19. Statistics Collection Per Outer VLAN Tag
Statistics are collected per outer VLAN tag, regardless of the encapsulation. In QinQ environments this translates to statistics collection on VLANs, while in dot1q environments, statistics are gathered per C-VLAN (which is the only VLAN tag in the frame).
The following VLAN statistics are supported per direction (ingress or egress):
- the number of forwarded bytes per VLAN (aggregated IPv4 plus IPv6)
- the number of forwarded packets per VLAN (aggregated IPv4 plus IPv6)
In addition, the number of subscriber hosts under a specific outer VLAN tag is also counted.
Statistics collection per outer VLAN tag is supported only in the ESM context and is based on the subscriber queue and policer statistics. SAP queue statistics are excluded from the outer VLAN tag count. In ESM, in addition to subscriber queues, each SAP hosting a subscriber (or subscribers) may have queues associated with the default QoS SAP policy or a configured QoS SAP policy.
When policers are deployed on egress, traffic flowing through them is also traversing a queue or a queue group to which the policer is associated. Policers are always associated with a queue or a queue group. To avoid double counting, statistics must be gathered only from a single entity in the chain (a policer or the next queue), but not both. The following is a list of supported egress deployments with policers that produce accurate VLAN statistics collection with no double counting:
- policers that are attached to the default queue-group
- policers that are attached to a specific queue-group
- policers that are attached to the subscriber (local) queues. In this case, only policer statistics are included in VLAN statistics while the post-policer queue statistics are ignored. This also means that if traffic is sent directly to this queue without first going through a policer (for example, traffic mapped through an FC directly to a queue), this traffic is omitted from VLAN statistics.
- HQoS-managed policers that are attached to the queue group (default or a specific one). Traffic traversing HQoS-managed policers is accounted for in HQoS, while traffic traversing non-HQoS-managed policers is not included in HQoS-managed calculations. The queue groups must have the no queues-hqos-manageable command configured to avoid double counting.
The no queues-hqos-manageable command prevents HQoS from using the queue group statistics in its calculation, and therefore, avoids double counting.
Figure 241 displays an example of how egress statistics are used.
Figure 241: Egress Statistics in Relation to QoS Deployment Models
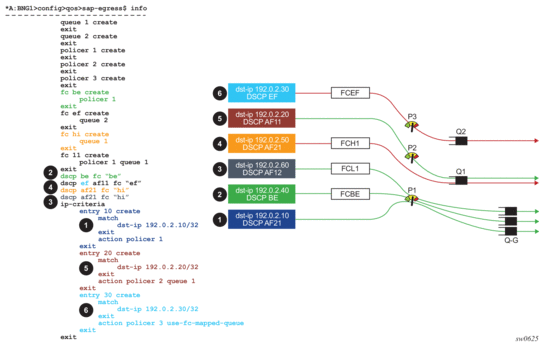
In Figure 241, the right side of the diagram represents traffic streams and their mapping to policers and queues according to the configuration statement shown on the left side. The four green lines represent traffic streams that are counted properly, and the two red lines represent the two streams that are counted incorrectly (they are either double counted, or not counted at all). The colored boxes numbered 1 through 6 represent a traffic stream with relevant classification fields. For example, the traffic stream in box 1 has the destination IP address set to 192.0.2.10 and DSCP value set to AF21.
- The dark blue traffic stream (box 1) is classified by IP criteria (dest-ip=102.0.2.10 in entry 10), which has a higher evaluation priority than classification using DSCP (DSCP=AF21). Traffic is matched directly to policer 1 and a default queue group after that, and not to queue 1 as DSCP=AF21 would suggest. Drops on the queue-group are reflected in forwarded statistics for policer 1.
- The green traffic stream (box 2) is not classified by IP criteria (dst-ip 192.0.2.40 is outside any configured entry in the IP criteria). Instead, this traffic is classified using DSCP=BE which is mapped to FC ‘BE’ and then to policer 1. In terms of statistics, this case is identical to the previous case (1).
- The grey traffic stream (box 3) is not classified by IP criteria (dst-ip 192.0.2.60 is outside any configured entry in the ip-criteria). Instead, this traffic is classified using DSCP=AF12 which is mapped to FC ‘l1’ and then to policer 1 followed by a local queue 1. In this case, only policer statistics are counted towards VLAN statistics. This is expected for accurate accounting (no double accounting).
