7. Route Policies
This chapter provides information about configuring route policies.
Topics in this chapter include:
7.1. Configuring Route Policies
This section contains information on the following topics:
Route policies are used to manage the label database for MPLS and to control entries to the routing table for dynamic routing (see Routing Policy and MPLS).
For routing, the 7705 SAR supports two databases to store routes. The routing database (RIB) is composed of the routing information learned by the routing protocols, including static routes. The forwarding database (FIB) is composed of the routes actually used to forward traffic through a router. In addition, link-state databases are maintained by interior gateway protocols (IGPs) such as OSPF and IS-IS. Refer to the 7705 SAR Routing Protocols Guide for information on OSPF, IS-IS, and other routing protocols.
Routing protocols calculate the best route to each destination and place these routes in the forwarding table. The routes in the forwarding table are used to forward IP packets to neighbors.
As an example, operators can configure a routing policy that will not place routes associated with a specific origin in the routing table. These routes will not be used to forward data packets and these routes are not advertised by the routing protocol to neighbors.
Routing policies control the size and content of the routing tables, the routes that are advertised, and the best route to take to reach a destination. Careful planning is essential to implement route policies that can affect the flow of routing information throughout the network. Before configuring and applying a route policy, operators should develop an overall plan and strategy to accomplish their intended routing actions.
There are no default route policies. Each policy must be created explicitly and applied. Policy parameters are modifiable.
7.1.1. Routing Policy and MPLS
Route policies can be used to manage the MPLS label database.
When used to manage the label database, route policies can be configured to determine which labels should be learned or advertised; for example, labels from a specified neighbor can be added to the label information base (LIB), while labels advertised by certain other neighbors can be discarded. Label learning of MPLS packets and, as a result, how the MPLS packets are forwarded, are based on the defined policies, if there are any. If no route policies are defined, all advertised labels received from neighbors are learned and placed in the LIB.
Refer to the “Label Distribution Protocol” section in the 7705 SAR MPLS Guide for more information on how routing policies can be used as LDP import or export policies to control the label bindings that an LSR accepts from, or advertises to, its peers.
7.1.2. Policy Statements
Route policies contain policy statements containing ordered entries that contain match conditions and actions that the user specifies. The entries should be sequenced from the most explicit to the least explicit. Packet forwarding and routing can be implemented according to defined policies. Policy-based routing allows the user to dictate where traffic can be routed, through specific paths, or whether to forward or drop the traffic. Route policies can match a given route policy entry and continue searching for other matches within either the same route policy or the next route policy.
The process can stop when the first complete match is found and the router executes the action defined in the entry, either to accept or reject packets that match the criteria or proceed to the next entry or the next policy. Matching criteria can be based on source, destination, or particular properties of a route. Route policies can be constructed to support multiple stages to the evaluation and setting various route attributes.
Other matching conditions can be provided by specifying criteria such as:
- autonomous system (AS) path policy options — a combination of AS numbers and regular expression operators
- community list — a group sharing a common property
- prefix list — a named list of prefixes
- to and from criteria — a route’s destination and source
7.1.2.1. Default Action Behavior
The default action of a policy applies to a route when the route does not match any of the entries of the policy. If a policy does not have any match entries, all routes are subject to the default action. If no default action is specified and the policy is the last one in a chain of policies, the default action is determined by the protocol that called the policy.
If a default action is defined for one or more of the configured route policies, the default action is handled as follows:
- The default action can be set to all available action states, including accept, reject, next-entry, and next-policy.
- If the action states accept or reject, the policy evaluation terminates and the appropriate result is returned.
- If a default action is defined and no matches occurred with the entries in the policy, the default action is used.
- If a default action is defined and one or more matches occurred with the entries of the policy, the default action is not used.
7.1.2.2. Denied IP Prefixes
The following IP address prefixes are not allowed by the routing protocols and the Route Table Manager and are not populated within the forwarding table:
- 0.0.0.0/8 or longer
- 127.0.0.0/8 or longer
- 224.0.0.0/4 or longer
- 240.0.0.0/4 or longer
Any other prefixes that need to be filtered can be filtered explicitly using route policies.
7.1.2.3. Controlling Route Flapping
Route flapping is defined as recurring changes of an advertised route between nodes. That is, the advertised route alternates (flaps) back and forth between two paths. This is typically caused by network problems that cause intermittent route failures. Route flap is defined in RFC 2439.
Route damping is a controlled acceptance of unstable routes from BGP peers so that any ripple effect caused by route flapping across BGP AS border routers is minimized. The rationale is to delay the use of unstable routes (flapping routes) to forward data and advertisements until the route stabilizes.
