5. NETCONF
5.1. NETCONF Overview
NETCONF is a standardized IETF configuration management protocol published in RFC 6241, Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF). It is secure, connection-oriented, and runs on top of the SSHv2 transport protocol as specified in RFC 6242, Using the NETCONF Configuration Protocol over Secure Shell (SSH). NETCONF is an XML-based protocol that can be used as an alternative to CLI or SNMP for managing an SR OS router.
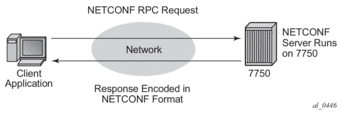
NETCONF uses RPC messaging for communication between a NETCONF client and the NETCONF server running on SR OS. An RPC message and configuration data is encapsulated within an XML document. These XML documents are exchanged between a NETCONF client and a NETCONF server in a request/response type of interaction. The SR OS NETCONF interface supports both configuration and retrieval of operational information. Figure 15 shows a NETCONF RPC request.
Figure 15: NETCONF RPC Request
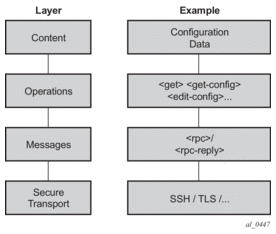
NETCONF can be conceptually partitioned into four layers as described in RFC 6241. Figure 16 shows the NETCONF layers.
Figure 16: NETCONF Layers (RFC 6241)
5.2. NETCONF in SR OS
NETCONF can be used on an SR OS router to perform router management operations including:
- Changing the configuration of the router (<edit-config> operation)
- Reading the configuration of the router (<get-config> operation, equivalent to the info command in the SR OS CLI)
- Reading operational status and data (and associated configuration information) (<get> operation, equivalent to the show commands in the SR OS CLI)
- Notifications on an SR OS router; equivalent to the SR OS log events.
The equivalent of some admin commands are available via the SR OS NETCONF interface:
- admin save can be done using the <copy-config> operation
- admin rollback commands are supported using a CLI content layer <cli-action> RPC
The bof, debug, tools, clear, and other general CLI operational commands (for example, telnet or ping) are not supported via SR OS NETCONF.
The SR OS NETCONF server advertises the base:1.1 capability (in addition to base:1.0).
SR OS NETCONF supports both a CLI content layer and an XML-based content layer.
5.2.1. Transport and Sessions
SSH transport for NETCONF is supported on TCP port 830 with IPv4 or IPv6 in the Base routing instance. NETCONF SSH sessions (same as CLI, SCP, and sFTP sessions) are subject to any configurable and non-configurable session limits; for example, inbound-max-sessions. Both the SSH server and NETCONF protocol must be enabled in the router configuration in order to use NETCONF. NETCONF sessions can be disconnected using the admin disconnect command. See the CLI section for details.
NETCONF sessions do not time out automatically and are not subject to the CLI session timeout. Operators can disconnect sessions manually if they need to.
A client establishing a NETCONF session must log into the router so user accounts must exist for NETCONF on SR OS. An access type 'netconf' is provided. For access to the Base-R13 SR OS YANG data models, both console and netconf access must be configured for the user. For access to the Nokia SR OS YANG data models, only netconf access is necessary.
Authentication via the local user database is supported for NETCONF users. NETCONF runs over SSH, and SSH supports RADIUS/TACACS+ user authentication. By adding "access netconf" under the default RADIUS/TACACS+ user-template, the NETCONF user is granted access.
Command authorization is not supported for the Nokia SR OS YANG data models. Once a NETCONF session is established and the user is authenticated then all configuration data is available via the Nokia SR OS YANG data models.
Command authorization is supported for the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules. Also, access to various CLI config and show commands (via the CLI content layer) is controlled through the profile assigned to the user that is used to authenticate the underlying SSH session.
Access to LI commands using the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules is based on the access li configuration setting for the user.
If a NETCONF request attempts to execute a CLI command which is outside the scope of its access profile, an error response will be sent.
Example - A user request, with show command, that is not in the scope of the user’s access profile.
Reply:
5.2.2. Datastores and URLs
SR OS supports the <running> datastore, the <candidate> datastore, the <startup> datastore, and <url> tag.
| Note: <url> is not a datastore in itself. |
Support for the <candidate> datastore capability is advertised via the SR OS NETCONF server <hello> as:
<capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:candidate:1.0</capability>
All configuration changes (using <edit-config>) made to the <running> datastore via NETCONF take immediate operational effect. Configuration changes to the <candidate> datastore take effect after a successful <commit> operation.
The <startup> datastore and <url> tag can only be used with <copy-config> and <delete-config> and are not supported with any other operations (including <edit-config>, <get-config>, <get>, <validate>, etc).
The :startup capability is advertised in the SR OS NETCONF server <hello> as:
<capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:startup:1.0</capability>
The <url> tag supports the same options as CLI <file-url>: local urls (CF) and remote urls (ftp and tftp).
