6. System Management
This chapter provides information about configuring basic system management parameters.
Topics in this chapter include:
6.1. System Management Parameters
System management commands allow you to configure basic system management functions such as the system name, the router’s location, coordinates, and CLLI code, as well as time zones, Network Time Protocol (NTP), Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) properties, CRON, and synchronization properties.
6.1.1. System Information
System information components include:
6.1.1.1. System Name
The system name is the MIB II (RFC 1907, Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)) sysName object. By convention, this text string is the node’s fully qualified domain name. The system name can be any ASCII printable text string of up to 32 characters.
6.1.1.2. System Contact
The system contact is the MIB II sysContact object. By convention, this text string is a textual identification of the contact person for this managed node, together with information on how to contact this person.The system contact can be any ASCII printable text string of up to 80 characters.
6.1.1.3. System Location
The system location is the MIB II sysLocation object, which is a text string conventionally used to describe the node’s physical location; for example, “Bldg MV-11, 1st Floor, Room 101”. The system location can be any ASCII printable text string of up to 80 characters.
6.1.1.4. System Coordinates
The Nokia Chassis MIB tmnxChassisCoordinates object defines the system coordinates. This text string indicates the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) coordinates of the location of the chassis.
Two-dimensional GNSS positioning offers latitude and longitude information as a four-dimensional vector:
(direction, hours, minutes, seconds)
where:
direction is one of the four basic values: N, S, W, E
hours range from 0 to 180 (for latitude) and 0 to 90 (for longitude)
minutes and seconds range from 0 to 60
<W, 122, 56, 89> is an example of longitude and <N, 85, 66, 43> is an example of latitude.
System coordinates can be expressed in different notations; for example:
- N 45 58 23, W 34 56 12
- N37 37' 00 latitude, W122 22' 00 longitude
- N36 × 39.246' W121 × 40.121
The system coordinates can be any ASCII printable text string up to 80 characters.
6.1.1.5. Common Language Location Identifier
A Common Language Location Identifier (CLLI) code string for the device is an 11-character standardized geographic identifier that uniquely identifies the geographic location of places and certain functional categories of equipment unique to the telecommunications industry. The CLLI code is stored in the Nokia Chassis MIB tmnxChassisCLLICode object.
The CLLI code can be any ASCII printable text string of up to 11 characters.
6.1.1.6. System Identifier
A system identifier is a manually configured IPv4 address that can be used to uniquely identify the 7705 SAR in the network in situations where the more commonly used system IP address may change dynamically, causing loss of historical data attributed to the node. For example, the system IP address can change dynamically using DHCP when the 7705 SAR is acting as a DHCP client and the DHCP server-facing interface is unnumbered. In this situation, a static system identifier may be desirable.
The system identifier can be any IPv4 address.
6.1.1.7. PoE Power Source
The 7705 SAR-H supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) on all four 10/100/1000 copper Ethernet ports. To use PoE, the PoE power source must be configured at the system level as either internal or external. When the system is configured for the internal PoE power source option, PoE capability can be enabled on ports 5 and 6 only. In addition, port 5 can be enabled for PoE+ but in that case, port 6 cannot support any PoE capability. When the system is configured for the external PoE power source option, a mix of PoE and PoE+ is available on ports 5, 6, 7, and 8. Refer to the 7705 SAR-H Chassis Installation Guide, “Ethernet Ports”, for information about supported combinations of PoE and PoE+.
To enable PoE or PoE+ on a PoE-capable port on the 7705 SAR-H, use the config>port>ethernet>poe command; refer to the 7705 SAR Interface Configuration Guide, “Configuration Command Reference”, for more information.
The PoE-capable ports on the 7705 SAR-H act as a Power Source Equipment (PSE) device. They support IEEE 802.3at and IEEE 802.3af.
The 7705 SAR-W supports PoE+ on the two RJ-45 Ethernet ports with PoE+. The 7705 SAR-Wx (variant 3HE07617AA) supports PoE+ on the RJ-45 Ethernet port with PoE+. The PoE+ ports are used to deliver power to a “Powered Device”, such as a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) or line-of-sight (LOS) microwave radio, at levels compatible with the IEEE 802.3at standard.
To enable PoE+ on a PoE+-capable port on the 7705 SAR-W or 7705 SAR-Wx, use the config>port>ethernet>poe plus command; refer to the 7705 SAR Interface Configuration Guide, “Configuration Command Reference”, for more information.
6.1.2. System Time
The 7705 SAR routers are equipped with a real-time system clock for time-keeping purposes. When set, the system clock always operates on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), but the 7705 SAR software has options for local time translation as well as system clock synchronization.
System time parameters include:
6.1.2.1. Time Zones
Setting a time zone in the 7705 SAR allows for times to be displayed in the local time rather than in UTC. The 7705 SAR has both user-defined and system-defined time zones.
A user-defined time zone has a user-assigned name of up to four printable ASCII characters that is different from the system-defined time zones. For user-defined time zones, the offset from UTC is configured as well as any summer time adjustment for the time zone.
The 7705 SAR system-defined time zones are listed in Table 23, which includes both time zones with and without summer time correction.
Table 23: System-defined Time Zones
Acronym | Time Zone Name | UTC Offset |
Europe: | ||
GMT | Greenwich Mean Time | UTC |
BST | British Summer Time | UTC +1 |
IST | Irish Summer Time | UTC +1* |
WET | Western Europe Time | UTC |
WEST | Western Europe Summer Time | UTC +1 |
CET | Central Europe Time | UTC +1 |
CEST | Central Europe Summer Time | UTC +2 |
EET | Eastern Europe Time | UTC +2 |
EEST | Eastern Europe Summer Time | UTC +3 |
MSK | Moscow Time | UTC +3 |
MSD | Moscow Summer Time | UTC +4 |
US and Canada: | ||
AST | Atlantic Standard Time | UTC -4 |
ADT | Atlantic Daylight Time | UTC -3 |
EST | Eastern Standard Time | UTC -5 |
EDT | Eastern Daylight Saving Time | UTC -4 |
ET | Eastern Time | Either as EST or EDT, depending on place and time of year |
CST | Central Standard Time | UTC -6 |
CDT | Central Daylight Saving Time | UTC -5 |
CT | Central Time | Either as CST or CDT, depending on place and time of year |
MST | Mountain Standard Time | UTC -7 |
MDT | Mountain Daylight Saving Time | UTC -6 |
MT | Mountain Time | Either as MST or MDT, depending on place and time of year |
PST | Pacific Standard Time | UTC -8 |
PDT | Pacific Daylight Saving Time | UTC -7 |
PT | Pacific Time | Either as PST or PDT, depending on place and time of year |
HST | Hawaiian Standard Time | UTC -10 |
AKST | Alaska Standard Time | UTC -9 |
AKDT | Alaska Standard Daylight Saving Time | UTC -8 |
Australia: | ||
AWST | Western Standard Time | UTC +8 |
ACST | Central Standard Time | UTC +9.5 |
AEST | Eastern Standard/Summer Time | UTC +10 |
6.1.2.2. NTP
NTP is the Network Time Protocol defined in RFC 1305, Network Time Protocol (Version 3) Specification, Implementation and Analysis and RFC 5905, Network Time Protocol Version 4: Protocol and Algorithms Specification. It allows for the participating network nodes to keep time more accurately and maintain time in a more synchronized fashion among all participating network nodes.
NTP uses stratum levels to define the number of hops from a reference clock. The reference clock is considered to be a Stratum-0 device that is assumed to be accurate with little or no delay. Stratum-0 servers cannot be used in a network. However, they can be directly connected to devices that operate as Stratum-1 servers. A Stratum-1 server is an NTP server with a directly connected device that provides Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), such as a GNSS or atomic clock. The 7705 SAR typically acts as a Stratum-2 device because a network connection to an NTP server is required.
The higher stratum levels are separated from the Stratum-1 server over a network path; thus a Stratum-2 server receives its time over a network link from a Stratum-1 server. A Stratum-3 server receives its time over a network link from a Stratum-2 server.
The following NTP elements are supported:
- authentication keys — both DES and MD5 authentication are supported as well as multiple keys, to provide increased security support in carrier and other networks
- server addressing — servers may be defined using IPv4 or IPv6 addresses
- broadcast or multicast modes — when operating in these modes, the node will receive or send using either a multicast (default 224.0.1.1) or a broadcast address. Multicast is supported on the CSM Management port. Only IPv4 addressing is supported.
- alert when NTP server is not available — when none of the configured servers are reachable on the node, the system reverts to manual timekeeping and issues a critical alarm. When a server becomes available, a trap is issued indicating that standard operation has resumed.
- NTP and SNTP — if both NTP and SNTP are enabled on the node, then SNTP transitions to an operationally down state. If NTP is removed from the configuration or shut down, then SNTP resumes an operationally up state.
- NTP priority — if a higher-priority time source such as GNSS or PTP is selected on the node, then NTP transitions to an operationally down state. If the higher-priority time source is disqualified or disabled, then NTP resumes an operationally up state.
- gradual clock adjustment — as several applications (such as Service Assurance Agent (SAA)) can use the clock, and if a major (128 ms or more) adjustment must be performed, the adjustment is performed by programmatically stepping the clock. If a minor (less than 128 ms) adjustment must be performed, then the adjustment is performed by either speeding up or slowing down the clock.
- in order to facilitate proper operation once the standby CSM takes over from the active CSM, it is required that the time on the secondary CSM be synchronized with the clock of the active CSM
- in order to avoid the generation of too many events and traps, the NTP module will rate limit the generation of events and traps to three per second. At that point, a single trap will be generated that indicates that event/trap squashing is taking place.
NTP accuracy depends on the accuracy of NTP packet timestamping. By default, NTP packets are timestamped by the CSM where the NTP protocol is executed. However, an enhanced NTP mode is available where the timestamping is performed on the adapter card by the network processor. This reduces variations introduced by packet delay within the router as well as by a busy CPU in the CSM. This enhanced mode is only available for in-band NTP over a network interface. When the enhanced NTP mode is used, NTP authentication is not supported.
6.1.2.3. SNTP Time Synchronization
For synchronizing the system clock with outside time sources, the 7705 SAR includes a Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client. As defined in RFC 2030, SNTP Version 4 is an adaptation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP). SNTP typically provides time accuracy within 100 ms of the time source. SNTP can only receive the time from NTP servers; it cannot be used to provide time services to other systems. SNTP is a compact, client-only version of NTP. SNTP does not authenticate traffic.
SNTP can be configured in both unicast client modes (point-to-point) and broadcast client modes (point-to-multipoint). SNTP should be used only at the extremities of the synchronization subnet. SNTP clients should operate only at the highest stratum (leaves) of the subnet and in configurations where no NTP or SNTP client is dependent on another SNTP client for synchronization. SNTP time servers should operate only at the root (Stratum 1) of the subnet and then only in configurations where no other source of synchronization other than a reliable radio clock is available.
The 7705 SAR SNTP client can be configured for either broadcast or unicast client mode.
6.1.2.4. PTP
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a timing-over-packet protocol defined in the IEEE 1588v2 standard 1588 2008.
PTP provides the capability to synchronize network elements to a Stratum-1 clock or primary reference clock (PRC) traceable source over a network that may or may not be PTP-aware. PTP has several advantages over ACR. It is a standards-based protocol, has lower bandwidth requirements, can transport both frequency and time, and can potentially provide better performance.
For more information about PTP, see IEEE 1588v2 PTP.
6.1.2.5. Time-of-Day Measurement (ToD-1pps)
The 7705 SAR can receive and extract time of day/phase recovery from a 1588 grand master clock or boundary clock and transmit the recovered time of day/phase signal to an external device such as a base station through an external time of day port, where available. Transmission is through the ToD or ToD/PPS Out port with a 1 pulse/s output signal. The port interface communicates the exact time of day by the rising edge of the 1 pulse/s signal.
For more information about ToD-1pps, see PTP Ordinary Slave Clock for Time of Day/Phase Recovery.
6.1.2.6. GNSS
The 7705 SAR supports frequency synchronization via a Layer 1 interface such as synchronous Ethernet, and ToD synchronization via a protocol such as NTP or PTP. In cases where these methods are not possible, or where accuracy cannot be ensured for the service, you can deploy a GNSS receiver as a synchronous timing source. GNSS data is used to provide network-independent frequency and ToD synchronization.
GNSS receivers on the following platforms support GPS reference only, or combined GPS and GLONASS reference:
- 7705 SAR-Ax
- 7705 SAR-H with a GPS Receiver module
- 7705 SAR-Wx variants with a GPS RF port
- 7705 SAR-8 (CSMv2 only) with a GNSS Receiver card
- 7705 SAR-18 with a GNSS Receiver card
A 7705 SAR chassis equipped with a GNSS receiver and an attached GNSS antenna can be configured to receive frequency traceable to Stratum-1 (PRC/PRS). The GNSS receiver provides a synchronization clock to the SSU in the router with the corresponding QL for SSM. This frequency can then be distributed to the rest of the router from the SSU as configured with the ref-order and ql-selection commands. The GNSS reference is qualified only if the GNSS receiver is operational, has five or more satellites locked, and has a frequency successfully recovered. A PTP master/boundary clock can also use this frequency reference with PTP peers.
In the event of GNSS signal loss or jamming resulting in the unavailability of timing information, the GNSS receiver automatically prevents output of clock or synchronization data to the system, and the system can revert to alternate timing sources.
6.1.2.7. CRON
The CRON feature supports the Service Assurance Agent (SAA) functions. CRON functionality includes the ability to specify the commands that need to be run, when they will be scheduled, including one-time-only functionality (oneshot), interval and calendar functions, as well as where to store the output of the results. In addition, CRON can specify the relationship between input, output, and schedule. Scheduled reboots, peer turn ups, and service assurance agent tests can be scheduled with CRON, as well as OAM events, such as connectivity checks or troubleshooting runs.
CRON features are saved to the configuration file on both primary and backup control modules. If a control module switchover occurs, CRON events are restored when the new configuration is loaded. If a control module switchover occurs during the execution of a CRON script, the failover behavior will be determined by the contents of the script.