The Nokia implementation of route damping is based on the following parameters:
- Figure of Merit — a route is assigned a Figure of Merit (FoM), which is proportional to the frequency of flaps. The FoM algorithm can characterize a route’s behavior over a period of time. See Damping for more information on FoM and damping.
- route flap — a route flap is not limited to the withdrawn route. It also applies to any change in the AS path or the next hop of a reachable route. A change in AS path or next hop indicates that the intermediate AS or the route-advertising peer is not suppressing flapping routes at the source or during the propagation. Even if the route is accepted as a stable route, the data packets destined for the route could experience unstable routing due to the unstable AS path or next hop.
- suppress threshold — when the configured suppress threshold is exceeded, the route is suppressed and not advertised to other peers. The state of the route is considered to be down from the perspective of the routing protocol.
- reuse threshold — when the FoM value falls below the configured reuse threshold and the route is still reachable, the route is advertised to other peers. The FoM value decays exponentially after a route is suppressed.
The two events that could trigger the route flapping algorithm are:
- route flapping — if a route flap is detected within a configured maximum route flap history time, the route’s FoM is initialized and the route is marked as a potentially unstable route. Every time a route flaps, the FoM is increased and the route is suppressed if the FoM crosses the suppress threshold.
- route reuse timer trigger — a suppressed route’s FoM decays exponentially. When it crosses the reuse threshold, the route is eligible for advertisement if it is still reachable.
If the route continues to flap, the FoM, with respect to time scale, looks like a sawtooth waveform with the exponential rise and decay of FoM. To control flapping, the following parameters can be configured:
- half-life — the half-life value is the time, expressed in minutes, required for a route to remain stable in order for one half of the FoM value to be reduced. For example, if the half-life value is 6 (min) and the route remains stable for 6 min, then the new FoM value is 3. After another 6 min passes and the route remains stable, the new FoM value is 1.5.
- max-suppress — the maximum suppression time, expressed in minutes, is the maximum amount of time that a route can remain suppressed
- suppress — if the FoM value exceeds the configured integer value, the route is suppressed for use or inclusion in advertisements
- reuse — if the FoM value falls below the configured reuse value, then the route can be reused
7.1.3. Regular Expressions
The ability to perform a filter match in the AS-PATH is supported. This feature allows customers to configure match criteria for specific sequences within the AS path so that they can be filtered out before cluttering the service provider’s routing information base (RIB).
The 7705 SAR uses regular expression strings to specify match criteria for:
- an AS path string; for example, “100 200 300”, where 100, 200, and 300 are AS numbers
- a community string; for example, “100:200”, where 100 is the AS number and 200 is the community value
A regular expression is expressed as a combination of Terms and Operators. Regular expressions should always be enclosed in quotes.
The 7705 SAR also supports community expressions that allow the use of AND, OR, and NOT logical operators. For more information, see Community Expressions.
7.1.3.1. Terms
A term for an AS path regular expression is:
- an elementary term; for example, an AS number “200”
- a range term composed of two elementary terms separated by the “-” character, such as “200-300”
- the “.” dot wildcard character, which matches any elementary term
- a regular expression enclosed in parentheses “( )”
- a regular expression enclosed in square brackets used to specify a set of choices of elementary or range terms; for example, [100-300 400] matches any AS number between 100 and 300 or the AS number 400
A term for a community string regular expression is a string that is evaluated character by character and is composed of:
- an elementary term, which for a community string is any single digit, such as “4”
- a range term composed of two elementary terms separated by the “-” character, such as “2-3”
- a colon “:” to delimit the AS number from the community value
- the “.” dot wildcard character, which matches any elementary term or “:”
- a regular expression enclosed in parentheses “( )”
- a regular expression enclosed in square brackets, which is used to specify a set of choices of elementary or range terms; for example, [1-3 7] matches any single digit between 1 and 3 or the digit 7
7.1.3.2. Operators
The regular expression operators are listed in Table 120.
Table 120: Regular Expression Operators
Operator | Description |
| | Matches the term on alternate sides of the pipe |
. | Matches any elementary term or “:” community string |
* | Matches multiple occurrences of the term |
? | Matches 0 or 1 occurrence of the term |
+ | Matches 1 or more occurrence of the term |
( ) | Used to parenthesize so a regular expression is considered as one term |
[ ] | Used to demarcate a set of elementary or range terms |
- | Used between the start and end of a range |
{m,n} | Matches at least m and at most n repetitions of the term |
{m} | Matches exactly m repetitions of the term |
{m,} | Matches m or more repetitions of the term |
: | Delimits the AS number from the community value — only allowed for communities |
^ | Matches the beginning of the string — only allowed for communities |
$ | Matches the end of the string — only allowed for communities |
\ | An escape character to indicate that the following character is a match criteria and not a grouping delimiter |
Examples of AS path and community string regular expressions are listed in Table 121.
