The purpose of the SID Structure Sub-Sub-TLV is twofold:
-
Advertise the structure of the SRv6 SID used in the service, including the length of the Locator block, node, function and argument. This is important for future support of microSIDs and avoids overlapping issues with future values of the argument.
-
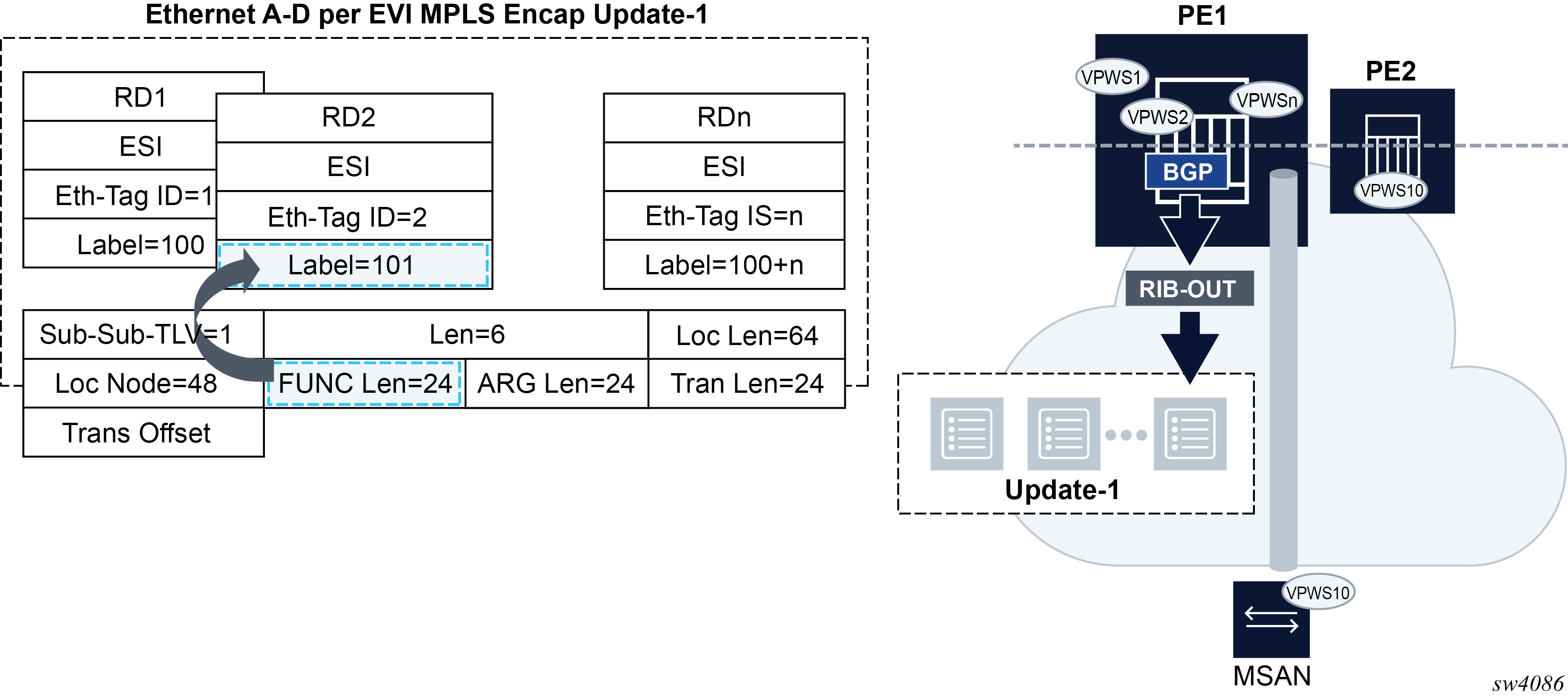
Support transposition procedures for efficient service route packing. The FUNCTION is transposed into the label field in the route’s NLRI. Because the rest of the SID is common for routes of the same type in the service, this transposition operation supports efficient packing of routes into the same BGP update.
Figure 1 shows how the FUNCTION part of the SID is transposed. SRv6 in Epipe services is not supported in Release 21.5, but the example illustrates how transposition works, and it would be similar for VPN-IP routes in Release 21.5.
