An Epipe service is the Nokia implementation of an Ethernet VLL based on the IETF "Martini Drafts" (draft-martini-l2circuit-trans-mpls-08.txt and draft-martini-l2circuit-encapmpls-04.txt) and the IETF Ethernet Pseudowire Draft (draft-so-pwe3-ethernet-00.txt).
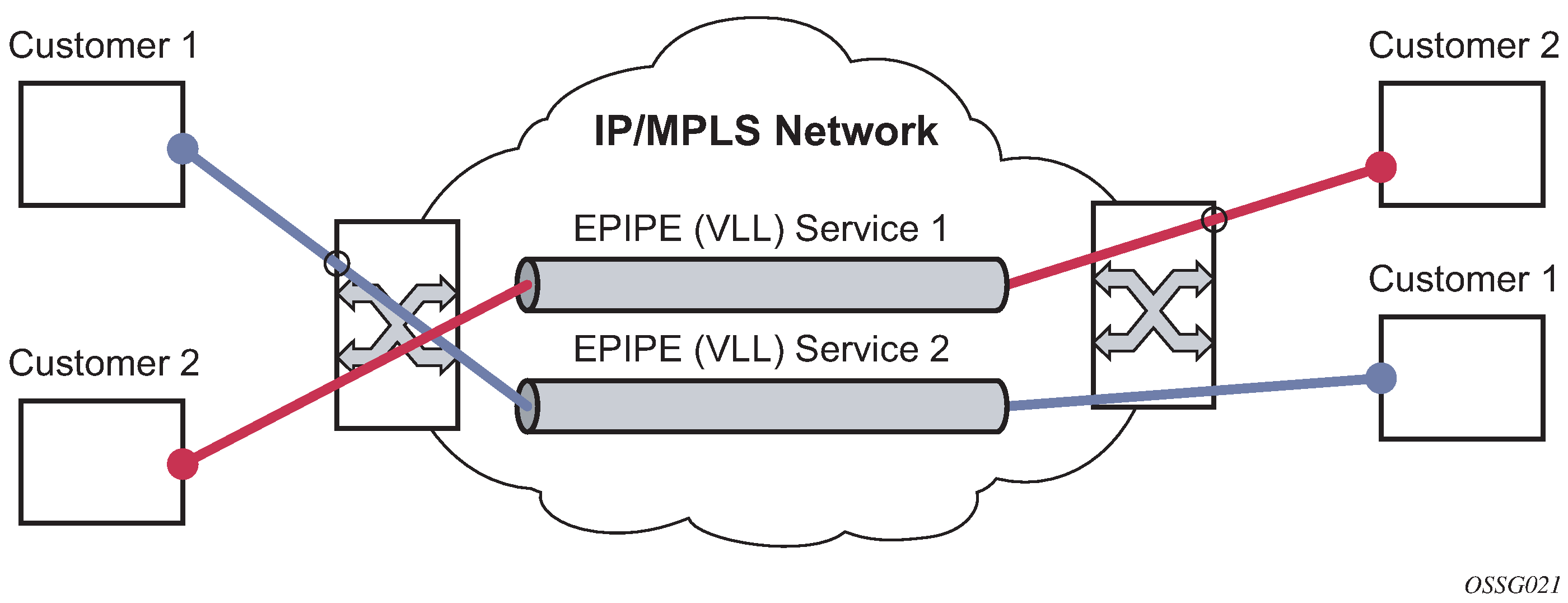
An Epipe service is a Layer 2 point-to-point service where the customer data is encapsulated and transported across a service provider IP, MPLS, or Provider Backbone Bridging (PBB) VPLS network. An Epipe service is completely transparent to the customer data and protocols. The Epipe service does not perform any MAC learning. A local Epipe service consists of two SAPs on the same node, whereas a distributed Epipe service consists of two SAPs on different nodes. SDPs are not used in local Epipe services.
Each SAP configuration includes a specific port or channel on which service traffic enters the router from the customer side (also called the access side). Each port is configured with an encapsulation type. If a port is configured with an IEEE 802.1Q (referred to as dot1q) encapsulation, a unique encapsulation value (ID) must be specified.