4. Boot Options
4.1. System Initialization
The primary copy of SR OS software is located on a compact flash card. The removable media is shipped with each router and contains a copy of the OS image.
Note:
|
Starting a router begins with hardware initialization (a reset or power cycle). By default, the system searches Compact Flash Slot #3 (cf3) for the boot.ldr file (also known as the bootstrap file). The boot.ldr file is the image that reads and executes the system initialization commands configured in the boot option file (BOF). The default value to initially search for the boot.ldr file on cf3 cannot be modified.
The following is an example of a console display output when the boot.ldr file cannot be located on cf3.
When the bootstrap image is loaded, the BOF is read to obtain the location of the image and configuration files. The BOF must be located on the same compact flash drive as the boot.ldr file.
Figure 4 displays the system initialization sequence. In the figure, “A” refers to Figure 5, and “B” refers to the list of files on the compact flash.
Figure 4: System Initialization - Part 1
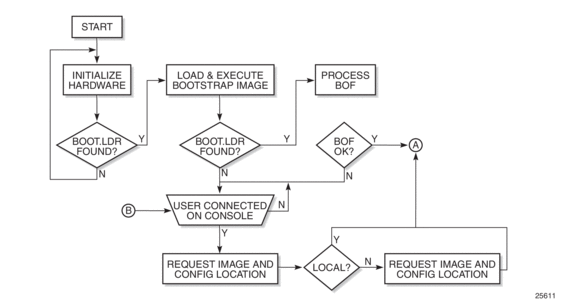
Figure 5 displays the compact flash directory structure and file names for the multislot models.
Figure 5: Files on the Compact Flash
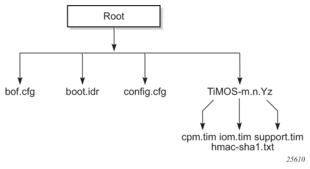
Files on compact flash are:
- bof.cfg — Boot option file
- boot.ldr — Bootstrap image
- config.cfg — Default configuration file
- TIMOS-m.n.Yz:m — Major release numbern — minor release numberY: A — Alpha releaseB — Beta releaseM — Maintenance releaseR — Released softwarez — Version number
- cpm.tim — CPM image file
- iom.tim — XCM/IOM image file
- support.tim — required data for SR OS .tim files
- hmac-sha1.txt (in FIPS-140-2 mode only)
Figure 6 displays the compact flash directory structure and file names for the 1-slot models (7750 SR-1 and 7750 SR-1s).
Figure 6: Files on the Compact Flash (1-slot and 1-slot non-redundant)
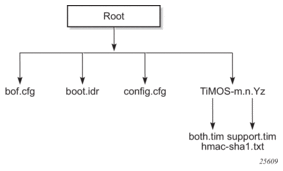
Files on the compact flash (1-slot models) are:
- bof.cfg — Boot option file
- boot.ldr — Bootstrap image
- config.cfg — Default configuration file
- TIMOS-m.n.Yz:m — Major release numbern — Minor release number
- Y: A — Alpha release
- B — Beta release
- M — Maintenance release
- R — Released software
z — Version number- both.tim — CPM and IOM image file
- support.tim — required data for SR OS .tim files
- hmac-sha1.txt (in FIPS-140-2 mode only)
The 7750 SR includes a boot option for running the node in a FIPS-140-2 mode. This mode limits the use of cryptographic algorithms on the CPM to only those that are in accordance with the FIPS-140-2 certifications associated with the 7750 SR.
4.1.1. Configuration and Image Loading
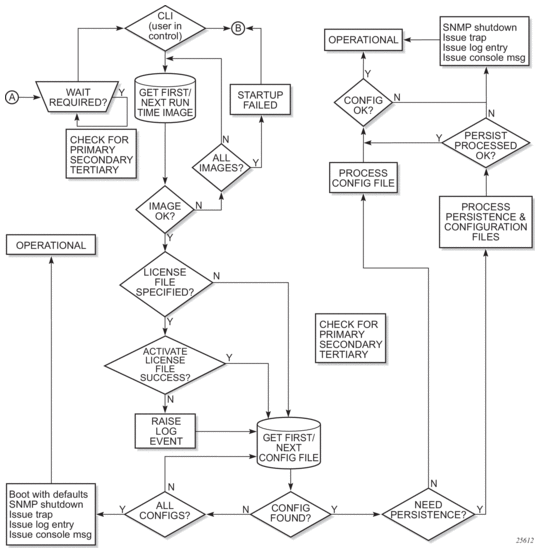
When the system executes the boot.ldr file, the initialization parameters from the BOF are processed. Three locations can be configured for the system to search for the files that contains the runtime image. The locations can be local or remote. The first location searched is the primary image location. If not found, the secondary image location is searched, and lastly, the tertiary image location is searched.
If the BOF cannot be found or loaded, then the system enters a console message dialog session prompting the user to enter alternate file locations and file names.