CRON features run serially with at least 255 separate schedules and scripts. Each instance can support a schedule where the event is executed any number of times.
The following CRON elements are supported:
- action — parameters for a script including the maximum amount of time to keep the results from a script run, the maximum amount of time a script may run, the maximum number of script runs to store, and the location to store the results.
- schedule — the schedule function configures the type of schedule to run, including one-time-only (oneshot), periodic, or calendar-based runs. All runs are determined by month, day of month or weekday, hour, minute, and interval (seconds).
- script — the script command opens a new nodal context that contains information on a script
6.2. High Availability
This section discusses the high availability routing options and features available to service providers that help diminish vulnerability at the network or service provider edge and alleviate the effect of a lengthy outage on IP/MPLS networks.
High availability is an important feature in service provider routing and switching systems. High availability is gaining momentum due to the unprecedented growth of IP/MPLS services and applications in service provider networks driven by the demand from the enterprise and residential communities. Downtime can be very costly, and, in addition to lost revenue, customer information and business-critical communications can be lost. High availability is the combination of continuous uptime over long periods (Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)) and the speed at which failover or recovery occurs (Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)).
The popularity of high availability routing is evident at the network or service provider edge where thousands of connections are hosted and rerouting options around a failed piece of equipment can often be limiting. Or, a single access link exists to a customer because of additional costs for redundant links. As service providers converge business-critical services such as real-time voice (VoIP), video, and VPN applications over their IP/MPLS networks, high availability becomes much more stringent compared to the requirements for best-effort data.
Network and service availability become critical aspects when offering advanced IP/MPLS services, which dictate that IP routers that are used to construct the foundations of these networks be resilient to component and software outages.
For high availability configuration information, see CSM Synchronization and Redundancy.
6.2.1. High Availability Features
As more and more critical commercial applications move onto the IP/MPLS networks, providing high availability services becomes increasingly important. This section describes high availability features for the 7705 SAR. Most of these features only apply to routers with two Control and Switching Modules (CSMs).
6.2.1.1. Redundancy
The following redundancy features enable the duplication of data elements and software functionality to maintain service continuation in case of outages or component failure.
6.2.1.1.1. Software Redundancy
Software outages are challenging even when baseline hardware redundancy is in place. There should be a balance to provide high availability routing; otherwise, router problems typically propagate throughout the service provider network and externally to other connected networks possibly belonging to other service providers. This could affect customers on a broad scale. There are several software availability features that contribute to the percentage of time that a router is available to process and forward traffic.
6.2.1.1.2. Configuration Redundancy
Features configured on the active CSM are saved on the standby CSM as well. When the active CSM fails, these features are brought up on the standby CSM that takes over the mastership.
Even with modern modular and stable software, the failure of hardware or software can cause the router to reboot or cause other service impacting events. In the best circumstances, failure leads to the initialization of a redundant route processor, which hosts the standby software configuration to become the active processor.
The 7705 SAR supports hot standby. With hot standby, the router image, configuration, and network state are already loaded on the standby; it receives continual updates from the active route processor and the swap over is immediate. Newer-generation service routers like the 7705 SAR have extra processing built into the system so that router performance is not affected by frequent synchronization, which consumes system resources.
6.2.1.1.3. Component Redundancy
7705 SAR component redundancy is critical to reducing MTTR for the routing system. Component redundancy consists of the following features:
- dual Control and Switching modules — for a highly available architecture, redundant Control and Switching Modules (CSMs) are essential
- redundant power supply feed — a power feed can be removed without impact on traffic
- redundant fan — if one fan fails, the others will continue to operate and provide cooling to the system without impacting traffic
- hot swap — components in a live system can be replaced or become active without taking the system down or affecting traffic flow to or from other modules
6.2.1.1.4. Accounting Configuration Redundancy
When there is a switchover and the standby CSM becomes active, the accounting servers will be checked, and if they are administratively up and capable of coming online (media present and so on), then the standby will be brought online and new accounting files will be created at that point. Users must manually copy the accounting records from the failed CSM.
6.2.1.1.5. Multi-Chassis LAG Redundancy
Multi-chassis LAG (MC-LAG) prevents service interruptions that are caused by 7705 SAR nodes that are taken out of service for maintenance, upgrades, or relocation. MC-LAG also provides redundancy for incidents of peer nodal failure. This improves network resiliency. When typically used at access or aggregation sites, MC-LAG ensures high availability without service disruptions by providing redundant access or aggregation nodes.
MC-LAG extends the link level redundancy provided by LAG to include protection against failure of a 7705 SAR node. With MC-LAG, a CE device can be connected to two redundant-pair peer nodes. The redundant-pair peer nodes act like a single node, using active/standby signaling to ensure that only one peer node is used at a time. The redundant-pair peer nodes appear to be a single system as they share the same MAC address and system priority when implementing MC-LAG. Availability and status information are exchanged through an MC-LAG Control Protocol (MCCP). It is used to ensure that one peer is active and to synchronize information between the peers.
| Note: The 7705 SAR nodes must be of the same type, except for the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18, which can be used together in a redundant-pair configuration. |
A peer is configured by specifying its IP address, to which the MCCP packets are sent. The LAG ID, system priority, and MAC address for the MC-LAG are also configured under the peer. Up to 16 MC-LAGs can be configured and they can either use the same peer or different peers up to a maximum of 4 peers.
It is possible to specify the remote LAG ID in the MC-LAG lag command to allow the local and remote LAG IDs to be different on the peers. If there are two existing nodes which already have LAG IDs that do not match, and an MC-LAG is to be created using these nodes, then the remote LAG ID must be specified so that the matching MC-LAG group can be found. If no matching MC-LAG group can be found between neighbor systems, the individual LAGs will operate as usual and no MC-LAG operation is established.
Two timer options, keep-alive-interval and hold-on-neighbor-failure, are available in the MC-LAG configuration. The keep-alive-interval option specifies the frequency of the messages expected to be received from the remote peer and is used to determine if the remote peer is still active. If hold-on-neighbor-failure messages are missed, then it is assumed that the remote peer is down.
Figure 10 shows an example of MC-LAG deployed at access and aggregation sites.
Figure 10: MC-LAG at Access and Aggregation Sites
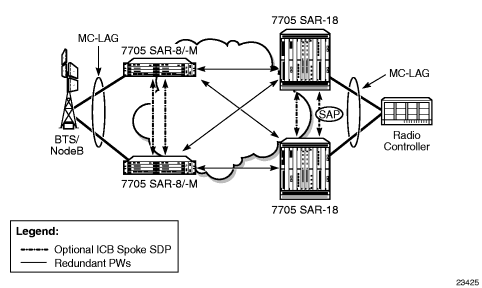
ICB (Inter-Chassis Backup) spoke SDPs are supported for use with Epipe services in an MC-LAG configuration. ICB spoke SDPs provide resiliency by reducing packet loss when an active endpoint is switched from a failed node of an MC-LAG group to a standby node. For example, if a port on an active MC-LAG node fails, the port on one of the peers becomes active, but traffic continues to route to the previously active MC-LAG node until it detects the failure. ICB spoke SDPs ensure that in-flight packets are delivered to the newly active MC-LAG node. Two ICB spoke SDPs must be created. The ICB associated with the MC-LAG on the first node must be associated with the pseudowire on the second node. Likewise, the ICB associated with the MC-LAG on the second node must be associated with the pseudowire on the first node.
| Note: A 7705 SAR node in an MC-LAG configuration that has an ICB spoke SDP configured on it with the MC-LAG in standby mode does not terminate Ethernet CFM frames. It transparently switches the frames to the other node of the MC-LAG group. This mode of operation is consistent with the 7705 SAR operating in S-PE mode. |
Enabling the LAG slave-to-partner parameter ensures synchronized activity switching between the multi-chassis and the single-chassis endpoints. When multi-chassis endpoints are configured in slave-to-partner mode, multi-chassis endpoints always follow the single-chassis activity. The link that is promoted as active via the single-chassis endpoint is used as the active link. Enabling slave-to-partner ensures that out-of-sync scenarios do not occur for the LAG. A multi-chassis pair with pseudowire redundancy and ICBs is always able to direct traffic to the active endpoint, so enabling slave-to-partner does not impose any risk on the network side.
MC-LAG includes support for hash–based peer authentication, configurable heartbeat timers between peers, heartbeat multiplier, LAG bound to MC-LAG with LACP and support for any valid IP link between peers for the multi-chassis Control Protocol (MCCP). MC-LAG supports a configurable fault propagation delay and also provides an option to shut down a MEP on a standby endpoint.
MC-LAG maintains state across a CSM switchover event. The switchover event is transparent to peer MC-LAG nodes where sessions and state are preserved. MC-LAG is supported on the following platforms, adapter cards, and modules:
- 7705 SAR-8/7705 SAR-18: 8-port Ethernet Adapter card, version 2
- 7705 SAR-8 Shelf V2 with CSMv2 only/7705 SAR-18: 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
- 7705 SAR-8/7705 SAR-18: 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card
- 7705 SAR-18: 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card
- 7705 SAR-8/7705 SAR-18: Packet Microwave Adapter card
- 6-port SAR-M Ethernet module
- 7705 SAR-M: all platform variants (the port must be in access mode and autonegotiation must be off or limited)
- 7705 SAR-X
6.2.1.2. Nonstop Routing (NSR)
With NSR on the 7705 SAR, routing neighbors are unaware of a routing process fault. If a fault occurs, a reliable and deterministic activity switch to the inactive control complex occurs such that routing topology and reachability are not affected, even in the presence of routing updates. NSR achieves high availability through parallelization by maintaining up-to-date routing state information, at all times, on the standby route processor. This capability is achieved independently of protocols or protocol extensions, providing a more robust solution than graceful restart protocols between network routers.
The NSR implementation on the 7705 SAR applies to all supported routing protocols. NSR makes it possible to keep the existing sessions (such as LDP) during a CSM switchover, including support for MPLS signaling protocols. Peers will not see any change.
Traditionally, high availability issues have been patched through non-stop forwarding solutions. NSR overcomes these limitations by delivering an intelligent hitless failover solution.
The following NSR entities remain intact after a switchover:
- ATM/IMA VPs/VCs
- LDP
- PPP and MLPPP sessions
- RIP neighbors
6.2.1.3. In-service Upgrade
In-service upgrades allow new routing engine software and microcode to be installed on the 7705 SAR while existing services continue to operate. Software upgrades can be performed only for certain maintenance releases (generally R4 loads and higher). Software upgrades also require NSR. If software or microcode on the CSM needs to be upgraded, CSM redundancy is required.
| Note: The in-service upgrade requires the adapter cards to be reset. This will cause a short outage. |
Follow the steps below to upgrade routing engine software on the 7705 SAR without affecting existing services:
- Install new software on the standby CSM.
- Reboot the standby CSM for the new software to take effect.
- Perform a manual switchover on the active CSM by using the force-switchover command on the CLI. The standby CSM becomes the active CSM, placing the formerly active CSM into standby.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 to upgrade the standby CSM.
6.2.1.4. CSM Switchover
During a switchover, system control and routing protocol execution are transferred from the active to the standby CSM. A switchover may occur automatically or manually.
An automatic switchover may occur under the following conditions:
- a fault condition arises that causes the active CSM to crash or reboot
- the active CSM is declared down (not responding)
- online removal of the active CSM
Users can manually force the switchover from the active CSM to the standby CSM by using the admin redundancy force-switchover now CLI command or the admin reboot active [now] CLI command.
With the 7705 SAR, the admin reboot active [now] CLI command does not cause both CSMs to reboot.
6.2.1.5. Synchronization
Synchronization between the CSMs includes the following:
6.2.1.5.1. Configuration and boot-env Synchronization
Configuration and boot-env synchronization are supported in admin>redundancy> synchronize and config>redundancy>synchronize contexts.
6.2.1.5.2. State Database Synchronization
If a new standby CSM is inserted into the system, it synchronizes with the active CSM upon a successful boot process.
If the standby CSM is rebooted, it synchronizes with the active CSM upon a successful boot process.
When configuration or state changes occur, an incremental synchronization is conducted from the active CSM to the standby CSM.
If the synchronization fails, the standby CSM does not reboot automatically. The show redundancy synchronization command displays synchronization output information.
If the active and standby CSMs are not synchronized for some reason, users can manually synchronize the standby CSM by rebooting the standby by issuing the admin reboot standby command.
6.3. CSM Synchronization and Redundancy
The 7705 SAR uses a 1:1 redundancy scheme. Redundancy methods facilitate system synchronization between the active and standby CSMs so that they maintain identical operational parameters to prevent inconsistencies in the event of a CSM failure.
When automatic system synchronization is enabled for an entity, any save or delete file operations configured on the primary, secondary, or tertiary choices on the active CSM file system are mirrored in the standby CSM file system.
Although software configurations and images can be copied or downloaded from remote locations, synchronization can only occur locally between compact flash drives (cf3-A: and cf3-B:).
Synchronization can occur:
- automatically — automatic synchronization is disabled by default. To enable automatic synchronization, the config>redundancy>synchronize command must be specified with either the boot-env parameter or the config parameter.When the boot-env parameter is specified, the BOF, boot.ldr, config, and image files are automatically synchronized. When the config parameter is specified, only the config files are automatically synchronized.Automatic synchronization also occurs whenever the BOF is modified with persistence on and when an admin>save command is entered with no filename specified.
- manually — to execute synchronization manually, the admin>redundancy> synchronize command must be entered with the boot-env parameter or the config parameter.When the boot-env parameter is specified, the BOF, boot.ldr, config, and image files are synchronized. When the config parameter is specified, only the config files are synchronized.
The following shows the output displayed during a manual synchronization of configuration files.
6.3.1. Active and Standby Designations
Typically, the first CSM installed in a 7705 SAR chassis assumes the role as active, regardless of being inserted in Slot A or B. The next CSM installed in the same chassis then assumes the role as the standby CSM. If two CSMs are inserted simultaneously (or almost simultaneously) and are booting at the same time, preference is given to the CSM installed in Slot A.
