13. Multiservice Integrated Service Adapter and Extended Services Appliance
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports the Multiservice Integrated Adapter (MS-ISA) and Extended Services Appliance as covered in the topics listed below:
13.1. IP Tunnels
This section describes the following functionality:
For general information on IP tunnel support, refer to the topics listed below in the “IP Tunnels” chapter of the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and VSR Multiservice Integrated Service Adapter and Extended Services Appliance Guide.
- IP Tunnels Overview
- Tunnels ISAs
- Operational Conditions
- Statistics Collection
- Security
- IKEv2
- SHA2 Support
- IPSec Client Lockout
- IPSec Tunnel CHILD_SA Rekey
- Multiple IKE/ESP Transform Support
- X.509v3 Certificate Overview
- Using Certificates for IPSec Tunnel Authentication
- Trust-Anchor-Profile
- Cert-Profile
- Certificate Management Protocol Version 2 (CMPv2)
- OCSP
- IPSec Deployment Requirements
- IKEv2 Remote-Access Tunnel
- Secured Interface
- Configuring IPSec with CLI
- IP Tunnel Command Reference
To configure and enable IP tunnels, the virtualized tunnel ISA MDA (isa-tunnel-v) must be configured in slot 5 on the router. Refer to the 7705 SAR-Hm and SAR-Hmc Interface Configuration Guide for information.
13.1.1. IPSec Secured Interface over Cellular
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports IPSec secured interfaces over cellular interfaces.
Figure 17 shows an example of an IPSec secured interface deployment over a cellular interface in a dual SIM environment.
Figure 17: IPSec Secured Interface over a Cellular Interface
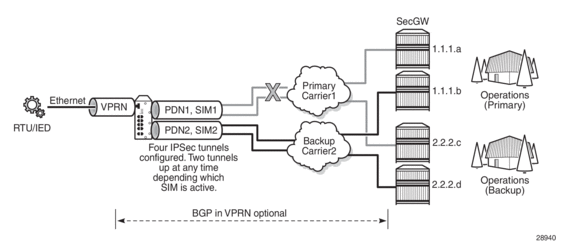
With IPSec secured interfaces, static IPSec tunnels can be created under the PDN router interface associated for each SIM. When the SIM is active and the node attaches to the cellular network, the PDN router interface becomes operational. At that time, IPSec secured interface tunnels configured on the interface also begin to establish towards the security gateway they are configured to connect to. When the tunnel is established, data traffic traverses the IPSec secured interface. In Figure 17, only the pair of tunnels associated with the active SIM is operational.
The tunnel pair on the second PDN router interface is kept down and becomes operational when the second SIM becomes active.
Each IPsec secured interface tunnel is associated with one service. The supported service types are IES and VPRN.
Each service that needs to be secured over the PDN router interface must be configured with its own IPSec secured interface tunnel. For example if VPRN1, VPRN2, and VPRN3 all need to be secured, then three different IPSec secured interfaces are required, one for each service.
IPSec secured interface is supported on IPv4 and IPv6 PDN router interfaces.
The CLI output below shows an example of IPSec secured interface configured on an IPv6 PDN router interface:
13.2. Network Address Translation
This section describes the following Network Address Translation (NAT) functionality supported on the 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers:
NAT runs on a single virtual ISA configured on the node. For general information on NAT support, refer to the topics listed below in “Network Address Translation” in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and VSR Multiservice Integrated Service Adapter and Extended Services Appliance Guide.
- Terminology
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Overview
- Large Scale NAT
- One-to-One (1:1) NAT
- NAT Logging
- Syslog/SNMP/Local-File Logging
- SNMP Trap Logging
- NAT Syslog
- ISA Feature Interactions
- MS-ISA Use with Service Mirrors
- Configuring NAT
13.2.1. NAT with Static Port Forwarding
With NAT, the source IP address and the port of the host on the private side (inside) of the network are translated to an external IP address and port on the public side (outside) of the network. The IP address on the inside can be assigned to a raw socket IP host connected to an RS-232 serial interface or assigned to an IP interface associated with an Ethernet port.
Static port forwarding is configured on the CLI using the following parameters:
- inside IP address
- inside port
- outside IP address
- outside port
- protocol
Figure 18 shows an example of a network with a 7705 SAR-Hm series node configured to use NAT with static port forwarding.