Table 121: AS Path and Community Regular Expression Examples
AS Path to Match Criteria | Regular Expression | Examples of Matches |
Null AS path | null 1 | Null AS path |
AS path is 11 | 11 | 11 |
AS path is 11 22 33 | 11 22 33 | 11 22 33 |
Zero or more occurrences of AS number 11 | 11* | Null AS path 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 … 11 |
Path of any length that begins with AS numbers 11, 22, 33 | 11 22 33 .* | 11 22 33 11 22 33 400 500 600 |
Path of any length that ends with AS numbers 44, 55, 66 | .* 44 55 66 | 44 55 66 100 44 55 66 100 200 44 55 66 100 200 300 44 55 66 100 200 300 … 44 55 66 |
One occurrence of the AS numbers 100 and 200, followed by one or more occurrences of the number 33 | 100 200 33+ | 100 200 33 100 200 33 33 100 200 33 33 33 100 200 33 33 33 … 33 |
One occurrence of the AS number 11, followed by one or more occurrences of AS number 22, followed by one or more occurrences of AS number 33 | 11+ 22+ 33+ | 11 22 33 11 11 22 33 11 11 22 22 33 11 11 22 22 33 33 11 ... 11 22 ... 22 33 ... 33 |
Path whose second AS number must be 11 or 22 | (. 11) | (. 22) .* or . (11 | 22) .* | 100 11 200 22 300 400 … |
Path of length one or two whose second AS number might be 11 or 22 | . (11 | 22)? | 100 200 11 300 22 |
Path whose first AS number is 100 and second AS number is either 11 or 22 | 100 (11 | 22) .* | 100 11 100 22 200 300 |
AS path 11, 22, or 33 | [11 22 33] | 11 22 33 |
Range of AS numbers to match a single AS number | 10-14 | Null AS path 10 or 11 or 12 |
[10-12]* | Null AS path 10 or 11 or 12 10 10 or 10 11 or 10 12 11 10 or 11 11 or 11 12 12 10 or 12 11 or 12 12 … | |
Zero or one occurrence of AS number 11 | 11? or 11{0,1} | Null AS path 11 |
One through four occurrences of AS number 11 | 11{1,4} | 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 |
One through four occurrences of AS number 11 followed by one occurrence of AS number 22 | 11{1,4} 22 | 11 22 11 11 22 11 11 11 22 11 11 11 11 22 |
Path of any length, except nonexistent, whose second AS number can be anything, including nonexistent | . .* or . .{0,} | 100 100 200 11 22 33 44 55 |
AS number is 100 and community value is 200 | ^100:200$ | 100:200 |
AS number is 11 or 22 and community value is any number | ^((11)|(22)):(.*)$ | 11:100 22:100 11:200 … |
AS number is 11 and community value is any number that starts with 1 | ^11:(1.*)$ | 11:1 11:100 11:1100 |
AS number is any number and community value is any number that ends with 1, 2, or 3 | ^(.*):(.*[1-3])$ | 11:1 100:2002 333:55553 … |
AS number is 11 or 22 and community value is any number that starts with 3 and ends with 4, 5 or 9 | ^((11)|(22)):(3.*[459])$ | 11:34 22:3335 11:3777779 … |
AS number is 11 or 22 and community value ends in 33 or 44 | [^((11|22)):(.*((33)|(44)))$ | 11:33 22:99944 22:555533 … |
- The null keyword matches an empty AS path.
Note:
7.1.4. Community Expressions
A community expression is a collection of community IDs separated by AND, OR, and NOT operations. A community expression is not the same as a regular expression. A community expression must be enclosed within quotes (“expression”) and may include parentheses to group expressions. An example of a community expression CLI command is:
For more information, see the community command description.