The boot.ldr can be interrupted during the boot sequence by pressing any key on the CPM console port. The operator must then type sros and press ENTER within 30 seconds or the boot.ldr continues to try to boot the system. This key sequence ensures that noise or misconfiguration does not inadvertently interrupt the boot sequence. If the operator types sros and presses ENTER within 30 seconds, they are brought to a console message dialog session prompting the user to enter file locations and other boot information.
When the runtime image is successfully loaded, control is passed from the bootstrap loader to the image. The runtime image first attempts to read the license file if one has been included in the bof. If a license file is found, it is activated. If there are any issues with the activation, a log event is raised but the startup processing continues with the reading of the configuration file. The runtime image next attempts to locate the configuration file as configured in the BOF. Like the runtime image, three locations can be configured for the system to search for the configuration file. The locations can be local or remote. The first location searched is the primary configuration location. If not found, the secondary configuration location is searched, and lastly, the tertiary configuration location is searched. The configuration file includes chassis, card, MDA, and port configurations, as well as system, routing, and service configurations.
Figure 7 displays the boot sequence.
Figure 7: System Initialization - Part 2
The following displays an example of BOF output:
4.1.1.1. Persistence
Optionally, the BOF persist parameter can specify whether the system should preserve system indexes when a save command is executed. During a subsequent boot, the index file is read along with the configuration file. As a result, a number of system indexes are preserved between reboots, including the interface index, LSP IDs, path IDs, etc. If persistence is not required and the configuration file is successfully processed, then the system becomes operational. If persist is required, then a matching x.ndx file must be located and successfully processed before the system can become operational. Matching files (configuration and index files) must have the same filename prefix such as test123.cfg and test123.ndx and are created at the same time when a save command is executed. Note that the persistence option must be enabled to deploy the Network Management System (NMS). The default is off.
Traps, logs, and console messages are generated if problems occur and SNMP shuts down for all SNMP gets and sets, however, traps are issued.
4.1.1.2. Lawful Intercept
Lawful Intercept (LI) describes a process to intercept telecommunications by which law enforcement authorities can unobtrusively monitor voice and data communications to combat crime and terrorism with higher security standards of lawful intercept capabilities in accordance with local law and after following due process and receiving proper authorization from competent authorities. The interception capabilities are sought by various telecommunications providers.
As lawful interception is subject to national regulation, requirements vary from one country to another. -This implementation satisfies most national standard’s requirements. LI is configurable for all service types.
4.1.1.3. FIPS-140-2 Mode
The 7750 SR includes a configurable parameter in the bof.cfg file to make the node run in FIPS-140-2 mode. When the node boots in FIPS-140-2 mode, the following behaviors are enabled on the node:
- The node performs an HMAC-SHA1 integrity test on the software images .tim files.
- The node limits the use of encryption and authentication algorithms to only those allowed for the associated FIPS-140-2 certification of the 7750-SR.
- Cryptographic module startup tests are executed on the CPM when the node boots to ensure the associated approved FIPS-140-2 algorithms are operating correctly.
- Cryptographic module conditional tests are executed when required during normal operation of associated when using FIPS-140-2 approved algorithms.
- When configuring user-defined encryption or authentication keys, the CLI prompts for the key to be re-entered. If the re-entered key does not match the original, the CLI command is canceled. This affects several protocols and applications.
To support FIPS-140-2, an HMAC-SHA-1 integrity check is performed to verify the integrity of the software images. The following file is included in the TIMOS-m.n.Yz software bundle containing the hmac-sha-1 signature:
- hmac-sha1.txt
During the loading of the cpm.tim or both.tim, a HMAC-SHA-1 check is performed to ensure that the calculated HMAC-SHA-1 of the loaded image matches that stored in the hmac-sha1.txt file.
The HMAC-SHA-1 check is performed on the data loaded from the .tim file. Note that when configuring the primary-image, secondary-image and tertiary-image, the hmac-sha1.txt file must exist in the same directory as the .tim files. If the load has been verified correctly from the HMAC-SHA-1 integrity check, the load continues to start up as normal. If the load is not verified by the HMAC-SHA-1 integrity check, the image load fails.
After the HMAC-SHA-1 integrity check passes, the nodes continue their normal startup sequence including reading the config.cfg file and loading the configuration. The config.cfg file used to boot the node in FIPS-140-2 mode must not contain any configuration that is not supported in FIPS-140-2 mode. If such configuration is present in the config.cfg file when the node boots, the node loads the config.cfg file until the location of the offending configuration and then halt the configuration at that point. Upon a failure to load the config.cfg file, a failure message is printed on the console.
Enabling FIPS-140-2 restricts the ability to configure and use cryptographic algorithms and functions that are not FIPS approved. FIPS-140-2 impacts the ability to configure SSH, SNMP and certificates. Refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide for details of FIPS-140-2 related items.