Figure 18: NAT with Static Port Forwarding
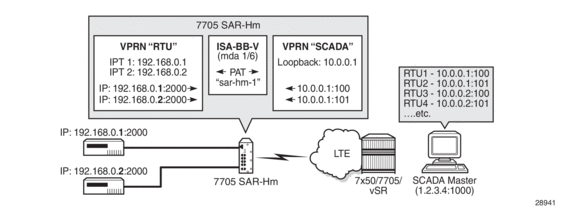
In the scenario shown above, the “RTU” VPRN service is inside and the “SCADA” VPRN service is outside. The “RTU” VPRN contains two IP transport services, one for each connected device. For information about IP transport services, see IP Transport Services and also refer to “Serial Transport over Raw Sockets” in the 7705 SAR-Hm and SAR-Hmc Interface Configuration Guide.
Figure 18 shows specific values for the inside IP address and port and outside IP address and port. The cellular interface of the node is used as the network-facing interface to transport the outside VPRN traffic.
When a packet is sent from the SCADA master to the node over the LTE network, it will be carried within the outside “SCADA” VPRN service towards the node. The node will send the packet to the BB-ISA MDA to perform the required NAT function based on the configured NAT policy. NAT is applied to the packet as needed. The packet is then processed by the inside “RTU” VPRN service, destined to the corresponding IP transport service.
When a packet is sent from the RTU towards the SCADA master, the inside “RTU” VPRN service sends the packet to the BB-ISA MDA where the NAT policy translates the IP address and port to the outside IP address and port, The BB-ISA MDA then sends the packet to the outside “SCADA” VPRN service where it is routed over the cellular interface using the “SCADA” VPRN service.
The steps and CLI outputs below show the configuration of NAT with static port forwarding based on Figure 18.
- Configure NAT on the BB-ISA MDA:configisanat-group 1mda 1/6
- Configure the inside “RTU” VPRN (1) service for the inside static port forwarding NAT function:configservicevprn 1interface 'rtu1'address 192.168.0.1/32loopbackinterface 'rtu2'address 192.168.0.2/32loopbackip-transport 1/3/1local-host ip-addr 192.168.0.1 port-num 2000 protocol udpremote-host ip-addr 1.2.3.4 port-num 1000 protocol udpip-transport 1/3/2local-host ip-addr 192.168.0.2 port-num 2000 protocol udpremote-host ip-addr 1.2.3.4 port-num 1000 protocol udpconfigservicevprn 1natinsidedestination-prefix 1.2.3.4/24 .nat-policy 'sar-hm-1'configservicenatnat-policy 'sar-hm-1pool 'pool-name-1' router 2port-forwardinglsn router 1 ip 192.168.0.1 protocol udp port 2000 outside-ip 10.0.0.1 outside-port 100 nat-policy "sar-hm-1"lsn router 1 ip 192.168.0.2 protocol udp port 2000 outside-ip 10.0.0.1 outside-port 101 nat-policy "sar-hm-1"
- Configure the outside “SCADA” VPRN (2) service for the outside static port forwarding NAT function:service vprn 2interface 'Outside_RTU'address 10.0.0.1/32loopbacknatoutsidepool 'pool-name-1'nat-group 1 type large-scaleaddress-range 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.1 createport-forwarding-range 30000port-reservations ports 1000
13.2.2. NAT Command Reference
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports the NAT commands listed in this section. For command descriptions, refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Classic CLI Command Reference Guide.
13.2.2.1. ISA Configuration Commands
13.2.2.2. NAT Service Configuration Commands
13.2.2.3. NAT VPRN Commands
13.2.2.4. NAT Persistence Commands
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports the persistence commands listed in this section. For command descriptions, refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Classic CLI Command Reference Guide.
13.2.2.5. NAT IPv4 Filter Policy Commands
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports the NAT IPv4 filter policy commands listed in this section. For command descriptions, refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Classic CLI Command Reference Guide.
13.2.2.6. NAT Routing Protocol Commands
The 7705 SAR-Hm series of routers supports the NAT routing protocol commands listed in this section. For command descriptions, refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Classic CLI Command Reference Guide.