- The orange (box 4) traffic stream is not accounted for in the VLAN statistics. Classification is performed based on DSCP=AF21 which is mapped to FC ‘h1’ and then to queue 1. For the purpose of VLAN statistics collection, counters on queue 1 in this example are not collected because this queue is an explicitly configured post-policer queue (both policer 1 and 2 are fed into this queue by explicit configuration). This excludes queue counters from being counted in the VLAN statistics. While this is the desired behavior when traffic is passed through a policer first, that is not the case here.
- The brown (box 5) traffic steam is classified by IP criteria (entry 20). Traffic is mapped to policer 2 and then to local queue 1. Similar to case 3, VLAN statistics are properly counted in this example. Drops on the queue 1 are reflected in forwarded statistics for policer 2.
- The light blue (box 6) traffic stream is classified by IP criteria (entry 30). Traffic is mapped to the policer 3 and the local post-policer queue which is derived from FC mapping (DSCP=EF to FC ‘ef’ to queue 2). This case is similar to dynamic policers. VLAN statistics are not counted properly, because the mapping between the policer and the post-policer local queue is not explicit using the configuration but instead it is implicitly derived using FC. As a result, double counting occurs.
19.1. Statistics Retention
The SR OS node preserves statistics from a subscriber even when the subscriber is disconnected, and the subscriber’s policers or queues are released. This prevents statistics fluctuation in relation to the subscriber’s presence and ensures that a statistic counter, once counted on a VLAN, remains accounted for during the life time of that VLAN, unless the VLAN stats are manually cleared by a clear command.
Reporting such absolute (or cumulative) counts in VLAN statistics allows smooth measurement of bandwidth per VLAN without dips caused by departing subscribers. The measurement is the difference in byte count between two consecutive stats polls, divided by the collection interval.
Sudden changes in bandwidth (the difference in byte count between two consecutive stats polls, divided by the collection interval) can arise only from a failed path to the subscriber (ports and access nodes) and this can be used to track per-VLAN failures in the network.
19.1.1. MIBs
VLAN statistics are provided in the form of a read-only MIB table for the currently- active VLANs.
The keys for the MIB table are the port ID (which can also be a LAG ID or PW port-ID) and SVLAN ID.
Once the VLAN is instantiated (either statically or through MSAP), an entry is created in the MIB table. Once the VLAN is no longer present in the system, it is automatically removed from the table.
Each VLAN can be queried through SNMP either directly or as an SNMP walk, in which case, all entries in the table are read.
The MIB table name is tmnxSubSvlanStatsTable and has the following format with up to 2000 tmnxSubSvlanStatsEntry entries. See Table 82.
Table 82: tmnxSubSvlanStatsEntry Objects
Entry Objects | |
Entry Keys Index | tmnxSubSVlanStatsPort The port ID |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsVlan The VLAN ID | |
Statistics | tmnxSubSVlanStatsLastCleared The most recent time when the stats were cleared |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsIngPkts The number of packets forwarded on ingress | |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsIngOctets The number of octets forwarded on ingress | |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsEgrPkts The number of packets forwarded on egress | |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsEgrOctets The number of octets forwarded on egress | |
tmnxSubSVlanStatsActiveSubHosts The number of subscriber hosts |
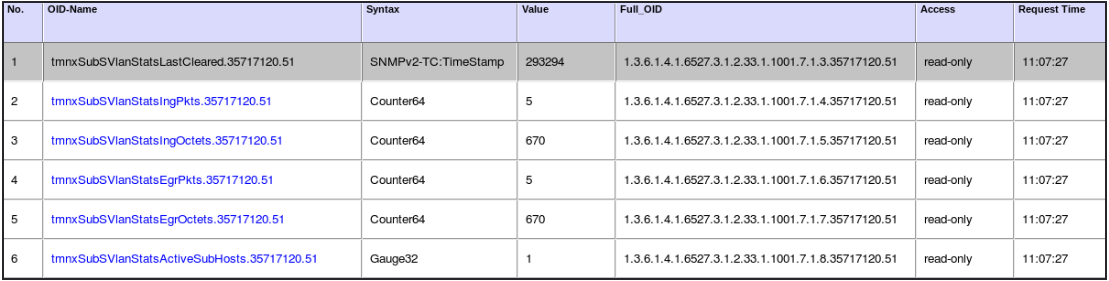
Figure 242 displays an example of output captured from an SNMP tool.
Figure 242: Output Captured from SNMP Tool
19.1.2. Enabling VLAN Statistics Collection
VLAN statistics collection is enabled by a configuration flag at a global level:
Once VLAN statistics collection is enabled, the MIB table is populated automatically with the current VLAN entries, up to the supported limit. This also means that online change (while subscribers are active) is supported for all subscribers that are currently active on the VLAN.