In addition, signature algorithms of the following combinations only are approved for FIPS:
- FIPS-140 Approved - Digital Signature Standard (DSS)
- DSA
- RSA
- ECDSA
- FIPS-140 Approved - Secured Hash Standard (SHS)
- SHA-1
- SHA-224
- SHA-256
- SHA-384
- SHA-512
Any other combination is not supported in FIPS mode. Using other FIPS signature algorithms in certificates affecting IPsec can cause tunnels to fail. Restrictions to cryptographic algorithms are listed in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide.
4.1.1.4. System Profiles
System profiles provide flexibility when using FP4-based line cards by supporting different system capabilities. The system profile is defined in the BOF and is used by the system when it is next rebooted. Contact your Nokia representative for system profile information.
The following system profiles are supported:
- Profile noneThis profile represents the existing system capabilities and allows FP3- and FP4-based hardware to co-exist within a system. This profile is indicated by the omission of the system-profile parameter in the BOF.
- Profile AThis profile is primarily targeted at subscriber services and Layer 2 and 3 VPN business services and is defined by configuring the BOF system-profile parameter to profile-a.
- Profile BThis profile is primarily targeted at infrastructure routing, core, peering, and DC-GW applications.
System profile profile-a and profile-b support only FP4-based line cards. Provisioning FP2- or FP3-based line cards is prohibited when the system profile is set to profile-a or profile-b. If FP2- or FP3-based card types are present in the boot configuration when using these profiles, the boot sequence aborts the loading of the configuration file when it encounters their configuration.
When changing between system profiles, it is mandatory to remove all configuration commands for features that are not supported in the target system profile before rebooting the system, otherwise the reboot fails at the unsupported configuration command on startup.
On 7750 SR-1 and 7750 SR-s systems, the following conditions apply:
- The BOF system-profile parameter should be configured to either profile-a or profile-b.
- If the system-profile parameter is omitted from the BOF, system profile profile-a is used by the system.
- If the BOF system-profile parameter is configured to an invalid value, it is ignored and system profile profile-a is used by the system.
On 7750 SR-7-B/12-B/12e and 7950 XRS-20/20e systems, the following conditions apply:
- The default system profile is none when the system-profile parameter is omitted from the BOF.
- The BOF system-profile parameter can be configured to either profile-a or profile-b, in which case only FP4-based line cards are supported.
- If the BOF system-profile parameter is configured to an invalid value, it is ignored and system profile none is used by the system.
On all other systems, the following conditions apply:
- These systems must use profile none (the existing system capabilities). As a result, the system-profile parameter must not be configured in the BOF.
- If the system-profile parameter is configured to profile-a or profile-b in the BOF, the system boots, allowing access using the console and CPM management interface, but FP2-based and FP3-based line cards cannot be provisioned; if these card types are present in the boot configuration, the boot sequence aborts loading the configuration file when it encounters their configuration. This issue can be corrected by removing the system-profile parameter from the BOF and rebooting the system.
- If the BOF system-profile parameter is configured to an invalid value, it is ignored and profile none is used by the system.
If a system has two CPMs, and the standby CPM boots with a different system-profile parameter than is used on the active CPM, the active CPM reboot the standby CPM and keep it in a down state. To correct the situation, the BOF can be reconfigured on the standby CPM to match the one configured on the active CPM, and then reboot the system. Alternatively, automatic BOF synchronization can be enabled to keep both CPMs in sync using the following command:
configure redundancy synchronize boot-env
When performing a minor or major ISSU software upgrade on dual CPM systems, it is important that the system profile in the BOF on both the active and standby CPM is the same and has a value supported on the pre-upgrade software release. If the standby CPM happened to have a system profile which is only supported in the post-upgrade release, the active CPM reboots the standby and keeps it down due to a system profile mis-match.
The BOF system profile can be displayed as follows:
The BOF system profile used by the system when it booted can be seen in the boot messages (using the show boot-messages command), which display the BOF read when rebooting.
The system profile in use on the system can be displayed as follows:
4.2. Initial System Startup Process Flow
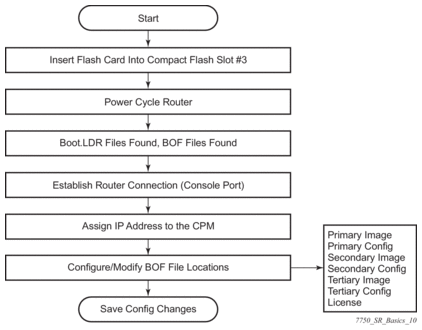
Figure 8 displays the process start your system. Note that this example assumes that the boot loader and BOF image and configuration files are successfully located.
Figure 8: System Startup Flow
4.3. Configuration Notes
This section describes BOF configuration caveats.
- For router initialization, the compact flash card must be installed in the Compact Flash #3 slot.
- The loading sequence is based on the order in which it is placed in the configuration file. It is loaded as it is read in at boot time.