2.6. Configuring Security with CLI
This section provides information to configure security using the command line interface.
2.6.1. Security Configurations
This section provides configuration examples for the following security capabilities:
- User profiles
- User access parameters
- Password management parameters
- Authentication, authorization and accounting using local, RADIUS, TACACS+, and/or LDAP
- Filtering using CPM filters and management access filters
Table 20 list the capabilities of authentication, authorization, and accounting configurations. For example, authentication can be enabled locally and on RADIUS, TACACS+, and LDAP servers. Authorization can be executed locally, on a RADIUS server, or on a TACACS+ server. Accounting can be performed on a RADIUS or TACACS+ server.
Table 20: Security Configuration Requirements
Authentication | Authorization | Accounting |
Local | Local | None |
RADIUS | Local and RADIUS | RADIUS |
TACACS+ | Local | TACACS+ |
LDAP | None | None |
2.6.2. Configuring Management Access Filters
The following is an example of a management access filter configuration that accepts packets matching the criteria specified in IP, IPv6 and MAC entries. Non-matching packets are denied.
2.6.3. Configuring IP CPM Filters
Nokia recommends using a strict CPM filter policy allowing traffic from trusted IP subnets for protocols and ports actively used in the router and to explicitly drop other traffic.
The configuration below is an example that follows the recommendations for SSH and BGP:
- Allow SSH from trusted subnet only
- Allow BGP from trusted subnet only
- Explicitly deny all other traffic and operationally log unexpected packets
2.6.4. Configuring IPv6 CPM Filters
Nokia recommends using a strict CPM filter policy allowing traffic from trusted IP subnets for protocols and ports actively used in the router and to explicitly drop other traffic.
The configuration below is an example that follows the recommendations for SSH and BGP:
- Allow SSH from trusted subnet only
- Allow BGP from trusted subnet only
- Explicitly deny all other traffic and operationally log unexpected packets
2.6.5. Configuring MAC CPM Filters
The following displays a MAC CPM filter configuration example:
2.6.6. Configuring CPM Queues
CPM queues can be used for troubleshooting purposes to provide rate limit capabilities for traffic destined to CPM as described in an earlier section of this document.
The following example displays a CPM queue configuration:
2.6.7. IPsec Certificates Parameters
The following is an example to importing a certificate from a PEM format:
The following is an example for exporting a certificate to PEM format:
The following displays an example of profile output:
The following displays an example of an ike-policy with cert-auth output:
The following displays an example of a static LAN-to-LAN configuration using cert-auth:
2.6.8. Configuring Local Command Authorization Profiles
Profiles are used to deny or permit access to a hierarchical branch or specific commands.
The following example displays a local command authorization profile called “ghost” that is associated with a user named “userA”:
2.6.8.1. Parameters
Matching in authorization profiles allows the use of parameters and optional parameters. A set of angle brackets <...> indicates matching on a parameter value and/or optional parameter.
| Note: Parameter values enclosed in angle brackets are optional in the MD-CLI. |
The following rules govern parameter matching:
Rule 1
Any parameter value and/or optional parameter can be present in the match string.
Rule 2
When a parameter value and an optional parameter is present in the user-profile match string, all parameters or optional parameters to its left must also be stated/present.
Rule 3
The user can either specifically state or completely omit unnamed parameters in the match string, as required. However, all unnamed parameter in the CLI command must be present in the match string when matching on an unnamed parameter is used.
For example, consider the OSPF command:
In this case, the user can match on OSPF to allow or deny the command per user-profile, as follows:
Or the user can decide to only allow a certain OSPF instance for a user, as follows:
| Note: Although the user’s matching is based on <ospf-instance-value> that is “an unnamed value”, all other unnamed values in the OSPF command (such as the <router-id-value>) must also be present in the match string. |
Rule 4
When multiple unnamed parameters are present in the match string, the parameters must be provided in the correct order as described in the command help to generate the correct match behavior. For example, using the order of parameters described in the OSPF command usage in Rule 3 above, use the following statement for a user-profile match:
The desired match behavior might not be achieved if the unnamed parameters <ospf-instance-value> and <router-id-value> are out of order with respect to the help screen.
