SR OS has a full implementation of the D-PATH attribute as described in draft-ietf-bess-evpn-ipvpn-interworking.
D-PATH is composed of a sequence of domain segments (similar to AS_PATH). Each domain segment is graphically represented as shown in the following figure..
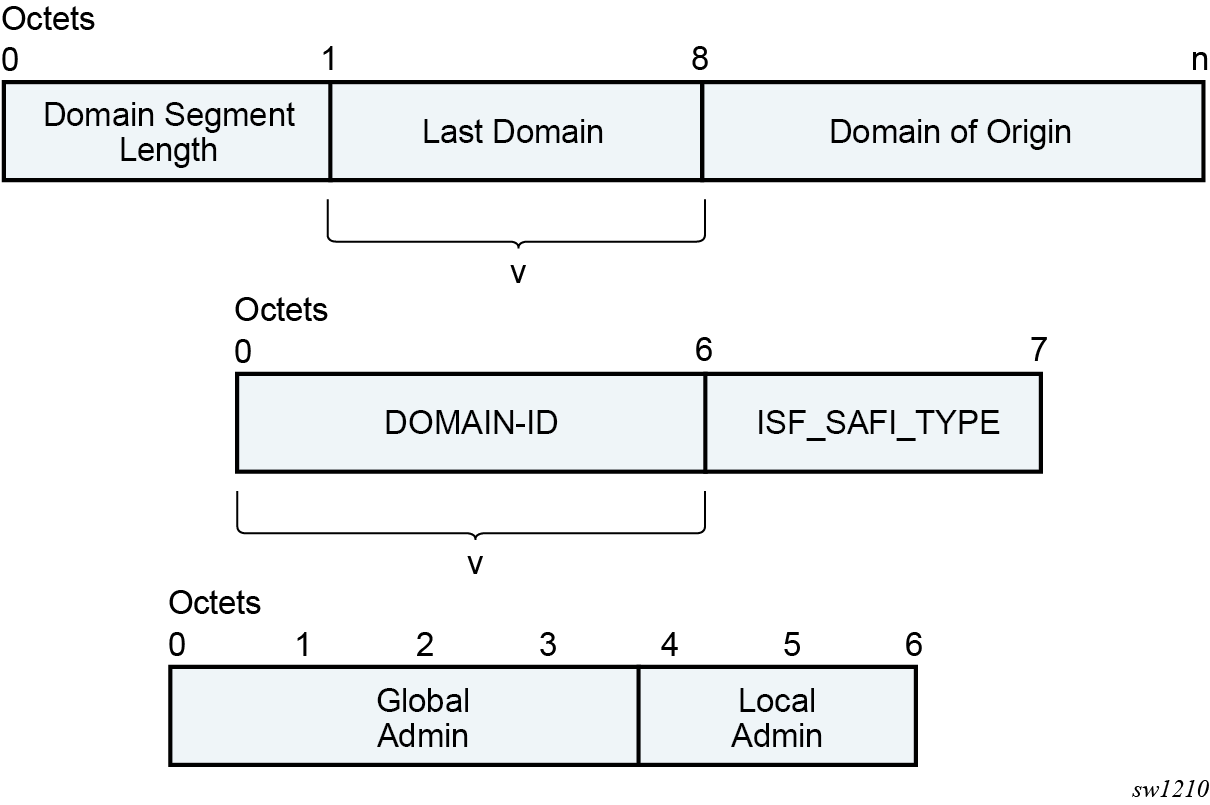
Where:
-
Each domain segment is comprised of <domain_segment_length, domain_segment_value>, where the domain segment value is a sequence of one or more domains.
-
Each domain is represented by <DOMAIN-ID:ISF_SAFI_TYPE>, where the newly added domain is added by a GW, is always prepended at the left of the existing last domain.
-
The supported ISF_SAFI_TYPE values are:
- 0 = Local ISF route
- 1 = safi 1 (typically identifies PE-CE BGP domains)
- 70 = evpn
- 128 = safi 128 (IPVPN domains)
-
Labeled unicast IP routes do not support D-PATH.
-
The D-PATH attribute is only modified by a gateway and not by an ABR/ASBR or RR. A gateway is defined as a PE where a VPRN is instantiated, and that VPRN advertises or receives routes from multiple BGP owners (for example, EVPN-IFL and BGP-IPVPN) or multiple instances of the same owner (for example, VPRN with two BGP-IPVPN instances
Suppose a router receives prefix P in an EVPN-IFL instance with the following D-PATH from neighbor N.