7.1.5. BGP and OSPF Route Policy Support
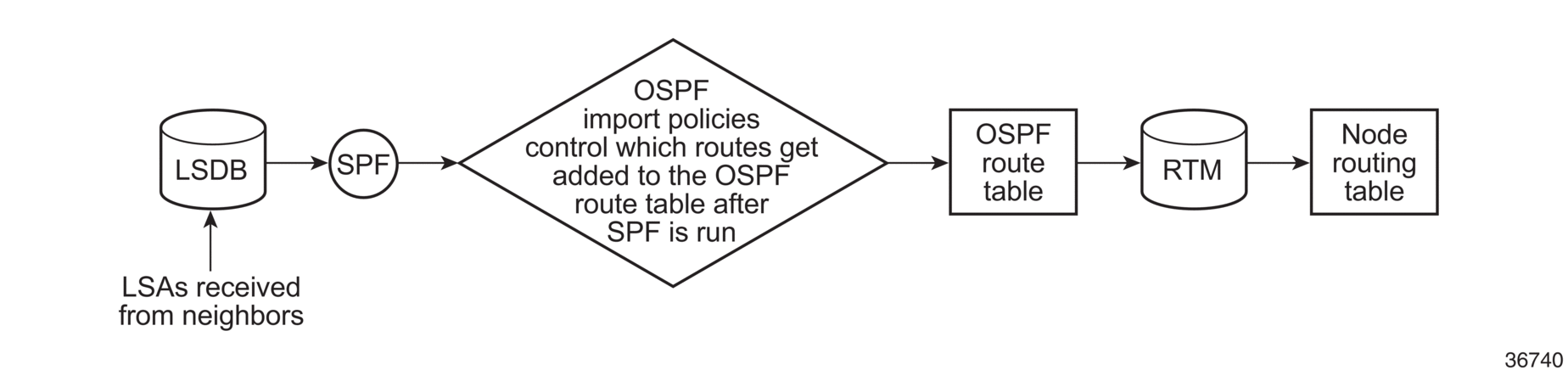
BGP and OSPF require route policy support. Figure 16, Figure 17, and Figure 18 show how route policies are evaluated in each protocol. Figure 16 shows BGP support, which applies a route policy as an internal part of the BGP route selection process. Figure 17 shows OSPF support for export policies, which applies routing policies at the edge of the protocol in order to control only the routes that are announced to or accepted from the Routing Table Manager (RTM). Figure 18 shows OSPF support for import policies, which applies import routing policies to control which routes are added to the OSPF route table after SPF is run.
Figure 16: BGP Route Policy Diagram
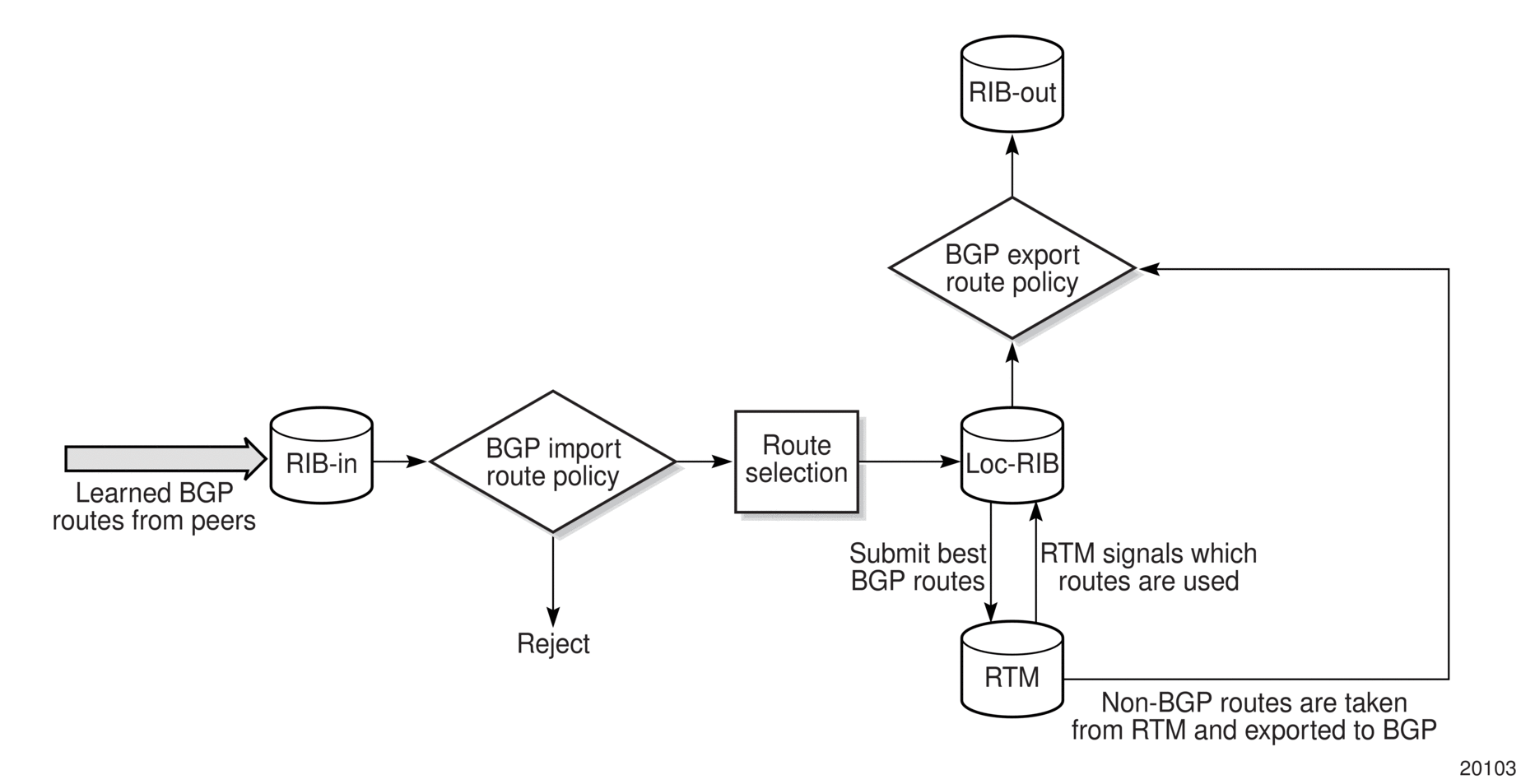
Figure 17: OSPF Export Route Policy Diagram
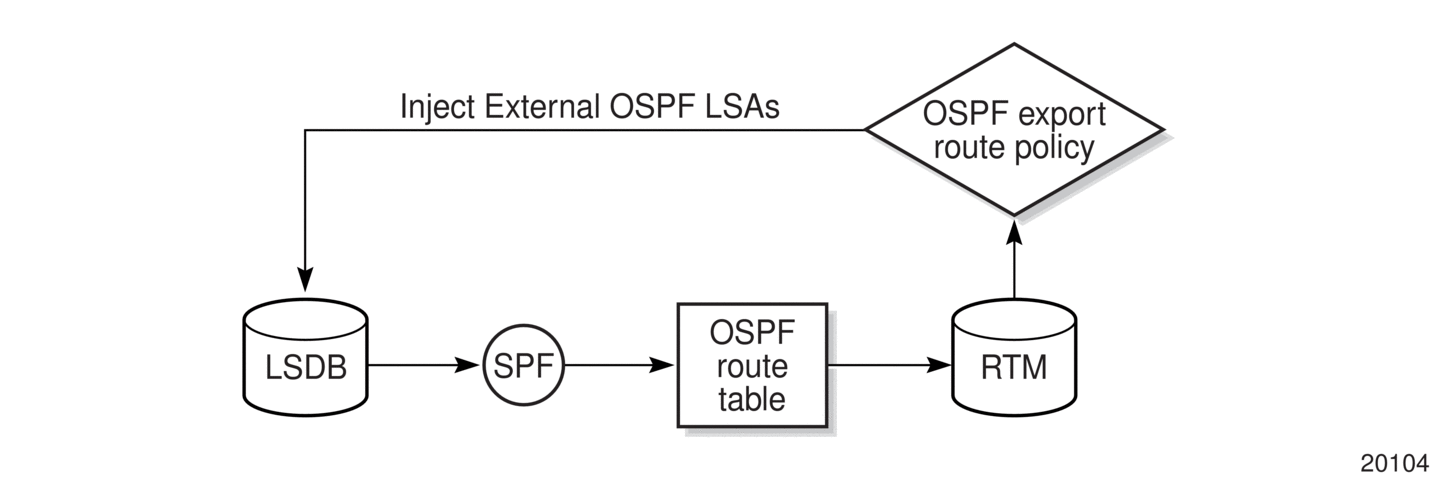
Figure 18: OSPF Import Route Policy Diagram
7.1.5.1. BGP Route Policies
The Nokia implementation of BGP uses route policies extensively. The implied or default route policies can be overridden by customized route policies. The default BGP properties, with no route policies configured, function as follows:
- accept all BGP routes into the RTM for consideration
- announce all used BGP learned routes to other BGP peers
- announce none of the IGP, static, or local routes to BGP peers
7.1.5.2. Readvertised Route Policies
Occasionally, within the network and as applicable to the VPRN service, BGP routes may be readvertised from BGP into OSPF and IS-IS. OSPF export policies (policies control which routes are exported to OSPF) are not handled by the main OSPF task but are handled by a separate task or an RTM task that filters the routes before they are presented to the main OSPF task.