The :url capability is advertised in the SR OS NETCONF server <hello> as:
<capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:url:1.0?scheme=ftp,tftp,file</capability>
The following examples show the format of each URL scheme:
- <target><url>ftp://name:passwd@a.b.c.d/usr/myfiles/myfile.cfg</url></target>
- <target><url>tftp://name:passwd@a.b.c.d/usr/myfiles/myfile.cfg</url></target>
- <target><url>file:///cf3:/myfiles/myfile.cfg</url></target>
- <target><url>cf3:/myfiles/myfile.cfg</url></target>
| Note: The examples use “///” for the file URL. Also, the file://localhost/... format is not supported. |
The <startup> datastore is identified by following the bof primary-config/secondary-config/tertiary-config paths as configured by the operator. The <startup> datastore is effectively an alias for a URL (a special URL used for system startup) with some extra resiliency (primary/secondary/tertiary).
The BOF is not considered part of any configuration datastore.
Debug configuration (such as debug mirrors, or anything saved with admin debug-save) is not considered part of any configuration datastore.
Lawful Interception configuration information is contained in the <running> datastore but is not saved in the <startup> datastore. The equivalent of the CLI li save command is available in an <edit-config> using the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules.
Configuration changes done via NETCONF are subject to CLI rollback (revert, save, and so on) and are included in the configuration when the operator performs an admin save in the CLI.
Only the Nokia SR OS YANG modules can be used with the <candidate> datastore. The Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules are not applicable to the <candidate> datastore, but are applicable to the <running> datastore. All <edit-config> requests to the candidate datastore must use the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf namespace.
The candidate datastore supports the XML content layer only. Requests/replies to/from the candidate datastore cannot contain the CLI content layer.
5.2.3. NETCONF Operations and Capabilities
The following base protocol operations are supported:
- <close-session>
- <kill-session>
The following optional capabilities from RFC 6241 are supported:
- Writable-Running Capability
- Candidate Configuration Capability
- <commit> operation
- <discard-changes> operation
- Confirmed Commit Capability
- Validate Capability
- <validate> operation
- Distinct Startup Capability
- URL Capability
The following capability from RFC 6243 is supported:
- With-defaults Capability
One rpc request can only contain one operation.
Table 60 shows supported NETCONF operations.
Table 60: NETCONF Operations
Operation | Arguments |
get-config | source [filter] |
edit-config | target [default-operation][test-option][error-option] config |
copy-config | target source |
delete-config | target |
lock | target |
unlock | target |
get | [filter] |
close-session | n/a |
kill-session | session-id |
discard-changes | n/a |
validate | source |
commit | n/a |
| Note: Bracketed arguments are optional. |
5.2.3.1. <get>
The CLI content layer <get> operation is supported with both configuration and state data returned in a <get> reply. An XML content layer <get> operation, supported with both configurations and state data, being returned in a <get> reply as per the NOKIA SR OS YANG data models only.
A <get> request is first analyzed for syntax errors before any execution starts. If a syntax error is found then a single global <rpc-error> for the entire request is sent in the reply.
Responses are provided for each item in the request until the first item with an error is found. The item with an error has a <response> tag containing some error information, followed by an <rpc-error> tag (and sub-tags). The reply is then returned and subsequent items are not executed.
The <rpc-error> for an individual item (i.e. for a non-syntax error) is after the </response> information and not inside the <response>.
Example — <get> request with a non-syntax error in the 2nd item:
Reply:
5.2.3.2. <get-config>
The <get-config> operation returns non-default configuration by default for the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules (the 'trim' mode as per RFC 6243).
The <get-config> operation returns data nodes that were set by a client to their default values for the NOKIA SR OS modules (the 'explicit' mode as per RFC 6243).
5.2.3.3. <edit-config>
The following values for the <test-option> parameter under <edit-config> are supported:
- test-then-set
- set
- test-only
The "replace" value for the "operation" parameter and the "default-operation" parameter is supported.
The <error-option> is not supported. SR OS implements the stop-on-error behavior by default. The continue-on-error and rollback-on-error are not supported.
5.2.3.4. <copy-config> and <delete-config>
The <copy-config> and <delete-config> base protocol operations are supported for specific combinations of source and target datastores.
The <copy-config> operation is supported for the following combinations of sources and targets:
- <source>=<url> and <target>=<startup> (as long as both are not remote urls)
- <source>=<startup> and <target>=<url> (as long as both are not remote urls)
- <source>=<running> and <target>=<url>
- Equivalent of “admin save <file-url>”
- An index file is also saved if “persist on” is configured in the bof
- <source>=<running> and <target>=<startup>
- Equivalent of “admin save”
- An index file is also saved if “persist on” is configured in the bof
The <running> datastore cannot be a <target> for a <copy-config>.
The <candidate> datastore cannot be a <target> or a <source> for a <copy-config>.
Remote URL to remote URL copies are not supported. For example, if primary-image is a remote URL, then a <startup> to copy will fail with an error.
The <copy-config> operation uses the CLI Content Layer format. The format of the source and target is block CLI.
The <delete-config> operation is supported for the following targets:
- <url>
- <startup>
The <delete-config> operation is not allowed on the <running> or <candidate> datastores.
5.2.3.5. <lock>
Taking the <candidate> datastore’s lock is equivalent to doing a CLI exclusive transaction.