If only one CSM is installed in a 7705 SAR, then it becomes the active CSM regardless of the slot it is installed in.
To visually determine the active and standby designations, the MS/CTL LED on the faceplate is lit green (steady) to indicate the active designation. The MS/CTL LED on the second CSM faceplate is flashing green to indicate the standby designation.
| Note: In the CLI, the CSMv2 is shown as csmv2-10g. The CSMv2 supports bandwidth of 10 Gb/s, 2.5 Gb/s and 1 Gb/s in the first two adapter card slots and 2.5 Gb/s and 1 Gb/s in the remaining four adapter card slots. Support for 2.5 Gb/s and 10 Gb/s adapter cards by the CSMv2 is only available on the 7705 SAR-8 Shelf V2. |
The following output shows that the CSMv2 installed in Slot A is acting as the active CSM and the CSMv2 installed in Slot B is acting as the standby.
6.3.2. When the Active CSM Goes Offline
When an active CSM goes offline (due to reboot, removal, or failure), the standby CSM takes control without rebooting or initializing itself. It is assumed that the CSMs are synchronized; therefore, there is no delay in operability. When the CSM that went offline boots and then comes back online, it becomes the standby CSM.
6.3.3. Persistence
The persistence feature allows lease information on DHCP servers to be kept across reboots. This information can include data such as the IP address, MAC binding information, and lease length information.
The system performs the following tasks to make data persistent. In systems with only one CSM, only task 1 applies. In systems with dual CSMs, both tasks apply.
- When a DHCP ACK is received from a DHCP server, the entry information is written to the active CSM compact flash. If persistence fails completely (bad cflash), a trap is generated indicating that persistence can no longer be guaranteed.
- DHCP message information is sent to the standby CSM, and the DHCP information is also written to the compact flash. If persistence fails on the standby CSM also, a trap is generated.
6.3.4. Administrative Tasks
This section contains information to perform administrative tasks:
6.3.4.1. Saving Configurations
Whenever configuration changes are made, the modified configuration must be saved so that it will not be lost when the system is rebooted.
Configuration files are saved by executing explicit command syntax that includes the file URL location to save the configuration file as well as options to save both default and non-default configuration parameters. Boot option file (BOF) parameters specify where the system should search for configuration and image files as well as other operational parameters during system initialization.
For more information about boot option files, see the chapter on Boot Options in this guide.
6.3.4.2. Specifying Post-Boot Configuration Files
Two post-boot configuration extension files are supported and are triggered when either a successful or failed boot configuration file is processed. The boot-bad-exec and boot-good-exec commands specify URLs for the CLI scripts to be run following the completion of the boot-up configuration. A URL must be specified or no action is taken.
For example, after a configuration file is successfully loaded, the specified URL can contain a nearly identical configuration file with certain commands enabled or disabled, or particular parameters specified and according to the script which loads that file.
6.3.5. Automatic Synchronization
Use the CLI syntax displayed below to configure synchronization components relating to active-to-standby CSM switchover. In redundant systems, synchronization ensures that the active and standby CSMs have identical operational parameters, including the active configuration, CSM, and IOM images in the event of a failure or reset of the active CSM.
The force-switchover command forces a switchover to the standby CSM card.
To enable automatic synchronization, either the boot-env parameter or the config parameter must be specified. The synchronization occurs when the admin save or bof save commands are executed.
When the boot-env parameter of the synchronize command is specified, the BOF, boot.ldr, config, and image files are automatically synchronized. When the config parameter is specified, only the configuration files are automatically synchronized.
Synchronization also occurs whenever the BOF is modified with persistence on and when an admin>save command is entered with no filename specified.
6.3.5.1. Boot-Env Option
The boot-env option enables a synchronization of all the files used in system initialization.
When configuring the system to perform this synchronization, the following occurs:
- The BOF used during system initialization is copied to the same compact flash on the standby CSM (in redundant systems).Note: The synchronization parameters on the standby CSM are preserved.
- The primary, secondary, and tertiary images (provided they are locally stored on the active CSM) are copied to the same compact flash on the standby CSM.
- The primary, secondary, and tertiary configuration files (provided they are locally stored on the active CSM) are copied to the same compact flash on the standby CSM.
6.3.5.2. Config Option
The config option synchronizes configuration files by copying the files specified in the active CSM BOF file to the same compact flash on the standby CSM.
6.3.6. Manual Synchronization
The admin redundancy synchronize command performs manual CSM synchronizations. The boot-env parameter synchronizes the BOF, image, and configuration files in redundant systems. The config parameter synchronizes only the configuration files in redundant systems.
6.3.6.1. Forcing a Switchover
The force-switchover now command forces an immediate switchover to the standby CSM card.
If the active and standby CSMs are not synchronized for some reason, users can manually synchronize the standby CSM by rebooting the standby by issuing the admin reboot standby command on the active CSM.
6.4. Node Timing
The 7705 SAR supports a centralized synchronization system with an SSU in each CSM. The SSU can be synchronized to a traceable primary reference clock through an external timing port, line interface, or timing-over-packet technology. The transmit clock of each T1/E1, DS3/E3, SONET/SDH port or synchronous Ethernet-capable port (referred to as a synchronous Ethernet port in this guide) can then be configured to use the node clock or alternatives.
The 7705 SAR supports three timing references — one external and two internal. The timing references can be configured as an ordered list of highest to lowest priority. The system uses an available valid timing reference with the highest priority. If a failure on the current timing reference occurs, the next highest timing reference takes over. The reference switching can be configured to operate in a revertive or non-revertive manner with the sync-if-timing revert command. Revertive switching always selects the highest-priority valid timing reference as the current source. If a reference with a higher priority becomes valid, the system automatically switches to that timing reference. Non-revertive switching means that the active timing reference remains selected while it is valid, even if a higher-priority timing reference becomes available. If the current timing reference becomes invalid, then a switch to the highest-priority available timing reference is initiated. If all the timing references fail or have not been configured, the SSU enters holdover mode of its Stratum 3 oscillator (if it was previously synchronized) or free-run mode.
The external timing reference input with a 2.048 MHz G.703 signal, 5 or 10 MHz sine wave, is available directly on the following:
- 7705 SAR-M (all variants)
- 7705 SAR-H
- 7705 SAR-Hc
- 7705 SAR-A (all variants)
- 7705 SAR-Ax
- 7705 SAR-X
The 7705 SAR-8 CSMv2 does not support a 5 MHz signal. On the 7705 SAR-18, the external timing reference input with a 2.048 MHz G.703, T1 (100 Ω), or E1 (120 Ω), is supported by the BITS ports 1 and 2 located on the Alarm module.
The two internal timing references originate from timing extracted from interface ports. This timing can be recovered directly from physical layer framing on a T1/E1 port, from adaptive timing recovery for TDM pseudowires, or from a synchronous Ethernet port.
On the 7705 SAR-M (all variants), all RJ-45 Ethernet ports and SFP ports support synchronous Ethernet and can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization. On the 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports), two T1/E1 ports can supply a timing reference. When installed on 7705 SAR-M variants with module slots, the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module or 6-port SAR-M Ethernet module can supply two timing references.
On the 7705 SAR-H and 7705 SAR-Hc, all RJ-45 Ethernet ports and SFP ports support synchronous Ethernet and can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization. When the 4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module is installed in the 7705 SAR-H, a single T1/E1 port on the module can supply a timing reference; it can be independently configured for loop-timing or node-timing. When the GPS Receiver module is installed in the 7705 SAR-H, the GPS RF port can be used as a source of node synchronization. All ports on the 4-port SAR-H Fast Ethernet module support synchronous Ethernet and can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization.
On the 7705 SAR-A (both variants), all synchronous Ethernet ports can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization. Synchronous Ethernet is supported on the XOR ports (1 to 4), configured as either RJ-45 ports or SFP ports. Synchronous Ethernet is also supported on SFP ports 5 to 8. Ports 9 to 12 do not support synchronous Ethernet (except when 10/100/1000BaseT copper SFP is used) and, therefore, cannot be used as a timing reference. On the 7705 SAR-A variant with T1/E1 ports, two T1/E1 ports can also supply a timing reference.
On the 7705 SAR-Ax, all Ethernet ports support synchronous Ethernet and IEEE 1588v2 PTP and can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization. The 7705 SAR-Ax can also derive its timing from a GPS antenna signal using the GNSS RF port.
On the 7705 SAR-W and 7705 SAR-Wx, all RJ-45 Ethernet ports and SFP ports support synchronous Ethernet and IEEE 1588v2 PTP, and can supply a timing reference to be used as a source of node synchronization. For 7705 SAR-Wx variants with a GPS RF port, the GPS RF port can be used as a source of node synchronization.
On the 7705 SAR-X, all Ethernet ports support synchronous Ethernet and IEEE 1588v2 PTP. Ethernet ports and T1/E1 ports can supply two timing references to be used as a source of node synchronization. In addition, each T1/E1 port can be independently configured for loop timing.
All DSL modules support Network Timing Reference (NTR). NTR is enabled automatically with no user-configurable commands. The GPON port on the GPON module also supports physical layer clock recovery via the downstream synchronous GPON physical layer. Both NTR and GPON physical layer timing can be used as a source of node synchronization.
The 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18 can receive one or two timing references depending on the port and card type supplying the reference. The 7705 SAR-8 supports two timing references only if a CSMv2 is installed. On the 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18, a timing reference can come from:
- a single SONET/SDH port on the 4-port OC3/STM1 Clear Channel Adapter card
- a single synchronous Ethernet port on the 8-port Ethernet Adapter card, version 2
- a single T1/E1 port on the 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, version 1 (not supported on the 7705 SAR-18)
- two DS3/E3 ports on the 4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card
- two SONET/SDH ports on the 2-port OC3/STM1 Channelized Adapter card or 4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card
- two synchronous Ethernet ports on:
- the 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
- the 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card
- the 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card (not supported on the 7705 SAR-8)
- the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter card
- two T1/E1 ports on the 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, version 2, or the 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card. References must be from different framers; the framers each have eight ports and are grouped as ports 1 to 8, 9 to 16, 17 to 24, and 25 to 32.
- two ports on the Packet Microwave Adapter card: on port 1 or 2, it could be a synchronous Ethernet or PCR-enabled port; on port 3 or 4, it could be a synchronous Ethernet (optical SFP only) or PCR-enabled port (copper-based SFP only); on ports 5 through 8, it could be a synchronous Ethernet (optical SFP only) port.
- the GNSS RF port on the GNSS Receiver card
The 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18 can also use IEEE 1588v2 PTP as a source of node synchronization.
Each T1/E1 port can be independently configured for loop-timing (recovered from an Rx line) or node-timing (recovered from the SSU in the active CSM).
In addition, T1/E1 CES circuits on the following can be independently configured for adaptive timing (clocking is derived from incoming TDM pseudowire packets):
- 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card (version 1 is not supported on the 7705 SAR-18)
- 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card
- 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports)
- 7705 SAR-A (variant with T1/E1 ports)
- T1/E1 ports on the 4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module
T1/E1 CES circuits on the following can be independently configured for differential timing (recovered from RTP in TDM pseudowire packets):
- 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, version 2
- 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card
- 4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card (DS1/E1 channels)
- 4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card (DS1/E1 channels on DS3 ports; E3 ports cannot be channelized); DCR on DS1/E1 channels is supported only on the first three ports of the card
- 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports)
- 7705 SAR-A (variant with T1/E1 ports)
- T1/E1 ports on the 4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module
Adaptive timing and differential timing are not supported on DS1 or E1 channels that have CAS signaling enabled.
A T1/E1 port can be configured to be a timing source for the node.
Each SONET/SDH port and each T1/E1 CES circuit on a 2-port OC3/STM1 Channelized Adapter card can be independently configured to be loop-timed or node-timed; each DS3 circuit can be independently configured to be loop-timed or free-run. A SONET/SDH port can be configured to be a timing source for the node.
Each SONET/SDH port on a 4-port OC3/STM1 Clear Channel Adapter card can be independently configured to be loop-timed or node-timed. A SONET/SDH port can be configured to be a timing source for the node.
Each SONET/SDH port on a 4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card can be independently configured to be node-timed; each T1/E1 CES circuit can be independently configured to be node-timed, loop-timed, or differential-timed. A SONET/SDH port can be configured to be a timing source for the node.
Each clear channel DS3/E3 port on a 4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card can be independently configured to be loop-timed, node-timed, or differential-timed. When a DS3 port is channelized, each DS1 or E1 channel can be independently configured to be loop-timed, node-timed, or differential-timed (differential timing on DS1/E1 channels is supported only on the first three ports of the card). When not configured for differential timing, a DS3/E3 port can be configured to be a timing source for the node.
6.4.1. External Timing Mode
The external input and output timing ports are located on the CSM on the 7705 SAR-8 and directly on the 7705 SAR-H and 7705 SAR-M (all variants). The 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, and 7705 SAR-X have an external timing input port only, located on their faceplates. The external input timing port allows the SSU to be synchronized to an external timing reference. The external output timing port provides a synchronization output signal from the 7705 SAR to an external device. These external timing references typically would come from a GNSS, Building Integrated Timing System (BITS), or the external output timing ports from other telecom equipment.
The timing ports can be configured for the following:
- 2.048 MHz G.703 section 13 signal
- 5 MHz sine wave (not available on 7705 SAR-8 CSMv2)
- 10 MHz sine wave
On the 7705 SAR-18, the BITS ports 1 and 2 can be configured for the following:
- 2.048 MHz G.703 section 13 signal
- T1 (ESF or SF)
- E1 (PCM30CRC or PCM31CRC)
When redundant CSMs are used on the 7705 SAR-8, the external synchronization inputs in each CSM must come from the same synchronization source; that is, you cannot select each input of the two CSMs as two of the three timing references. A Y-cable can be used to connect to a single reference connector. The synchronization output on each CSM is clocked by its own SSU clock.