7.1.5.3. Route Policies for BGP Next-Hop Resolution and Peer Tracking
The 7705 SAR can attach a route policy to the BGP next-hop resolution process and can allow a route policy to be associated with the optional BGP peer-tracking function. These two features are supported for BGP and VPRN BGP services.
7.1.5.3.1. BGP Next-Hop Resolution Policy Overview
BGP next-hop resolution is a fundamental part of BGP protocol operation. It determines the best matching route (or tunnel) for the BGP next-hop address and uses information about this resolving route when running the best-path selection algorithm and programming the forwarding table. Attaching a policy to BGP next-hop resolution provides additional control over which IP routes in the routing table can become resolving routes.
See Route Policy Support for BGP Next-Hop Resolution for details.
7.1.5.3.2. BGP Peer Tracking Policy Overview
Peer tracking is a BGP feature that triggers teardown of a BGP session if there is no IP reachability to the neighbor address or if the best matching IP route is rejected by the peer-tracking policy. This feature is configurable down to the peer level and is disabled by default. Peer tracking accelerates routing reconvergence when a failure leads to hold-timer expiry on the BGP session. BFD for BGP sessions has a similar function and is often used instead of peer tracking.
In the BGP implementation, an IPv4 or IPv6 neighbor address is considered reachable by the peer-tracking algorithm if there is any active and eligible IP route that matches the neighbor address. Policy support for peer tracking is useful so that the network administrator can restrict the set of eligible routes used to determine the reachability of an IPv4 or IPv6 BGP neighbor address when peer tracking is enabled.
See Route Policy Support for BGP Peer Tracking for details.
7.1.5.3.3. Route Policy Support for BGP Next-Hop Resolution
A route policy can be used for BGP next-hop resolution through the use of the policy command in the config>router>bgp>next-hop-resolution and config>service>vprn>bgp>next-hop-resolution contexts. The policy command specifies the route policy to be used.
If the BGP configuration references a next-hop resolution policy (for example, policy1) and BGP has an unlabeled unicast IPv4 or IPv6 route with IPv4 or IPv6 next-hop address nh1 that is resolvable by an IP route from the RTM, BGP determines the resolving route for nh1 as follows.
- BGP looks for the most specific IP route in the candidate set that matches nh1 (call this route R1). If there is no matching, route the BGP route is unresolved and the process is exited.
- If R1 is rejected by an entry or the default-action of policy1, the route is unresolved and the process is exited.
- If R1 is accepted by an entry or the default-action of policy1, R1 is the resolving route.
All policy actions are supported in a next-hop resolution policy; however, the following points should be noted:
- next-policy is ignored and matching routes are handled as per the default-action. Chaining multiple policies is not supported by this feature.
- next-entry is supported and causes evaluation of the policy to continue on to the next entry or the default-action is applied if this is the last entry
- no route attributes are modified as part of an accept action. The route is accepted but no modification of the AIGP metric, AS path, community, damping parameters, local preference, MED, next-hop, origin, and so on, occurs.
When no default-action is explicitly configured by the user, the implicit default-action is accept.
All from match conditions are supported in a next-hop resolution policy except as noted below:
- family is ignored. When resolving an IPv4 BGP route, only IPv4 routes are eligible for resolving the next hop and when resolving an IPv6 BGP route, only IPv6 routes are eligible for resolving the next hop. This logic cannot be changed by policy.
- group-address, host-ip, and source-address are ignored because they pertain only to multicast routes
The default next-hop resolution policy, used when the configuration has no policy, is equivalent to a user-configured policy with no entries and a default-action of accept.
It is possible to add, remove, or change the next-hop resolution policy at any time, without requiring BGP to first be shut down. The new policy is processed immediately and any indirect next-hop resolution changes that result from the new policy are immediately pushed down to the datapath.
7.1.5.3.4. Route Policy Support for BGP Peer Tracking
A route policy can be used for BGP peer tracking through the use of the peer-tracking-policy command in the config>router>bgp and config>service>vprn>bgp contexts. The policy command specifies the route policy to be used.
If the command references a policy (for example, policy1) and peer tracking is enabled with a BGP neighbor A having IPv4 or IPv6 address p1, the route BGP uses to determine the reachability of p1 is determined as follows.
- BGP initializes the set of candidate IP routes to all active routes installed in the forwarding table, excluding aggregate routes.
- BGP looks for the most specific IP route in the candidate set that matches p1 (call this route R1). If there is no matching route, the peer is unreachable and the process is exited.