Although the NETCONF protocol allows specifying a target datastore for a lock operation, SR OS only implements a single lock:
- taking the running datastore’s lock locks both the running and candidate datastores (creating a single lock)
- taking the candidate datastore’s lock locks both the running and candidate datastores (creating a single lock)
When either the running datastore’s lock or the candidate datastore’s lock is taken by a NETCONF session:
- no NETCONF session can take the <running> datastore lock
- no NETCONF session can take the <candidate> datastore lock
- no other NETCONF session can do an <edit-config> on the running datastore
- no other NETCONF session can do an <edit-config> on the candidate datastore
- no other NETCONF session can do a <commit> on the candidate datastore
- no other NETCONF session can do a <discard-changes> on the candidate datastore
- CLI becomes read-only
- rollback revert is blocked
- SNMP set requests fail on objects that are part of the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf-* namespace
A datastore’s lock is unlocked when disconnecting a NETCONF session (either from the CLI using Ctrl-c, or by performing a <kill-session> or <close-session> operation). Upon disconnecting a NETCONF session that had acquired a datastore’s lock, SR OS:
- releases the lock
- discards the “uncommitted” changes (if any)
| Note: The behavior is different if the disconnected NETCONF session had the "implicit" lock (see the <edit-config> with XML Content Layer section). In that case, SR OS keeps the "uncommitted" changes in the <candidate> datastore. |
Timeouts of locks are not supported. No specific admin/tools commands are provided to release the lock without disconnecting the session that holds it, but the session that holds the lock can be administratively disconnected using a CLI command to release the lock.
Using a CLI show command, the operator can determine if the <running> datastore is locked, the <candidate> datastore is locked, or both are locked, and the session ID of the session that holds the lock; see the NETCONF Show and Debug Command Reference.
From CLI, the operator can configure whether users that belong to a specific profile have permission to lock NETCONF sessions; see the NETCONF Configuration Command Reference.
An active NETCONF session can be disconnected from the CLI using the session ID. The user can use the show command to find the NETCONF session ID then use the admin command to disconnect the NETCONF session using the session ID obtained from the show command. For details, see the NETCONF Show and Debug Command Reference.
5.2.3.6. <unlock>
Because there is a single lock per datastore regardless of what the scope of that lock is, the following applies.
- The <running> datastore’s lock is unlocked by using the <unlock> command only on the <running> datastore. An error results and the lock stays if a different datastore is used with the <unlock> operation.
- The <candidate> datastore’s lock is unlocked by using the <unlock> command only on the <candidate> datastore. An error results and the lock stays if a different datastore is used with the <unlock> operation.
Performing an <unlock> operation on the candidate datastore discards all pending (not committed) candidate datastore changes.
5.2.3.7. <commit>
The <commit> command has the following characteristics.
- It represents the equivalent of the CLI command candidate commit.
- When a <commit> operation fails, only the first error is returned.
- When SR OS cannot commit all the changes in the candidate datastore, SR OS keeps the <running> datastore unchanged.
- When a NETCONF session is disconnected (using Ctrl-c or <kill-session>) in the middle of a <commit> operation, SR OS keeps the running datastore unchanged.
- The persistency of changes made via a <commit> operation is operator-controlled. A copy of the running datastore to the startup datastore can be automatically performed after each successful <commit> operation. This behavior can be enabled or disabled through a CLI command.
- When some changes exist in the candidate datastore (prior to being committed to the running datastore), there are impacts to:
- a CLI user trying to make immediate changes, as SR OS blocks all CLI immediate configurations
- an SNMP set request, as SR OS blocks the request and returns an error
- an <edit-config> to the running datastore, as SR OS blocks all <edit-config> requests to the running datastore and returns an error
The :confirmed-commit capability is advertised in the SR OS NETCONF server <hello> as:
<capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:confirmed-commit:1.1</capability>
The :confirmed-commit capability has the following characteristics:
- The capability is not advertised if the operator disables the candidate DS capability using the available SR OS CLI command.
- The parameters listed in Table 61 are supported for the <commit> operation.
Table 61: Parameters for a <commit> Operation
Parameter
Description
<confirmed>
This parameter indicates it is a confirmed <commit> operation.
<confirm-timeout>
This parameter specifies the timeout period for confirmed commit (in seconds). If unspecified, the confirmed commit timeout defaults to 600 seconds (10 minutes).
<persist>
This parameter configures the confirmed commit changes to survive a session termination. It sets a token on the ongoing confirmed commit. If <persist> is not given in the confirmed commit operation, any follow-up commit and the confirming commit must be issued on the same session that issued the confirmed commit. If <persist> is given in the confirmed commit operation, a follow-up commit and the confirming commit can be given on any session, but they must include a <persist-id> element with a value equal to the value of the <persist> element in the confirmed commit. The <persist> element can not be changed through a follow-up confirmed commit.
<persist-id>
This parameter issues a follow-up confirmed commit or the confirming commit from any session, using the same token from the <persist> element of the confirmed commit. The <persist-id> element cannot be changed through a follow-up confirmed commit.
- If <persist> was specified in the confirmed commit, the configuration changes are rolled back only if the timeout expires before receiving a confirming commit. The confirming commit has to include a <persist-id> tag with a value equal to the value of the <persist> tag that was in the confirmed commit.
- If the NETCONF session that initiated the confirmed commit is closed while waiting for the confirming commit (for example, disconnected), then SR OS restores the configuration to its state before the confirmed commit was issued. This is valid only if <persist> was not defined in the confirmed commit.If a follow-up confirmed commit is issued before the timer expires, the timer is reset to the new value.