On the 7705 SAR-18, either BITS port 1 or port 2 is available as an input and output source. When both inputs are connected and available, then the quality level (QL) from Synchronization Status Messaging (SSM) is used to determine which port is used by the CSMs as the BITS input. If SSM is not available, then BITS port 1 is the preferred input. BITS port 2 is used if BITS port 1 is not available. In this case, the operation is non-revertive. The BITS output ports 1 and 2 are clocked by the active CSM’s SSU clock.
The BITS output source command can be used to configure the BITS output ports’ source path on the 7705 SAR-18 to be either:
- the filtered clock from the Synchronous Equipment Timing Generator (SETG)
- the alternate unfiltered path from the BITS output port via Selector A and C, as per ITU-T G.8262
Figure 11 shows an example of a timing source path. The BITS port is configured to deliver an input reference directly to a dedicated timing device such as a BITS or standalone synchronization equipment (SASE) device in a customer facility. The external BITS clock can have multiple references and can provide a common high-quality clock to all network elements at the customer location, including the 7705 SAR-18 node.
Figure 11: BITS Timing Source Path
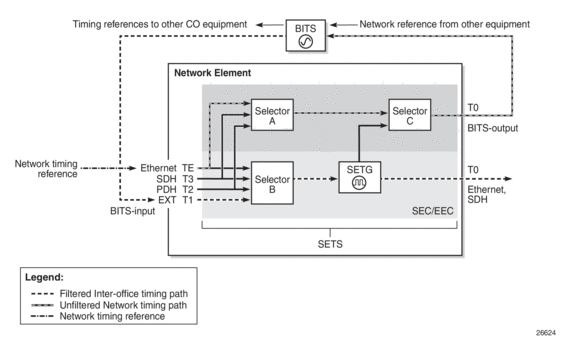
When configuring the priority order of the timing references with the ref-order command for unfiltered BITS output (T4), all reference sources are valid options, except the BITS input, which is excluded to avoid a timing loop. Because the same priority order is used for the SETG output (T0), the BITS input option must be set as the first (highest-priority) reference option.
Because both input and output clock pins are inside the physical RJ-45 port for each BITS port, a custom cable is required to connect input and output ports to different equipment. Refer to the 7705 SAR-18 Chassis Installation Guide, BITS Ports and Pinouts.
6.4.2. Line Timing Mode
Line timing from a synchronous port, such as a T1/E1 port or synchronous Ethernet port, provides the best synchronization performance through a synchronization distribution network. Line timing mode derives an 8 kHz clock from the framing of T1/E1, DS3/E3, and SONET/SDH signaling that can be used as an accurate reference between nodes in a network. Line timing mode is immune to any packet delay variation (PDV) occurring on Layer 2 or Layer 3 links.
On the 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports), line timing is supported on T1/E1 ports. Line timing is also supported on all RJ-45 Ethernet ports and SFP ports on the 7705 SAR-M (all variants).
On the 7705 SAR-X, line timing is supported on T1/E1 ports and Ethernet ports.
In addition, line timing is supported on the following modules when they are installed in chassis variants with module slots:
- GPON module
- 8-port xDSL module (NTR over ADSL2, ADSL2+, or VDSL2)
- 6-port DSL Combination module (two references are available: NTR over SHDSL and NTR over ADSL2, ADSL2+, or VDSL2)
- 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module
- 6-port SAR-M Ethernet module
On the 7705 SAR-H and 7705 SAR-Hc, line timing is supported on all Ethernet ports. Line timing is also supported on the T1/E1 ports of the T1/E1 ASAP and RS-232 Combination module when it is installed in the 7705 SAR-H.
On the 7705 SAR-A variant with T1/E1 ports, line timing is supported on T1/E1 ports. Line timing is also supported on all synchronous Ethernet ports on both 7705 SAR-A variants. Synchronous Ethernet is supported on the XOR ports (1 to 4), configured as either RJ-45 ports or SFP ports. Synchronous Ethernet is also supported on SFP ports 5 to 8. Ports 9 to 12 do not support synchronous Ethernet and, therefore, do not support line timing.
On the 7705 SAR-Ax, line timing is supported on all Ethernet ports.
On the 7705 SAR-W and 7705 SAR-Wx, line timing is supported on all Ethernet RJ-45 ports and SFP ports.
On the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18, line timing is supported on the following adapter cards:
- 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card (version 1 is not supported on the 7705 SAR-18)
- 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card
- 8-port Ethernet Adapter card, version 2, on the two Ethernet SFP ports with SFPs that support synchronous Ethernet
- 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
- 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card (dual-rate and copper SFPs do not support synchronous Ethernet)
- 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter card
- 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card (not supported on the 7705 SAR-8)
- 4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card
- 2-port OC3/STM1 Channelized Adapter card
- 4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card
- 4-port OC3/STM1 Clear Channel Adapter card
- Packet Microwave Adapter card on ports that support synchronous Ethernet and on ports that support PCR
6.4.3. Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR)
Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) is a timing-over-packet technology that transports timing information via periodic packet delivery over a pseudowire. ACR may be used when there is no other Stratum 1 traceable clock available.
ACR is supported on T1/E1 CES circuits on the following:
- 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card (version 1 is not supported on the 7705 SAR-18)
- 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card
- 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports)
- 7705 SAR-A (variant with T1/E1 ports)
- T1/E1 ports of the 4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module when it is installed in the 7705 SAR-H
- T1/E1 ports on the 7705 SAR-X
ACR is not supported on DS1 or E1 channels that have CAS signaling enabled.
ACR is supported for Cpipe services. In addition, ACR is supported on MEF 8 Epipe services. The MEF 8 Epipe may be a TDM SAP to Ethernet SAP or a TDM SAP to spoke SDP. Refer to the 7705 SAR Services Guide, “MEF 8”, for information on MEF 8.
There is no extra equipment cost to implement ACR in a network because this technique uses the packet arrival rate of a TDM pseudowire within the 7705 SAR to regenerate a clock signal. Additionally, the nodes in the network that are traversed between endpoints do not need special ACR capabilities. However, because the TDM pseudowire is transported over Layer 2 links, the packet flow is susceptible to PDV.
To achieve the best ACR performance, follow these recommendations:
- use a packet rate between 1000 pps and 4000 pps. Lower packet rates cause ACR to be more susceptible to PDV in the network.
- limit the number of nodes traversed between the source-end and the ACR-end of the TDM pseudowire
- enable QoS in the network with the TDM pseudowire enabled for ACR classified as NC (network control)
- maintain a constant temperature, as much as possible, because temperature variations will affect the natural frequency on the internal oscillators in the 7705 SAR
- ensure that the network does not contain a timing loop when it is designed
6.4.3.1. ACR States
There are five potential ACR states:
- normal
- phase tracking
- frequency tracking
- holdover
- free-run
When a port’s ACR state is normal, phase tracking, or frequency tracking, the recovered ACR clock is considered to be a qualified reference source for the SSU. If this reference source is being used, then transitions between any of these three states will not affect SSU operation.
When a port’s ACR state is free-run or holdover, the recovered ACR clock is disqualified as a reference source for the SSU. If this reference source is being used, then transitions to either of these two states cause the SSU to drop the reference and switch to the next highest prioritized reference source. This can potentially be SSU holdover.
6.4.3.2. ACR Statistics
The system collects statistics on all ACR-capable ports. ACR statistics detail how the digital phase locked loop (DPLL) is functioning in one or more ACR instances in the adapter card. ACR statistics assist with isolating a problem during degraded synchronization performance or with anticipating future issues.
Within the DPLL, there are two values that contribute to ACR statistics:
- DCO frequency
- input phase error of each 2-second update interval
The DCO is the digitally controlled oscillator that produces the regenerated clock signal. The input phase error is the correction signal that provides feedback to the DPLL in order to tune the DCO output. The input phase error should approach zero as the DPLL locks in to the source timing information and stabilizes the output.
The continuous 2-second updates to the output DCO frequency are directly applied as the clock output of the ACR instance. ACR statistics allow you to view the mean frequency and the standard deviation of the output DCO frequency.
During every 2-second update interval, the input phase error and the output DCO frequency are recorded. The input phase error mean, input phase error standard deviation, output DCO mean (Hz and ppb), and output DCO standard deviation are calculated every 60 seconds.
Entering a show CLI command on a port with ACR displays the mean and standard deviation values for the previous 60-second interval. A show detail command on the same port displays the previous 15 sets of 60-second intervals and a list of state and event counts. An SNMP MIB is also available with these statistics.
6.4.4. Differential Clock Recovery (DCR)
Differential Clock Recovery (DCR) is an alternative method to ACR to maintain the service clock across the packet network for a circuit emulated service. DCR is supported on:
- 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, version 2
- 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card
- 4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card (DS1/E1 channels)
- 4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card (clear channel DS3/E3 ports and DS1/E1 channels on channelized DS3 ports (E3 ports cannot be channelized)); DCR on DS1/E1 channels is supported only on the first three ports of the card
- 7705 SAR-M (variants with T1/E1 ports)
- 7705 SAR-A (variant with T1/E1 ports)
- T1/E1 ports of the 4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module
- T1/E1 ports on the 7705 SAR-X
In addition, DCR is supported between TDM SAPs and Ethernet SAPs and between TDM SAPs and spoke SDPs in a MEF 8 configuration for the above platforms, adapter cards, and modules. Refer to the 7705 SAR Services Guide, “MEF 8”, for information on MEF 8.
DCR is not supported on DS1 or E1 channels that have CAS signaling enabled.
DCR uses channel group 1 for timing recovery. If a T1 or E1 port is channelized, all TDM PWs that share the port use the timing recovered from channel group 1.
To enable DCR, the network must have a common clock between the routers performing the TDM-to-packet interworking function or between the two terminating SAPs or SAP/spoke SDP using MEF 8. The common clock can come from two PRC-traceable clocks or one clock that is made available to both ends, such as the transmitted clock of a SONET/SDH or synchronous Ethernet port.
In each direction, the service clock is compared to the common clock and the difference is encoded into the RTP header in the TDM PW overhead. At the other end of the network, the original service clock is reproduced by comparing the common clock to the frequency difference in the RTP header. Figure 12 shows an example of a network using DCR.
Figure 12: Differential Clock Recovery on a Network
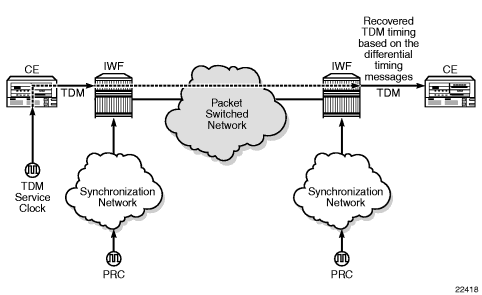
RTP headers are disabled by default and must be enabled for all circuit emulation services that require DCR. RTP must be enabled for the TDM PW that uses channel group 1. All channel groups on the same DS1 or E1 channel must be configured for the same mode of operation.
To achieve the best DCR performance, it is recommended that you use a Layer 1 network synchronization method to ensure the common clock has the best stability. If a timing-over-packet technique is used to transfer the common clock, then the number and type of nodes, the traffic profile, and the temperature variations will affect DCR synchronization performance. As well, a packet rate of at least 200 pps is recommended (up to 4000 pps is supported). Packet rates lower than 200 pps may affect system performance.
6.4.4.1. DCR Frequencies
Each DS1, E1, DS3, or E3 circuit configured with DCR executes its own clock recovery from the packet stream. This allows each circuit to have an independent frequency.
Table 24 lists the supported timestamp frequencies for each platform and adapter card.
Table 24: Supported Timestamp Frequencies for DCR-timed Circuits
Timestamp Frequency (MHz) | ||||
103.68 | 77.76 | 25 | 19.44 | |
16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, version 2 | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ||
32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ||
4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter card | ✓ (default) | |||
4-port DS3/E3 Adapter card | ✓ (default) | |||
7705 SAR-M | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
7705 SAR-A | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
4-port T1/E1 and RS-232 Combination module | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
7705 SAR-X | ✓ (default) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
The timestamp frequency is configured at the adapter card level and is used by all DCR ports or channels on the supporting platforms and cards. Both ends of a TDM pseudowire using DCR must be running the same frequency. If a network contains different types of equipment using DCR, a common frequency must be selected that is supported by all equipment.
DCR complies with published jitter and wander specifications (G.823, G.824, and G.8261) for traffic interfaces under typical network conditions and for synchronous interfaces under specified packet network delay, loss, and delay variance (jitter) conditions.
6.4.5. Proprietary Clock Recovery (PCR)
PCR is a copper synchronous Ethernet-based, timing-over-packet technology. It is supported on the Packet Microwave Adapter card on the two copper RJ-45 synchronous Ethernet 1000Base-T Microwave Awareness (MWA) ports (ports 1 and 2) and on a copper SFP Ethernet port (ports 3 and 4).
There is no CLI configuration requirement for PCR; it is turned on automatically when a microwave link is enabled on an MWA RJ-45 port or on a copper SFP Ethernet port (ports 3 and 4).
| Note: On the MPR-e side, PCR requires that the MAC address of the 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18 be configured on the MPR-e radio that is connected to the 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18 chassis. Refer to the latest version of the MPR-e user manual for the required information. |
PCR provides the same frequency recovery capability as standard-based copper synchronous Ethernet without having to endure a traffic hit whenever a synchronous source switching occurs. See Figure 13.
Figure 13: Proprietary Clock Recovery

By running PCR between the MPR-e radio and the MWA port, frequency synchronization can be delivered in either direction.With standard-based copper synchronous Ethernet, there is a traffic hit every time a clock source change occurs on a 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18 because the 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18 and the MPR-e radio to which it is connected must bring down the Ethernet link MAC layer before it can renegotiate and reverse the master and slave clock role. This MAC layer renegotiation affects the data plane and the signaling and routing plane. All MPLS signaling links and the label switched path (LSP) are taken down during the renegotiation process; the routing signaling advertises the down state of the link throughout the network.