+----------+------------+
|Seg Len=1 | 65000:1:128|
+----------+------------+
If the router imports the route in VPRN-1, BGP-EVPN SRv6 instance with domain 65000:2, the router readvertises the route to its BGP-IPVPN MPLS instance as follows:
+----------+----------+-----------+
|Seg Len=2 |65000:2:70|65000:1:128|
+----------+----------+-----------+
If the router imports the route in VPRN-1, BGP-EVPN SRv6 instance with domain 65000:3, the router readvertises the route to its BGP-EVPN MPLS instance as follows:
+----------+----------+-----------+
|Seg Len=2 |65000:3:70|65000:1:128|
+----------+----------+-----------+
If the router imports the route in VPRN-1, BGP-EVPN MPLS instance with domain 65000:4, the router readvertises the route to its PE-CE BGP neighbor as follows:
+----------+----------+-----------+
|Seg Len=2 |65000:4:70|65000:1:128|
+----------+----------+-----------+
When a BGP route of families that support D-PATH is received and must be imported in a VPRN, the following rules apply.
-
All domain IDs included in the D-PATH are compared with the local domain IDs configured in the VPRN. The local domain IDs for the VPRN include a list of (up to four) domain IDs configured at the vprn or vprn bgp instance level, including the domain IDs in local attached R-VPLS instances.
-
If one or more D-PATH domain IDs match any local domain IDs for the VPRN, the route is not installed in the VPRN’s route table.
-
In the case where the IP-VPN or EVPN route matches the import route target in multiple VRFs, the D-PATH loop detection works per VPRN. For example, for each VPRN, BGP checks if the received domain IDs match any locally configured (maximum 4) domain IDs for that VPRN. A route may have a looped domain for one VPRN and not the other. In this case, BGP installs a route only in the VPRN route table that does not have a loop; the route is not installed in the VPRN that has the loop.