- The confirming commit and the follow-up confirmed commit cannot introduce additional changes to the configuration.The <cancel-commit> operation is supported. It can cancel an ongoing confirmed commit (that is, cancel the timer and rollback the changes introduced with the confirmed commit).
- If the <persist> parameter is not given, the <cancel-commit> operation must be issued on the same session that issued the confirmed commit.
5.2.3.8. <discard-changes>
The <discard-changes> operation causes the <candidate> datastore to revert back to match the <running> datastore and releases the “implicit” lock. From the CLI, the operator can do the equivalent of a <discard-changes> operation which releases the implicit lock as well (seeNETCONF Admin Command Reference).
5.2.3.9. <validate>
The validate capability is supported in the following ways:
- The validate:1.1 and 1.0 capabilities are advertised in the NETCONF server's <hello> as:
- <capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:validate:1.0</capability>
- <capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:validate:1.1</capability>
- The <validate> operation is supported for an XML content layer request but not for a CLI content layer request. Detection of a <config-format-cli-block> or <oper-data-format-cli-block> tag in a <validate> request will result in an “operation not supported” error response.
- A <validate> operation is supported for a selection of config (<source><config>) for both the <candidate> datastore and the <running> datastore, which only returns 'OK'. The <validate> request is not supported for URL sources or the <startup> datastore.
- A <validate> operation checks mainly the syntax. Only the first error is returned.
5.2.4. Data Model, Datastore and Operation Combinations
Table 62 shows the which operations are supported by data model and datastore combination.
Table 62: Data Model, Datastore and Operation Combinations
Operation | R13 Modules | Nokia Modules | ||
<running> | <candidate> | <running> | <candidate> | |
<edit-config> | supported | not supported | not supported | supported |
<get-config> | supported | not supported | supported | supported |
<get>* | not supported | retrieves both configuration and state data (XML format only) | ||
* - Note that datastore is not applicable for a <get> operation
A <get> operation can retrieve CLI content layer state data.
5.2.5. General NETCONF Behavior
Pressing Ctrl-c in a NETCONF session will immediately terminate the session.
The SR OS NETCONF implementation does support XML namespaces (xmlns).
If an invalid namespace is specified within the client's hello message, no error will be returned as the NETCONF server is still waiting for the client to send a valid <hello/>. Further NETCONF requests (without sending a proper hello message) even though correct, SR OS returns an error in that case indicating that “Common base capability not found.”
In the <rpc> element, the allowed XML namespaces are:
- the standard NETCONF “urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0” namespace
- the SR OS “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-r13” namespace
- the SR OS “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace
In the <rpc> element, prefixes are accepted and have to be specified with a valid URI. If an incorrect URI is declared with a prefix, then SR OS detects the invalid URI and sends an <rpc-error> response.
If any other XML namespace is declared (or assigned to a prefix) in the RPC tag, then SR OS returns an error.
Any prefix declarations in the rest of the request are ignored and unused. The SR OS NETCONF server puts the correct NETCONF namespace declaration (“urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0”) in all replies.
An <edit-config> request must specify which data model (Alcatel-Lucent Base-r13 or Nokia SR OS) is being used in the top level <configure> element.
- SR OS accepts a request with only a single namespace at the top <configure> element. For example:<configure xmlns="urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf"><system>....Or:<configure xmlns="urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-r13"><system>....
- The NETCONF client can declare those two namespaces with prefixes at the <rpc> tag itself and use the corresponding prefixes later in the request's <configure/> block.
- SR OS returns an error if the request contains one or more incorrect namespaces.
Example 1 — the standard NETCONF namespace “urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0” is used more than once in the <rpc> element:
Reply (no error message):
Example 2 — an allowed non-default NETCONF base namespace is used in the <rpc> element:
Reply (non-NETCONF base namespace is allowed and no error is returned):
Example 3 — an invalid NETCONF namespace is declared in the <rpc> element:
Reply (SR OS returns an error):
Example 4 — a non-default NETCONF namespace/prefix declared in any child tag overrides the one declared under rpc tag:
Reply (non-standard namespace/prefix used in tag is ignored):
The chunked framing mechanism is supported (in addition to the EOM mechanism). As per RFC 6242, Section 4.1 - Framing Protocol, “[...] If the :base:1.1 capability is advertised by both peers, the chunked framing mechanism (see Section 4.2) is used for the remainder of the NETCONF session. Otherwise, the end-of-message-based mechanism (see Section 4.3) is used.”
Example 5 — Chunked message:
Example 6 — Chunked message:
Handling of default data (for example, 'info' vs 'info detail') uses the mechanisms detailed in RFC 6243. The SR OS NETCONF server supports the 'trim' method as the default for the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules. It supports the 'explicit' method as the default for the NOKIA SR OS Yang modules and also supports the 'report-all' method and advertises that in the <hello>:
A user can save a rollback checkpoint (for example, prior to doing an <edit-config> or a series of <edit-config>) and perform a rollback revert if needed later using the <cli-action> RPC.