- If R1 is a BGP route or R1 is rejected by an entry or the default-action of policy1, the peer is unreachable and the process is exited.
- If R1 is accepted by an entry or the default-action of policy1, the peer is reachable via R1.
If the above algorithm determines that the peer is unreachable, the BGP session with A is closed after a 1-second delay to dampen route flaps and stays closed until there is a route R1 that is accepted (that is, meets the step 4 condition). Reachability is evaluated before a new session is established, whenever the most specific route that matches the neighbor address changes, and whenever there is a change to the peer-tracking policy.
All policy actions are supported in a peer-tracking policy; however, the following points should be noted:
- next-policy is ignored and matching routes are handled per the default-action. Chaining multiple policies is not supported by this feature.
- next-entry is supported and causes evaluation of the policy to continue on to the next entry or the default-action is applied if this is the last entry
- no route attributes are modified as part of an accept action. The route is accepted but no modification of the AIGP metric, AS path, community, damping parameters, local preference, MED, next-hop, origin, and so on, occurs.
When no default-action is explicitly configured by the user, the implicit default-action is accept.
All from match conditions are supported in a peer-tracking policy except as noted below:
- family is ignored. When determining the reachability of an IPv4 peer address, only IPv4 routes are eligible and when determining the reachability of an IPv6 peer address, only IPv6 routes are eligible. This logic cannot be changed by policy.
- group-address, host-ip, and source-address are ignored because they pertain only to multicast routes
The default peer-tracking policy, used when the configuration has no peer-tracking policy, is equivalent to a user-configured policy with no entries and a default-action of accept.
It is possible to add, remove, or change the peer-tracking policy at any time, without requiring BGP to first be shut down. The new policy is processed immediately and this may trigger one or more sessions to be torn down.
7.1.6. When to Use Route Policies
The following are examples of when to configure and apply unique route policies:
- to control the protocol to allow all routes to be imported into the routing table. This enables the routing table to learn about particular routes to enable packet forwarding and redistributing of routes into other routing protocols.
- to control the export of a protocol’s learned active routes
- to enable the MP-BGP routing protocol to announce active routes learned from another routing protocol (that is, the static routes configured in the 7705 SAR). This function is sometimes called route redistribution.
- to allow unique behaviors to control route characteristics; for example, change the route preference, AS path, or community values to manipulate or control the route selection
- to control BGP route flapping by use of route flap damping
7.1.7. Troubleshooting the FIB
Adapter cards that are installed in a 7705 SAR-8 Shelf V2 or 7705 SAR-18 chassis may have different hardware limitations with respect to IPv4 and IPv6 FIB routing. Alarms may be generated on the node when IPv4 or IPv6 routing faults related to scaling, capability, or a datapath route lookup problem are detected on an adapter card. Table 122 lists the applicable alarms.
Table 122: FIB Alarms
Alarm | Description |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV6_UNSUPPORTED_SUBNET_MASK Error Detected!” | A /65 to /127 IPv6 route was downloaded to an adapter card without hardware support |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV4_SCALE_EXCEEDED Error Detected!” | The total number of IPv4 routes in the FIB exceeds the adapter card hardware capability |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV4_VRF_SCALE_EXCEEDED Error Detected!” | The total number of IPv4 routing instances in the FIB (for example, number of VPRNs) exceeds the adapter card hardware capability |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV6_SCALE_EXCEEDED Error Detected!” | The total number of IPv6 routes in the FIB exceeds the adapter card hardware capability |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV6_VRF_SCALE_EXCEEDED Error Detected!” | The total number of IPv6 routing instances in the FIB (for example, number of VPRNs) exceeds the adapter card hardware capability |
“Class MDA Module : runtime event, details: Fatal FIB_STATUS_IPV4_DP_LOOKUP_FAULT Error Detected!” | The software has detected faults with datapath IPv4 route lookups |
If any of the alarms in Table 122 are generated, the IPv4 or IPv6 datapath on the adapter card will operate in a random way. For example, traffic may continue to flow as expected in some cases, but in other cases, traffic could be blackholed or misrouted.
The show router fib 1 ipv4 summary and show router fib 1 ipv6 summary commands can be used to confirm that the FIB limits are exceeded.
For example:
To restore a FIB that is in a failed state, the user must do the following.
- If possible, resolve the condition that led to the alarm being generated. For example, for scaling alarms, reduce the size of the routing table below the maximum for the affected adapter card.