The following displays a parameter matching output:
2.6.8.2. Wildcards
In addition, parameter configuration is facilitated by the availability of wildcards (.*) in the OAM subtree and for commands such as ping, traceroute and mtrace. For example, consider the following command:
Instead of listing all the permitted IP addresses in the policy, as shown in the following example,
The wildcard<ip-address> parameter allows a simpler search criterion. In the following example, the use of <.*> wildcard enables the ability to ping any address in the router 10 context, that is, any address in VRF 10:
| Note: While wildcards are available and allowed for all parameters in the OAM subtree, Nokia recommends that caution is exercised when using wildcards and limit their use to commands such as ping, traceroute, and mtrace. The use of wildcards in certain formats may be a security concern and result in making the IP addresses in the VRF, including the base routing table, unreachable. Or it could allow the customer to ping any IP address in the VRF, including the base routing table. This may be a potential security concern and should be avoided. |
For example, the following usage is not advised:
2.6.8.3. CLI Session Resource Management
SR OS has the capability to manage telnet/ssh sessions per user and at a higher level per system. At the system level, the user can configure a cli-session-group for different customer priorities. The cli-session-group is a container that sets the maximum number of CLI sessions for a class of customers, with a unique session limit for each customer. For example, as depicted in Figure 10, “Gold” category customers can have a cli-session-group that allows them more telnet/ssh sessions compared to “Silver” category customers.
Figure 10: cli-session-group for Customer Classes
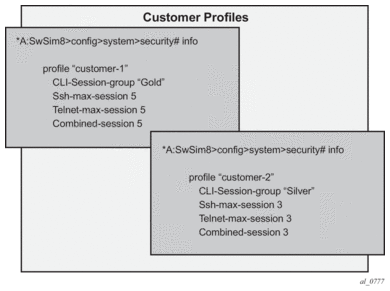
The configured cli-session-group can be assigned to user-profiles. At the user profile level, each profile can be configured with its own max ssh/telnet session and it will be policed/restricted by the higher order cli-session-group that is assigned to it.
As depicted in Figure 11, the final picture is a hierarchical configuration with top-level cli-session-groups that control each customer’s total number of SSH or telnet sessions and the user-profile for each user for that customer.
Figure 11: Hierarchy of cli-session-group Profiles
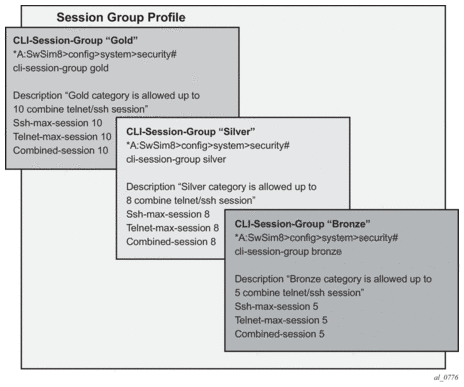
Every profile will subtract one from it’s corresponding max-session when a TELNET or SSH session is established in the following cases:
- where multiple profiles are configured under a user
- where multiple profiles arrive from different AAA servers (Local Profile, RADIUS Profile or TACACS Profile)
The first profile to run out of corresponding max-session will limit future TELNET or SSH sessions. In other words, while each profile for the user can have its independent max-session, only the lowest one will be honored. If the profile with the lowest max-session is removed, the next lower profile max-session will be honored and so on. All profiles for a user are updated when a TELNET or SSH session is established.
For information about login control, see Configuring Login Controls.
Use the following CLI commands to configure CLI session resources:
2.6.9. Configuring Users
Configure access parameters for individual users. For user, define the login name for the user and, optionally, information that identifies the user.
The following displays a user configuration example:
2.6.10. Configuring Keychains
The following displays a keychain configuration.