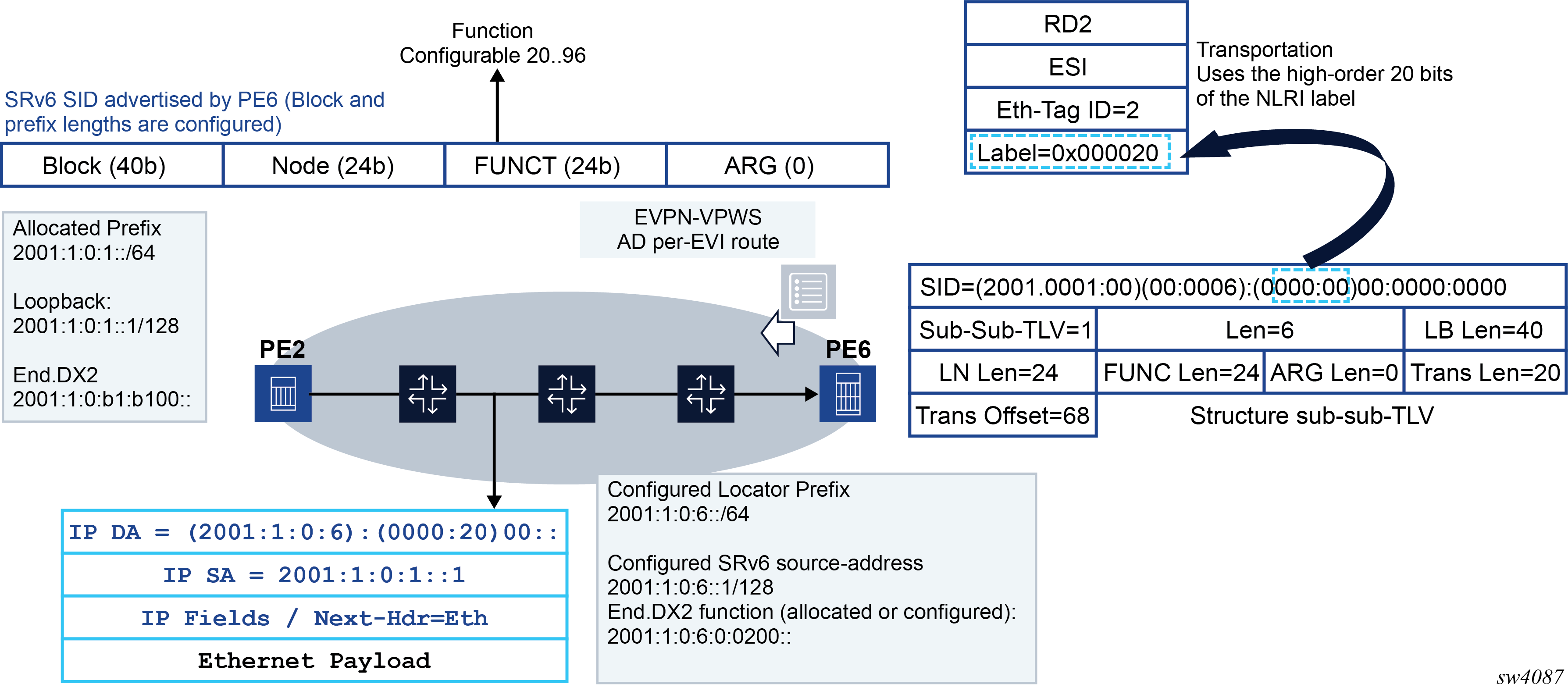
In the Figure 1 example, PE6 is configured with an Epipe that uses a configured locator with LB length = 40 bits and LN length = 24 bits. The FUNC length is set at 24, and 20 bits are always transposed into the NLRI (non-configurable). Based on the example in Figure 1, the following rules apply:
-
On reception, the router can build any SID out of the received route, irrespective of transposition, as long as the lengths are correctly encoded.