- Execute the tools perform mda-table-refresh command to restore the FIB. Refer to the 7705 SAR OAM and Diagnostics Guide, “Tools Perform Commands” for a command description.Wait a few minutes to ensure that no new alarm is raised; if there are no new alarms, the fault has been successfully resolved.If a new alarm is raised, this indicates that the adapter card must be replaced.
Alternatively, when an alarm is generated, replace the card with a new adapter card that supports the higher scaling limit (for scaling alarms) or replace the card to resolve persistent datapath lookup faults.
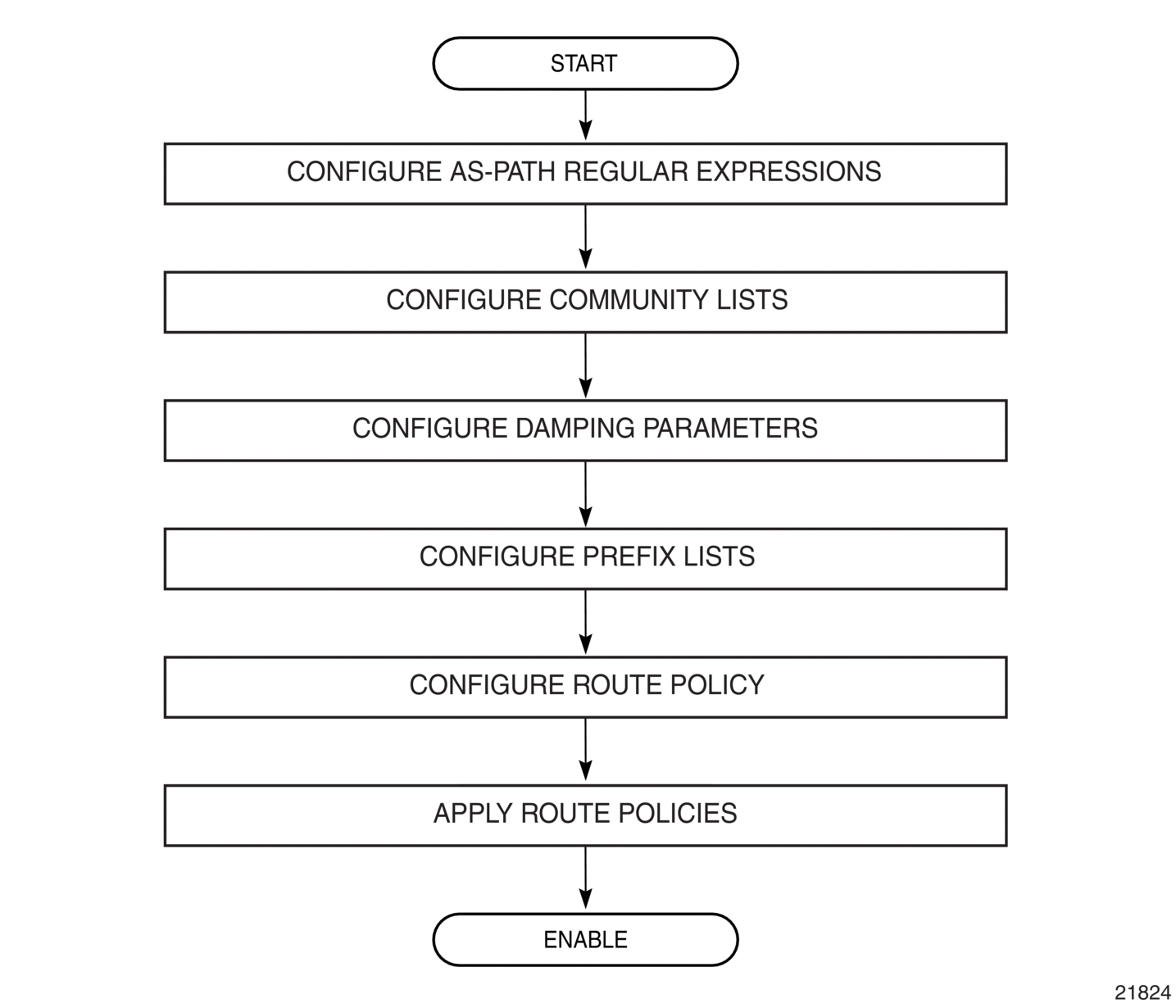
7.2. Route Policy Configuration Process Overview
Figure 19 displays the process to provision basic route policy parameters.
Figure 19: Route Policy Configuration and Implementation Flow
7.3. Configuration Notes
When configuring policy statements, the policy statement name must be unique.
7.3.1. Reference Sources
For information on supported IETF drafts and standards, as well as standard and proprietary MIBs, refer to Standards and Protocol Support.