2.6.11. Copying and Overwriting Users and Profiles
You can copy a profile or user. You can copy a profile or user or overwrite an existing profile or user. The overwrite option must be specified or an error occurs if the destination profile or user name already exists.
2.6.11.1. User
The following output displays the copied user configurations:
| Note: The cannot-change-password flag is not replicated when a copy user command is performed. A new-password-at-login flag is created instead. |
2.6.11.2. Profile
The following output displays the copied profiles:
2.6.12. RADIUS Configurations
2.6.12.1. Configuring RADIUS Authentication
RADIUS is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled. The mandatory commands to enable RADIUS on the local router are radius and server server-index address ip-address secret key.
Also, the system IP address must be configured in order for the RADIUS client to work. See “Configuring a System Interface” of the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Router Configuration Guide.
The other commands are optional. The server command adds a RADIUS server and configures the RADIUS server’s IP address, index, and key values. The index determines the sequence in which the servers are queried for authentication requests.
On the local router, use the following CLI commands to configure RADIUS authentication:
The following displays a RADIUS authentication configuration example:
2.6.12.2. Configuring RADIUS Authorization
In order for RADIUS authorization to function, RADIUS authentication must be enabled first. See Configuring RADIUS Authentication.
In addition to the local configuration requirements, VSAs must be configured on the RADIUS server. See Vendor-Specific Attributes (VSAs).
On the local router, use the following CLI commands to configure RADIUS authorization:
The following displays a RADIUS authorization configuration example:
2.6.12.3. Configuring RADIUS Accounting
On the local router, use the following CLI commands to configure RADIUS accounting:
The following displays RADIUS accounting configuration example:
2.6.13. Configuring 802.1x RADIUS Policies
Use the following CLI commands to configure generic authentication parameters for clients using 802.1x EAPOL. Additional parameters are configured per Ethernet port. Refer to the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Interface Configuration Guide.
To configure generic parameters for 802.1x authentication, enter the following CLI syntax.
The following displays a 802.1x configuration example:
2.6.14. TACACS+ Configurations
2.6.14.1. Enabling TACACS+ Authentication
To use TACACS+ authentication on the router, configure one or more TACACS+ servers on the network.
Use the following CLI commands to configure profiles:
The following displays a TACACS+ authentication configuration example:
2.6.14.2. Configuring TACACS+ Authorization
In order for TACACS+ authorization to function, TACACS+ authentication must be enabled first. See Enabling TACACS+ Authentication.
On the local router, use the following CLI commands to configure RADIUS authorization:
The following displays a TACACS+ authorization configuration example:
2.6.14.3. Configuring TACACS+ Accounting
On the local router, use the following CLI commands to configure TACACS+ accounting:
The following displays a TACACS+ accounting configuration example:
2.6.14.4. Enabling SSH
Use the SSH command to configure the SSH server as SSH1, SSH2 or both. The default is SSH2 (SSH version 2). This command should only be enabled or disabled when the SSH server is disabled. This setting should not be changed while the SSH server is running since the actual change only takes place after SSH is disabled or enabled.
The following displays a SSH server configuration as both SSH and SSH2 using a host-key:
2.6.15. LDAP Configurations
2.6.15.1. Configuring LDAP Authentication
LDAP is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled. To use LDAP authentication on the router, configure one or more LDAP servers on the network.
TLS certificates and clients must also be configured. Refer to the “TLS” section of the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide for more information about configuring TLS.
Use the following CLI commands to configure LDAP:
The following displays an LDAP authentication configuration example:
2.6.15.2. Configuring Redundant Servers
Up to five redundant LDAP servers can be configured. The following examples show configuration of two servers, Server-1 and Server-5.
Configuration of Server-1:
Configuration of Server-5 (backup):
2.6.15.3. Enabling SSH
SSH must be enabled to use LDAP authentication. See Enabling SSH for more information.
2.6.16. Configuring Login Controls
Configure login control parameters for console, Telnet, and FTP sessions.
The following displays a login control configuration example: