VSR-NRC to NSP partial synchronization of TE database (TE-DB) and LSP database (LSP-DB) allows the VSR-NRC to send incremental TE-DB and LSP-DB records to the NRC-P when the CPROTO session flaps. Without this feature, a full synchronization of all records is performed each time the CPROTO session flaps which increases the convergence time of the NRC-P PCE.
With partial synchronization, VSR-NRC keeps track of the last record acknowledged by the NRC-P before the CPROTO session went down. When the CPROTO session is re-established, VSR-NRC sends only the records received from the network after the last acknowledged record.
Figure 1 illustrates the behavior of the partial synchronization of the TE-DB and LSP-DB.
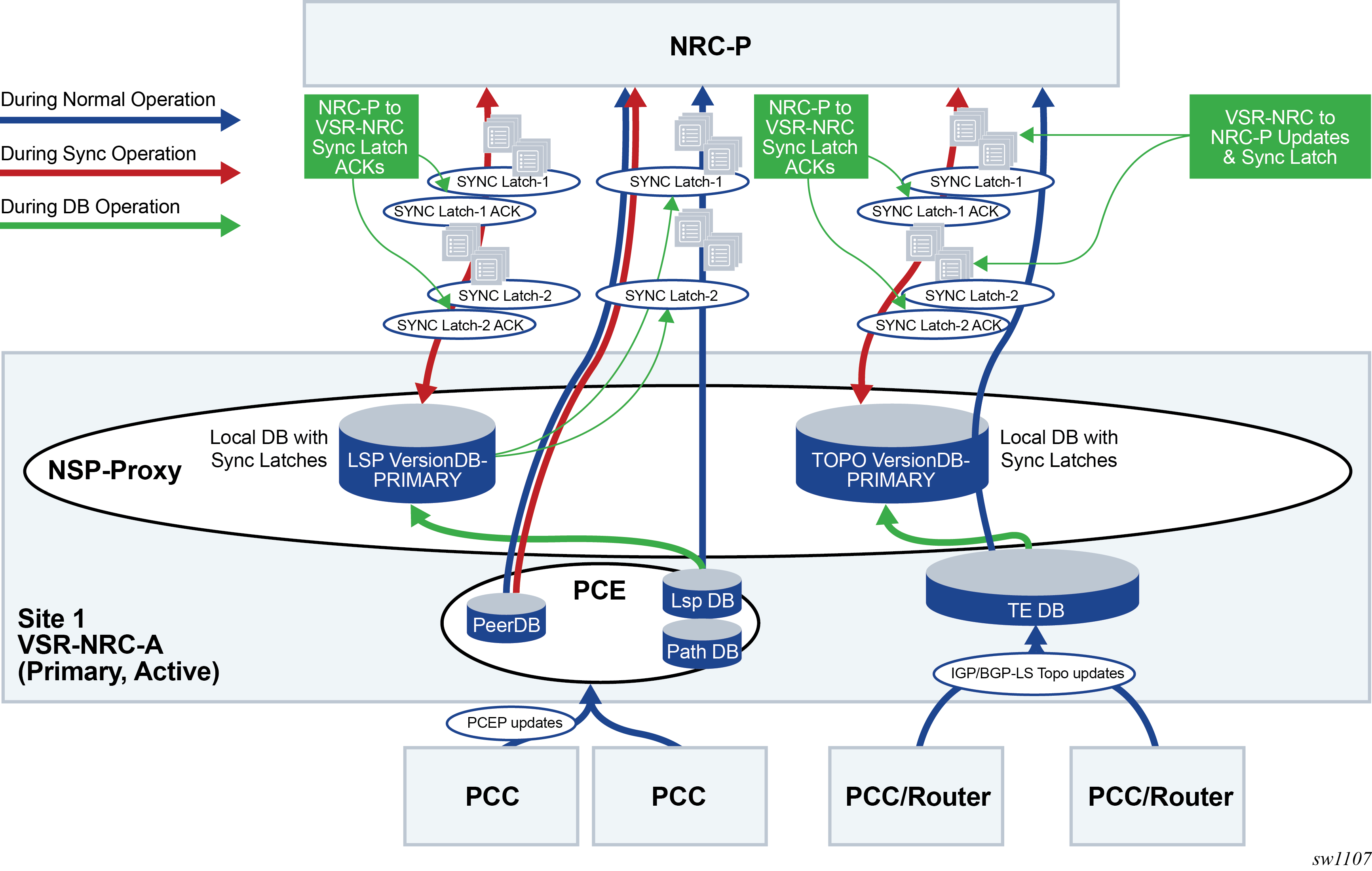
DB refers to the local TE-DB or LSP-DB maintained by the NSP-PROXY on the VSR-NRC.
The phrase Version-DB refers to the new copy of the same DB, TE-DB or LSP-DB, augmented with synchronization latches, and is used during the synchronization process to play back the records and latches to the NRC-P.
- Enhancements to DB maintenance in active VSR-NRC:
- The active VSR-NRC, VSR-NRC-A or VAR-NRC-B (see VSR-NRC 1+1 Redundancy), maintains a local copy of the database, referred to as Version-DB, for each record NSP-PROXY sends to NRC-P.
- Every 10 seconds, the NSP-PROXY also sends to NRC-P a message which contains a Latch Reference ID (LRID) only.
