7. VPRN Services
This chapter provides information about the Virtual Private Routed Network (VPRN) service and implementation notes.
Topics in this chapter include:
7.1. VPRN Service Overview
Topics in this section include:
RFC 2547bis, an extension of RFC 2547, details a method of distributing routing information and forwarding data to provide a Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to end customers.
Each Virtual Private Routed Network (VPRN) consists of a set of customer sites connected to one or more PE routers. Each associated PE router maintains a separate IP forwarding table for each VPRN. Additionally, the PE routers exchange the routing information configured or learned from all customer sites via MP-BGP peering. Each route exchanged via the MP-BGP protocol includes a route distinguisher (RD), which identifies the VPRN association.
The service provider uses BGP to exchange the routes of a particular VPN among the PE routers that are attached to that VPN. This is done in a way that ensures that routes from different VPNs remain distinct and separate, even if two VPNs have an overlapping address space. Within a particular VPN, the PE routers distribute route information from and to the CE routers. Since the CE routers do not peer with each other, there is no overlay visible to the VPN routing algorithm.
When BGP distributes a VPN route, it also distributes an MPLS label for that route. On an individual 7705 SAR, a single label is assigned to (advertised for) all routes in a VPN. A VRF lookup is used to determine the egress interface for a packet.
Before a customer data packet travels across the service provider’s backbone network, it is encapsulated with the MPLS label that corresponds, in the customer’s VPN, to the route that best matches the packet’s destination address. That label (called the inner label) is the label that was advertised from the destination 7705 SAR, as described in the previous paragraph. The MPLS packet is further encapsulated with either another MPLS label or GRE tunnel header, so that it gets tunneled across the backbone to the proper PE router.
Each route exchanged by the MP-BGP protocol includes a route distinguisher (RD), which identifies its VPRN association. Thus, the backbone core routers do not need to know the VPN routes.
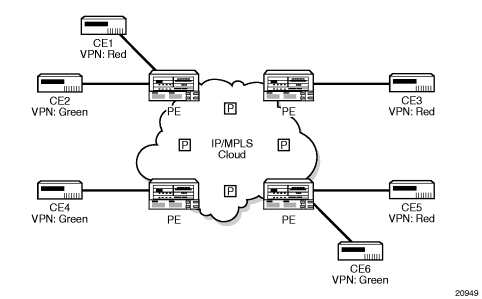
Figure 109 shows an example of a VPRN network diagram, showing two VPNs (labeled “Red” and “Green”) attached to PEs. The core routers are labeled “P”.
Figure 109: Virtual Private Routed Network
7.1.1. Routing Prerequisites
RFC 2547bis requires the following features:
- multiprotocol extensions
- LDP support
- extended BGP community support
- BGP capability negotiation
- parameters defined in RFC 2918, BGP Route Refresh, and RFC 2796, Route Reflector
- a 4-byte autonomous system (AS) number
Tunneling protocol requirements are as follows:
- RFC 2547bis, BGP/MPLS VPNs, recommends implementing Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) to set up a full mesh of LSPs based on the IGP
- MPLS RSVP-TE tunnels can be used instead of LDP
- BGP route tunnels can be used as defined in RFC 3107
- alternatively, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels can also be used
7.1.2. BGP Support
BGP is used with BGP extensions, as mentioned in Routing Prerequisites, to distribute VPRN routing information across the service provider’s network.
BGP was initially designed to distribute IPv4 routing information. Therefore, multiprotocol extensions and the use of a VPN-IPv4 address were created to extend the ability of BGP to carry overlapping routing information. A VPN-IPv4 address is a 12-byte value consisting of the 8-byte route distinguisher (RD) and the 4-byte IPv4 IP address prefix. The RD must be unique within the scope of the VPRN. This allows the IP address prefixes within different VRFs to overlap. In addition, 128-bit VPN-IPv6 addresses extend the capability to distribute VPRN routing information.
BGP route tunnels can be used to distribute label mapping information for a particular route, as defined in RFC 3107. For more information on BGP route tunnels, refer to the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide, “BGP Route Tunnel”.
| Note: The 7705 SAR supports 4-byte AS numbers, as defined in RFC 4893, BGP Support for Four-octet AS Number Space. This allows up to 4 294 967 295 unique AS numbers. |
VPRN BGP is configured through the config>service>vprn>bgp context. Global BGP is configured through the config>router>bgp context.
7.1.2.1. BGP Fast Reroute with Prefix-Independent Convergence in a VPRN
BGP Fast Reroute (FRR) creates an alternate path to support fast rerouting of BGP traffic around failed or unreachable next hops. When BGP FRR is enabled, the system switches to a precalculated alternate path as soon as a failure is detected.
BGP Prefix-Independent Convergence (PIC) is supported on the 7705 SAR and is automatically enabled when a BGP backup path is enabled. With BGP FRR and PIC, alternate paths are precalculated and the FIB is updated with all alternate next hops. When a prefix has a backup path, and its primary paths fail, the affected traffic is rapidly diverted to the backup path without waiting for control plane reconvergence to occur. When many prefixes share the same primary paths, and in some cases also share the same backup path, the time to switch traffic to the backup path can be very fast and is independent of the number of prefixes.
In the VPRN context, BGP FRR is supported using unlabeled IPv4 /IPv6 and VPN-IPv4/VPN-IPv6 routes. The supported VPRN scenarios are outlined in Table 116.
Table 116: BGP FRR Scenarios
Ingress Packet | Primary Route | Backup Route | PIC |
IPv4 (ingress PE) | IPv4 route with next hop A resolved by an IPv4 route | IPv4 route with next hop B resolved by an IPv4 route | Yes |
IPv4 (ingress PE) | VPN-IPv4 route with next hop A resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP or BGP tunnel | VPN-IPv4 route with next hop B resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP or BGP tunnel | Yes |
IPv6 (ingress PE) | VPN-IPv6 route with next hop A resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP, or BGP tunnel | VPN-IPv6 route with next hop B resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP, or BGP tunnel | Yes |
MPLS (egress PE) | IPv4 route with next hop A resolved by an IPv4 route | IPv4 route with next hop B resolved by an IPv4 route | Yes |
MPLS (egress PE) | IPv4 route with next hop A resolved by an IPv4 route | VPN-IPv4 route with next hop B resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP or BGP tunnel | Yes |
MPLS (egress PE) | IPv6 route with next hop A resolved by an IPv6 route | VPN-IPv6 route with next hop B resolved by a GRE, LDP, RSVP or BGP tunnel | Yes |
If all IP prefixes require backup path protection, use a combination of the BGP context backup-path command and the VPRN context enable-bgp-vpn-backup command. If only specific IP prefixes require backup path protection, use route policies to apply the install backup path action to the best paths of the IP prefixes requiring protection.
For information about BGP FRR specific to the BGP context, refer to the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide, “BGP FRR with Prefix-Independent Convergence”.
7.1.2.2. BGP Next-Hop Resolution and Peer Tracking
The 7705 SAR can attach a route policy to the BGP next-hop resolution process and can allow a route policy to be associated with the optional BGP peer-tracking function. These two features are supported for VPRN BGP service.
BGP next-hop resolution determines the best matching route (or tunnel) for the BGP next-hop address and uses information about this resolving route when running the best-path selection algorithm and programming the forwarding table. Attaching a policy to BGP next-hop resolution provides additional control over which IP routes in the routing table can become resolving routes. Similar flexibility and control is available for BGP peer tracking, which is an optional feature that allows a session with a BGP neighbor to be taken down if there is no IP route to the neighbor address or if the best matching IP route is rejected by the policy.
Use the following CLI syntax to configure next-hop resolution and peer-tracking policies:
For details, refer to the “Route Policies for BGP Next-Hop Resolution and Peer Tracking” section in the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide.
7.1.3. IPSec Support
The 7705 SAR supports IPSec and IPSec tunnels, where VPRN or IES is used as a public (untrusted) network-facing service and VPRN is used as a private (trusted) network-facing service. VPRN interfaces support provisioning of tunnel SAPs as part of IPSec provisioning. The sap-id for a public-side IPSec tunnel SAP is tunnel-1.public:tag. The sap-id for a private-side IPSec tunnel SAP is tunnel-1.private:tag
For more information, see the IPSec chapter in this guide.
7.1.4. Security Zones and VPRN
The 7705 SAR supports a number of mechanisms for node security, including Access Control Lists (ACLs), Network Address Translation (NAT), and stateful, zone-based firewalls. For information about ACLs, NAT, and firewalls, refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Configuring Security Parameters”.
NAT and firewall security configurations are both based on zones. Zones segment a network, making it easier to control and organize traffic. A zone consists of a group of Layer 3 interfaces with common criteria, bundled together. Security policies, which define a set of rules that determine how NAT or firewall should direct traffic, can be applied to the entire zone or to multiple zones. To enable NAT or firewall functionality, security policy, application group, host group, and profile parameters must be configured under the config>security context in the CLI, and a security zone must be configured under one or more of the following contexts:
- config>router>zone
- config>service>vprn>zone
- config>service>ies>zone
A zone is created by adding at least one Layer 3 interface to the zone configuration. Multiple zones can be created within each service context or within the router context. Layer 3 interfaces from different services cannot be grouped into a single common zone. Table 117 lists the supported interfaces that can be added to zones in each CLI context for NAT or firewall.
Table 117: Security Zone Interfaces per Context
CLI Context | Interface Type | NAT | Firewall |
Router | Layer 3 | ✓ | ✓ |
VPRN | SAP | ✓ | ✓ |
Spoke-SDP termination | ✓ | ✓ | |
IPSec private | ✓ | ✓ | |
IPSec public | ✓ | ||
Routed VPLS | ✓ | ✓ | |
MP-BGP | ✓ | ✓ | |
IES | SAP | ✓ | ✓ |
Spoke-SDP termination | ✓ | ✓ | |
IPSec public | ✓ | ||
Routed VPLS | ✓ | ✓ |
A zone configured in the VPRN context could be used to create border security for Layer 3 service traffic traversing from the secure edge VPRN into the network core.
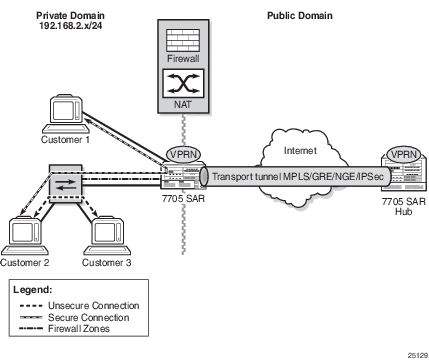
Figure 110 shows a firewall on a VPRN, where the core of the network is protected from access devices and from any traffic entering the VPRN through the transport tunnel. A VPRN configured with access security policies can also protect access networks or LANs from each other.
Figure 110: Firewall Protection for the Network Core
A security zone can also be created with spoke SDPs or auto-bind tunnels that have been configured for a VPRN service using MP-BGP. For auto-bind tunnels, the auto-bind-tunnel resolution-filter type can be set to gre, ldp, rsvp, sr-isis, sr-ospf, or sr-te. When a zone contains spoke SDPs or auto-bind MPLS tunnels, it cannot contain any other type of interface. A zone configured with spoke SDPs or auto-bind MPLS tunnels will firewall traffic arriving from the access side to this zone for any MP-BGP transport tunnel residing in that Layer 3 service. Once a security zone is created for MP-BGP transport tunnels, all MP-BGP transport tunnels going to far-end peers are part of this zone. Traffic entering or exiting the zone is firewalled; however, traffic traveling from one auto-bind tunnel to another within the same zone is not firewalled.
7.1.5. Static One-to-One NAT and VPRN
With static one-to-one NAT, NAT is performed on packets traveling from an inside (private) interface to an outside (public) interface or from an outside interface to an inside interface. Static one to-one NAT can be applied to a single IP address or a subnet of IP addresses and is performed on the IP header of a packet, not on the UDP/TCP port.
Mapping statements, or entries, can be configured to map an IP address range to a specific IP address. The direction of the NAT mapping entry dictates whether NAT is performed on a packet source IP address or subnet or on a packet destination IP address or subnet. The 7705 SAR supports inside mapping entries that map an inside IP address range to an outside IP address range sequentially.
With an inside mapping entry, the following points apply.
- Packets that originate from an inside interface and are destined for an inside interface are forwarded without any NAT being applied.
- If there is a matching one-to-one NAT mapping entry, packets that originate from an inside interface and are destined for an outside interface undergo static one-to-one NAT where NAT changes the source IP address of the packet IP header. The packet is forwarded whether or not a NAT mapping entry is found unless the drop-packets-without-nat-entry command is enabled. When a mapping entry is not found and the drop-packets-without-nat-entry command is enabled, the packet is not forwarded.
- If there is a matching one-to-one NAT mapping entry, packets that originate from an outside interface and are destined for an inside interface undergo static one-to-one NAT where NAT changes the destination IP address of the packet IP header. The packet is forwarded whether or not a NAT mapping entry is found unless the drop-packets-without-nat-entry command is enabled. When a mapping entry is not found and the drop-packets-without-nat-entry command is enabled, the packet is not forwarded.