However, with PCR running on the microwave link, the physical layer transmit clock on a copper synchronous Ethernet port on the Packet Microwave Adapter card is always set to master. The reversal of the clock role only occurs at the PCR “layer”. This means that a synchronous source change does not disrupt the data plane and the signaling and routing plane on the 7705 SAR-8 or 7705 SAR-18.
6.4.6. IEEE 1588v2 PTP
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a timing-over-packet protocol defined in the IEEE 1588v2 standard 1588 2008.
PTP may be deployed as an alternative timing-over-packet option to ACR. PTP provides the capability to synchronize network elements to a Stratum-1 clock or primary reference clock (PRC) traceable source over a network that may or may not be PTP-aware. PTP has several advantages over ACR. It is a standards-based protocol, has lower bandwidth requirements, can transport both frequency and time, and can potentially provide better performance.
There are five basic types of PTP devices, as listed below:
- ordinary clock (master or slave)
- boundary clock
- end-to-end transparent clock
- peer-to-peer transparent clock
- management node
Table 25 lists the types of PTP support on each fixed platform; Table 26 lists the types of PTP support on each card for the 7705 SAR-8 and the 7705 SAR-18.
Table 25: IEEE 1588v2 PTP Support per Fixed Platform
Sync Type | PTP Clock Type | 7705 SAR-A (Both Variants) 7705 SAR-Ax 7705 SAR-H 7705 SAR-Hc 7705 SAR-M (All Variants) 7705 SAR-W 7705 SAR-Wx (All Variants) 7705 SAR-X |
Freq | Ordinary Slave | Yes |
Boundary Clock | Yes | |
End-to-End Transparent Clock | Yes | |
Ordinary Master | Yes | |
Time of day/phase | Ordinary Slave | Yes |
Boundary Clock | Yes | |
End-to-End Transparent Clock | Yes | |
Ordinary Master | Yes 1 |
- Only supported on the 7705 SAR-H with a GPS Receiver module and 7705 SAR-Wx variants with a GPS RF port.
Note:
All of the platforms listed in Table 25 support one ordinary slave clock, ordinary master clock, or boundary clock. They also support an additional PTP clock for transparent clock functionality. The 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module supports transparent clock functionality when installed in the 7705 SAR-M (variants with module slot).
Table 26: IEEE 1588v2 PTP Support per Card on the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18
Sync Type | PTP Clock Type | 8-port Ethernet Adapter Card, Version 2 | 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter Card | 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Card | Packet Microwave Adapter Card | 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter Card | 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter Card 1 |
Freq | Ordinary Slave | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Boundary Clock | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
End-to-End Transparent Clock | |||||||
Ordinary Master | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Time of day/phase | Ordinary Slave | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
Boundary Clock | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
End-to-End Transparent Clock | |||||||
Ordinary Master | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 |
- Not supported on the 7705 SAR-8.
- Supported on chassis with an active GNSS Receiver card.
Notes:
The 7705 SAR-8 supports up to six ordinary slave clocks, ordinary master clocks, or boundary clocks. The 7705 SAR-18 supports up to eight ordinary slave clocks, ordinary master clocks, or boundary clocks.
Each of the cards listed in Table 26 support one PTP clock.
A nodal clock is equipped in each CSM on the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18, or directly on the fixed platforms listed in Table 25. Up to two PTP ordinary or boundary clocks can be configured per node as references to the nodal clock.
Each PTP slave clock can be configured to receive timing from up to two PTP master clocks in the network.
IEEE 1588 PTP messaging for slave and master clocks is supported over module ports on the 7705 SAR-M and 7705 SAR-H, on Ethernet ports on the 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, and 7705 SAR-Wx, and on all of the adapter cards listed in Table 26.
When a node loopback address is used as the source interface for 1588 packets, the packets can ingress and egress the module ports. Module ports do not support transparent clock, except for the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module which does.
For all 7705 SAR platforms and clock types, when the node loopback address is used as the source interface for 1588 packets, the packets can ingress and egress over IES interfaces.
IP messaging between the PTP master clock and PTP slave clock over the PTP-enabled IP interface is done using IPv4 unicast mode.
Each PTP instance supports up to 128 synchronization messages per second. The default is 64 synchronization messages per second when the profile is set to the default of ieee1588-2008.
Each master clock has its own configuration for IP address, packet rate, and messaging timeouts, and for statistics, alarms, and events. Each available master clock advertises its presence and information using announce messages. If both master clocks are available, the slave clock uses the Best Master Clock Algorithm (BMCA) to dynamically compare the information in the announce messages of each master clock to determine to which of the two master clocks it should synchronize. This master clock is known as the best master. After the slave clock has determined which is the best master, it may begin to negotiate with it for unicast synchronization communication.
The configured setting for the profile command determines the precedence order for selecting the best master clock algorithm. The 7705 SAR supports the following profile settings: ieee1588-2008, itu-telecom-freq, and g8275dot1-2014. For information about the g8275dot1-2014 profile parameter, see ITU-T G.8275.1.
If the profile setting for the clock is ieee1588-2008, the precedence order for the best master selection algorithm is as follows:
- priority1 (user-configurable on the master clock side)
- clock class
- clock accuracy
- PTP variance (offsetScaledLogVariance)
- priority2 (user-configurable on the master clock side)
- clock identity
- distance (number of boundary clocks)
If the profile setting for the clock is itu-telecom-freq (ITU-T G.8265.1 profile), the precedence order for the best master selection algorithm is as follows:
- clock class
- peer ID
If the profile setting for the clock is g8275dot1-2014, the precedence order for the best master selection algorithm is as follows if the grand master clock is connected to a primary reference time clock (PRTC) in locked mode:
- clock class
- clock accuracy
- PTP variance (offsetScaledLogVariance)
- priority2 (user-configurable on the master clock side)
- localPriority
- steps removed from the grand master
- port identities
- port numbers
If the profile setting for the clock is g8275dot1-2014, the precedence order for the best master selection algorithm is as follows if the grand master clock is in holdover and out of holdover specification, or is without a time reference since startup:
- clock class
- clock accuracy
- PTP variance (offsetScaledLogVariance)
- priority2 (user-configurable on the master clock side)
- localPriority
- clock identity
- steps removed from the grand master
- port identities
- port numbers
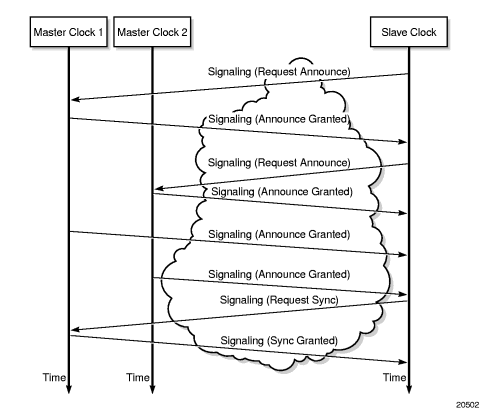
Figure 14 shows an example of the messaging sequence between the PTP slave clock and the two PTP master clocks.
Figure 14: Messaging Sequence Between the PTP Slave Clock and PTP Master Clocks
6.4.6.1. PTP Clock Synchronization
The IEEE 1588v2 standard synchronizes the frequency and time from a master clock to one or more slave clocks over a packet stream. This packet-based synchronization can be over UDP/IP or Ethernet and can be multicast or unicast. For UDP/IP, only IPv4 unicast mode with unicast negotiation is supported.
As part of the basic synchronization timing computation, a number of event messages are defined for synchronization messaging between the PTP slave clock and PTP master clock. A one-step or two-step synchronization operation can be used, with the two-step operation requiring a follow-up message after each synchronization message. Currently, only one-step operation is supported when the 7705 SAR is a master clock; PTP frequency and time can be recovered from both one-step and two-step operation when the 7705 SAR is acting as a slave or boundary clock.
During startup, the PTP slave clock receives the synchronization messages from the PTP master clock before a network delay calculation is made. Prior to any delay calculation, the delay is assumed to be zero. A drift compensation is activated after a number of synchronization message intervals occur. The expected interval between the reception of synchronization messages is user-configurable.
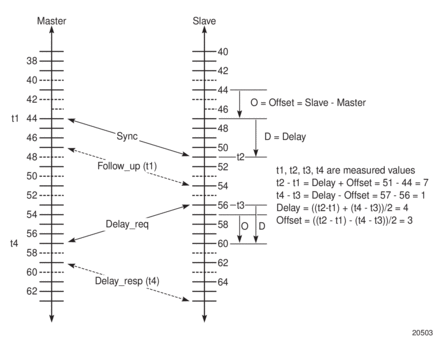
The basic synchronization timing computation between the PTP slave clock and PTP best master is illustrated in Figure 15. This figure illustrates the offset of the slave clock referenced to the best master signal during startup.
Figure 15: PTP Slave Clock and Master Clock Synchronization Timing Computation
6.4.6.2. Performance Considerations
Although IEEE 1588v2 can be used on a network that is not PTP-aware, the use of PTP-aware network elements (boundary clocks) within the packet switched network improves synchronization performance by reducing the impact of PDV between the grand master clock and the slave clock.
Note:
|
The performance objective is to meet the synchronization interface maximum time interval error (MTIE) mask. Similar to ACR, the number of factors with the PSN will contribute to how well PTP can withstand, and still meet, those requirements.
6.4.6.3. PTP Capabilities
PTP messages are supported via IPv4 unicast with a fixed IP header size.
Table 27 describes the supported message rates for slave and master states for IP-encapsulated PTP traffic, based on the profile configured. The ordinary clock can be either in the slave or master state. The boundary clock can be in both of these states.
Table 27: Rates for IP-Encapsulated PTP Messages
ieee1588-2008 | itu-telecom-freq | g8275dot1-2014 | ||
Announce | Minimum rate | 1 per 16 seconds | 1 per 16 seconds | 1 per 16 seconds |
Maximum rate | 8 per second | 8 per second | 8 per second | |
Default rate | 1 per 2 seconds | 1 per 2 seconds | 8 per second | |
Sync and Delay | Minimum rate 1 | 16 per second | 16 per second | 16 per second |
Maximum rate | 128 per second | 128 per second | 128 per second | |
Default rate | 64 per second | 64 per second | 16 per second | |
- In the master clock state, the minimum rate granted is 1 per 16 seconds if requested by the slave clock.
Note:
See Table 29 for the supported message rates for Ethernet-encapsulated PTP traffic.
State and statistics data for each master clock are available to assist in the detection of failures or unusual situations.
The PTP algorithm is able to recover the clock using both the upstream and downstream directions in both ordinary slave and boundary clock modes. The ability to perform bidirectional clock recovery will improve the performance of networks where the upstream and downstream load is not symmetrical.
6.4.6.4. PTP Ordinary Slave Clock For Frequency
The PTP ordinary clock with slave capability on the 7705 SAR provides an option to reference a Stratum-1 traceable clock across a packet switched network. The recovered clock can be referenced by the internal SSU and distributed to all slots and ports.
Figure 16 shows a PTP ordinary slave clock network configuration.
Figure 16: Slave Clock
The PTP slave capability is implemented on the Ethernet ports of the platforms listed in Table 25 and on the cards listed in Table 26.
The 7705 SAR-8 can support up to six slave clocks and the 7705 SAR-18 can support up to eight slave clocks.
All other fixed platforms listed in Table 25 can support up to two PTP clocks when one of those clock types is configured as transparent; otherwise, they support only one slave clock.
Each slave clock can provide a separate frequency reference to the SSU.
Figure 17 shows the operation of an ordinary PTP clock in slave mode.
Figure 17: Ordinary Slave Clock Operation
Each PTP ordinary slave clock is configured for a specific slot where the card (see Table 26) or Ethernet port (see Table 25) will perform the slave function. On the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, and 7705 SAR-Wx, this slot is always 1/1. On the 7705 SAR-X, this slot is always either 1/2 or 1/3. When the 7705 SAR-M is receiving PTP packets on the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module, its PTP clock continues to use slot 1/1. Each slave is also associated with an IP interface on a specific port, adapter card, or loopback address for the router; however, the IP interface configured on a 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module cannot be associated with a slave clock.
For best performance, the network should be designed so that the IP messaging between the master clock and the slave clock will ingress and egress through a port where the slave is configured. If the ingress and egress flow of the PTP messages is via a different port or adapter card on the 7705 SAR, then the packets will be routed through the fabric to the Ethernet card with the PTP slave.
It is possible that the PTP IP packets may be routed through another Ethernet port/VLAN, OC3/STM1 or OC12/STM4 clear channel POS, OC3/STM1 or OC12/STM4 channelized MLPPP, DS3/E3 PPP, or DS1/E1 MLPPP. The PTP slave performance may be slightly worse in this case because of the extra PDV experienced through the fabric. Packets will be routed this way only if the clock is configured with a loopback address. If the clock is configured with an address tied to a physical port, the packets will arrive on that physical port as described above.
6.4.6.5. PTP Ordinary Master Clock For Frequency
The 7705 SAR supports the PTP ordinary clock in master mode. Normally, a 1588v2 grand master is used to support many slaves and boundary clocks in the network. In cases where only a small number of slaves and boundary clocks exist and only frequency is required, a PTP integrated master clock can greatly reduce hardware and management costs to implement PTP across the network. It also provides an opportunity to achieve better performance by placing a master clock deeper into the network, as close to the slave clocks as possible.
Figure 18 shows a PTP master clock network configuration.
Figure 18: PTP Master Clock

The PTP master clock capability is implemented on the Ethernet ports of the platforms listed in Table 25 and on the cards listed in Table 26.
The 7705 SAR-8 can support up to six master clocks and the 7705 SAR-18 can support up to eight master clocks. The fixed platforms listed in Table 25 can each support one master clock.
Figure 19 shows the operation of an ordinary PTP clock in master mode.