The set of supported actions are as follows:
- admin>rollback compare [to checkpoint2]
- admin>rollback compare checkpoint1 to checkpoint2
- admin>rollback delete checkpoint | rescue
- admin>rollback save [comment comment] [rescue]
- admin>rollback revert checkpoint | rescue [now]
- admin>rollback view [checkpoint | rescue]
Example 7 — Two rollback items with responses:
Reply:
Example 8 — Syntax error in the request resulting in global rpc-error reply:
Reply:
Example 9 — Error processing the request:
Reply:
Example 10 — Error in the 2nd item of the request, resulting in no 3rd item in the reply:
Reply:
A debug system netconf info command can be used to dump NETCONF debug message streams. For further details and an example, see the NETCONF Show and Debug Command Reference.
5.2.5.1. System-Provisioned Configuration (SPC) Objects
There is a set of configuration objects that are provisioned (added to the <running> datastore) automatically by SR OS; for example, log-id 99. Some SPC objects are created at bootup time, and some are created or removed dynamically based on configuration. The dynamically created SPC objects are typically children objects created as a side effect of the creation of their parent object.
Some of these objects can be deleted/removed by a user (Deletable SPC Objects).
- In the CLI these are removed by specifying the keyword no, which is then visible in an info command or in a saved config (admin save); for example, no log-id 99.
- The Deletable SPC Objects can be removed or recreated via NETCONF <edit-config> requests, but they are not visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13” namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules) when they are:
- set to their default values (including all child leaves and objects)
- removed or deleted
- The Deletable SPC Objects are visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13” namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules) if a child leaf or object is changed away from the default value; for example, changing log-99 to time-format local.
- The Deletable SPC objects are not visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules) if the child leaves are all at default values.
- Some example deletable SPC objects are:
Some SPC objects cannot be deleted (Non-Deletable SPC Objects).
- Although these objects cannot be deleted, some of them contain leaves that can be modified.
- The Non-Deletable SPC Objects are not visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13” namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules) when they are set to their default values (including all child leaves and objects).
- The Non-Deletable SPC Objects are visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13” namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules) if a child leaf or object is changed away from the default value; for example, setting the card-type.
- The Non-Deletable SPC objects are not visible in a <get-config> response in the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules) if the child leaves are all at default values.
- Some example non-deletable SPC objects are:
Some Non-Deletable SPC Objects are visible in a <get-config> request in the “urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13” namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules), even if they are set to default values:
5.3. Establishing a NETCONF Session
The following example shows a client on a Linux PC initiating a connection to an SR OS NETCONF server. The SSH session must be invoked using an SSH subsystem (as recommended in RFC 6242):
The following example shows an exchange of hello messages which include advertisement of capabilities.
From the SR OS server:
A NETCONF client can reply with a hello message like the following:
5.4. XML Content Layer
XML is the default content layer format for the SR OS NETCONF server. When using the XML format at the NETCONF content layer, configuration changes and configuration information retrieved are expressed as XML tags.
5.4.1. <get> with XML Content Layer
A <get> operation with an XML content layer is supported with the <candidate> datastore only. A <get> request retrieves both the configuration and state data from the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules) only. If any nodes from the configure tree are included in a <get> request filter, then at minimum the <configure> tag must contain a namespace. If the namespace is not specified, SR OS returns an error.
Example 1: The <configure> tag contains a namespace
Reply: no errors
Example 2: The <configure> tag does not contain a namespace
Reply: SR OS errors
Example 3: The <state> tag contains a namespace
Reply: No errors
Example 4: The <state> tag does not contain a namespace
Reply: SR OS errors
5.4.2. <edit-config> with XML Content Layer
An <edit-config> operation is supported with the <running> datastore and the <candidate> datastore.
The <edit-config> requests to the <candidate> datastore can only write XML-formatted content.
The <edit-config> requests that specify the running datastore as a target while using the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules) result in an error response.
Example 1: using the <running> datastore with the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace
Reply: with SR OS errors
There is an internal “implicit” lock that has a scope of all configuration commands in SR OS (not just the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace). The following actions take/release the “implicit” lock:
- The first NETCONF <edit-config> on a <candidate> datastore triggers the “implicit” lock
- The completion of a NETCONF <commit> releases the “implicit” lock
- A CLI admin command can release the “implicit” lock. For more information, see 5.11
- The NETCONF <discard-changes> command is supported in SR OS which releases the “implicit” lock as well
The following scenarios are impacted when an “implicit” lock is taking place:
- A NETCONF session attempting an <edit-config> (on either the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS data model or the Nokia SR OS data model) is blocked and SR OS replies with an error (the <error-info> element includes the <session-id> of the lock owner).
- A CLI command (on either the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 configuration set or the Nokia SR OS data model) is blocked and SR OS returns an error.
- A SNMP set request (on objects that are part of the “urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf” namespace only) is blocked and SR OS returns an error.
One or more <edit-config> requests can be performed on the candidate datastore before the changes are committed or discarded.
NETCONF <edit-config> and <commit> operations impact the configuration of the router and, as with some CLI or SNMP configuration changes, additional actions or steps may need to occur before certain configuration changes take operational effect. Some examples include:
- Configuration changes that require a shutdown and then no shutdown to be performed by an operator in order to take operational effect also need this explicit shutdown and then no shutdown to be performed via NETCONF (in separate edit-configs/commits) in order to take operational effect after those configuration items are changed. Some examples include:
- changes to Autonomous System or Confederation value require a BGP shutdown and then no shutdown
- changes to VPRN Max-routes requires a shutdown and then no shutdown on the VPRN service
- changes to OSPF/ISIS export-limit require a shutdown and then no shutdown on OSPF/ISIS
- Configuration changes to an msap-policy that normally require a tools perform subscriber-mgmt eval-msap command to take operational effect on subscribers that are already active. NETCONF can be used to change the msap-policy configuration, but if it must have the configuration changes applied to the active subscribers then the operator must run the eval-msap tools command.