- Packets that originate from an outside interface and are destined for an outside interface are forwarded without any NAT being applied.
Static one-to-one NAT is supported in the GRT and in VPRNs. For more information about static one-to-one NAT, refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Static One-to-One NAT”.
For VPRNs, one-to-one NAT can be configured between an inside interface and a outside MP-BGP MPLS transport tunnel interface. Policies should be used to not leak the inside interface/IP address via MP-BGP to the peer. Policies should be used to leak the NAT routes to the MP-BGP peer.
Table 118 lists the types of outside and inside interfaces that are supported in a VPRN for one-to-one NAT.
Table 118: VPRN Interfaces Supported for Static One-to-One NAT
VPRN Interface Type | Outside | Inside |
SAP interface | Yes | Yes |
R-VPLS interface | Yes | Yes |
Layer 3 spoke SDP interface | Yes | Yes |
IPSec private interface | Yes | Yes |
Auto-bind GRE/MPLS (MP-BGP), where MPLS includes segment routing, LDP, and RSVP | Yes | No |
7.1.6. Route Distinguishers
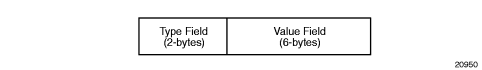
The route distinguisher (RD) is an 8-byte value consisting of two major fields: the Type field and Value field. The Type field determines how the value field should be interpreted. The 7705 SAR implementation supports the three (3) Type-Value combinations, as defined in RFC 2547bis. Figure 111 illustrates the RD structure.
Figure 111: Route Distinguisher Structure
The three Type-Value combinations supported are described in Table 119.
Table 119: Route Distinguisher Type-Value Fields
Type Field | Value Field | Notes |
Type 0 | Administrator subfield (2 bytes) | The Administrator field must contain an AS number (using private AS numbers is discouraged) |
Assigned number subfield (4 bytes) | The Assigned field contains a number assigned by the service provider | |
Type 1 | Administrator subfield (4 bytes) | The Administrator field must contain an IP address (using private IP address space is discouraged) |
Assigned number subfield (2 bytes) | The Assigned field contains a number assigned by the service provider | |
Type 2 | Administrator subfield (4 bytes) | The Administrator field must contain a 4-byte AS number (using private AS numbers is discouraged) |
Assigned number subfield (2 bytes) | The Assigned field contains a number assigned by the service provider |
7.1.6.1. PE-to-CE Route Exchange
Routing information between the Provider Edge (PE) and Customer Edge (CE) can be exchanged by the following methods:
- EBGP (for IPv4 and IPv6 address families)
- OSPF
- OSPFv3
- RIP
- static routes
Each protocol provides controls to limit the number of routes learned from each CE router.
7.1.6.1.1. Route Redistribution
Routing information learned from the PE-to-CE routing protocols and configured static routes is injected into the associated local virtual routing and forwarding table (VRF). In the case of the dynamic routing protocols, there may be protocol-specific route policies that modify or reject certain routes before they are injected into the local VRF.
Route redistribution from the local VRF to the PE-to-CE routing protocols is controlled via the route policies in each routing protocol instance, in the same manner that is used by the base router instance.
The advertisement or redistribution of routing information from the local VRF to or from the MP-BGP instance is specified per VRF and is controlled by VRF route target associations or by VRF route policies.
A route belonging to a VPRN must use the protocol owner, VPN-IPv4, to denote that it is a VPRN route. This can be used within the route policy match criteria.
7.1.6.1.2. CPE Connectivity Check
Static routes are used within many IES and VPRN services. Unlike dynamic routing protocols, there is no way to change the state of routes based on availability information for the associated CPE. CPE connectivity check adds flexibility so that unavailable destinations are removed from the service provider’s routing tables dynamically, and wasted bandwidth is minimized.
Figure 112 and Figure 113 illustrate the use of CPE connectivity check in directly connected and multiple-hop connected routes.
Figure 112: Directly Connected IP Target
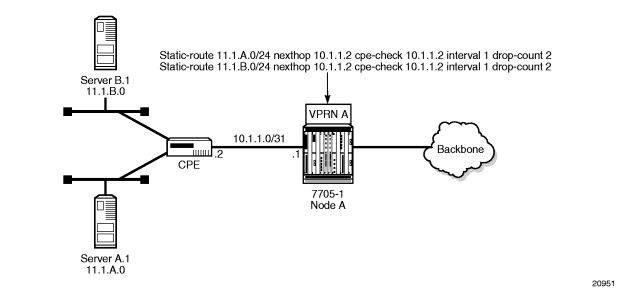
Figure 113: Multiple Hops to IP Target
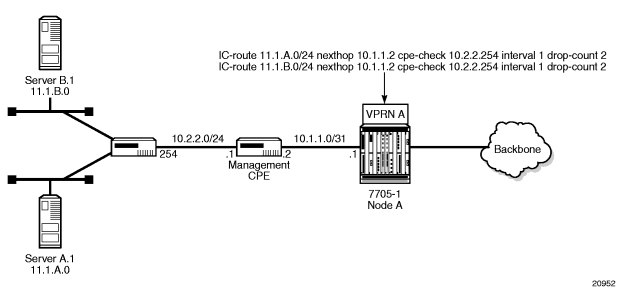
The availability of the far-end static route is monitored through periodic polling. The polling period is configured. If the poll fails a specified number of sequential polls, the static route is marked as inactive.
Either ICMP ping or unicast ARP mechanism can be used to test the connectivity. ICMP ping is preferred.
If the connectivity check fails and the static route is deactivated, the 7705 SAR router will continue to send polls and reactivate any routes that are restored.
7.1.7. Route Target Constraint
Route Target Constraint (RTC) is a mechanism that allows a router to advertise route target membership information to its BGP peers to indicate interest in receiving only VPN routes tagged with specific route target extended communities. Upon receiving RTC route information, peers restrict the advertised VPN routes to only those requested, minimizing control plane load in terms of protocol traffic and potentially reducing RIB memory usage.
The route target membership information is carried using MP-BGP, using an AFI value of 1 and SAFI value of 132. The NLRI of an RTC route encodes an Origin AS and a route target extended community using prefix type encoding with host bits after the prefix-length set to zero.
In order for two routers to exchange route target membership NLRI, they must advertise the corresponding AFI and SAFI to each other during capability negotiation. The use of MP-BGP means route target membership NLRI are propagated, loop-free, within an autonomous system and between autonomous systems, using well-known BGP route selection and advertisement rules.
Route target constrained route distribution and outbound route filtering (ORF) both allow routers to advertise which route target extended communities they want to receive in VPN routes from peers. RTC, however, is more widely supported, is simpler to configure, and its distribution scope is not limited to a direct peer.
7.1.7.1. Configuring the Route Target Address Family
RTC is supported only by the base router BGP instance. When the family command in the BGP router group or neighbor CLI context includes the route-target keyword, the RTC capability is negotiated with the associated set of EBGP and IBGP peers.
ORF and RTC are mutually exclusive for a particular BGP session. The CLI does not attempt to block the configuration of both ORF and RTC, but if both capabilities are enabled for a session, the ORF capability will not be included in the OPEN message sent to the peer.
7.1.7.2. Originating RTC Routes
When the base router has one or more RTC peers (BGP peers with which the RTC capability has been successfully negotiated), one RTC route is created for each route target extended community imported into a locally configured Layer 3 VPN service. These imported route targets are configured in the following contexts:
- config>service>vprn
- config>service>vprn>mvpn
By default, RTC routes are automatically advertised to all RTC peers without the need for an export policy to explicitly accept them. Each RTC route has a prefix, a prefix length, and path attributes. The prefix value is the concatenation of the origin AS (a 4-byte value representing the 2-octet or 4-octet AS of the originating router, as configured using the config>router>autonomous-system command) and 0 or 16 to 64 bits of a route target extended community encoded in one of the following formats: 2-octet AS specific extended community, IPv4 address specific extended community, or 4-octet AS specific extended community.
A router may be configured to send the default RTC route to a group or neighbor with the default-route-target CLI command. The default RTC route is a special route that has a prefix length of zero. Sending the default RTC route to a peer conveys a request to receive all VPN routes from that peer, whether they match the route target extended community. The default RTC route is typically advertised by a route reflector to PE clients. Advertising the default RTC route to a peer does not suppress other more specific RTC routes from being sent to that peer. A received default RTC route is never propagated to other routers.
7.1.7.3. Receiving and Readvertising RTC Routes
All received RTC routes that are considered valid are stored in the RIB-In. RTC routes are considered invalid and treated as withdrawn if the prefix length is configured to be any of the following:
- 1 to 31
- 33 to 47
- 48 to 96 and the 16 most-significant bits are not 0x0002, 0x0102, or 0x0202
If multiple RTC routes are received for the same prefix value (same NLRI), then standard BGP best-path selection procedures are used to determine the best route. The propagation of the best path installs RIB-Out filter rules as it travels from one router to the next, and this process creates an optimal VPN route distribution tree rooted at the source of the RTC route.
The best RTC route per prefix is readvertised to RTC peers based on the following rules.
- The best path for a default RTC route (prefix length 0, origin AS only with prefix length 32, or origin AS plus 16 bits of a route target type with prefix-length 48) is never propagated to another peer.
- A PE with only IBGP RTC peers that is not a route reflector or an ASBR does not readvertise the best RTC route to any RTC peer, due to standard IBGP split-horizon rules.
- A route reflector that receives its best RTC route for a prefix from a client peer readvertises that route (subject to export policies) to all its client and non-client IBGP peers (including the originator), per standard route reflector operation. When the route is readvertised to client peers, the route reflector sets the ORIGINATOR_ID to its own router ID and modifies the NEXT_HOP to be its local address for the sessions (for example, system IP).
- A route reflector that receives its best RTC route for a prefix from a non-client peer readvertises that route (subject to export policies) to all its client peers, per standard route reflector operation. If the route reflector has a non-best path for the prefix from any of its clients, it advertises the best of the client-advertised paths to all non-client peers.
- An ASBR that is not a PE or a route reflector, that receives its best RTC route for a prefix from an IBGP peer, readvertises that route (subject to export policies) to its EBGP peers. The NEXT_HOP and AS_PATH of the re-advertised route are modified per standard BGP rules. No aggregation of RTC routes is supported.
- An ASBR that is not a PE or a route reflector, that receives its best RTC route for a prefix from an EBGP peer, readvertises that route (subject to export policies) to its EBGP and IBGP peers. The NEXT_HOP and AS_PATH of the re-advertised route are modified per standard BGP rules. No aggregation of RTC routes is supported.
| Note: These advertisement rules do not handle hierarchical route reflector topologies properly. This is a limitation of the current RTC standard. |
7.1.7.4. Using RTC Routes
In general, the best VPN route for every prefix or NLRI in the RIB is sent to every peer supporting the VPN address family. Export policies may be used to prevent some prefixes or NLRIs from being advertised to specific peers. These export policies may be configured statically, or created dynamically by using ORF or RTC with a peer. ORF and RTC are mutually exclusive for a session.
When RTC is configured on a session that also supports VPN address families using route targets (VPN-IPv4, VPN-IPv6, or MVPN-IPv4), the advertisement of the VPN routes is affected as follows.
- When the session comes up, the advertisement of the VPN routes is delayed for a short while to allow RTC routes to be received from the peer.
- After the initial delay, the received RTC routes are analyzed and acted upon. If S1 is the set of routes previously advertised to the peer and S2 is the set of routes that should be advertised based on the most recent received RTC routes, then:
- the set of routes in S1 but not in S2 are withdrawn immediately (subject to the minimum route advertisement interval (MRAI)
- the set of routes in S2 but not in S1 are advertised immediately (subject to the MRAI)
- If a default RTC route is received from a peer P1, the set of VPN routes that are advertised to P1 are routes that:
- are eligible for advertisement to P1 per BGP route advertisement rules
- have not been rejected by manually configured export policies
- have not been advertised to the peer
This applies whether or not P1 advertised the best route for the default RTC prefix.A default RTC route is a route with any of the following:- NLRI length = zero
- NLRI value = origin AS and NLRI length = 32
- NLRI value = {origin AS+0x0002 | origin AS+0x0102 | origin AS+0x0202} and NLRI length = 48
- If an RTC route for prefix A (origin-AS = A1, RT = A2/n, n > 48) is received from an IBGP peer I1 in autonomous system A1, the set of VPN routes that are advertised to I1 are the routes that:
- are eligible for advertisement to I1 per BGP route advertisement rules
- have not been rejected by manually configured export policies
- carry at least one route target extended community with value A2 in the n most significant bits
- have not been advertised to the peer
This applies whether or not I1 advertised the best route for A. - If the best RTC route for a prefix A (origin-AS = A1, RT = A2/n, n > 48) is received from an IBGP peer I1 in autonomous system B, the set of VPN routes that are advertised to I1 are routes that:
- are eligible for advertisement to I1 per BGP route advertisement rules
- have not been rejected by manually configured export policies
- carry at least one route target extended community with value A2 in the n most significant bits
- have not been advertised to the peer
This applies only if I1 advertised the best route for A. - If the best RTC route for a prefix A (origin-AS = A1, RT = A2/n, n > 48) is received from an EBGP peer E1, the set of VPN routes that are advertised to E1 are the routes that:
- are eligible for advertisement to E1 per BGP route advertisement rules
- have not been rejected by manually configured export policies
- carry at least one route target extended community with value A2 in the n most significant bits
- have not been advertised to the peer
This applies only if E1 advertised the best route for A.