-
A route that is not installed in any VPRN RTM (due to the domain ID matching any of the local domain IDs in the importing VPRNs) is still kept in the RIB-IN. The route is displayed in the show router bgp routes command with a DPath Loop VRFs field, indicating the VPRN in which the route is not installed due to a loop.
-
Route target-based leaking between VPRNs and D-PATH loop detection is described in the following example.
Consider an EVPN-IFL route to prefix P imported in VPRN 20 (configured with domain 65000:20) is leaked into VPRN 30.
When the route to prefix P is readvertised in the context of VPRN 30, which is enabled for BGP-IPVPN MPLS and BGP-EVPN MPLS, the readvertised BGP-IPVPN and BGP-EVPN routes have a D-PATH with a prepended domain 65000:20:0. That is, leaked routes are readvertised with the domain ID of the VPRN of origin and an ISF_SAFI_TYPE = 0, as described in draft-ietf-bess-evpn-ipvpn-interworking.
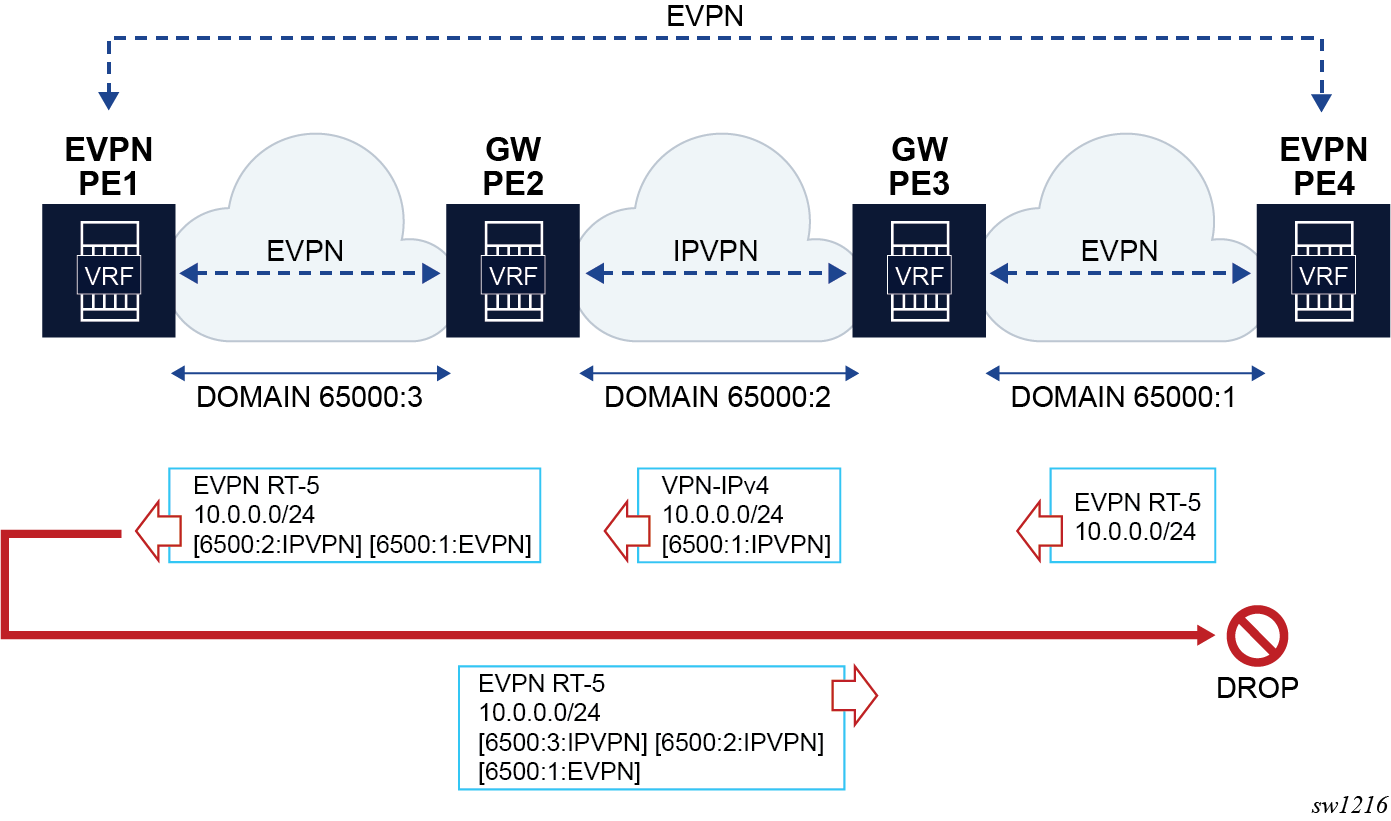
In the D-PATH example shown in the following figure, the different gateway PEs along the domains modify the D-PATH attribute by adding the source domain and family. If PE4 receives a route for the prefix with the domain of PE4 included in the D-PATH, PE4 does not install the route in order to avoid control plane loops.
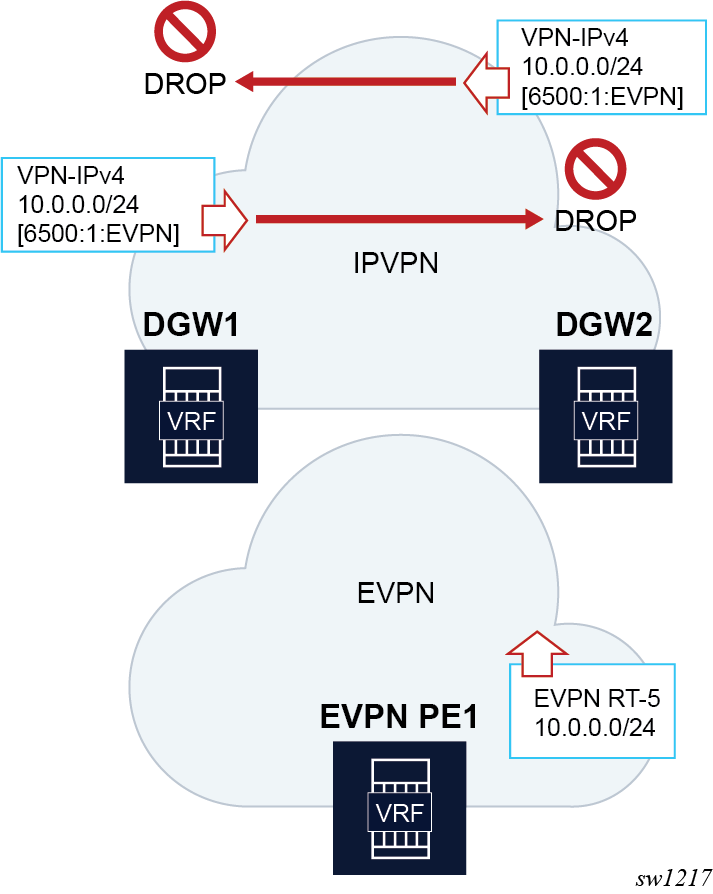
In the D-PATH example shown in the following figure, DGW1 and DGW2 rely on the D-PATH attribute to automatically discard the prefixes received from the peer gateway in IPVPN and avoid loops by reinjecting the route back into the EVPN domain.