The supported <edit-config> operation attribute values are listed in Table 63.
Table 63: <edit-config> Operation Attribute Values
Command | Notes |
urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13 namespace Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules | |
merge (Base-R13 SR OS modules) |
|
remove (Base-R13 SR OS modules) |
|
delete (Base-R13 SR OS modules) |
|
create (Base-R13 SR OS modules) |
|
replace (Base-R13 SR OS modules) |
|
urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf namespace Nokia SR OS YANG modules | |
merge (Nokia SR OS modules) |
|
remove (Nokia SR OS modules) |
|
delete (Nokia SR OS modules) |
|
create (Nokia SR OS modules) |
|
replace (Nokia SR OS modules) |
|
The <edit-config> operation’s <default-operation> parameter is supported with the following values:
- replace
- merge
- none
- In the urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13 namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules), an operation of “none” on a leaf node (inherited or direct) causes that leaf statement to be ignored. No error will be returned if the leaf does not exist in the data model.
- In the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules), an operation of "none" (inherited or direct) on a leaf node that does not exist in the data model causes SR OS to return an error with an <error-tag> value of data-missing.
For <delete> and <remove> operations in the Nokia SR OS namespace, the SR OS NETCONF server will recursively “unwind” any children of the node being deleted or removed first before removing the node itself. The 'deepest' child branch of the request is examined first and any leaves are processed, after which the server works backwards out of the deepest branches back up to the object where the delete operation was specified.
For urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13 namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules), if child branches of an object are required to be removed before deleting the object in the CLI, then the equivalent delete request in a NETCONF <edit-config> request must contain all those children if they exist). For example:
In the example above, SR OS will first shut down the test interface, then delete the interface, then shut down the VPLS, and then finally remove it.
| Note: In the urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13 namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules), the 'operation="merge"' is required in the shutdown nodes; otherwise the inherited operation is delete, which is not supported on boolean leaves. |
In the example above, if other children of vpls 11 exist in the config besides the interface test specified in the delete request above, and those children are required in the CLI to be deleted before removing vpls 11, then the deletion request above will fail. All configured children must be specified in the delete request.
The following applies to the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules).
- SR OS returns an error if an explicitly defined <edit-config> operation (such as “delete”) is specified on a “key” leaf.
- The “operation” attribute is inherited from the parent node if not explicitly specified (same as namespaces). If no parent node is available, then the “default-operation” value is used. In other words, the “operation” attribute has a “scope” that it applies to the nested nodes until it is redefined. The following scenarios simplify the “operation” inheritance, where the first line in each scenario represents the operation value of the parent node and the following lines represent the possible operation values for the child nodes and the SR OS behavior in each case:
- CreateCreate/Merge: SR OS processes request (request succeeds/fails based on operation’s behavior)Delete/Remove: SR OS returns an error
- MergeCreate/Merge/Delete/Remove: SR OS processes request (request succeeds/fails based on operation’s behavior)
- Delete/RemoveCreate/Merge: SR OS returns an errorDelete/Remove: SR OS processes request (request succeeds/fails based on operation’s behavior)
5.4.3. <get-config> with XML Content Layer
A <get-config> operation is supported with the <running> datastore and the <candidate> datastore.
The <get-config> requests on the <candidate> datastore return only XML-formatted content.
On a <candidate> datastore, if no filter is specified, SR OS returns the Nokia SR OS configurations only.
On the <running> datastore, if no filter is specified, SR OS returns both the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 configurations and the Nokia SR OS configurations.
On the <running> datastore, to return configurations from the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 configurations only (or the Nokia SR OS configurations only), the user must specify at least a top-level tag and a namespace in the filter. If the namespace is not specified, SR OS returns an error.
The following applies to the urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-*-r13 namespace (the Alcatel-Lucent Base-R13 SR OS YANG modules):
- <get-config> requests that specify a non-existing list node or presence container will result in a reply that contains no data for those list nodes or containers. An <rpc-error> is not sent in this case.
The following applies to the urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf namespace (the Nokia SR OS YANG modules):
- <get-config> requests that specify a non-existing list node or presence container result in an <rpc-error> response
- <get-config> requests that specify a list without specifying a key result in an <rpc-error> response
Using the 'report-all' value with the <with-defaults> tag (RFC 6243) in an XML-content layer <get-config>, returns the equivalent of the CLI command info detail (the returned data includes attributes that are set to their default values).
Example 1: use of <with-defaults> with a value of "report-all"
Reply: returns even attributes with default values
Example 2: without using <with-defaults>
Reply: Attributes with default values are not returned
Subtree filtering for basic subtree selection is supported for XML content layer <get-config> requests. Post-filtering of the selected subtrees is not supported.
The subtree filtering behavior is as follows.
- Attribute match expressions (section 6.2.2 of RFC 6241) are not supported. See details below about content match nodes.
- Only containers are supported as selection nodes (section 6.2.4 of RFC 6241). Empty leaf nodes or list name nodes are not supported as selection nodes.