7.1.8. In-Band Management using a VPRN
VPRN in-band management is supported on the 7705 SAR. In-band management of the 7705 SAR is performed using the global routing table (GRT) to perform a lookup on the system IP address of the 7705 SAR.
On network ingress, when a packet arrives from the transport tunnel to the VPRN, a lookup is performed within the VPRN on the inner customer packet IP header. If a destination IP address in the packet header matches any system IP address configured under grt-lookup with a GRT static-route-entry set to the system IP address specified under vprn>static-route-entry>grt, the packet is extracted to the CSM for processing. If the vprn>grt-lookup>enable-grt>allow-local-management command is not enabled, the packet is routed using the 7705 SAR VRF FIB.
If the 7705 SAR system IP address is the same as any local IP address within the VPRN and the arriving packet destination IP matches this address, the packet is extracted to the CSM for processing only if the allow-local-management command is enabled. Any ICMP packet destined for local interfaces will be processed by the system IP. If the local interface is operationally down, the system IP will still reply to ICMP packets successfully. Having a single IP address shared by the system IP and VPRN local interface is not recommended because some GRT-supported management protocols, such as Telnet and SSH, will not function with this configuration.
For MP-BGP VPRNs, the system IP address can be advertised to the far-end node using a static route configured under vprn>static-route-entry>grt. If the command allow-local-management is enabled under the VPRN instance, a packet arriving on a transport tunnel will be extracted to the CSM before hitting the blackhole route. In this case, the only effect of the blackhole route will be to advertise the system IP address to the far-end peer. If the command allow-local-management is not enabled, packet forwarding will be the default forwarding mode; that is, all packets destined for the system IP address will be blackholed because of the static route configuration.
For MP-BGP VPRNs, when the command allow-local-management is enabled, at least one interface (such as a loopback interface) must be configured on the VPRN and have an operational status of Up.
On network egress, the packets generated from the CSM with a source IP address that matches the local IP address and destination IP address of either the far-end NSP NFM-P or other management entity must perform a GRT route lookup in order to be resolved. A route policy can be configured with an IP address prefix of the far-end management entity and with the action to accept. This policy is configured for the GRT under the config>router>policy-options context and is installed in the GRT FIB using the export-grt command. The route installed in the GRT FIB will have a next hop of the corresponding VRF tunnel. This prevents any user data traffic in the GRT data path from leaking into the VPRN, and ensures that only the management traffic originating from the system IP address and the CSM gets transported through the VPRN. This forces the management packet to get routed by the corresponding VPRN transport tunnel, which means the VPRN route is leaked into the GRT so the GRT resolves the route using the corresponding VPRN.
Table 120 lists the management protocols supported by IPv4 and IPv6 GRT in the reverse and forward directions.
Table 120: IPv4 and IPv6 GRT-Supported Management Protocols
Protocol | Reverse Direction (Towards the 7705 SAR) | Forward Direction (From the 7705 SAR) |
FTP Passive and Active | Yes 1 | Yes 2 |
SFTP | Yes 1 | — |
NTP | — | Yes 3 |
RADIUS | Yes | — |
SCP | Yes 1 | Yes 3 |
SNMP | Yes | — |
SNMP Trap | — | Yes |
SSH | Yes 1 | Yes 3 |
TACACS+ | Yes | — |
Telnet | Yes 1 | Yes 3 |
TWAMP 4 | Yes 5 | Yes 6 |
TWAMP Light | Yes 5 | Yes 6 |
- Supported, if the 7705 SAR is acting as a server
- Supported, if the 7705 SAR is acting as an active client
- Supported, if the 7705 SAR is acting as a client
- Supported on IPv4 only
- Supported, if the 7705 SAR is acting as a server (control packets)
- Supported, if the 7705 SAR is acting as a session reflector (test packets)
Notes:
Figure 114 shows an example of IPv4 in-band management of the 7705 SAR and the switches behind it by the NSP NFM-P and a TACACS+ server. In the example, an IPSec tunnel is being used as the VPRN in order to transport the management traffic via a secure and encrypted medium over the public internet.
Figure 114: IPv4 In-Band Management Using a VPRN Configured with GRT Lookup
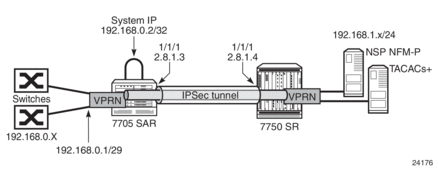
In this example, the 7705 SAR system IP address is in the same subnet as the local interface; that is, subnet 192.168.0.x.
On network ingress in the above example, when allow-local-management is configured for the VPRN, packets arriving on the 192.168.0 subnet are treated as follows.
- If the packet destination IP address is 192.168.0.2, the packet is extracted to the CSM to be processed as management traffic.
- If the packet is destined for subnet 192.168.0.x/29, it is forwarded out of interface 192.168.0.1.
On network egress in the above example, routing is as follows.
- A static route can be installed in the 7705 SAR VPRN for subnet 192.168.1.0/24 with a next hop to IPSecTunnel_1.
- A route policy can be created with an IP address prefix of 192.168.1.0/24 and an action to accept. This route policy is configured under the config>router>policy-options context, and can be exported to the GRT FIB using the export-grt command.
- The above configuration will add route 192.168.1.0/24 to the GRT FIB with the next hop being the corresponding VPRN IPSec tunnel. This entry will force the CSM-generated packets destined for the 192.168.1.x subnet to be resolved by the VPRN IPSec tunnel.
Figure 115 shows an example of IPv6 in-band management of the 7705 SAR and the switches behind it by the NSP NFM-P and a TACACS+ server.
Figure 115: IPv6 In-Band Management Using a VPRN Configured with GRT Lookup
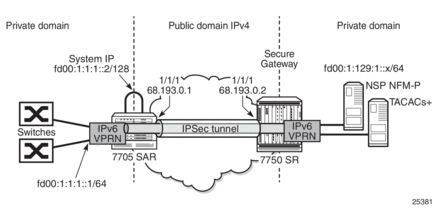
On network ingress in the above example, the 7705 SAR system IP address is in the same subnet as the local interface IPv6 VPRN address. When allow-local-management is configured for the IPv6 VPRN, packets arriving on the fd00:1:1:1 subnet are treated as follows.
- If the packet destination IP address is fd00:1:1:1::2, then the packet is extracted to the CSM to be processed as management traffic.
- If the packet is destined for subnet fd00:1:1:1::/64, it is forwarded out of interface fd00:1:1:1::1.
On network egress in the above example, routing is as follows.
- A static route can be installed at the 7705 SAR VPRN for subnet fd00:1:129:1::/64 with a next hop to IPSecTunnel_1.
- A route policy can be created with an IP address prefix of fd00:1:129:1::/64 and an action to accept. This route policy is configured under the config>router>policy-options context, and can be exported to the GRT FIB using the export-grt command.The above configuration adds route fd00:1:129:1::/64 to the GRT FIB with the next hop being the corresponding VPRN IPSec tunnel. This entry forces the CSM-generated packets destined for the fd00:1:129:1::x subnet to be resolved by the VPRN IPSec tunnel.
7.2. VPRN Features
This section describes the 7705 SAR service features and any special capabilities or considerations as they relate to VPRN services:
7.2.1. IP Interfaces
VPRN customer IP interfaces can be configured with most of the same options found on the core IP interfaces. The advanced configuration options supported are:
- Unnumbered interfaces (see Unnumbered Interfaces)
- DHCP options (see DHCP and DHCPv6)
- Local DHCP server options (see Local DHCP and DHCPv6 Server)
- IPSec tunnel interfaces (see IPSec Support)
- IPCP options (see IPCP)
- ICMP options (see Troubleshooting and Fault Detection Services)
- VRRP options (see VRRP on VPRN Interfaces)
Configuration options found on core IP interfaces not supported on VPRN IP interfaces are:
- NTP broadcast receipt
7.2.1.1. Unnumbered Interfaces
Unnumbered interfaces are supported on VPRN and IES services for IPv4. Unnumbered interfaces are point-to-point interfaces that are not explicitly configured with a dedicated IP address and subnet; instead, they borrow (or link to) an IP address from another interface on the system (the system IP address, another loopback interface, or any other numbered interface) and use it as the source IP address for packets originating from the interface.
This feature is supported via both dynamic and static ARP for unnumbered interfaces to allow interworking with unnumbered interfaces that may not support dynamic ARP.
The use of unnumbered interfaces has no effect on IPv6 routes; however, the unnumbered command must only be used in cases where IPv4 is active (IPv4 only and mixed IPv4/IPv6 environments). When using an unnumbered interface for IPv4, the loopback address used for the unnumbered interface must have an IPv4 address. The interface type for the unnumbered interface is automatically point-to-point.
7.2.1.2. DHCP and DHCPv6
DHCP is a configuration protocol used to communicate network information and configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a DHCP-aware client. DHCP is based on the BOOTP protocol, with additional configuration options and the added capability of allocating dynamic network addresses. DHCP-capable devices are also capable of handling BOOTP messages.
A DHCP client is an IP-capable device (typically a computer or base station) that uses DHCP to obtain configuration parameters such as a network address. A DHCP server is an Internet host or router that returns configuration parameters to DHCP clients. A DHCP/BOOTP Relay agent is a host or router that passes DHCP messages between clients and servers.
DHCPv6 is not based on, and does not use, the BOOTP protocol.
The 7705 SAR can act as a DHCP client, a DHCP or DHCPv6 Relay agent, or a local DHCP or DHCPv6 server.
Home computers in a residential high-speed Internet application typically use the DHCP protocol to have their IP address assigned by their Internet service provider.
Since IP routers do not forward broadcast or multicast packets, this would suggest that the DHCP client and server must reside on the same network segment. However, for various reasons, it is sometimes impractical to have the server and client reside in the same IP network.
When the 7705 SAR is acting as a DHCP Relay agent, it processes these DHCP broadcast or multicast packets and relays them to a preconfigured DHCP server. Therefore, DHCP clients and servers do not need to reside on the same network segment.
When the 7705 SAR is acting as a local DHCP server, it processes these DHCP broadcast or multicast packets and allocates IP addresses for the DHCP client as needed.
The 7705 SAR supports a maximum of 16 servers per node on the 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-W, 7705 SAR-Wx, and 7705 SAR-X. The 7705 SAR supports a maximum of 62 servers per node on the 7705 SAR-8 with a CSMv2 and on the 7705 SAR-18. Any Layer 3 interface configured using the global routing table or Layer 3 services supports up to 8 servers.
7.2.1.2.1. DHCP Relay and DHCPv6 Relay
The 7705 SAR provides DHCP/BOOTP Relay agent services and DHCPv6 Relay agent services for DHCP clients. DHCP is used for IPv4 network addresses and DHCPv6 is used for IPv6 network addresses. Both DHCP and DHCPv6 are known as stateful protocols because they use dedicated servers to maintain parameter information.
Unless stated otherwise, DHCP is equivalent to “DHCP for IPv4”, or DHCPv4.
In the stateful autoconfiguration model, hosts obtain interface addresses and/or configuration information and parameters from a server. The server maintains a database that keeps track of which addresses have been assigned to which hosts.
The 7705 SAR supports DHCP Relay on access IP interfaces associated with IES and VPRN and on network interfaces. Each DHCP instance supports up to eight DHCP servers.
The 7705 SAR supports DHCPv6 Relay on access IP interfaces associated with IES and VPRN. Each DHCPv6 instance supports up to eight DHCPv6 servers.
Note:
|
7.2.1.2.1.1. DHCP Relay
The 7705 SAR provides DHCP/BOOTP Relay agent services for DHCP clients. DHCP is a configuration protocol used to communicate network information and configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a DHCP-aware client. DHCP is based on the BOOTP protocol, with additional configuration options and the added capability of allocating dynamic network addresses. DHCP-capable devices are also capable of handling BOOTP messages.
A DHCP client is an IP-capable device (typically a computer or base station) that uses DHCP to obtain configuration parameters such as a network address. A DHCP server is an Internet host or router that returns configuration parameters to DHCP clients. A DHCP/BOOTP Relay agent is a host or router that passes DHCP messages between clients and servers.
Home computers in a residential high-speed Internet application typically use the DHCP protocol to have their IP address assigned by their Internet service provider.
The DHCP protocol requires the client to transmit a request packet with a destination broadcast address of 255.255.255.255 that is processed by the DHCP server. Since IP routers do not forward broadcast packets, this would suggest that the DHCP client and server must reside on the same network segment. However, for various reasons, it is sometimes impractical to have the server and client reside in the same IP network. When the 7705 SAR is acting as a DHCP Relay agent, it processes these DHCP broadcast packets and relays them to a preconfigured DHCP server. Therefore, DHCP clients and servers do not need to reside on the same network segment.
