supported and configuration guidelines applicable to CFM entities on the 7210 SAS.
The following table lists ETH-CFM acronym expansions.
| Acronym | Expansion |
|---|---|
1DM |
One-way Delay Measurement (Y.1731) |
AIS |
Alarm Indication Signal |
BNM |
Bandwidth Notification Message (Y.1731 sub OpCode of GMN) |
CCM |
Continuity Check Message |
CFM |
Connectivity Fault Management |
DMM |
Delay Measurement Message (Y.1731) |
DMR |
Delay Measurement Reply (Y.1731) |
GMN |
Generic Message Notification |
LBM |
Loopback Message |
LBR |
Loopback Reply |
LTM |
Linktrace Message |
LTR |
Linktrace Reply |
ME |
Maintenance Entity |
MA |
Maintenance Association |
MA-ID |
Maintenance Association Identifier |
MD |
Maintenance Domain |
MEP |
Maintenance Association Endpoint |
MEP-ID |
Maintenance Association Endpoint Identifier |
MHF |
MIP Half Function |
MIP |
Maintenance Domain Intermediate Point |
OpCode |
Operational Code |
RDI |
Remote Defect Indication |
TST |
Ethernet Test (Y.1731) |
SLM |
Synthetic Loss Message (Y.1731) |
SLR |
Synthetic Loss Reply (Y.1731) |
ETH-CFM capabilities may be deployed in many different Ethernet service architectures. The Ethernet-based SAPs and SDP bindings provide the endpoint on which the management points may be created. The basic functions can be used in different services, VPLS and Epipe. The following figures show two possible example scenarios for ETH-CFM deployment in Ethernet access and aggregation networks.
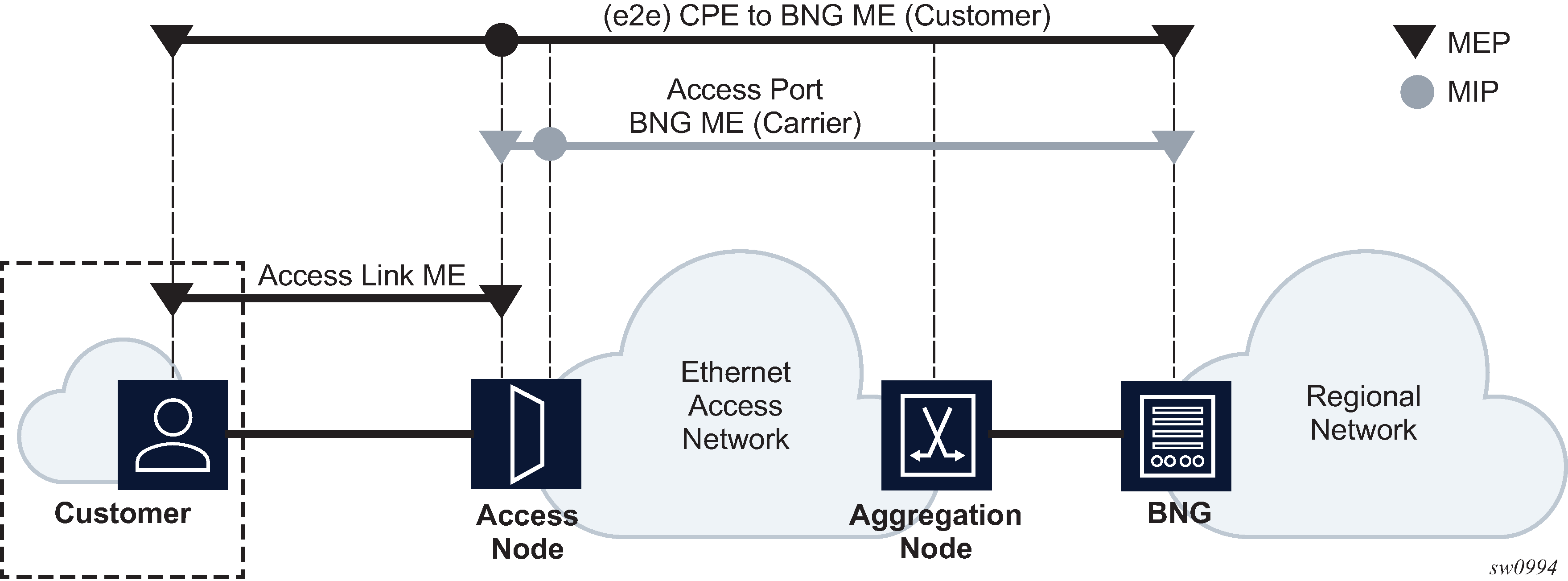
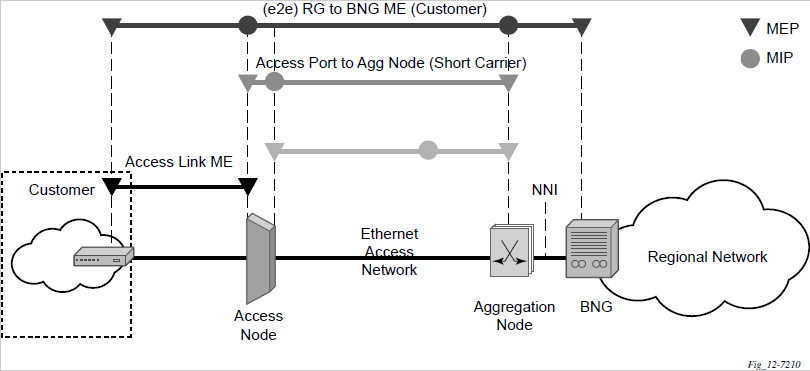
The following functions are supported:
CFM can be enabled or disabled on a SAP or SDP bindings basis.
The eight ETH-CFM levels are suggested to be broken up numerically between customer 7 to 5, service provider 4 to 3 and operator 2 to 1. Level 0 typically is meant to monitor direct connections without any MIPs and should be reserved for port-based G8032 MEPs. These can be configured, deleted or modified.
Down MEP and Up MEP with an MEP-ID on a SAP/SDP binding for each MD level can be configured, modified, or deleted. Each MEP is uniquely identified by the MA-ID, MEP-ID tuple.
MEP creation on a SAP is only allowed for Ethernet ports (with null, q-tags, QinQ encapsulations).
MEP support in different services and the endpoints configured in the services (SAPs, SDPs, IP interfaces, and so on) varies across services and 7210 platforms. See the 7210 SAS-Mxp, R6, R12, S, Sx, T OAM and Diagnostics Guide for more information about MEP support on 7210 SAS platforms.
MIP creation on a SAP for each MD level can be enabled and disabled. MIP creation is automatic or manual when it is enabled. When MIP creation is disabled for an MD level, the existing MIP is removed. The 7210 SAS platforms have the notion of ingress and egress MIPs. Ingress MIP responds to OAM messages that are received. Egress MIP responds to OAM messages that are sent. Ingress and egress MIP support for SAP, SDP bindings and services varies and is listed in the following table. See the 7210 SAS-Mxp, R6, R12, S, Sx, T OAM and Diagnostics Guide for more information about MEP support on 7210 SAS platforms.