Figure 19: Ordinary Master Clock Operation

Each PTP master clock is configured for a specific slot where the card (see Table 26) or Ethernet port (see Table 25) will perform the master function. On the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, and 7705 SAR-Wx, this slot is always 1/1. On the 7705 SAR-X, this slot is always either 1/2 or 1/3. When the 7705 SAR-M is receiving PTP packets on a 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module, its PTP clock continues to use slot 1/1. Each master is also associated with an IP interface on a specific port, adapter card, or loopback address for the router; however, the IP interface configured on a 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module cannot be associated with a master clock. All packets that ingress or egress through a port where the master is configured are routed to their destination via the best route as determined in the route table.
Each master clock can peer with up to 50 slaves or boundary clocks. The IP addresses of these peers can be statically configured via CLI or dynamically accepted via PTP signaling messages. A statically configured peer may displace a dynamic peer on a particular PTP port. If there are fewer than 50 peers, then that dynamic peer can signal back and be granted a different PTP-port instance.
6.4.6.6. PTP Boundary Clock For Frequency
The 7705 SAR supports boundary clock PTP devices in both master and slave states. IEEE 1588v2 can function across a packet network that is not PTP-aware; however, the performance may be unsatisfactory and unpredictable. PDV across the packet network varies with the number of hops, link speeds, usage rates, and the inherent behavior of the routers. By using routers with boundary clock functionality in the path between the grand master clock and the slave clock, one long path over many hops is split into multiple shorter segments, allowing better PDV control and improved slave performance. This allows PTP to function as a valid timing option in more network deployments and allows for better scalability and increased robustness in certain topologies, such as rings.
Boundary clocks can simultaneously function as a PTP slave of an upstream grand master (ordinary clock) or boundary clock, and as a PTP master of downstream slaves (ordinary clock) and/or boundary clocks. Figure 20 shows the operation of a boundary clock.
Figure 20: Boundary Clock
The PTP boundary clock capability is implemented on the Ethernet ports of the platforms listed in Table 25 and on the cards listed in Table 26.
The 7705 SAR-8 can support up to six boundary clocks and the 7705 SAR-18 can support up to eight boundary clocks. The fixed platforms listed in Table 25 can each support one boundary clock.
Each PTP boundary clock is configured for a specific slot where the card (see Table 26) or Ethernet port (see Table 25) will perform the boundary clock function. On the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, and 7705 SAR-Wx, this slot is always 1/1. On the 7705 SAR-X, this slot is always either 1/2 or 1/3. When the 7705 SAR-M is receiving PTP packets on a 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module, its PTP clock continues to use slot 1/1. Each boundary clock is also associated with a loopback address for the router; however, the IP interface configured on a 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module cannot be associated with a boundary clock.
Each boundary clock can be peered with up to 50 slaves, boundary clocks, or grand master clocks. The IP addresses of these peers can be statically configured via CLI or dynamically accepted via PTP signaling messages. A statically configured peer may displace a dynamic peer on a particular PTP port. If there are fewer than 50 peers, then that dynamic peer can signal back and be granted a different PTP-port instance.
Figure 21 shows an example of boundary clock operation.
Figure 21: Boundary Clock Operation
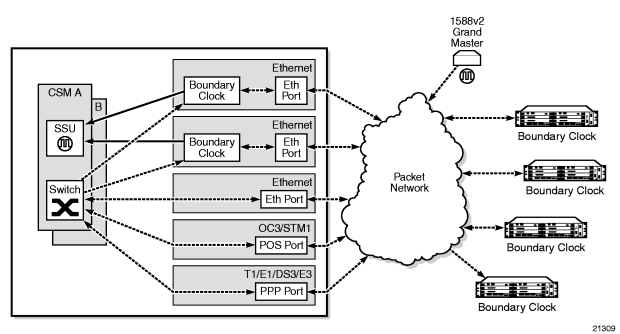
6.4.6.7. PTP Ordinary Slave Clock for Time of Day/Phase Recovery
The following equipment supports PTP slave clock for time of day/phase recovery:
The 7705 SAR can receive and extract time of day/phase recovery from a 1588 grand master clock or boundary clock and transmit the recovered time of day/phase signal to an external device such as a base station through an external time of day port, where available. The PTP slave clock can be used as a reference for the router system time clock, providing high-accuracy OAM timestamping and measurements for the following equipment:
- 7705 SAR-8
- 7705 SAR-18
- 7705 SAR-A
- 7705 SAR-Ax
- 7705 SAR-H
- 7705 SAR-Hc
- 7705 SAR-M
- 7705 SAR-W
- 7705 SAR-Wx
- 7705 SAR-X
On the 7705 SAR-8 CSMv2, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-M, and 7705 SAR-X, transmission is through the ToD port with a 1 pulse/s output signal that is phase-aligned with other routers that are similarly time of day/phase synchronized. An RS-422 serial interface within the ToD port connector communicates the exact time of day of the rising edge of the 1 pulse/s signal. The serial interface on the ToD out port and the ToD in port on the CSMv2 are currently not supported; therefore, the 7705 SAR-8 does not support Time of Day messages.
On the 7705 SAR-H, transmission is through the IRIG-B Out port. An RJ-45 interface is used for the IRIG-B Out port to communicate the exact time of day by the rising edge of the 1 pulse/s signal, an IRIG-B000 unmodulated time code signal, and an IRIG-B12X modulated time code signal.
This Time of Day message output is only available when the router is configured with an active IP PTP slave clock or boundary clock. It is not available when Time of Day is recovered from an Ethernet PTP clock or integrated GNSS.
Table 28 lists the 1 pulse/s signal (1pps) support and Time of Day messaging support per platform.
Table 28: 1pps/ToD Message Support
1pps Out | ToD Messages Out | 1pps In | ToD Messages In | |
7705 SAR-8 with CSMv2 | Yes | No | No | No |
7705 SAR-A | Yes | Yes for IP PTP No for Ethernet PTP | No | No |
7705 SAR-Ax | Yes | Yes for IP PTP No for Ethernet PTP | No | No |
7705 SAR-H | Yes | Yes for IP PTP No for Ethernet PTP | No | No |
7705 SAR-M | Yes | Yes for IP PTP No for Ethernet PTP | No | No |
7705 SAR-X | Yes | Yes for IP PTP No for Ethernet PTP | No | No |
For incoming IEEE 1588 packets, the destination IP address is the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, 7705 SAR-Wx, or 7705 SAR-X loopback address. The ingress interface can be an SFP Ethernet port on the faceplate of the chassis, an RJ-45 port on the faceplate of the chassis, or a port on an installed module.
Each PTP slave clock can be configured to receive timing from up to two PTP master clocks in the network. If both master clocks are available, the slave clock uses default BMCA to determine which of the two master clocks it should synchronize.
PTP messaging between the PTP master clock and PTP slave clock is done over UDP/IP using IPv4 unicast mode with a fixed IP header size. Unicast negotiation is supported. Each PTP instance supports up to 128 synchronization messages per second.
PTP recovered time accuracy depends on the delay of the forward path and the reverse path being symmetrical. It is possible to correct for known path delay asymmetry by using the ptp-asymmetry command for PTP packets destined for the local slave clock or downstream PTP slave clock.
6.4.6.8. PTP Boundary Clock for Time of Day/Phase Recovery
The following equipment supports PTP boundary clock capability for time of day/phase recovery:
The 7705 SAR-8 can support up to six boundary clocks and the 7705 SAR-18 can support up to eight boundary clocks. The fixed platforms can each support one boundary clock. PTP boundary clocks that recover time of day/phase from a grand master clock or another boundary clock can be used as a reference for the router system time clock, providing high-accuracy OAM timestamping and measurements for the following equipment:
- 7705 SAR-8
- 7705 SAR-18
- 7705 SAR-A
- 7705 SAR-Ax
- 7705 SAR-H
- 7705 SAR-Hc
- 7705 SAR-M
- 7705 SAR-W
- 7705 SAR-Wx
- 7705 SAR-X
Each PTP boundary clock for time of day/phase is configured for a specific slot where the adapter card or port will perform the boundary clock function. On fixed platforms, with the exception of the 7705 SAR-X, this slot is always 1/1. On the 7705 SAR-X, this slot is always either 1/2 or 1/3. Each boundary clock is also associated with a loopback or system address for the router.
6.4.6.9. PTP End-to-End Transparent Clock for Time of Day/Phase Recovery
PTP end-to-end transparent clock for time of day/phase recovery is supported on the following:
- the fixed platforms listed in Table 25
- 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module
Transparent clock functionality is supported for PTP packets over UDP/IP over Ethernet (with and without VLAN tags).
For high-accuracy 1588 PTP clock recovery, timestamping of incoming and outgoing messages should be done as close to ingress and egress as possible when the 7705 SAR is acting as a 1588 transparent clock. Edge timestamping is performed on all packets from all Ethernet ports, including SFP and RJ-45 ports on the faceplate of the chassis or a port on an installed module.
PTP recovered time accuracy depends on the delay of the forward path and the reverse path being symmetrical. It is possible to correct for known path delay asymmetry by using the ptp-asymmetry command to configure an asymmetry delay setting in nanoseconds per direction for each edge.
To enable transparent clock processing at the node level, configure a PTP clock with the transparent-e2e clock type (using the clock-type command). Deconfiguring such a PTP clock will disable transparent clock processing.
6.4.6.10. PTP Master Clock for Time of Day/Phase Distribution
PTP master clock capability for time of day/phase distribution is implemented on the following platforms:
- 7705 SAR-Ax
- 7705 SAR-H with a GPS Receiver module
- 7705 SAR-Wx variants with a GPS RF port
- 7705 SAR-8 (CSMv2 only) with a GNSS Receiver card
- 7705 SAR-18 with a GNSS Receiver card
Time of day input must be enabled using the use-node-time command before the node can be used as a PTP grand master clock. GNSS must also be the active system time reference for nodes that are being used as a grand master clock. When the use-node-time command is enabled, the PTP master clock uses the system time as a source of PTP time and can be used for time of day/phase distribution. When the use-node-time command is disabled, the PTP master clock can be used for frequency only.
6.4.6.11. PTP Clock Redundancy
Each PTP slave clock can be configured to receive timing from up to two PTP master clocks. If two PTP master clocks are configured, and if communication to the best master is lost or if the BMCA determines that the other PTP master clock is better, then the PTP slave clock switches to the other PTP master clock.
For a redundant or simple CSM configuration on the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18, a maximum of two PTP slave clocks can be configured as the source of reference (ref1 and ref2) to the SSU. If a failure occurs between the PTP slave clock and the master clock, the SSU detects that ref1 or ref2 is unavailable and automatically switches to the other reference source. This switching provides PTP hot redundancy for hardware failures (on the 8-port Ethernet Adapter card, version 2, 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card, 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card, 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card, or Packet Microwave Adapter card) or port or facility failures (SFP or cut fiber). If a loopback address is used, PTP packets may arrive on any router network interface and the PTP clock will remain up.
The 7705 SAR-M (all variants), 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A (both variants), 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, 7705 SAR-Wx (all variants), and 7705 SAR-X support only one PTP slave clock. This slave clock can be configured as the source of reference (ref1 or ref2) to the SSU.
6.4.6.12. PTP Ethernet Capabilities
The 7705 SAR can be configured to transmit and receive PTP messages over a port that uses Ethernet encapsulation. The encapsulation type can be null, dot1q, or qinq. Ethernet-encapsulated PTP messages are processed on the node CSM or CSM functional block, and they are supported on ordinary slave, ordinary master, or boundary clocks for either frequency or time of day/phase recovery. The 7705 SAR-Ax can also support a grand master clock. The 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Wx, 7705 SAR-8 (CSMv2 only), and 7705 SAR-18 can also support a grand master clock when equipped to support GNSS. A PTP clock using Ethernet encapsulation can support up to 50 external peer clocks.
All platforms and cards that support PTP functionality support Ethernet-encapsulated PTP messages, except for the 8-port Ethernet Adapter card v2, and the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter card/module. See Table 25 and Table 26 for a complete list of supported platforms and cards.
Ethernet encapsulation is configured on a per-port basis using the config>system> ptp>clock command, with the clock-id parameter set to csm. Ports can simultaneously support IPv4-encapsulated PTP messages and Ethernet-encapsulated PTP messages. As well, the 7705 SAR supports the interworking of a PTP slave using IPv4-encapsulated messages with a PTP master using Ethernet-encapsulated messages.
Table 29 describes the supported message rates for slave and master states for Ethernet-encapsulated PTP traffic, based on the profile configured. The ordinary clock can be either in the slave or master state. The boundary clock can be in both of these states.
Table 29: Rates for Ethernet-Encapsulated PTP Messages
ieee1588-2008 | g8275dot1-2014 | ||
Announce | Minimum rate | 1 per 16 seconds | 1 per 16 seconds |
Maximum rate | 8 per second | 8 per second | |
Default rate | 1 per 2 seconds | 8 per second | |
Sync | Minimum rate | 1 per second | 1 per second |
Maximum rate | 64 per second | 64 per second | |
Default rate | 64 per second | 16 per second | |
Delay | Minimum rate | 1 per second | 1 per second |
Maximum rate | 64 per second | 64 per second | |
Default rate | 64 per second | 16 per second | |
See Table 27 for the supported message rates for IP-encapsulated PTP traffic.
PTP messages are transported within Ethernet frames with the Ethertype set to 0X88F7. Ports can be configured with one of two reserved multicast destination addresses:
- 01-1B-19-00-00-00 — used for all PTP messages except for peer delay mechanism messages
- 01-80-C2-00-00-0E — used for peer delay mechanism messages
The ITU-T allows either address to be used depending on customer requirements. Refer to Recommendation ITU-T G.8275.1/Y.1369.1.
When a PTP clock is configured for Ethernet encapsulation, there are two profiles available: ieee1588-2008 or g8275dot1-2014. When the profile configuration is ieee1588-2008, the PTP clock’s priority1 and priority2 settings are used by the BMCA to help determine which clock should provide timing for the network. When the profile configuration is g8275dot1-2014, the local-priority value is used to choose between PTP masters in the BMCA. See ITU-T G.8275.1 for information about the g8275dot1-2014 profile.