DHCP OFFER messages are not dropped if they contain a yiaddr that does not match the local configured subnets on the DHCP relay interface. This applies only to regular IES and VPRN interfaces with no lease-populate configured on the DHCP relay interface.
7.2.1.2.1.1.1. DHCP Options
DHCP options are codes that the 7705 SAR inserts in packets being forwarded from a DHCP client to a DHCP server. Some options have additional information stored in suboptions.
The 7705 SAR supports the Relay Agent Information Option 82 as specified in RFC 3046. The following suboptions are supported:
- circuit ID
- remote ID
- vendor-specific options
7.2.1.2.1.2. DHCPv6 Relay
DHCPv6 Relay operation is similar to DHCP in that servers send configuration parameters such as IPv6 network addresses to IPv6 nodes, but DHCPv6 Relay is not based on the DHCP or BOOTP protocol. DHCPv6 can be used instead of stateless autoconfiguration (refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Neighbor Discovery”) or in conjunction with it.
DHCPv6 is also oriented around IPv6 methods of addressing, especially the use of reserved, link-local scoped multicast addresses. DHCPv6 clients transmit messages to these reserved addresses, allowing messages to be sent without the client knowing the address of any DHCP server. This transmission allows efficient communication even before a client has been assigned an IP address. When a client has an address and knows the identity of a server, it can communicate with the server directly using unicast addressing.
The DHCPv6 protocol requires the client to transmit a request packet with a destination multicast address of ff02::1:2 (all DHCP servers and relay agents on the local network segment) that is processed by the DHCP server.
Similar to DHCP address allocation, if a client needs to obtain an IPv6 address and other configuration parameters, it sends a Solicit message to locate a DHCPv6 server, then requests an address assignment and other configuration information from the server. Any server that can meet the client’s requirements responds with an Advertise message. The client chooses one of the servers and sends a Request message, and the server sends back a Reply message with the confirmed IPv6 address and configuration information.
If the client already has an IPv6 address, either assigned manually or obtained in some other way, it only needs to obtain configuration information. In this case, exchanges are done using a two-message process. The client sends an Information Request message, requesting only configuration information. A DHCPv6 server that has configuration information for the client sends back a Reply message with the information.
The 7705 SAR supports the DHCPv6 Relay Agent option in the same way that it supports the DHCP Relay Agent option. This means that when the 7705 SAR is acting as a DHCPv6 Relay Agent, it relays messages between clients and servers that are not connected to the same link.
7.2.1.2.1.2.1. DHCPv6 Options
DHCPv6 options are codes that the 7705 SAR inserts in packets being forwarded from a DHCPv6 client to a DHCPv6 server. DHCPv6 supports interface ID and remote ID options as defined in RFC 3315, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPV6) and RFC 4649, DHCPv6 Relay Agent Remote-ID Option.
7.2.1.2.2. Local DHCP and DHCPv6 Server
The 7705 SAR supports local DHCP server functionality on the base router and on access IP interfaces associated with VPRN, by dynamically assigning IPv4 or IPv6 addresses to access devices that request them. This standards-based, full DHCP server implementation allows a service provider the option to decentralize IP address management into the network. The 7705 SAR can support public and private addressing in the same router, including overlapped private addressing in the form of VPRNs in the same router.
The 7705 SAR can act as a DHCP server or a DHCPv6 server.
An administrator creates pools of addresses that are available for assigned hosts. Locally attached hosts can obtain an address directly from the server. Routed hosts receive addresses through a relay point in the customer’s network.
When a DHCP server receives a DHCP message from a DHCP Relay agent, the server looks for a subnet to use for assigning an IP address. If configured with the use-pool-from-client command, the server searches Option 82 information for a pool name. If a pool name is found, an available address from any subnet of the pool is offered to the client. If configured with the use-gi-address command, the server uses the gateway IP address (GIADDR) supplied by the Relay agent to find a matching subnet. If a subnet is found, an address from the subnet is offered to the client. If no pool or subnet is found, then no IP address is offered to the client.
When a DHCPv6 server receives a DHCP message from a DHCPv6 Relay agent, the server looks for a subnet to use for assigning an IP address. If configured with the use-pool-from-client command, the server searches Option 17 information for a pool name. If a pool name is found, an available address from any subnet of the pool is offered to the client. If configured with the use-link-address command, the server uses the address supplied by the Relay agent to find a matching subnet prefix. If a prefix is found, an address from the subnet is offered to the client. If no pool or prefix is found, then no IP address is offered to the client.
IPv4 and IPv6 address assignments are temporary and expire when the configured lease time is up. The server can reassign addresses after the lease expires.
If both the no use-pool-from-client command and the no use-gi-address command or no use-link-address command are specified, the server does not act.
7.2.1.2.2.1. DHCP and DHCPv6 Server Options
Options and identification strings can be configured on several levels.
DHCPv4 servers support the following options, as defined in RFC 2132:
- Option 1—Subnet Mask
- Option 3—Default Routers
- Option 6—DNS Name Servers
- Option 12—Host Name
- Option 15—Domain Name
- Option 44—Netbios Name Server
- Option 46—Netbios Node Type Option
- Option 50—IP Address
- Option 51—IP Address Lease Time
- Option 53—DHCP Message Type
- Option 54—DHCP Server IP Address
- Option 55—Parameter Request List
- Option 58—Renew (T1) Timer
- Option 59—Renew (T2) Timer
DHCPv4 servers also support Suboption 13 Relay Agent Information Option 82 as specified in RFC 3046, to enable the use of a pool indicated by the DHCP client.
DHCPv6 servers support the following options, as defined in RFC 3315:
- Option 1—OPTION_CLIENTID
- Option 2—OPTION_SERVERID
- Option 3—OPTION_IA_NA
- Option 4—OPTION_IA_TA
- Option 5—OPTION_IAADDR
- Option 6—OPTION_ORO
- Option 7—OPTION_PREFERENCE
- Option 8—OPTION_ELAPSED_TIME
- Option 9—OPTION_RELAY_MSG
- Option 11—OPTION_AUTH
- Option 12—OPTION_UNICAST
- Option 13—OPTION_STATUS_CODE
- Option 14—OPTION_RAPID_COMMIT
- Option 15—OPTION_USER_CLASS
- Option 16—OPTION_VENDOR_CLASS
- Option 17—OPTION_VENDOR_OPTS
- Option 18—OPTION_INTERFACE_ID
- Option 19—OPTION_RECONF_MSG
- Option 20—OPTION_RECONF_ACCEPT
These options are copied into the DHCP reply message, but if the same option is defined several times, the following order of priority is used:
- subnet options
- pool options
- options from the DHCP client request
A local DHCP server must be bound to a specified interface by referencing the server from that interface. The DHCP server will then be addressable by the IP address of that interface. A normal interface or a loopback interface can be used.
A DHCP client is defined by the MAC address and the circuit identifier. This implies that for a certain combination of MAC and circuit identifier, only one IP address can be returned; if more than one request is made, the same address will be returned.
7.2.1.3. IPCP
Similar to DHCP over Ethernet interfaces, Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP) extensions to push IP information over PPP/MLPPP VPRN (and IES) SAPs are supported. Within this protocol, extensions can be configured to define the remote IP address and DNS IP address to be signaled via IPCP on the associated PPP interface. The IPCP-based IP and DNS assignment process is similar to DHCP behavior; IPCP-based IP/DNS assignment is a natural use of PPP/MLPPP IP layer protocol handshake procedures. PPP/MLPPP connected devices hooked up to VPRN (and IES) can benefit from this feature for the assignment of IP and DNS to the associated interface.
7.2.1.4. Troubleshooting and Fault Detection Services
Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) can be configured on the VPRN interface. BFD is a simple protocol for detecting failures in a network. BFD uses a “hello” mechanism that sends control messages periodically to the far end and expects to receive periodic control messages from the far end. On the 7705 SAR, BFD is implemented for IGP and BGP protocols, including static routes, in asynchronous mode only, meaning that neither end responds to control messages; rather, the messages are sent periodically from each end.
To support redundancy with fast switchover, BFD must be enabled to trigger the handoff to the other route in case of failure.
Due to the lightweight nature of BFD, it can detect failures faster than other detection protocols, making it ideal for use in applications such as mobile transport.
If BFD packets are not received in the configured amount of time, the associated route is declared “not active”, causing a reroute to an alternative path, if any.
| Note: Link failures detected by BFD will disable the IP interface. |
The 7705 SAR also supports Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). ICMP is a message control and error reporting protocol that also provides information relevant to IP packet processing.
7.2.1.5. VRRP on VPRN Interfaces
VRRP can be implemented on VPRN service interfaces to participate as part of a virtual router instance. This implementation prevents a single point of failure by ensuring access to the gateway address, which is configured on all VPRN service interfaces in the VRRP. VRRPv3 can also be implemented on VPRN service interfaces, including r-VPLS interfaces for VPRN.
The 7705 SAR supports VRRPv3 for IPv4 and IPv6 as described in RFC 5798. Within a VRRP router, the virtual routers in each of the IPv4 and IPv6 address families are a domain unto themselves and do not overlap.
| Note: VRRPv3 for IPv6 is not supported on a Layer 3 spoke-SDP termination. |
For information on VRRP and VRRP VPRN service interface parameters, as well as the configuration parameters of VRRP policies, refer to the “VRRP” section in the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide. CLI command descriptions for VRRP policies are also given in the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide.
For CLI command descriptions related to VPRN service interfaces, see VPRN Services Command Reference.
7.2.1.6. IP ECMP Load Balancing
IP ECMP allows the configuration of load balancing across all IP interfaces at the system level or interface level on the network side. Layer 4 port attributes and the TEID attribute in the hashing algorithm can be configured with the l4-load-balancing and teid-load-balancing commands in the config>service>vprn> interface context. Configuration of the l4-load-balancing command at the interface level overrides the system-level settings for the specific interface. The teid-load-balancing command can only be configured at the interface level.
The system IP address can be included in or excluded from the hashing algorithm with the system-level system-ip-load-balancing command.
For more information on IP ECMP, refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Static Routes, Dynamic Routes, and ECMP”.
7.2.1.7. Proxy ARP
Proxy ARP is supported on VPRN interfaces.
Proxy ARP is a technique by which a router on one network responds to ARP requests intended for another node that is physically located on another network. The router effectively pretends to be the destination node by sending an ARP response to the originating node that associates the router’s MAC address with the destination node’s IP address (acts as a proxy for the destination node). The router then takes responsibility for routing traffic to the real destination.
For more information on proxy ARP, refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Proxy ARP”.
7.2.1.8. Configurable ARP Retry Timer
A timer is available to configure a shorter retry interval when an ARP request fails. An ARP request may fail for a number of reasons, such as network connectivity issues. By default, the 7705 SAR waits 5000 ms before retrying an ARP request. The configurable retry timer makes it possible to shorten the retry interval to between 100 and 30 000 ms.
| Note: The ARP retry default value of 5000 ms is intended to protect CPU cycles on the 7705 SAR, especially when it has a large number of interfaces. Configuring the ARP retry timer to a value shorter than the default should be done only on mission-critical links, such as uplinks or aggregate spoke SDPs transporting mobile traffic; otherwise, the retry interval should be left at the default value. |
The configurable ARP retry timer is supported on VPRN and IES service interfaces, as well on the router interface.
7.2.2. SAPs
Topics in this section include:
VPRN service also supports SAPs for IPSec tunnels (see IPSec Support).
7.2.2.1. Encapsulations
The following SAP encapsulations are supported on the 7705 SAR VPRN service:
- Ethernet null
- Ethernet dot1q
- Ethernet qinq
- PPP
- MLPPP
- MC-MLPPP
- LAG
| Note: When gathering statistics on VPRN SAPs and ports, the SAP ingress counters might be different from the port counters as the SAP takes into account encapsulation headers. For Ethernet-encapsulated SAPs, counters can be adjusted by configuring the packet byte offset, which adjusts the packet size that schedulers, shapers, and the SAP counters take into account by offsetting the configured number of bytes. For information on packet byte offset, refer to the 7705 SAR Quality of Service Guide, “Packet Byte Offset (PBO)”. |
7.2.2.2. QoS Policies
For each instance of VPRN service, QoS policies can be applied to the ingress and egress VPRN interface SAPs.
At VPRN access ingress, traffic can be classified as unicast or multicast traffic types. In a VPRN access ingress QoS policy, users can create queues that map to forwarding classes. For each forwarding class, traffic can be assigned to a queue that is configured to support unicast, multicast, or both. As shown in the following example, for fc “af”, both unicast and multicast traffic use queue 2, and for fc “l2”, only multicast traffic uses queue 3.
VPRN service egress QoS policies function in the same way as they do for other services, where the class-based queues are created as defined in the policy.
Both the Layer 2 and Layer 3 criteria can be used in the QoS policies for traffic classification in a VPRN.
For VPRN services, the fabric mode needs to be set to aggregate mode as opposed to per-destination mode. VPRN services are only supported with aggregate-mode fabric profiles. When the fabric mode is set to per-destination mode, creation of VPRN service is blocked through the CLI. The user must change the fabric mode to aggregate mode before being able to configure VPRN services. As well, when a VPRN service is configured, changing from aggregate mode is blocked. The fabric mode is configured under the config>qos>fabric-profile context. For more information, refer to the 7705 SAR Quality of Service Guide.
