2. Network interface shell
2.1. Overview
Modern network node architectures are moving toward disaggregated solutions for specific applications, such as the following examples:
- Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS) deployments
- Microservices operating as multiple, interconnected applications able to scale through independent addition and removal, run different software versions, and support rolling upgrades
The SR OS Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) CUPS feature is an example of a CUPS deployment architecture with multiple SR OS network nodes (both physical and virtual) operating as a cluster of independent nodes. By acting as one unit, the BNG CUPS cluster supports flexible and scalable BNG deployment.
For this type of CUPS deployment, the Network Interface Shell (NISH) solution for Linux platforms provides efficient remote control of the SR OS MD-CLI, by enabling management of multiple nodes that are running different versions of SR OS from the same MD-CLI shell.
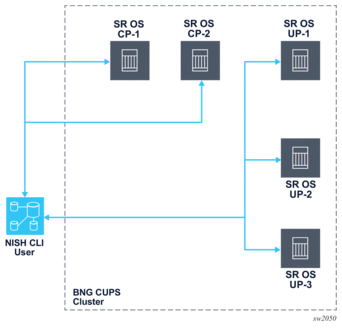
Figure 1 shows the NISH CLI management of a BNG CUPS deployment with two Control Plane function (CPF) nodes and three User Plane function (UPF) nodes.
Figure 1: NISH management of BNG CUPS cluster
2.2. Components
The NISH solution incorporates the following three components:
- SR OS (required)The NISH solution requires one or more network nodes (physical or virtual) running SR OS in MD mode. An authorized user with gRPC access and the gRPC MD-CLI service enabled is also required.
- NISH client (required)The NISH client is a utility that runs on a Linux platform and provides the interface to access SR OS nodes and use MD-CLI to configure a single node or multiple nodes defined either in a static local configuration file or dynamically using a NISH manager.
- NISH manager (optional)The NISH manager is a service that runs on a Linux server and listens for communications from SR OS nodes that are configured to use the SR OS Remote Manager feature to create a dynamic inventory for one or more NISH clients. When SR OS nodes register with the NISH manager, their profile information is provided during the connection.For more information about the SR OS Remote Manager feature, refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide, section “gRPC MD-CLI”.
2.3. Linux man pages
Linux manual (man) pages are provided by the installation of the NISH client and the NISH manager. To access the man pages, enter one of the following commands from the Linux terminal:
- man nish
- man nish-manager
2.4. MD-CLI features support
The NISH solution for Linux platforms provides remote control of SR OS MD-CLI and supports management of multiple SR OS nodes running different SR OS versions from the same MD-CLI shell. NISH provides similar functionality to operating MD-CLI directly on a node; however, the experience is not identical.
The following are some of the MD-CLI features that NISH does not support:
- MD-CLI show, clear, tools, and debug commands
- MD-CLI logging
- switching to the classic CLI
- XML and JSON output formatting
- BOF
- SSH
- Telnet