- Nodes that represent lists must also include content match nodes for all keys of the list; for example, <configure><router><interface><interface-name>abc</interface-name>.
- A selection node that is a list but does not have a key specified is not supported; for example, <configure><router><interface/> is not supported. An alternative is to request the parent containment node that contains the desired list node; for example, <configure><router> instead of <configure><router><interface/>.
- Content match nodes (section 6.2.5 of RFC 6241) are only supported for key leaves; for example, <configure><router><interface><interface-name>abc</interface-name>.
- Content match nodes that are leaves but are not also keys will result in an error (not silently ignored).
Example 3 — A non key leaf is specified (for example, shutdown)
Reply: SR OS errors
Multiple key leafs for the same key cannot be requested inside the same instance of the list name node; for example, <interface-name>abc</interface-name> <interface-name>def</interface-name>. Each key value must be inside its own instance of the list name node; for example, <interface> <interface-name>abc</interface-name> </interface> <interface> <interface-name>def</interface-name> </interface>.
Example 4 — A valid <get-config> request (content match on a list key):
Reply:
Example 5 — A valid <get-config> request (selection node that is a container):
The reply will contain all the configuration for all child nodes of config>router
Example 6 — An invalid <get-config> request (list name node - invalid selection node):
Reply: SR OS errors
Example 7 — An invalid <get-config> request (empty leaf node - invalid selection node):
Reply:
Example 8 — An invalid <get-config> request (key repeated in the same instance of the list node):
Reply: SR OS errors
The full configuration (equivalent to the CLI command 'admin display-config') can be obtained via a <get-config> request:
- A — when the <filter> tag is not presentFor example:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"><get-config><source><running/></source></get-config></rpc>]]>]]><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"><get-config><source><candidate/></source></get-config></rpc>]]>]]>
- B — when only the <configure> tag is present inside a <filter> tagFor example:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"><get-config><source><running/></source><filter><configure xmlns="urn:alcatel-lucent.com:sros:ns:yang:conf-r13"/></filter></get-config></rpc>]]>]]><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><rpc message-id="101" xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0"><get-config><source><candidate/></source><filter><configure xmlns="urn:nokia.com:sros:ns:yang:sr:conf"/></filter></get-config></rpc>]]>]]>
5.5. XML Content Layer Examples
The following examples can be used after a NETCONF session has been established including the exchange of the <hello> messages.
The following is an example of a <get-config> request on the <running> datastore to check on whether netconf is shut down or not on the router:
Reply:
The following is an example for a <get-config> request on the <candidate> datastore to get the full configurations of the system, qos and log branches:
Reply:
The following is an example of an <edit-config> request om the <running> datastore to create a basic VPRN service:
Reply:
The following is an example of an <edit-config> request on the <candidate> datastore to create a basic epipe service:
Reply:
5.6. CLI Content Layer
When using the CLI format at the NETCONF content layer, configuration changes and configuration information retrieved are expressed as untagged (non-XML) CLI commands; for example, CLI script.
The script must be correctly ordered and has the same dependencies and behavior as CLI. The location of CR/LF (ENTER) within the CLI for an <edit-config> is significant and affects the processing of the CLI commands, such as what CLI branch is considered the “working context”. In the following two examples, the “working context” after the commands are issued are different.
Example 1:
Example 2:
After example 1, the CLI working context is the root and immediately sending 'dst-zone CEST' would return an error. After example 2, the CLI working context is config>system>time and sending 'dst-zone CEST' would work as expected.
Configuration changes done via NETCONF trigger the same “change” log events (for example, tmnxConfigCreate) as a normal CLI user doing the same changes.
The <with-defaults> tag (RFC 6243, With-defaults capability for NETCONF) is not supported in a CLI content layer request.
The operator can get a full configuration including defaults for a CLI Content Layer using an empty <cli-info-detail>. The full configuration (equivalent to the CLI command admin display-config [detail]) can be obtained via a <get-config> request in a CLI Content Layer format with an empty <cli-info> or <cli-info-detail> tag inside a <config-format-cli-block>. <report-all> is not supported.
Post-processing commands are ignored: "| match" (pipe match), "| count" (pipe count) and ">" (redirect to file) and CLI ranges are not supported for any command; for example, show card [1..5].
5.7. CLI Content Layer Examples
The following examples can be used after a NETCONF session has been established including the exchange of the <hello> messages.
The following shows an example of a configuration change request and response.
| Note: The exit all command is not required at the beginning of the CLI block; it is automatically assumed by the SR OS NETCONF server. |
Reply:
The following is an example of a <get-config> request and response to retrieve configuration information:
Reply:
The following example shows a <get-config> request and response to retrieve full configuration information.
| Note: The <cli-info-detail/> request can be used to get the full configuration, including default settings. |
Reply:
The following is an example of a <get> request and the response to it:
Reply:
5.8. NETCONF Notifications
NETCONF notifications support is a standard IETF asynchronous notification delivery service for the Network Configuration protocol (NETCONF) that is published in RFC 5277.
The :notification capability and the :interleave capability are advertised in the SR OS NETCONF server <hello> as:
<capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:notification:1.0</capability> <capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:capability:interleave:1.0</capability>
The following are characteristics of the NETCONF notifications capabilities supported in SR OS.