7.2.2.2.1. CoS Marking for Self-generated Traffic
For each instance of VPRN service, DSCP marking and dot1p marking for self-generated traffic QoS can be configured for the applications supported by the 7705 SAR.
For VPRN service, DSCP marking is configured in the vprn>sgt-qos>application context. For more information about DSCP marking and self-generated QoS traffic, see “CoS Marking for Self-generated Traffic” in the 7705 SAR Quality of Service Guide.
7.2.2.3. QinQ (VPRN)
VPRN supports QinQ functionality. For details, see QinQ Support.
7.2.2.4. Filter Policies on a VPRN SAP
IPv4 and IPv6 filter policies can be applied to ingress and egress VPRN SAPs.
Refer to the 7705 SAR Router Configuration Guide, “Filter Policies”, for information on configuring IP filters.
7.2.3. PE-to-CE Routing Protocols
The 7705 SAR supports the following PE-to-CE routing protocols for VPRN service:
- EBGP (for IPv4 and IPv6 address families)
- OSPF
- OSPFv3
- RIP
- static routes
EBGP is supported within both the router context and VPRN service context. Both OSPF and OSPFv3 are supported within the router context as well as within the VPRN service context; however, there are some minor differences in the command sets depending on the context.
7.2.3.1. Using OSPF or OSPFv3 in IP VPNs
Using OSPF or OSPFv3 as a PE-to-CE routing protocol allows the version of OSPF that is currently running as the IGP routing protocol to migrate to an IP-VPN backbone without changing the IGP routing protocol, introducing BGP as the PE-CE, or relying on static routes for the distribution of routes into the service provider’s IP-VPN.
The following features are supported:
- transportation of OSPF/OSPFv3 learned routes as OSPF/OSPFv3 externalsThis feature uses OSPF or OSPFv3 as the protocol between the PE and CE routers; however, instead of transporting the OSPF/OSPFv3 LSA information across the IP-VPN, the OSPF/OSPFv3 routes are “imported” into MP-BGP as AS externals. As a result, other OSPF- or OSPFv3-attached VPRN sites on remote PEs receive these via type 5 LSAs.
- advertisement/redistribution of BGP-VPN routes as summary (type 3) LSAs flooded to CE neighbors of the VPRN OSPF/OSPFv3 instanceThis occurs if the OSPF or OSPFv3 route type (in the OSPF/OSPFv3 route type BGP extended community attribute carried with the VPN route) is not external (or NSSA) and the locally configured domain ID matches the domain ID carried in the OSPF/OSPFv3 domain ID BGP extended community attribute carried with the VPN route.
7.2.3.1.1. DN Bit
When a type 3 LSA is sent from a PE router to a CE router, the DN bit in the LSA options field is set. This ensures that if any CE router sends this type 3 LSA to a PE router, the PE router will not redistribute it further.
When a PE router needs to distribute to a CE router a route that comes from a site outside the CE router’s OSPF/OSPFv3 domain, the PE router presents itself as an autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) and distributes the route in a type 5 LSA. The DN bit must be set in these LSAs to ensure that they will be ignored by any other PE routers that receive them.
DN bit loop avoidance is also supported.
7.2.3.2. TTL Security
TTL security provides protection for EBGP peering sessions against CPU utilization-based attacks such as denial of service (DoS) attacks. This feature is supported for directly connected peering sessions and for multihop EBGP peering sessions. The BGP session can be over spoke-SDP terminated VPRN interfaces, SAP interfaces, and loopback interfaces, as well as over router interfaces and IPSec interface tunnels.
TTL security is most important for EBGP PE-CE sessions because CE devices can be multiple hops away, which adds a higher level of risk. TTL security provides a mechanism to better ensure the validity of BGP sessions from the CE device.
For more information on TTL security, refer to the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide, “TTL Security”.
7.2.4. PE-to-PE Tunneling Mechanisms
The 7705 SAR supports multiple mechanisms to provide transport tunnels for the forwarding of traffic between PE routers within the RFC 2547bis network.
The 7705 SAR VPRN implementation supports the use of:
- RSVP-TE protocol to create tunnel LSPs between PE routers
- LDP protocol to create tunnel LSPs between PE routers
- GRE tunnels between PE routers
These transport tunnel mechanisms provide the flexibility of using dynamically created LSPs, where the service tunnels are automatically bound (the “auto-bind” feature) and there is the ability to provide certain VPN services with their own transport tunnels by explicitly binding SDPs, if desired. When the auto-bind-tunnel command is used, all services traverse the same LSPs and do not allow alternate tunneling mechanisms (such as GRE) or the ability to configure sets of LSPs with bandwidth reservations for specific customers, as is available with explicit SDPs for the service.
7.2.5. Per-VRF Route Limiting
The 7705 SAR allows setting the maximum number of routes that can be accepted in the VRF for a VPRN service. There are options to specify a percentage threshold at which to generate an event that the VRF is nearly full and an option to disable additional route learning when the VRF is full or only generate an event.
7.2.6. RIP Metric Propagation in VPRNs
When RIP is used as the PE-CE protocol for VPRNs (IP-VPNs), the RIP metric is used only by the local node running RIP with the Customer Equipment (CE). The metric is not used with the MP-BGP path attributes that are exchanged between PE routers. Figure 116 shows an example of RIP metric propagation in a VPRN across two autonomous systems.
Figure 116: RIP Metric Propagation in VPRNs
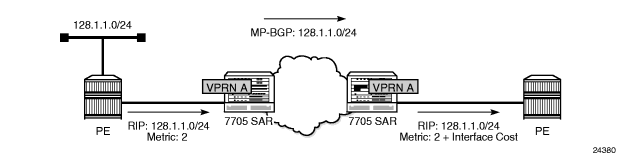
The RIP metric can also be used to exchange routing information between PE routers if a customer network is dual homed to separate PEs. The RIP metric learned from the CE router can be used to choose the best route to the destination subnet. The RIP metric sets the BGP MED attribute, which allows remote PEs to choose the lowest MED and the PE with the lowest advertised RIP metric as the preferred egress point for the VPRN.
7.2.7. Multicast VPN (MVPN)
The two main multicast VPN (MVPN) service implementations are the draft-rosen-vpn-mcast and the Next-Generation Multicast VPN (NG-MVPN).
The 7705 SAR supports NG-MVPNs, which use BGP for customer-multicast (C-multicast) signaling.
The 7705 SAR conforms to the relevant sections of the following RFCs related to MVPNs:
- RFC 6388, Label Distribution Protocol Extensions for Point-to-Multipoint and Multipoint-to-Multipoint Label Switched Paths
- RFC 6512, Using Multipoint LDP When the Backbone Has No Route to the Root (only as source router)
- RFC 6513, Multicast in MPLS/BGP IP VPNs
This section includes information on the following topics:
7.2.7.1. Multicast in IP-VPN Applications
This section focuses on IP-VPN multicast functionality. As a prerequisite for MVPN, readers should be familiar with the “IP Multicast” material in the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide, where multicast protocols (PIM, IGMP, and MLD) are described.
Applications for this feature include enterprise customers implementing a VPRN solution for their WAN networking needs, video delivery systems, and customer applications that include stock-ticker information as well as financial institutions for stock and other types of trading data.
Implementation of next-generation VPRN (NG-VPRN) requires the separation of the provider’s core multicast domain from customer multicast domains, and the customer multicast domains from each other.
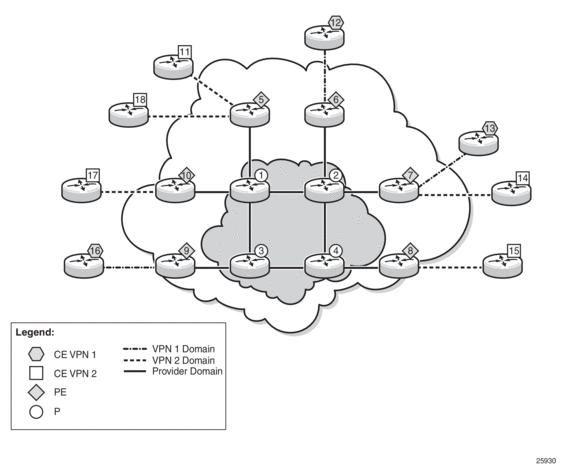
Figure 117 shows an example of multicast in an IP-VPN application and shows the following domains:
- provider's domain
- core routers (1 through 4)
- edge routers (5 through 10)
- customers’ IP-VPNs, each having their own multicast domain
- VPN-1 (CE routers 12, 13, and 16)
- VPN-2 (CE routers 11, 14, 15, 17, and 18)
In this VPRN multicast example, VPN-1 data generated by the customer behind router 16 is multicast by PE router 9 to PE routers 6 and 7 for delivery to CE routers 12 and 13, respectively. VPN-2 data generated by the customer behind router 15 is forwarded by PE router 8 to PE routers 5, 7, and 10 for delivery to CE routers 11 and 18, 14, and 17, respectively.
The demarcation points for these domains are in the PEs (routers 5 through 10). The PE routers participate in both the customer multicast domain and the provider multicast domain. The customer CEs are limited to a multicast adjacency with the multicast instance on the PE, where the PE multicast instance is specifically created to support that specific customer IP-VPN. As a result, customers are isolated from the provider core multicast domain and other customer multicast domains, while the provider core routers only participate in the provider multicast domain and are isolated from all customer multicast domains.
The PE for a customer's multicast domain becomes adjacent to the CE routers attached to that PE and to all other PEs that participate in the IP-VPN (customer) multicast domain. The adjacencies are set up by the PE that encapsulates the customer multicast control data and the multicast streams inside the provider's multicast packets. The encapsulated packets are forwarded only to the PE nodes that are attached to the same customer's edge routers as the originating stream and are part of the same customer VPRN. This process prunes the distribution of the multicast control and data traffic to the PEs that participate in the customer's multicast domain.
Figure 117: Multicast in an IP-VPN Application
7.2.7.2. MVPN Building Blocks
This section includes information on the following topics:
7.2.7.2.1. PMSI
A provider-multicast (P-multicast) service interface (PMSI), described in RFC 6513, refers to an abstract service in the service provider's core network that can take a packet from one PE, belonging to one MVPN, and deliver a copy of the packet to some or all of the other PEs supporting that MVPN.
The most common PMSI uses a multicast distribution tree (MDT). An MDT is a point-to-multipoint traffic path that is instantiated using forwarding table entries that support packet replication. For example, an MDT forwarding entry would specify the incoming interface—where the node expects to receive a packet flowing up or down the MDT—and the set of outgoing interfaces that each receive a copy of the packet. The MDT forwarding state can be set up using an IP multicast signaling protocol such as PIM, or an MPLS protocol such as multicast LDP (mLDP) or RSVP-TE.
The 7705 SAR supports only mLDP PMSI.
This section includes information on the following topics:
7.2.7.2.1.1. PMSI Types
There are two types of PMSIs: inclusive and selective.
An inclusive PMSI (I-PMSI) includes all of the PEs supporting an MVPN. A selective PMSI (S-PMSI) includes a subset of the PEs supporting an MVPN (that is, an S-PMSI is a subset of an I-PMSI). An MVPN can have more than one S-PMSI.
7.2.7.2.1.1.1. Inclusive PMSIs (I-PMSIs)
An MVPN has one I-PMSI. The I-PMSI carries MVPN-specific control information between the PEs of the MVPN. In the 7705 SAR implementation, by default, all C-multicast flows use the I-PMSI. This minimizes the number of PE router states in the service provider core, but wastes bandwidth because a C-multicast flow on an I-PMSI is delivered to all PEs in the MVPN, even when only a subset of the PEs have receivers for the flow. To reduce wasted bandwidth, a service provider can migrate the C-multicast flow from the I-PMSI to an S-PMSI that includes only the PEs with receivers interested in that (S,G) flow.
On a 7705 SAR, migration of a C-multicast-flow from I-PMSI to S-PMSI can be configured to be initiated automatically by the PE closest to the source of the C-multicast-flow, where the migration trigger is based on the data rate of the flow. Migration occurs when the data rate exceeds the configured threshold.
7.2.7.2.1.1.2. Selective PMSIs (S-PMSIs)
A selective PMSI is one that includes a subset of the PEs supporting an MVPN. Each MVPN can have zero or more S-PMSIs. As stated above, the transition from I-PMSI to S-PMSI is triggered when the data rate exceeds the user-configured threshold.
7.2.7.2.1.1.3. I-PMSI versus S-PMSI
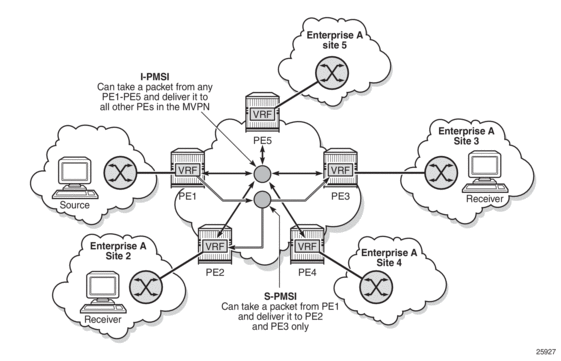
Figure 118 illustrates the difference between an I-PMSI and an S-PMSI. In the figure, the arrowheads indicate send and receive capabilities supported by the PMSI. Two-way arrows imply sender and receiver transmissions, and one-way arrows imply sender-only or receiver-only transmission.