6.4.6.13. ITU-T G.8275.1
The 7705 SAR implements Recommendation ITU-T G.8275.1, which specifies the architecture that allows the distribution of time/phase with full timing support from the network. The Recommendation details the profile for using IEEE 1588 to distribute time in an environment where every node is either a grand master, boundary, or ordinary clock. When configured for the G.8275.1 profile, the 7705 SAR can operate as boundary clock, an ordinary master clock, or an ordinary slave clock.
When the 7705 SAR is configured for the G.8275.1 profile, it uses an alternate BMCA for best master clock selection. This BMCA includes a PTP dataset comparison that is defined in IEEE 1588-2008, but with the following differences:
- the priority1 attribute value is removed from the dataset comparison
- the master-only parameter value must be considered
- multiple active grand master clocks are allowed; therefore, the BMCA will select the nearest clock of equal quality
- a port-level local-priority attribute value is used to select a slave port if two ports receive an Announce message. This attribute is used as a tie-breaker in the dataset comparison algorithm if all other previous attributes of the datasets being compared are equal.
- the local-priority parameter value is considered for the default dataset
| Note: The local-priority parameter is only supported for Ethernet-encapsulated ports; it is not supported for IP-encapsulated ports. |
The ITU-T G.8275.1 profile has the following characteristics.
- The default domain setting is 24; the allowed range is 24 to 43.
- Both one-step and two-step clocks are supported.
- Both IP encapsulation and Ethernet encapsulation are supported. When Ethernet encapsulation is used, the following points apply.
- Ethernet multicast addressing is used for transmitting PTP messages. Both the non-forwardable multicast address 01-80-C2-00-00-0E and forwardable multicast address 01-1B-19-00-00-00 are supported.
- Virtual local area network (VLAN) tags within Ethernet frames carrying PTP messages are not supported. When a PTP clock receives a PTP message within a frame containing a VLAN tag, it discards this frame. A PTP clock that is compliant with the profile described in Recommendation ITU-T G.8275.1 must comply with IEEE 1588 – 2008 Annex F.
- Synchronization messages are sent at a rate of 16 packets/s; announce messages are sent at a rate of 8 packets/s.
- On the 7705 SAR, the priority1 value is set to the default value (128) and cannot be changed.
- On the 7705 SAR, if the clock-type parameter is set to ordinary slave, the priority2 value is set to the default value (255) and cannot be changed.
For further details, refer to Recommendation ITU-T G.8275.1/Y.1369.1.
6.4.6.13.1. Synchronization Certainty/Uncertainty
As described in IEEE 1588v2 PTP, master clocks transmit Announce messages containing the clock priority and quality. Each clock in the network can use the BMCA and the clock properties received from the Announce messages to select the best clock to synchronize to.
Within a PTP-aware network, there could be situations where boundary clocks advertise clockClass 6 in the Announce message, which indicates that the parent clock is connected to a traceable primary reference source/clock (PRS/PRC) in locked mode (for example, locked to GNSS), and is therefore designated as the synchronization time source. However, the PTP network may still be in a transient state and stabilizing.
For example, this may occur when:
- a grand master clock locks and relocks to GNSS
- an intermediate boundary clock is started or restarted
- a new parent clock is chosen
Depending on the application, it may be important for a downstream boundary clock or slave clock to know whether the PTP network has stabilized or is still “synchronization uncertain”.
Specifically when the G.8275.1 profile with IP encapsulation is used, the synchronizationUncertain flag is added to the Announce message. The use of this flag is optional. The 7705 SAR PTP grand master, boundary, and slave clocks will optionally support the processing of the synchronization state as follows.
- If a grand master clock has its synchronous equipment timing source (SETS) frequency clock and time clock locked to GNSS and its clockClass equals 6, it is in a “synchronization certain” state. The synchronizationUncertain flag in the Announce message is set to FALSE.
- If a grand master clock does not meet the above criteria, it is in a “synchronization uncertain” state. The synchronizationUncertain flag in the Announce message is set to TRUE.
- In order for a boundary clock to be in the “synchronization certain” state, its parent clock’s clockClass must be “synchronization certain”, its SETS must be locked and PRS/PRC traceable, and PTP must have sufficient time to stabilize to the parent clock. At that point, its PTP port state will transition from an Uncalibrated state to a Slave state.
- A boundary clock can fall back to the “synchronization uncertain” state if its parent clock changes to the “synchronization uncertain” state, its SETS becomes unlocked or not PRS/PRC traceable, or the local clock is restarted or reset. The PTP port state will transition away from the Slave state.
This behavior is shown in Figure 22.
Figure 22: Synchronization Certain/Uncertain States

Because the synchronizationUncertain flag is newly agreed upon in standards, most base station slave clocks do not look at this bit. Therefore, in order to ensure that the downstream clocks are aware of the state of the network, the PTP clock (grand master, boundary, slave) may optionally be configured to transmit Announce and Sync messages only if the clock is in a “synchronization certain” state. This is done using the no tx-while-sync-uncertain command.
6.4.6.14. PTP Statistics
The 7705 SAR provides the capability to collect statistics, state, and events data for the PTP slave clock’s interaction with PTP peer clock 1 and PTP peer clock 2. This data is collected separately for each peer clock and can be displayed using the show system ptp clock ptp-port command. This data can be used to monitor the PTP slave clock performance in relation to the peer clocks and to diagnose a problem or analyze the performance of a packet switched network for the transport of synchronization messages. The following data is collected:
PTP peer-1/PTP peer-2 statistics:
- number of signaling packets
- number of unicast request announce packets
- number of unicast request announce timeouts
- number of unicast request announce packets rejected
- number of unicast request synchronization packets
- number of unicast request synchronization timeouts
- number of unicast request synchronization packets rejected
- number of unicast request delay response packets
- number of unicast request delay response packets timeouts
- number of unicast request delay response packets rejected
- number of unicast grant announce packets
- number of unicast grant announce packets rejected
- number of unicast grant synchronization packets
- number of unicast grant synchronization packets rejected
- number of unicast grant delay response packets
- number of unicast grant delay response packets rejected
- number of unicast cancel announce packets
- number of unicast cancel synchronization packets
- number of unicast cancel delay response packets
- number of unicast acknowledge cancel announce packets
- number of unicast acknowledge cancel synchronization packets
- number of unicast acknowledge cancel delay response packets
- number of announce packets
- number of synchronization packets
- number of delay response packets
- number of delay request packets
- number of follow-up packets
- number of out-of-order synchronization packets
- total number of UDP (port 320) packets
- total number of UDP (port 319) packets
- number of alternate master packets discarded
- number of bad domain packets discarded
- number of bad version packets discarded
- number of duplicate messages packets discarded
- number of step RM greater than 255 discarded
PTP master-1/PTP master-2 algorithm state statistics (in seconds):
- number of free-run states
- number of acquiring states
- number of phase-tracking states
- number of hold-over states
- number of locked states
PTP master-1/PTP master-2 algorithm event statistics:
- number of excessive frequency errors detected
- number of excessive packet losses detected
- number of packet losses spotted
- number of excessive phase shifts detected
- number of high PDVs detected
- number of synchronization packet gaps detected
6.4.7. Network Timing Reference (NTR)
On the 7705 SAR-M, the 6-port DSL Combination module and 8-port xDSL module support network timing reference (NTR) clock recovery. Using NTR, a synchronized clock can be derived from the xDSL physical layer or the SHDSL interface. NTR delivers a highly accurate synchronized clock while eliminating the need for advanced synchronization hardware in the DSL modem, thereby reducing the overall cost of the network.
NTR is equivalent to physical layer synchronization and, at cell sites, is the preference for delivering frequency synchronization over a DSL network. Alternative, packet-based methods of synchronization, such as ACR and IEEE 1588v2 PTP, cannot offer the same level of accuracy as physical layer synchronization due to the inherent PDV characteristics of DSL.
On the 8-port xDSL module, a single NTR timing reference is available to signal back to the 7705 SAR-M. On the 6-port DSL Combination module, there are two DSL interfaces and therefore two separate NTR timing references available to the 7705 SAR-M: one for SHDSL and one for xDSL. On SHDSL interfaces, NTR locks the DSL symbol clock directly to the reference clock. On xDSL interfaces, NTR maps DSL frame phase difference bits information between the reference clock and the DSL free-running clock.
6.4.7.1. NTR on xDSL Interfaces
On xDSL interfaces, all CPE lines must be connected to the same LT because the clock source for all lines must be identical. While operating in VDSL2 mode, all pairs on an 8-port xDSL module must have their VDSL2 DMT signals aligned.
When NTR on xDSL is in use, a message is sent to the 7705 SAR-M indicating which pair is currently being used to derive NTR. However, once all lines are in show-time mode, NTR is carried on all lines. If there is an NTR status change from one pair to another, a status change is indicated in the CLI for the 7705 SAR-M. The status change is also visible through the NSP NFM-P.
The chipset automatically selects the line with the best signal-to-noise ratio on the pilot tone. If there is a line drop, or if the signal-to-noise ratio degrades, the system automatically switches NTR to another line in show-time mode to recover clock synchronization. When NTR is locked to a particular line, the status is updated and indicated in the CLI and on the NSP NFM-P.
If the line carrying NTR is taken out of show-time mode, there may be phase drift during the switchover if a phase delta difference has been missed.
6.4.7.2. NTR on SHDSL Interfaces
NTR for SHDSL is carried equally across all lines because all lines must connect back to the same LT on the same DSLAM. NTR for SHDSL operates in auto-detect mode. The 6-port DSL Combination module automatically selects an SHDSL pair that will be used to extract NTR and transmit to the SSU. The SHDSL pair is selected based on clock activity monitoring, coarse frequency monitoring, and chipset level indications on the active status of individual lines.
The auto-detect algorithm on the 6-port DSL Combination module selects an SHDSL pair used for NTR by first checking SHDSL pair 1. If pair 1 is not considered an acceptable source, the algorithm checks each pair in sequence until it finds an acceptable source or reaches SHDSL pair 4. The ID of the in-use line is displayed in CLI; however, it is not user-configurable.
When NTR on SHDSL interfaces is in use, the status is indicated to the 7705 SAR-M. The pair currently being used to derive NTR is shown in the CLI and is updated to the NSP NFM-P. However, once all lines are in show-time mode, NTR is carried on all lines. If there is an NTR status change from one pair to another, a status change is indicated in the CLI for the 7705 SAR-M. The status change is also visible through the NSP NFM-P.
The 6-port DSL Combination module automatically selects the SHDSL pair for NTR to use based on the selection algorithm. If there is a line drop, or if the signal-to-noise ratio degrades, the system automatically switches NTR to another line in show-time mode to recover clock synchronization. When NTR is locked to a particular line, the status is updated and indicated in the CLI and on the NSP NFM-P.
If the line carrying NTR is taken out of show-time mode, there will be phase drift during the switchover and clock recovery may enter the holdover state if this was the only external timing reference available. If this happens, the 6-port DSL Combination module selects a new SHDSL line if one is available.
6.4.8. Synchronous Ethernet
Synchronous Ethernet is a variant of line timing that derives the physical layer transmitter clock from a high-quality timing reference, traceable to a primary reference clock. Synchronous Ethernet uses the physical layer of the Ethernet link to distribute a common clock signal to all nodes in the network. Each node has a local or system clock that determines the outgoing clock rate of each interface. The system clock of each node in the network is derived from the incoming clock at an input interface or from a dedicated timing interface; for example, a BITS port.
Synchronous Ethernet works at Layer 1 and is concerned only with the precision of the timing of signal transitions to relay and recover accurate frequencies. It is not impacted by traffic load and is therefore not affected by packet loss or PDV that occurs with timing methods that use higher layers of the networking technology.
Synchronous Ethernet is automatically enabled on ports and SFPs that support synchronous Ethernet. The operator can select an Ethernet SFP port as a candidate timing reference. The recovered timing from this port is distributed to the nodes in the network over the physical layer of the Ethernet link. This allows the operator to ensure that any of the system outputs are locked to a stable, traceable frequency source. The transmit timing of all SFP ports with SFPs that support synchronous Ethernet is then derived from the node’s SSU.
Synchronous Ethernet can only be used for end-to-end network synchronization when all intermediate switching nodes in the network have hardware and software support for synchronous Ethernet.
Synchronous Ethernet is supported on the following cards and platforms:
- 8-port Ethernet Adapter card (ports 7 and 8), version 2
- 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
- 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card
- 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter card
- 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module
- 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card
- Packet Microwave Adapter card
- 6-port SAR-M Ethernet module
- 7705 SAR-M (all variants) (on all Ethernet ports)
- 7705 SAR-Hc (on all Ethernet ports)
- 7705 SAR-W (on all Ethernet ports)
- 7705 SAR-Wx (all variants) (on all Ethernet ports)
- 7705 SAR-H (on all Ethernet ports)
- 4-port SAR-H Fast Ethernet module
- 7705 SAR-A (both variants) (supported on the XOR ports (1 to 4), configured as either RJ-45 ports or SFP ports, and on SFP ports 5 to 8. Ports 9 to 12 do not support synchronous Ethernet.)
- 7705 SAR-Ax (on all Ethernet ports)
- 7705 SAR-X (on all Ethernet ports)
If an SFP that does not support synchronous Ethernet is installed, the Ethernet card will use its local oscillator for transmit timing and an event is logged. If the Ethernet port is configured as a source of node synchronization and an SFP that does not support synchronous Ethernet is installed, a clock will not be supplied to the SSU and an event is logged.