-
On transmission, the system performs a transposition for VPN-IP and EVPN service routes as follows:
-
If Function Length is greater than 20 in the Locator configuration, the function bits are put at the right-most bits of the L bits. For example, if LB LEN is 40 bits and the LN Len is 24 bits:
-
If Function Length = 20, the entire function is transposed into the label field, and the following is signaled in the route:
Length [LBL, LNL, FL, AL] : [40, 24, 20, 0]
TL:20, TO:64
*A:PE-4>config>router>segment-routing>srv6>locator# info ---------------------------------------------- shutdown block-length 40 termination-fpe 1 prefix ip-prefix cafe:1:0:4::/64 exit static-function max-entries 10 exit ---------------------------------------------- *A:PE-4>config>router>segment-routing>srv6>locator# no shutdown 3 2021/01/19 08:21:16.827 UTC MINOR: DEBUG #2001 Base Peer 1: 2001:db8::3 "Peer 1: 2001:db8::3: UPDATE Peer 1: 2001:db8::3 - Send BGP UPDATE: Withdrawn Length = 0 Total Path Attr Length = 102 Flag: 0x90 Type: 14 Len: 33 Multiprotocol Reachable NLRI: Address Family VPN_IPV4 NextHop len 12 NextHop 192.0.2.4 10.0.0.3/32 RD 192.0.2.4:20 Label 524254 Flag: 0x40 Type: 1 Len: 1 Origin: 0 Flag: 0x40 Type: 2 Len: 0 AS Path: Flag: 0x40 Type: 5 Len: 4 Local Preference: 100 Flag: 0xc0 Type: 16 Len: 8 Extended Community: target:64500:20 Flag: 0xc0 Type: 40 Len: 37 Prefix-SID-attr: SRv6 Services TLV (37 bytes):- Type: SRV6 L3 Service TLV (5) Length: 34 bytes, Reserved: 0x0 SRv6 Service Information Service Information sub-TLV Type 1 Type: 1 Len: 30 Rsvd1: 0x0 SRv6 SID: cafe:1:0:4:: SID Flags: 0x0 Endpoint Behavior: 0x14 Rsvd2: 0x0 SRv6 SID Sub-Sub-TLV Type: 1 Len: 6 BL:40 NL:24 FL:20 AL0 TL:20 TO:64 -
If Function Length = 32, part of the function is transposed into the label field, and the following is signaled in the route:
Length [LBL, LNL, FL, AL] : [40, 24, 20, 0]
TL:20, TO:76
-
*A:PE-4>config>router>segment-routing>srv6>locator# function-length 32 *A:PE-4>config>router>segment-routing>srv6>locator# info ---------------------------------------------- shutdown block-length 40 function-length 32 termination-fpe 1 prefix ip-prefix cafe:1:0:4::/64 exit static-function max-entries 10 exit ---------------------------------------------- *A:PE-4>config>router>segment-routing>srv6>locator# no shutdown 8 2021/01/19 08:27:09.318 UTC MINOR: DEBUG #2001 Base Peer 1: 2001:db8::3 "Peer 1: 2001:db8::3: UPDATE Peer 1: 2001:db8::3 - Send BGP UPDATE: Withdrawn Length = 0 Total Path Attr Length = 102 Flag: 0x90 Type: 14 Len: 33 Multiprotocol Reachable NLRI: Address Family VPN_IPV4 NextHop len 12 NextHop 192.0.2.4 10.0.0.3/32 RD 192.0.2.4:20 Label 524254 Flag: 0x40 Type: 1 Len: 1 Origin: 0 Flag: 0x40 Type: 2 Len: 0 AS Path: Flag: 0x40 Type: 5 Len: 4 Local Preference: 100 Flag: 0xc0 Type: 16 Len: 8 Extended Community: target:64500:20 Flag: 0xc0 Type: 40 Len: 37 Prefix-SID-attr: SRv6 Services TLV (37 bytes):- Type: SRV6 L3 Service TLV (5) Length: 34 bytes, Reserved: 0x0 SRv6 Service Information Service Information sub-TLV Type 1 Type: 1 Len: 30 Rsvd1: 0x0 SRv6 SID: cafe:1:0:4:: SID Flags: 0x0 Endpoint Behavior: 0x14 Rsvd2: 0x0 SRv6 SID Sub-Sub-TLV Type: 1 Len: 6 BL:40 NL:24 FL:32 AL0 TL:20 TO:76
-
-
The label field of the NLRI (VPN-IP and EVPN routes) encodes the FUNCTION that is dynamically or statically allocated for the service.
With the transposition procedure, multiple NLRIs with the same common SRv6 SID (minus the function) can be packed into the same BGP update, as is done for regular VPN-IP or EVPN route for MPLS tunnels. The packing benefit is illustrated in Figure 2.