In Figure 118, all the VRFs that are part of the MVPN domain receive PDUs from the I-PMSI MDT entries, whether or not the VRFs are configured to receive the PDUs. When the traffic for an (S,G) exceeds the configured data rate threshold, the multicast tree for that (S,G) switches from an I-PMSI to an S-PMSI. Each (S,G) has its own S-PMSI tree built when the threshold for that (S,G) has been exceeded.
Figure 118: I-PMSI and S-PMSI
7.2.7.2.1.2. Creating a PMSI
The 7705 SAR supports only multicast LDP (mLDP) as the mechanism to build a PMSI tunnel.
When the C-multicast protocol for a leaf node in an MVPN initiates a multicast request, it triggers mLDP to generate an LSP. The C-multicast protocol can be IGMP or PIM, which is configured under the VPRN service.
Multicast LDP tries to resolve the source address of (S,G) by looking up the source (S) in the routing table manager (RTM). If there is a resolution, mLDP generates a FEC toward the source (S). The mLDP FEC, as described in RFC 6388, contains the root node’s system IP address and an opaque value. The opaque value contains a point-to-multipoint LSP ID, which uniquely identifies the point-to-multipoint LSP in the context of the root node. Figure 119 illustrates a point-to-multipoint FEC element and an opaque value.
The P2MP ID is generated on the root node and is advertised to the leaf node via a BGP MVPN address family route update (see Figure 120).
In Figure 119, the point-to-multipoint FEC element contains of the address of the root of the point-to-multipoint LSP and an opaque value. The opaque value consists of one or more LDP multiprotocol (MP) opaque value elements. The opaque value is unique within the context of the root node, and for the 7705 SAR it is the P2MP ID. The combination of “Root Node Address Type”, “Root Node Address”, and “Opaque Value” uniquely identifies a point-to-multipoint LSP within the MPLS network.
Figure 119: P2MP FEC and MP LDP Opaque Value as per RFC 6388
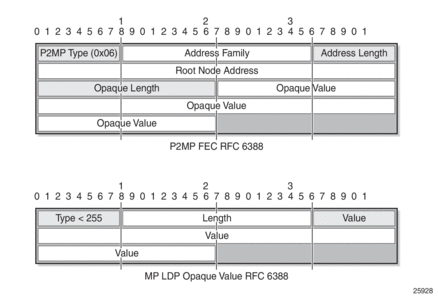
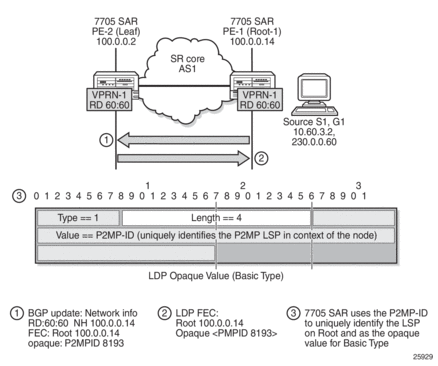
Figure 120 shows the following items:
- the BGP MVPN address family update (#1), which contains the unique P2MP ID
- the LDP FEC (#2), which is generated when the C-multicast IGMP or PIMv4 prompts the LDP to generate the mLDP FEC from the leaf to the root node
- the opaque value (basic type) (#3), which is encoded into the mLDP FEC and contains the P2MP ID
Figure 120: BGP MVPN Address Family Updates
7.2.7.2.2. MVPN Using BGP Control Plane
To communicate auto-discovery routes and C-multicast signaling, add the mvpn-ipv4 address family to the BGP address family configuration. For more information, refer to the “Configuring BGP Address Families” section in the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide.
The 7705 SAR MVPN implementation is based on NG-VPRN standards and supports the following features:
- auto-discovery
- PE-PE transmission of C-multicast routing using BGP
- IPv4
- use of mLDP for S-PMSIs used as PMSIs
- inter-AS with direct VRF connect
- inter-AS as root router only (source connect) (options B and C)
7.2.7.2.3. Auto-Discovery
Auto-discovery for multicast VPN refers to the process by which a PE with a multicast MVPN service dynamically learns about the other PEs supporting the same MVPN.
The basic auto-discovery function is to discover the identity of all other PEs in the MVPN. This information is essential for setting up the I-PMSI.
Advanced auto-discovery functions are:
- discovering the subsets of PEs in the MVPN that are interested in receiving a specific multicast flow
- discovering Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) in other ASs that are interested in receiving a specific multicast flow
- discovering C-multicast sources that are actively sending traffic across the service provider backbone (in a PMSI)
- discovering bindings between multicast flows and PMSIs
The MVPN standards define two different options for MVPN auto-discovery, BGP and PIM. The 7705 SAR only uses MP-BGP for auto-discovery and S-PMSI signaling.
With BGP auto-discovery, MVPN PEs advertise special auto-discovery routes to their peers using multiprotocol extensions to BGP.
Using BGP for auto-discovery does not imply that BGP must be used for C-multicast signaling, nor does it impose any restrictions about the technology used to tunnel MVPN packets between PEs in the service provider backbone.
7.2.7.2.3.1. MVPN Membership Auto-Discovery Using BGP
BGP-based auto-discovery is performed by referring to a multicast VPN address family (for example, mvpn-ipv4). Any PE that attaches to an MVPN must issue a BGP update message containing an NLRI in the address family, along with a specific set of attributes.
The PE router uses route targets to specify an MVPN route import and export policy. The route target may be the same target as the one used for the corresponding unicast VPN, or it may be a different target. For a given MVPN, the PE router can specify separate import route targets for sender sites and receiver sites.
The route distinguisher (RD) that is used for the corresponding unicast VPN can also be used for the MVPN.
In addition, the bindings of C-trees to P-tunnels are discovered using BGP S-PMSI auto-discovery routes.
7.2.7.2.4. PE-CE Multicast Protocols and Services
A PE with an MVPN service must learn about the networks and multicast receivers located beyond the CE devices at the MVPN customer site. Typically, IGMP or a PIM protocol is used by the CE to inform the PE that it (the CE) wants to receive a particular multicast flow because it has downstream receivers of that flow. The 7705 SAR supports both IGMP (versions 1, 2, and 3) and PIM Source Specific Multicast (SSM) as the CE-to-PE protocol.
The use of PIM as the CE-to-PE protocol requires that the PE learn about networks beyond the CE so that the PE can appropriately select the correct upstream next hop for sending PIM join and prune messages. The join and prune messages normally follow the reverse path of unicast data traffic and establish the required multicast forwarding state in the PE, CE, and other PIM routers at the customer site. The reachability of networks beyond the CE can be learned through a routing protocol such as OSPF, RIP, or BGP, or it can be configured statically when static routes or multiprotocol BGP are used between the CE and a 7705 SAR PE.
Layer 2 services, such as routed VPLS, can be used to snoop IGMP from the VPLS access interface and translate IGMP to PIM on the PE-CE Layer 3 interface.
The 7705 SAR supports IPv4 PE-CE protocols (for example, IGMP and PIM).
7.2.7.2.5. PE-PE Transmission of C-Multicast Routing Using BGP
MVPN C-multicast routing information is exchanged between PEs by using C-multicast routes that are carried by the MVPN NLRI.
7.2.7.2.6. PE-PE Multicast Protocols
When a PE gets a request for a multicast flow from a connected CE in an MVPN, it must convey that request to the PE closest to the source of the multicast traffic. In order for a PE to know that another PE is closer to a source, unicast routes must be exchanged between the PEs. This is done by exchanging VPN-IP routes using multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP). The VPN-IP routes exchanged for this purpose may carry additional information as compared to VPN-IP routes used only for unicast routing. In particular, when NG-MVPN signaling is used, as per RFC 6513, a route that is a candidate for upstream multicast hop (UMH) selection carries two additional BGP extended communities: a source-AS extended community and a VRF route import extended community.
C-multicast signaling is the signaling of joins and prunes from a PE that is connected to a site with receivers of a multicast flow to another PE that is closest to a sender of the multicast flow. Similar to auto-discovery, the MVPN standards allow either PIM or BGP to be used for C-multicast signaling.
The 7705 SAR uses only BGP for C-multicast signaling and multicast route advertisement between PEs.
When BGP is used for C-multicast signaling, a PE announces its desire to join a source C-tree by announcing a special source-join BGP NLRI using BGP multiprotocol extensions. The source-join BGP NLRI has the same AFI and SAFI as the BGP auto-discovery routes (described in RFC 6513). When a PE wants to leave an inter-site source tree, it withdraws the source-join BGP NLRI that it had previously advertised. A PE directs a source-join BGP NLRI to a specific upstream PE—the one it determines to be closest to the source—by including the VRF route import extended community associated with that upstream PE; other PEs may receive the source-join BGP NLRI, but do not import and use it.
Using C-multicast signaling protocols with BGP means that each MVPN PE typically has a small number of BGP sessions (for example, two interior border gateway protocol (IBGP) sessions with two route reflectors in the local AS).
The use of BGP minimizes the control plane load, but may lead to slightly longer join and leave latencies than is the case for the faster recovery of lost BGP messages by the TCP layer underlying the BGP sessions. This is due to the route reflector propagating join and prune messages from downstream PEs to upstream PEs.
7.2.7.2.7. PE-PE Multicast Data Transmission
A PMSI can be built on one or more point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, or multipoint-to-multipoint tunnels that carry customer multicast packets transparently through the service provider core network. The MVPN standards provide several technology options for PMSI tunnels:
- RSVP-TE LSP (point-to-point and point-to-multipoint)
- mLDP LSP (point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-multipoint)
- GRE tunnel (point-to-point and point-to-multipoint)
Only point-to-multipoint mLDP as a PMSI tunnel is supported.
The 7705 SAR platforms support the following transport options:
- I-PMSI – mLDP point-to-multipoint LSPs
- S-PMS – mLDP point-to-multipoint LSPs
7.2.7.3. Provider Tunnel Support
The following provider tunnel features are supported:
- I-PMSI
- S-PMSI
Topics in this section include:
7.2.7.3.1. Point-to-Multipoint I-PMSI and S-PMSI
BGP C-multicast signaling must be enabled for an MVPN instance to use point-to-multipoint mLDP to create an I-PMSI or S-PMSI.
By default, all PE nodes participating in MVPN receive data traffic over an I-PMSI. Optionally, for efficient data traffic distribution, S-PMSIs can be used to send traffic to PE nodes that have at least one active receiver connected.
Only one unique multicast flow is supported over each mLDP point-to-multipoint LSP S-PMSI.
The number of S-PMSIs that can be initiated per MVPN instance is set by the maximum-p2mp-spmsi command. A point-to-multipoint LSP S-PMSI cannot be used for more than one (S,G) stream once the maximum number of S-PMSIs per MVPN is reached. Multicast flows that cannot switch to an S-PMSI remain on the I-PMSI.
7.2.7.3.2. Point-to-Multipoint LDP I-PMSI and S-PMSI
A point-to-multipoint LDP LSP as an inclusive or selective provider tunnel is available with BGP NG-MVPN only. A point-to-multipoint LDP LSP is set up dynamically from leaf nodes upon auto-discovery of leaf PE nodes that are participating in multicast VPN. Each LDP I-PMSI or S-PMSI LSP can be used with a single MVPN instance only.
The multicast-traffic command (under config>router>ldp>interface-parameters>interface) must be configured on a per-LDP interface basis to enable a point-to-multipoint LDP setup. Point-to-multipoint LDP must also be configured as an inclusive or selective provider tunnel on a per-MVPN basis. Use the mldp command (under provider-tunnel>inclusive or >selective) to dynamically initiate a point-to-multipoint LDP LSP to leaf PE nodes learned via NG-MVPN auto-discovery signaling. S-PMSI is for efficient data distribution and is optional.
7.2.7.3.3. Point-to-Multipoint LSP S-PMSI
NG-MVPN allows the use of a point-to-multipoint LDP LSP as the S-PMSI. An S-PMSI is generated dynamically, based on the user-configured traffic bandwidth threshold for a number of multicast flows. Use the data-threshold command (under provider-tunnel>selective) to set the bandwidth threshold.
In MVPN, the root node PE discovers all the leaf PEs via I-PMSI auto-discovery routes. All multicast PDUs traverse through the I-PMSI until the configured threshold is reached on the root node. When the configured threshold is reached on the root node, the root node signals the desire to switch to an S-PMSI via BGP signaling of the S-PMSI auto-discovery NLRI.
Because of the way that LDP normally works, mLDP point-to-multipoint LSPs are set up (unsolicited) from the leaf PEs towards the root node PE. The leaf PE discovers the root node PE via auto-discovery routes (I-PMSI or S-PMSI). The tunnel identifier carried in the PMSI attribute is used as the point-to-multipoint FEC element.