- The active VSR-NRC maintains a latch in Version-DB for each LRID sent to NRC-P. This latch is used to identify the start point for SYNC_START message processing based on the LRID received from NRC-P.
- Enhancements to active VSR-NRC and NRC-P DB synchronization:
- After opening a PCEP or a BGP_LS service channel, the NRC-P in the primary site sends a SYNC_START with an LRID (empty for full sync) to the active VSR-NRC (VSR-NRC-A or VSR-NRC-B).
- The NSP-PROXY on the active VSR-NRC begins sync with the NRC-P of the Version-DB records, which include saved interleaved synchronization latches, from LRID specified in SYNC_START. An empty SYNC_START means the full content of the Version-DB is played back to NRC-P.
- After processing all the records up to the specified LRID, NRC-P sends an acknowledgement of that LRID to NSP-PROXY using SYNC_ACK.
- After initial sync, the NSP-PROXY on the active VSR-NRC resumes sending records from the main DB and inserts every 10 seconds an LRID message between the records it sends to NRC-P. The same stream of records interleaved with LRID messages is saved in the local Version-DB.
- As in the initial synchronization phase, NRC-P acknowledges back an LRID to NSP-PROXY using a SYNC_ACK after the complete processing of all the records up to that LRID.
Figure 2 shows the enhancements to the CPROTO protobuf messages exchanged between VSR-NRC and NRC-P to provide full or partial synchronization of the TE-DB.
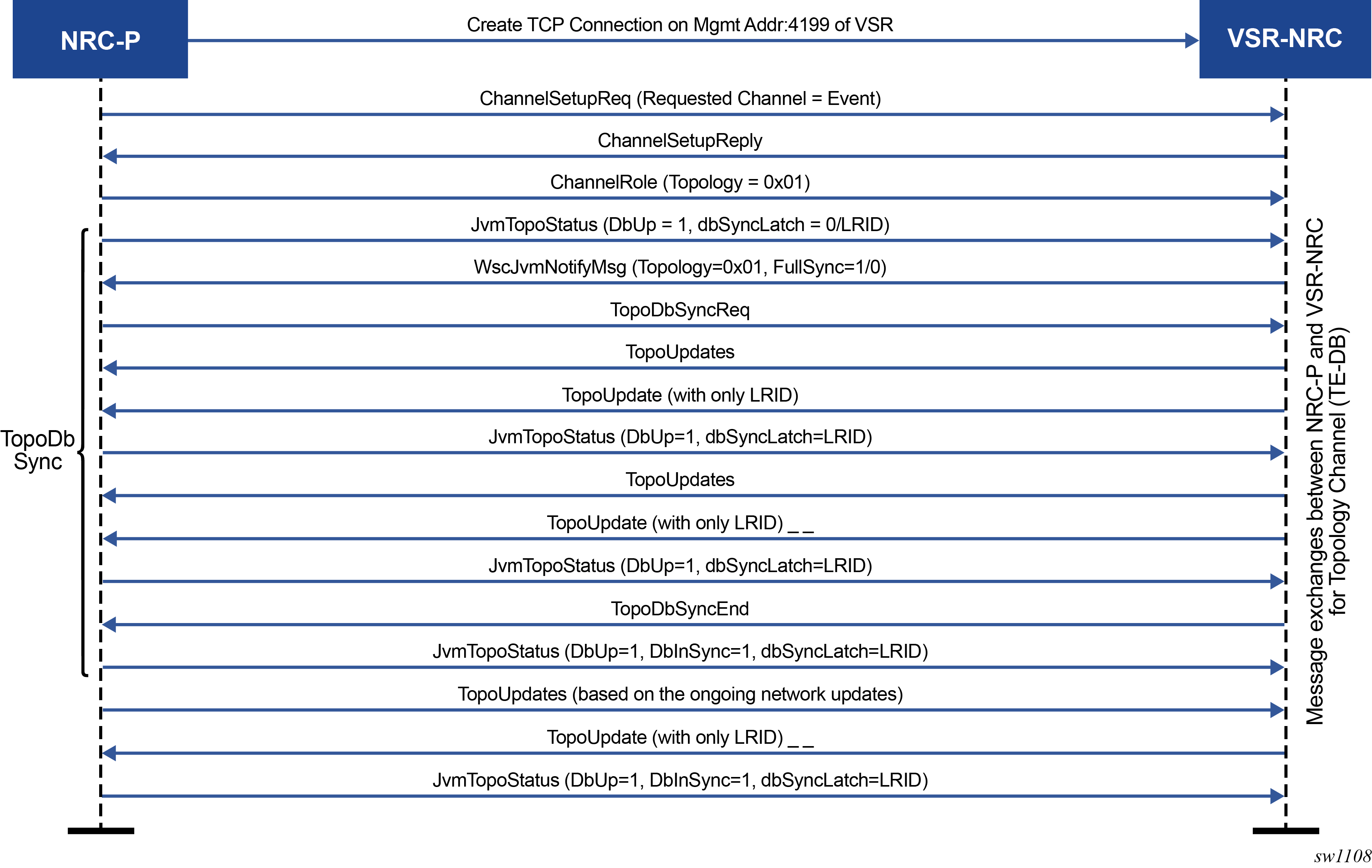

Figure 3 shows the enhancements to the CPROTO protobuf messages exchanged between VSR-NRC and NRC-P to provide full or partial synchronization of the LSP-DB.