- The :notification capability indicates that the SR OS NETCONF server can process a subscription and send event notifications to the NETCONF client.
- The :interleave capability indicates that the SR OS NETCONF server supports receiving, processing, and responding to NETCONF requests on the same NETCONF session that has an active notification subscription.
- A NETCONF client needs to maintain an open NETCONF session with the NETCONF server in order to receive NETCONF notifications (that is, connection oriented).
- A NETCONF client can send a <create-subscription> operation to the SR OS NETCONF server to start receiving notification messages.
- If the SR OS NETCONF server can satisfy the request, SR OS sends an <OK> element within the <rpc-reply>.
- If the SR OS NETCONF server cannot satisfy the request, SR OS sends an <rpc-error> element within the <rpc-reply>.
- Subscriptions are non persistent and their lifetime is defined by their NETCONF session (not maintained with a router reboot).
- An optional parameter that can be defined for a <create-subscription> operation is: [stream]. The following are characteristics of the [stream] parameter:
- An event stream is a set of event notifications matching a specified forwarding criteria and available to the NETCONF clients for subscription.
- A NETCONF session can subscribe to only one stream at a time.
- One stream can be subscribed-to by many NETCONF sessions.
- The SR OS NETCONF server maintains one or more event streams.
- SR OS uses the SR OS event reporting framework for NETCONF notifications.
- A log-id can be configured to be a NETCONF stream. A “netconf-stream” exists per a log-id. It is used to assign a NETCONF "stream" name with a log-id. A “netconf-stream” is unique per SR OS device. It must be configured with “to netconf” for subscriptions to be accepted. If a “netconf-stream” is changed, active subscriptions to the changed NETCONF stream name are terminated by SR OS.
- There is one pre-configured stream with the "netconf-stream" set to "NETCONF”, that is, log-id 101. It is used by default if the [stream] parameter is not specified. It is modifiable but not deletable.
- Other streams can be configured via NETCONF or CLI. These streams are user-configured, which means that they are modifiable and can be deleted. A user-configured stream's “netconf-stream” cannot be set to “NETCONF” as “NETCONF” is reserved for the pre-configured stream (that is, log-id 101).
- When a NETCONF client tries to subscribe to the SNMP log-id or a non-configured log-id, SR OS returns an error.
- SR OS supports a maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to all streams of 64.
- Notifications can be filtered out using a log-id's “filter” or using base-op for create-subscriptions rpc.
- After the NETCONF server receives an SR OS event through a stream, a <notification> element is ready to be sent to all NETCONF sessions subscribed to that stream as per their filters.
- SR OS supports the following NETCONF notifications:
- sros-config-change-event: sent with every configuration change; that is, any new, deleted, or modified configuration
- sros-state-change-event: sent with every state change
- sros-command-accounting-event: sent to keep track of which user did what activity on the SR OS device
- sros-log-generic-event: contains the rest of the SR OS log events (except for the LI ones)
The following example shows a <create-subscription> operation and the received response:
Reply:
The following is an example for a sros-config-change-event notification:
The following is an example for a sros-state-change-event notification:
The following is an example for a sros-cli-accounting-event notification:
The following is an example for a sros-log-generic-event notification:
In a <create-subscription>, a <startTime> is an optional argument. This argument triggers the starting time of a replay. If it is not present, the subscription cannot be used to replay. A <startTime> cannot specify a time that is later than the current time (that is, in the future). SR OS supports timezones.
In a <create-subscription>, a <stopTime> is another optional argument. If this argument is not present, notifications continue to be sent until the subscription is terminated. A <stopTime> can specify a time that is later than the current time (that is, in the future). SR OS supports timezones.
A replay buffer is maintained by the SR OS server (per-stream) and sorted by the order they were initially sent out (that is, by sequence-id, and not by timestamps).
- A replay request from the client causes stored events to be sent to the client for the specified time interval.
- A stream that supports replay is not expected to have an unlimited supply of saved notifications available to accommodate any replay request.
- The <startTime> and <stopTime> arguments are to specify when collections begin and end, respectively.
- A <replayComplete> notification is sent to indicate that all the replay notifications have been sent.
- If a <stopTime> was specified, then the session then becomes a normal NETCONF session, and the NETCONF server then accepts <rpc> operations. A <notificationComplete> notification is expected after the <replayComplete> if the <stopTime> was specified. The following is an example of a session with a <stopTime> specified:C S| || capability exchange ||-------------------------->||<------------------------->|| || <create-subscription> | (startTime,|-------------------------->| stopTime)|<--------------------------|| <rpc-reply> || || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| <notification> | (replayComplete)|<--------------------------|| <notification> |(notificationComplete)|<--------------------------|| || || || <rpc> ||-------------------------->||<--------------------------|| <rpc-reply> || |
- If <stopTime> was not specified, the session will continue to send notifications as they arise in the system. The following is an example of a session without a <stopTime> specified:C S| || capability exchange ||-------------------------->||<------------------------->|| || <create-subscription> | (startTime)|-------------------------->||<--------------------------|| <rpc-reply> || || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| <notification> | (replayComplete)|<--------------------------|| || || || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| || || <notification> ||<--------------------------|| || |
- If neither <startTime> and <stopTime> arguments are present, no replay is present and notifications continue to be sent until the subscription is terminated.