Each synchronous Ethernet port can be configured to recover received timing and send it to the SSU. On the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-H, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, and 7705 SAR-Wx, any synchronous Ethernet-capable port can be used as an available reference. In addition, two references are available on the 7705 SAR-X, and on the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) module or 6-port SAR-M Ethernet module when the modules are installed in the 7705 SAR-M (variants with module slot). On the 7705 SAR-8 and 7705 SAR-18:
- one reference is available on the 8-port Ethernet Adapter card, version 2
- two references are available on:
- the 6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
- the 8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card
- the 2-port 10GigE (Ethernet) Adapter card
- the 10-port 1GigE/1-port 10GigE X-Adapter card (not supported on the 7705 SAR-8)
- the Packet Microwave Adapter card
Synchronous Ethernet ports always use node timing from the SSU. Configuration of one port automatically configures the other port.
If timing is recovered from a synchronous Ethernet port from an upstream non-synchronous Ethernet free-running port and selected as the reference to the SSU, then this clock may not be of sufficient quality or accuracy for node operations. This reference may be disqualified because the frequency may not be within the pull-in range of the SSU Stratum 3 oscillator.
On the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-Hc, 7705 SAR-A, 7705 SAR-Ax, 7705 SAR-W, 7705 SAR-Wx, 7705 SAR-X, and on the Packet Microwave Adapter card, a copper-based, RJ-45 synchronous Ethernet port phy-tx-clock must be configured as slave before the port is configured to be a timing source for the node. If a copper-based, RJ-45 synchronous Ethernet port is a timing source for the node, the port phy-tx-clock cannot be changed to another mode.
6.4.9. Synchronization Status Messaging with Quality Level Selection
Synchronization Status Messaging (SSM) provides a mechanism for downstream network elements to determine the quality level of the source.
The quality level values are processed by the 7705 SAR system timing module (SSU) to track the network timing flow and select the highest-quality source. The selection process is described in Timing Reference Selection Based on Quality Level. Also see Figure 23. SSM also allows the network elements to autonomously reconfigure the timing path to select the best possible source for timing and to avoid timing loops. This function is especially useful in a ring topology where network timing may be passed in both directions around the ring.
Synchronization status messages containing the quality level values are placed in prescribed overhead bytes for SONET and SDH signals and in bit-oriented messages within the data link for DS1 (ESF) and E1 physical ports.
For synchronous Ethernet and DSL interfaces, there is no equivalent fixed location to convey synchronization status messages; therefore, the quality level values are transported using Ethernet frames over a message channel. This channel, called the Ethernet Synchronization Message Channel (ESMC), uses an Ethernet protocol based on an IEEE Organization Specific Slow Protocol (OSSP). The 4-bit quality level value is carried within a Type-Length-Value (TLV) byte of an Ethernet OAM Protocol Data Unit (PDU) that uses the OSSP subtype.
The clock source quality levels identified for the purpose of tracking network timing flow are listed below. They make up all of the defined network deployment options given in Recommendations G.803 and G.781 (option I pertains to the SDH model and Option II pertains to the SONET model).
The received quality level values for the two network options based on the specific interfaces within these options are provided in the first two columns of Table 30 (for SONET, SDH, and Synchronous Ethernet interfaces) and Table 31 (for E1 and T1 interfaces). The transmitted quality level values are shown in the last two columns of Table 30 and Table 31.
- prs — SONET Primary Reference Source Traceable
- stu — SONET Synchronous Traceability Unknown
- st2 — SONET Stratum 2 Traceable
- tnc — SONET Transit Node Clock Traceable
- st3e — SONET Stratum 3E Traceable
- st3 — SONET Stratum 3 Traceable
- smc — SONET Minimum Clock Traceable
- eec1 — SDH Ethernet Equipment Clock Option 1 Traceable
- eec2 — SONET Ethernet Equipment Clock Option 2 Traceable
- prc — SDH Primary Reference Clock Traceable
- ssu-a — SDH Primary Level Synchronization Supply Unit Traceable
- ssu-b — SDH Second Level Synchronization Supply Unit Traceable
- sec — SDH Synchronous Equipment Clock Traceable
The user may override the received quality level value of the system synchronization reference input by using the ql-override command to configure one of the above values as a static value. This in turn may affect the transmitted quality level value on each SSM-capable port. Also, the user may use the tx-dus command to force the quality level value that is transmitted on the SSM channel to be set to dnu (do not use) or dus (do not use for synchronization). This capability is provided to block the interface from being a timing source for the 7705 SAR. The dus/dnu quality level value cannot be overridden.
Figure 23: Timing Reference Selection Based on Quality Level

The G.803 and G.781 standards also define additional codes for internal use.
- QL-INVx is generated internally by the system when an unallocated synchronization status message value is received; x represents the binary value of this synchronization status message. Within the 7705 SAR, all these independent values are assigned a single value of QL-INVALID.
- QL-FAILED is generated internally by the system when the terminated network synchronization distribution trail is in the signal fail state.
- QL-UNKNOWN is generated internally by the system to differentiate from a received QL-STU code. It is equivalent to QL-STU for the purposes of quality level selection.
Table 30: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (SDH, SONET, SyncE)
SSM Quality Level Value Received on Port | Internal Relative Quality Level | SSM Quality Level Value to be Transmitted | ||
SDH interface SyncE interface in SDH mode | SONET interface SyncE interface in SONET mode | SDH interface SyncE interface in SDH mode | SONET interface SyncE interface in SONET mode | |
0010 (prc) | 0001 (prs) | Best quality 1 | 0010 (prc) | 0001 (prs) |
— | 0000 (stu) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 0000 (stu) |
— | 0111 (st2) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 0111 (st2) |
0100 (ssu-a) | 0100 (tnc) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 0100 (tnc) |
— | 1101 (st3e) |
| 1000 (ssu-b) | 1101 (st3e) |
1000 (ssu-b) | — |
| 1000 (ssu-b) | 1010 (st3/eec2) |
— | 1010 (st3/eec2) |
| 1011 (sec/eec1) | 1010 (st3/eec2) |
1011 (sec/eec1) | — | Lowest quality qualified in QL-enabled mode | 1011 (sec/eec1) | 1100 (smc) |
— | 1100 (smc) | See note 2 | 1111 (dnu) | 1100 (smc) |
1111 (dnu) | 1111 (dus) | See note 2 | 1111 (dnu) | 1111 (dus) |
Any other | Any other | QL-INVALID | 1111 (dnu) | 1111 (dus) |
— | — | QL-FAILED | 1111 (dnu) | 1111 (dus) |
— | — | QL-UNC | 1011 (sec/eec1) | 1010 (st3/eec2) |
- As the received QL on the port drops from prc/prs to sec/eec1 (row 1 to row 8), the quality level of the internal SSU drops from “Best quality” to “Lowest quality”.
- These quality level indications are considered to be lower than the internal clock of the system. They are relayed to the line interfaces when ql-selection is disabled. When ql-selection is enabled, these inputs are never selected. If there is no valid reference available for the internal clock, then the clock enters holdover mode and the quality level is QL-UNC.
Notes:
Table 31: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (E1 and T1)
SSM Quality Level Value Received on Port | Internal Relative Quality Level | SSM Quality Level Value to be Transmitted | ||
E1 interface | T1 interface (ESF) | E1 interface | T1 interface (ESF) | |
0010 (prc) | 00000100 11111111 (prs) | Best quality 1 | 0010 (prc) | 00000100 11111111 (prs) |
— | 00001000 11111111 (stu) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 00001000 11111111 (stu) |
— | 00001100 11111111 (st2) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 00001100 11111111 (st2) |
0100 (ssu-a) | 01111000 11111111 (tnc) |
| 0100 (ssu-a) | 01111000 11111111 (tnc) |
— | 01111100 11111111 (st3e) |
| 1000 (ssu-b) | 01111100 11111111 (st3e) |
1000 (ssu-b) | — |
| 1000 (ssu-b) | 00010000 11111111 (st3) |
— | 00010000 11111111 (st3) |
| 1011 (sec) | 00010000 11111111 (st3) |
1011 (sec) | — | Lowest quality qualified in QL-enabled mode | 1011 (sec) | 00100010 11111111 (smc) |
— | 00100010 11111111 (smc) | See note 2 | 1111 (dnu) | 00100010 11111111 (smc) |
1111 (dnu) | 00110000 11111111 (dus) | See note 2 | 1111 (dnu) | 00110000 11111111 (dus) |
Any other | N/A | QL-INVALID | 1111 (dnu) | 00110000 11111111 (dus) |
— | — | QL-FAILED | 1111 (dnu) | 00110000 11111111 (dus) |
— | — | QL-UNC | 1011 (sec) | 00010000 11111111 (st3) |
- As the received QL on the port drops from prc/prs to sec/eec1 (row 1 to row 8), the quality level of the internal SSU drops from “Best quality” to “Lowest quality”.
- These quality level indications are considered to be lower than the internal clock of the system. They are relayed to the line interfaces when ql-selection is disabled. When ql-selection is enabled, these inputs are never selected. If there is no valid reference available for the internal clock, then the clock enters holdover mode and the quality level is QL-UNC.
Notes:
6.4.9.1. Timing Reference Selection Based on Quality Level
For a SONET/SDH interface, a BITS DS1 or E1 physical port, or an E1 port interface that supports SSM, or for a synchronous Ethernet interface that supports ESMC, a timing input provides a quality level value to indicate the source of timing of the far-end transmitter. These values provide input to the selection processes on the nodal timing subsystem. This selection process determines which input to use to generate the signal on the SSM egress ports and the reference to use to synchronize the nodal clock, as described below.
- For the two reference inputs (ref1 and ref2) and for the BITS input ports, if the interface configuration supports the reception of a QL over SSM or ESMC, then the quality level value is associated with the timing derived from that input.
- For the two reference inputs and for the BITS input ports, if the interface configuration is T1 with SF framing, then the quality level associated with the input is QL-UNKNOWN.
- For the two reference inputs, if they are synchronous Ethernet ports and the ESMC is disabled, then the quality level value associated with that input is QL-UNKNOWN.
- For the two reference inputs and for the BITS input ports, if the interface configuration supports the reception of a QL over SSM (and not ESMC), and no SSM value has been received, then the quality level value associated with the input is QL-STU.
- For the two reference inputs and for the BITS input ports, if the interface configuration supports the reception of a QL over SSM or ESMC, but the quality level value received over the interface is not valid for the type of interface, then the quality level value associated with that input is QL-INVALID.
- For the two reference inputs, if they are external synchronization, DS3, or E3 ports, then the quality level value associated with the input is QL-UNKNOWN.
- For the two reference inputs, if they are synchronous Ethernet ports and the ESMC is enabled but no valid ESMC Information PDU has been received within the previous 5 s, then the quality level value associated with that input is QL-FAILED.
- If the user has configured an override for the quality level associated with an input, the node displays both the received and override quality level value for the input. If no value has been received, then the associated value is displayed instead.
After the quality level values have been associated with the system timing inputs, the two reference inputs and the external input timing ports are processed by the system timing module to select a source for the SSU. This selection process is described below.
- Before an input can be used as a potential timing source, it must be enabled using the ql-selection command. If ql-selection is disabled, then the priority order of the inputs for the Synchronous Equipment Timing Generator (SETG) is the priority order configured under the ref-order command.
- If ql-selection is enabled, then the priority of the inputs is calculated using the associated quality level value of the input and the priority order configured under the ref-order command. The inputs are ordered by the internal relative quality level (shown in the middle row in Table 30) based on their associated quality level values. If two or more inputs have the same quality level value, then they are placed in order based on where they appear in the ref-order priority. The priority order for the SETG is based on both the reference inputs and the external synchronization input ports.
- Once a prioritized list of inputs is calculated, the SETG and the external synchronization output ports are configured to use the inputs in their respective orders.
- Once the SETG and external synchronization output ports priority lists are programmed, then the highest-qualified priority input is used. To be qualified, the signal is monitored to ensure that it has the expected format and that its frequency is within the pull-in range of the SETG.
6.4.9.1.1. SSM/ESMC QL Transmission
If a port is using the SETG output as its timing reference, the port transmits the SSM corresponding to the QL of the SETG.
On the port that is selected as the reference for the SETG, the port transmits the DNU/DUS value in the SSM/ESMC.
If a BITS port is selected as the reference for the SETG, both BITS ports transmit DNU/DUS value.
An Ethernet port with a copper SFP always transmits DNU/DUS when SSM is enabled on the port. When SSM is enabled on a copper-based RJ45 Ethernet port, DNU/DUS is transmitted if the port phy-tx-clock is not configured as master. When SSM is enabled on a copper-based RJ45 Ethernet port and the port phy-tx-clock is configured as master, the port transmits the SSM value corresponding to the determined by the SSU.
6.4.9.1.1.1. DS1 Physical Port QL Transmission
DS1 signals can carry the quality level value of the timing source via the SSM transported within the 1544 kb/s signal Extended Super Frame (ESF) Data Link (DL), as specified in Recommendation G.704.
The format of the ESF data link messages is 0xxx xxx0 1111 1111, with the rightmost bit transmitted first. The 6 bits denoted by xxx xxx contain the message; some of these messages are reserved for synchronization messaging. It takes 32 frames (4 ms) to transmit all 16 bits of a complete DL message.
SSM over DS1 ESF is supported on the 7705 SAR-18 via the BITS ports.
6.4.9.1.1.2. E1 Physical Port QL Transmission
E1 signals can carry the quality level value of the timing source via one of the Sa bits (Sa4 to Sa8) in a synchronization status message, as described in G.704, section 2.3.4. Choosing which Sa bit carries the SSM is user-configurable.
SSM over E1 is supported on the 7705 SAR-18 via the BITS ports. SSM via an E1 port is supported on the 16-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, the 32-port T1/E1 ASAP Adapter card, and the 7705 SAR-M, 7705 SAR-A, and 7705 SAR-X nodes.
6.5. System Configuration Process Overview
Figure 24 displays the process to provision basic system parameters.
Figure 24: System Configuration and Implementation Flow
6.6. Configuration Notes
This section describes system configuration guidelines and caveats.
- The 7705 SAR must be properly initialized and the boot loader and BOF files successfully executed in order to access the CLI.
6.6.1. Reference Sources
For information on supported IETF drafts and standards as well as standard and proprietary MIBs, refer to Standards and Protocol Support.