The tunnel identifier consists of the root node PE address, along with a point-to-multipoint LSP ID. The generic LSP identifier value is automatically generated by the root node PE.
7.2.7.3.4. MVPN Sender-only and Receiver-only
The I-PMSI can be optimized by configuring PE nodes that behave as a sender-only or receiver-only node. By default, PE nodes are both sender and receiver nodes (sender-receiver).
In MVPN, by default, if multiple PE nodes form a peering within a common MVPN instance, then each PE node originates a local multicast tree towards the other PE nodes in this MVPN instance. This behavior creates an I-PMSI mesh across all PE nodes in the MVPN. Typically, a VPN has many sites that host multicast receivers only, and has a few sites that host sources only or host both receivers and sources.
MVPN sender-only and receiver-only commands allow the optimization of control-plane and data-plane resources by preventing unnecessary I-PMSI mesh setups when a PE device hosts only multicast sources or only multicast receivers for an MVPN.
For PE nodes that host only multicast sources for a VPN, operators can configure the MVPN to block those PE nodes from joining I-PMSIs that belong to other PEs in the MVPN. For PE nodes that host only multicast receivers for a VPN, operators can block those PE nodes in order to set up a local I-PMSI to other PEs in this MVPN.
MVPN sender-only and receiver-only commands are supported with NG-MVPN using IPv4 LDP provider tunnels for both IPv4 and IPv6 customer multicast. Figure 121 shows a four-site MVPN with sender-only, receiver-only, and sender-receiver (default) sites.
| Note: Attention needs to be paid to the physical location of the BSR and RP nodes when sender-only or receiver-only is enabled. Since the source DR sends unicast-encapsulated traffic towards RP, the RP needs to be at a sender-receiver or sender-only site, so that (*,G) traffic can be sent over the tunnel. The BSR needs to be deployed at the sender-receiver site. The BSR can be at a sender-only site if the RPs are at the same site. The BSR needs to receive packets from other candidate-BSR and candidate-RP nodes and also needs to send BSM packets to all other BSR and RP nodes. |
Figure 121: I-PMSI Sender-Receiver, Sender-Only, and Receiver-Only: Optimized I-PMSI Mesh
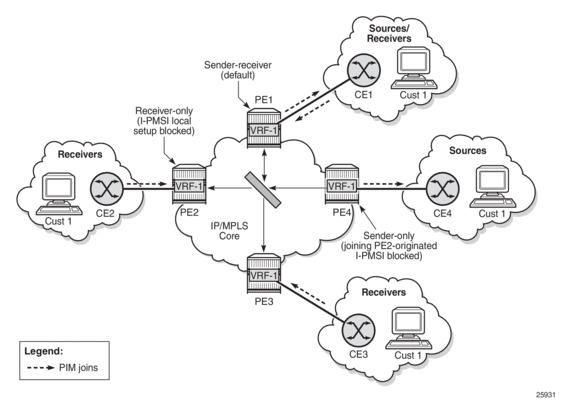
7.2.7.4. Inter-AS and Intra-AS Solutions
An MVPN service that spans more than one AS is called an inter-AS MVPN. As is the case with unicast-only IP VPN services, there are different approaches for supporting inter-AS MVPNs. Generally, the approaches belong to one of two categories:
- all P-tunnels and P-multicast trees start and end on PEs and ASBRs in the same AS
- P-tunnels and P-multicast trees extend across multiple ASs
In the first category, the P-tunnels and P-multicast trees start on PEs and ASBRs of an AS, and end on PEs and ASBRs in that same AS (extending no further). In this scenario, C-multicast traffic that must cross an AS boundary is handed off natively between the ASBRs on each side of the AS boundary.
From the perspective of each ASBR, the other ASBR is simply a collection of CEs, each reachable through separate logical connections (for example, VPRN SAPs). In this type of deployment, no auto-discovery signaling is required between the different ASs, and the exchange of C-multicast routes and C-multicast signaling uses the same protocols and procedures as described in PE-CE Multicast Protocols and Services for PE-CE interfaces.
In the second category, P-tunnels and P-multicast trees extend across the boundaries between different ASs. In this scenario, the PMSI extends end-to-end between the PEs of the MVPN, even when those PEs are in different ASs. ASBRs need to exchange auto-discovery information in order to determine whether, for a given MVPN:
- the neighbor AS has PEs with sites in the MVPN
- the neighbor AS is a transit node on the best path to a remote AS that has sites of the MVPN
If a P-multicast tree is used to transport the PMSI, there are two options for extending the P-tree across multiple ASs:
- non-segmented inter-AS MDTThe end-to-end P-tree is end-to-end between all the PEs supporting the MVPN, passing through ASBRs as necessary.
- segmented inter-AS MDT (see Figure 122)The end-to-end P-tree is formed by stitching together a sub-tree from each AS. A sub-tree of an AS connects only the PEs and ASBRs of that AS. A point-to-point tunnel between ASBRs on each side of an AS boundary is typically used to stitch the sub-trees together.
| Note: The 7705 SAR supports non-segmented inter-AS trees only as a root node. |
Constructing and using a non-segmented inter-AS MDT is similar to constructing and using an intra-AS MDT, except that BGP auto-discovery messages are propagated by ASBRs across AS boundaries, where the BGP auto-discovery messages are I-PMSI intra-AS auto-discovery routes, despite the reference to intra-AS.
When segmented inter-AS tunnels are used for an NG-MVPN, the ASBRs configured to support that MVPN will originate inter-AS I-PMSI auto-discovery routes for that MVPN toward their external peers after having received intra-AS I-PMSI auto-discovery routes for the MVPN from one or more PEs in their own AS. The inter-AS I-PMSI auto-discovery messages are propagated through all ASs that support the MVPN (that is, through all ASs that have PEs or ASBRs for the MVPN).
When an ASBR receives an inter-AS I-PMSI auto-discovery route, and it is the best route for the NLRI, the ASBR sends a leaf auto-discovery route to the exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) peer that advertised the route. The leaf auto-discovery route is used to set up a point-to-point, one-hop MPLS LSP that stitches together the P-multicast trees of each AS.
The 7705 SAR supports inter-AS and intra-AS option A.
The 7705 SAR does not support non-segmented inter-AS and intra-AS options B and C as an ABR or ASBR router or as a leaf router. However, the 7705 SAR can be part of non-segmented inter-AS and intra-AS options B and C as a root node.
7.2.7.4.1. 7705 SAR as Source of Non-Segmented Inter-AS or Intra-AS Network
The 7705 SAR can be the source of a non-segmented inter-AS or intra-AS network, as per RFC 6512 and RFC 6513.
Figure 122 shows inter-AS option B connectivity via non-segmented mLDP, and Figure 123 shows inter-AS option C. In inter-AS solutions, the leaf and ABR/ASBR nodes need recursive opaque FEC to route the mLDP FEC through the network.
| Note: Currently, the 7705 SAR does not support recursive opaque FEC. Therefore, the 7705 SAR only can be positioned as a root node in inter-AS option B and C solutions. |
Figure 122: Inter-AS Option B: Non-Segmented Solution
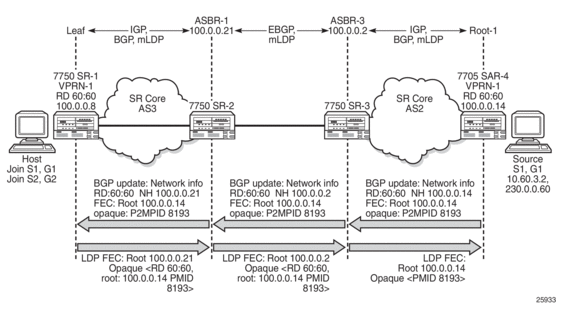
Figure 123: Inter-AS Option C: Non-Segmented Solution
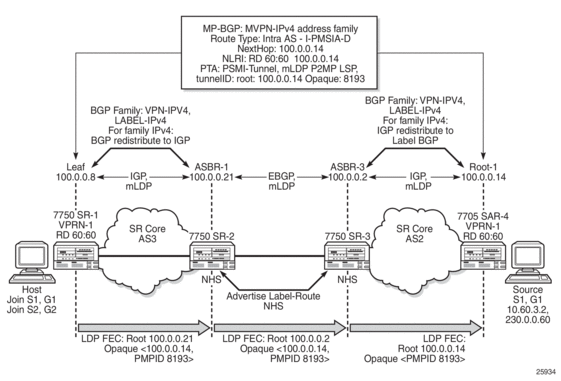
7.2.7.5. Mrinfo and Mtrace
When using mrinfo and mtrace in a Layer 3 VPN context, the configuration for the VPRN should have a loopback address configured that has the same address as the core VPRN instance's system address (that is, the BGP next hop).
For more information, refer to the “IP Multicast Debugging Tools” section in the 7705 SAR OAM and Diagnostics Guide.
7.2.7.6. Multicast-only Fast Reroute (MoFRR)
The 7705 SAR supports MoFRR in the context of GRT for mLDP. The multicast traffic is duplicated on a primary mLDP multicast tree and a secondary mLDP multicast tree.
For more information, refer to the “Multicast-only Fast Reroute (MoFRR)” section in the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide.
7.2.7.7. mLDP Point-to-Multipoint Support
The 7705 SAR supports mLDP point-to-multipoint traffic.
For more information, refer to the “LDP Point-to-Multipoint Support” section in the 7705 SAR MPLS Guide.
7.2.7.8. mLDP Fast Upstream Switchover
This feature allows a downstream LSR of an mLDP FEC to perform a fast switchover in order to source the traffic from another upstream LSR while IGP and LDP are converging due to a failure of the upstream LSR, where the upstream LSR is the primary next hop of the root LSR for the point-to-multipoint FEC.
For more information, refer to the “Multicast LDP Fast Upstream Switchover” section in the 7705 SAR MPLS Guide.
7.2.7.9. Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
7705 SAR supports Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) for MVPNs.
MSDP is a mechanism that allows rendezvous points (RPs) to share information about active sources. When RPs in remote domains hear about the active sources, they can pass on that information to the local receivers and multicast data can be forwarded between the domains. MSDP allows each domain to maintain an independent RP that does not rely on other domains, but it also enables RPs to forward traffic between domains. PIM-SM is used to forward the traffic between the multicast domains.
In addition to supporting MSDP on MVPNs in the VPRN service context, the 7705 SAR supports MSDP in the base router context. For information about MSDP, refer to the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide.
In an MVPN, a PE node can act as an RP and run the MSDP functionality.
To interconnect multicast domains and to learn about source in other domains, MSDP peering is maintained between RP nodes. MSDP peering occurs over a TCP connection and control information is exchanged between peers to learn about multicast sources in other domains and to distribute information about multicast sources in the local domain.
When MSDP is configured in a service provider MVPN for a given IP VPN customer, at least one of the PEs that are part of that MVPN becomes an MSDP peer to customer-instance RPs. MSDP groups are configured on PEs to limit source-active (SA) advertisements to routers within a group. As the PE RP learns about multicast sources within its domain via PIM-SM, it encapsulates the first data packet in an MSDP SA message and distributes it to all of its peer RP nodes. Based on the RPF check, each peer node sends the control message to other peers to distribute information about the active source. If there is an existing entry for the multicast group, the RP node joins the shortest path tree towards the source.
7.2.8. VPRN Auto-binding Tunnels
The 7705 SAR supports auto-binding for selecting tunnels in the tunnel table manager (TTM) in the following resolution contexts:
- resolution of RFC 3107 BGP label route prefix using tunnels to a BGP next hop
- resolution of a VPN-IPv4 or VPN-IPv6 prefix to a BGP next hop
The command to auto-bind tunnels is config>service>vprn>auto-bind-tunnel, which has resolution and resolution-filter options.
The user configures the resolution option to enable auto-bind resolution to tunnels in the TTM. If the resolution option is explicitly set to disabled, the auto-binding to the tunnel is removed.
If resolution is set to any, any supported tunnel type in the resolution context will be selected following the TTM preference. The following tunnel types are selected in order of preference: RSVP, LDP, segment routing, and GRE. The user can configure the preference of the segment routing tunnel type in the TTM for a specific IGP instance.
If resolution is set to filter, one or more explicit tunnel types are specified using the resolution-filter option, and only these specified tunnel types will be selected according to the TTM preference.
Note:
|
7.2.9. Spoke SDPs
For VPRN service, spoke SDPs can be used only for providing network connectivity between the PE routers.
7.2.10. Spoke SDP Termination to VPRN
This feature enables a customer to exchange traffic between a VLL or VPLS (Layer 2) service and an IES or VPRN (Layer 3) service. Customer premises traffic coming in from a VLL or VPLS service (SAP to spoke SDP) is forwarded over the IP/MPLS network to the IES or VPRN service, and vice versa. Network QoS policies can be applied to the spoke SDP to control traffic forwarding to the Layer 3 service.
In a Layer 3 spoke SDP termination to an IES or VPRN service, where the destination IP address resides within the IES or VPRN network, CE device-generated ARP frames must be processed by the Layer 3 interface. When an ARP frame is received over the spoke SDP at the Layer 3 interface endpoint, the 7705 SAR responds to the ARP frame with its own MAC address. When an ARP request is received from the routed network and the ARP entry for the CE device that is connected to the spoke SDP is not known, the 7705 SAR initiates an ARP frame to resolve the MAC address of the next hop or CE device.
Figure 124 shows traffic terminating on a specific IES or VPRN service that is identified by the SDP ID and VC label present in the service packet.
Figure 124: SDP ID and VC Label Service Identifiers (Conceptual View of the Service)
Figure 125 shows a spoke SDP terminating directly into a VPRN. In this case, a spoke SDP could be tied to an Epipe or a hierarchical VPLS service. There is no configuration required on the PE connected to the CE.
Figure 125: VPRN Spoke SDP Termination
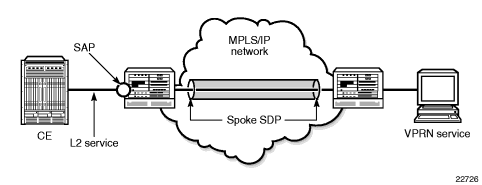
Ethernet spoke SDP termination for VPRN service is supported over the following network uplinks:
- Ethernet network ports (null or dot1q encapsulation)
- PPP/MLPPP network ports. For information on PPP/MLPPP ports, refer to the 7705 SAR Interface Configuration Guide, “Access, Network, and Hybrid Ports”
- GPON module ports and DSL module ports when the module is installed in the 7705 SAR-M (variants with module slots)
- POS ports
Spoke SDP termination for VPRN supports the following:
- Ethernet PW to VRF
- interface shutdown based on PW standby signaling
- spoke SDP ingress IP filtering with filter logging
- label withdrawal for spoke SDPs terminated on VPRN
- statistics collection
- VCCV ping (type 2)
A spoke SDP on a VPRN interface service can be connected to the following entities:
- Epipe spoke SDP
- Epipe spoke SDP redundancy with standby-signal-master enabled
- IES interface
- VPRN interface
- VPLS spoke SDP
- VPLS spoke SDP redundancy with suppress-standby-signaling disabled
There are three scenarios to backhaul traffic from a given site that uses PWs and VPRN on a 7705 SAR.
- Scenario 1 (Figure 126): An individual PW is configured on a per-CE device or a per-service basis. For routing services, this PW can be terminated to a VPRN at the 7750 SR end. This scenario offers per-service OAM and redundancy capabilities. Also, because there is no local communication on the remote 7705 SAR, traffic between any two devices connected to the 7705 SAR must traverse through the 7750 SR at the MTSO/CO.
Figure 126: Pseudowire-Based Backhaul (Spoke SDP Termination at 7750 SR)
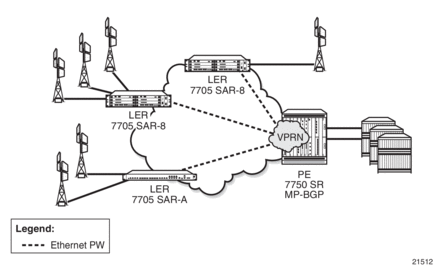
- Scenario 2 (Figure 127): An MP-BGP-based solution can provide a fully routed scenario.
Figure 127: VPRN in Mobile Backhaul Application
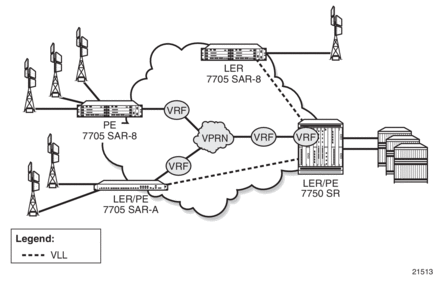
- Scenario 3 (Figure 128): In the hybrid scenario, IP forwarding among locally connected devices is handled by the 7750 SR directly, but instead of using MP-BGP to backhaul traffic, a PW is used to backhaul traffic to the MTSO/CO 7750 SR or possibly to a 7705 SAR node.
Figure 128: Spoke-SDP Termination to VPRN
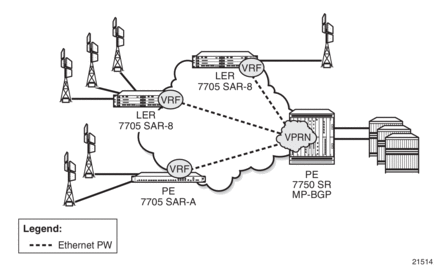
7.2.11. IPv6 on Virtual Private Edge Router
The IPv6 on Virtual Private Edge Router (6VPE) feature allows customers that are migrating from an IPv4 to an IPv6 environment to use their existing IPv4 core infrastructure for transporting IPv6 traffic. Customers can migrate their access network to IPv6, including the eNodeBs, and keep the IPv4 core. The IPv4 core can be used for transporting eNodeB IPv6 traffic over MPLS or GRE tunnels. See IPv6 over IPv4 LAN-to-LAN IPSec Tunnels for a description of how the 6VPE functionality is achieved.
| Note: The 6VPE feature is not supported on the 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card or the 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card. This applies to both the access side (VPRN interfaces) and network side (MPLS/GRE tunnels). On the network side, 6VPE is not supported on DS3/OC3 network interfaces, but is supported on SAR-A, SAR-M, SAR-H, and SAR-X T1/E1 ASAP network interfaces. On the access side, 6VPE (VPRN SAP interfaces) is not supported on any T1/E1 ASAP adapter cards/blocks. VPRN spoke-SDP interfaces (spoke-SDP termination) are supported on SAR-A, SAR-M, SAR-H, and SAR-X T1/E1 ASAP blocks but not on T1/E1 adapter cards. |
The classification of packets on a 6VPE access network is based on a customer packet Transaction Code (TC) field. The TC field is one byte long, but only the first six bits are used for the classification process. The use of six bits offers 64 different classes. The marking of the network outer tunnel DSCP/EXP bits is based on this access classification.
The supported protocols for 6VPE are listed in Table 120. The Access Control Lists for 6VPE are provided by Table 121, Table 122, and Table 123.
Table 121: 6VPE Access Control List, SAP
Service | IngV4 | IngV6 | IngMac | EgrV4 | EgrV6 | EgrMac |
Network | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
Epipe | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
IES | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
Ipipe | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
VPLS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
VPRN | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
Table 122: 6VPE Access Control List, SDP
Service | IngV4 | IngV6 | IngMac | EgrV4 | EgrV6 | EgrMac |
Epipe | No | No | No | No | No | No |
IES | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
Ipipe | No | No | No | No | No | No |
VPLS | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
VPRN | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
Table 123: 6VPE Access Control List, r-VPLS Override
Service | Ingress Override-v4 | Ingress Override-v6 |
IES | Yes | Yes |
VPRN | Yes | Yes |
7.2.12. IPv6 over IPv4 LAN-to-LAN IPSec Tunnels
In order to support the 6VPE functionality described in IPv6 on Virtual Private Edge Router, access (customer) IPv6 traffic is aggregated using a service VPRN and encrypted via an IPSec IPv4 static LAN-to-LAN tunnel, as shown in Figure 129. BGPv4 or BGPv6 can be configured over the IPSec IPv4 static LAN-to-LAN tunnel with an IPv6 address family to advertise the IPv6 VPRN routes to the peer VPRN.
The management IP addresses of all customer switches are migrated to IPv6. The system IP address of the 7705 SAR is configured as an IPv6 address and also migrated to IPv6. The OAM customer traffic is aggregated via an r-VPLS (IPv6 r-VPLS) into a 6VPE OAM VPRN. An IPv6 static route carries the IPv6 OAM traffic to an IPv4 static LAN-to-LAN tunnel, where the traffic is encrypted and encapsulated in an IPSec IPv4 transport tunnel. The IPSec IPv4 transport tunnel uses a NAT-to-single public IP address method, that is, NAT-T.
Figure 129: Access IPv6 Traffic Aggregation and Encryption
7.2.13. Bandwidth Optimization for Low-speed Links
The 7705 SAR can be used in deployments where the uplink bandwidth capacity and requirements are considerably less than if the router is used for fixed or mobile backhaul applications. For example, the 7705 SAR can be used to direct traffic from multiple individual homes for applications such as smart meter aggregation or relay connectivity. Connecting to end systems such as smart meters or relays requires uplink bandwidth capacity in terms of hundreds of kilobits per second, rather than hundreds of megabits per second.
The 7705 SAR is optimized to operate in environments with megabits per second of uplink capacity for network operations. Therefore, many of the software timers are designed to ensure the fastest possible detection of failures, without considering bandwidth limitations. In deployments with very low bandwidth constraints, the system must also be optimized for effective operation of the routers without any interruption to mission-critical customer traffic. This can be achieved by:
- minimizing head-of-line (HoL) blocking by supporting a lower MTU
- redirecting self-generated traffic (SGT) to data queues (refer to the 7705 SAR Quality of Service Guide, “SGT Redirection”, for information)
One way to optimize operation in lower-bandwidth applications is to minimize HoL blocking caused by large packets. HoL blocking occurs when transmission of a large non-mission-critical packet delays a mission-critical packet beyond acceptable limits. The propagation delay of large packets over a slow link is fairly significant. For example, the propagation delay when transmitting a 1500-byte packet over a 100 kb/s link is 120 ms. If a mission-critical packet is queued immediately after the first bit of a non-mission-critical 1500-byte packet begins transmission, the mission-critical packet must wait 120 ms before the uplink is available again.
To minimize HoL blocking, the 7705 SAR now supports a lower MTU of 128 bytes (from the original 512-byte minimum) so that large IP packets can be fragmented into 128-byte chunks. In the preceding example, transmitting a 128-byte packet over a 100 kb/s link will only delay the next packet by 10.24 ms.
This lower MTU is supported on IES and VPRN interfaces (access interfaces) and on network interfaces. The IP MTU is derived from the port MTU, unless specifically configured with the ip-mtu command. This command is supported on access interfaces only.
The following must be considered when using a lower IP MTU:
- applicability – the lower IP MTU is only applicable for IP forwarded traffic and cannot be applied to pseudowire or VPLS traffic
- reassembly – the far-end/destination node must reassemble the packet before it can process the data, which may impact the performance of the end system and/or may require different hardware to perform the reassembly
- extra overhead – each fragment must have an IPv4 header so that all fragments of the packet can be forwarded to the destination. Care must be taken to ensure that the extra IP overhead for each fragment does not offset the gain achieved by using the lower MTU. As an example, for a 128-byte packet, the IPv4 header, which is 20 bytes in length, constitutes approximately 15% of the total packet size.
Note:
|
7.2.13.1. OAM Diagnostics Restrictions with Lower IP MTU
OAM tests require a minimum network port MTU in order to run; this value depends on the test. If the port MTU is set to a value lower than the minimum requirement, the test will fail.
If the port MTU is set to a value that meets the minimum requirement, the packet size parameter can be configured for the test (for example, oam sdp-ping 1 size 102).
If the size parameter is not specified, the system builds the packet based on the default payload size. If the size parameter is configured and is greater than the default payload size, padding bytes are added to equal the configured value.
The packet size is dependent on the port MTU value; that is, if the minimum port MTU value is used, there are restrictions on the packet size. If the configured size is greater than the maximum value supported with the minimum port MTU, the test will fail.
Table 124 and Table 125 list the minimum port MTU required for each OAM test and the maximum size of the OAM packet that can be configured when the minimum port MTU is used, based on SDP tunnel type.
| Note: RSVP LSPs will not come up if the network port MTU value is lower than 302 bytes. |
Table 124: Port MTU Requirements for OAM Diagnostics (GRE Tunnels)
SDP Type: GRE | ||
Test Type | Minimum Network Port MTU Requirement over Ethernet Dot1q Encapsulation (Bytes) | OAM Test Size Range (Bytes) |
sdp-ping | 128 | 72 to 82 |
svc-ping | 196 | N/A 1 |
vccv-ping | 143 | 1 to 93 |
vccv-trace | 143 | 1 to 93 |
vprn-ping | 182 | 1 to 136 |
vprn-trace | 302 | 1 to 256 |
mac-ping | 188 | 1 to 142 |
mac-trace | 240 | 1 to 194 |
cpe-ping | 186 | N/A 1 |
- Size is not configurable
Note:
Table 125: Port MTU Requirements for OAM Diagnostics (LDP Tunnels)
SDP Type: LDP | ||
Test Type | Minimum Network Port MTU Requirement over Ethernet Dot1q Encapsulation (Bytes) | OAM Test Size Range (Bytes) |
lsp-ping | 128 | 1 to 106 |
lsp-trace | 128 | 1 to 104 |
sdp-ping | 128 | 72 to 102 |
svc-ping | 176 | N/A 1 |
vccv-ping | 128 | 1 to 98 |
vccv-trace | 128 | 1 to 98 |
vprn-ping | 182 | 1 to 156 |
vprn-trace | 302 | 1 to 276 |
mac-ping | 168 | 1 to 142 |
mac-trace | 220 | 1 to 194 |
cpe-ping | 166 | N/A 1 |
- Size is not configurable
Note:
For information on OAM diagnostics, refer to the 7705 SAR OAM and Diagnostics Guide.