16. Dynamic Data Services
16.1. Introduction to Dynamic Data Services
Dynamic Data Services enables a zero-touch, single-ended provisioning model for business services. Two deployment models are available:
- With control channel: triggered by the authentication of a single or dual-stack PPPoE or IPoE session as a business CPE control channel, parameters are passed in a RADIUS Access-Accept or CoA message to set up a Layer 2 or Layer 3 data service.
- Without control channel: RADIUS or local authentication of a Dynamic Data Service data trigger provides the required parameters to set up a Layer 2 or Layer 3 data service.
Dynamic Data Services support includes:
- Epipe VLL services
- Epipe VLL services with dynamic MS-PWs (FEC 129) or spoke SDP
- EVPN based Epipe service
- VPLS services
- VPLS services with BGP-AD pseudowire
- VPLS service with spoke SDP or mesh SDP
- EVPN based VPLS service
- IES and VPRN services
- MVPN services
- Routing policy, filter, operational groups and OAM-PM provisioning
The full list of supported configuration commands can be displayed with the tools dump service dynamic-services command-list CLI command. Dynamic Data Service SAPs must be located on dot1q- or qinq-encapsulated Ethernet, anchoring or satellite ports and can be part of a LAG.
A Python script interface adds a flexible abstraction layer that reduces the OSS integration cost; only the business user specific service parameters, such as service type, IP address, QoS, and filter parameters, are required from RADIUS or local authentication. These parameters are then used in the Python script to generate a CLI template to set up the target Dynamic Data Service.
Dynamic Data Services configuration can be updated via a RADIUS CoA message.
Both XML accounting and RADIUS accounting for up to two different RADIUS destinations can be activated on a dynamic data service SAP.
16.2. RADIUS-Triggered Dynamic Data Services Associated With a PPPoE or IPoE Session as Control Channel
Refer to the “RADIUS-Triggered Dynamic Data Service Provisioning” section in the Advanced Configuration Guide for a detailed description.
16.3. Data-Triggered Dynamic Data Services
In the data-triggered dynamic data services model, as shown in Figure 194, any frame arriving on a dynamic data services capture SAP can result in RADIUS or local authentication. The dynamic data service is then created from a Python script that generates CLI snippets using parameters obtained from authentication.
Figure 194: Data-Triggered Dynamic Data Services
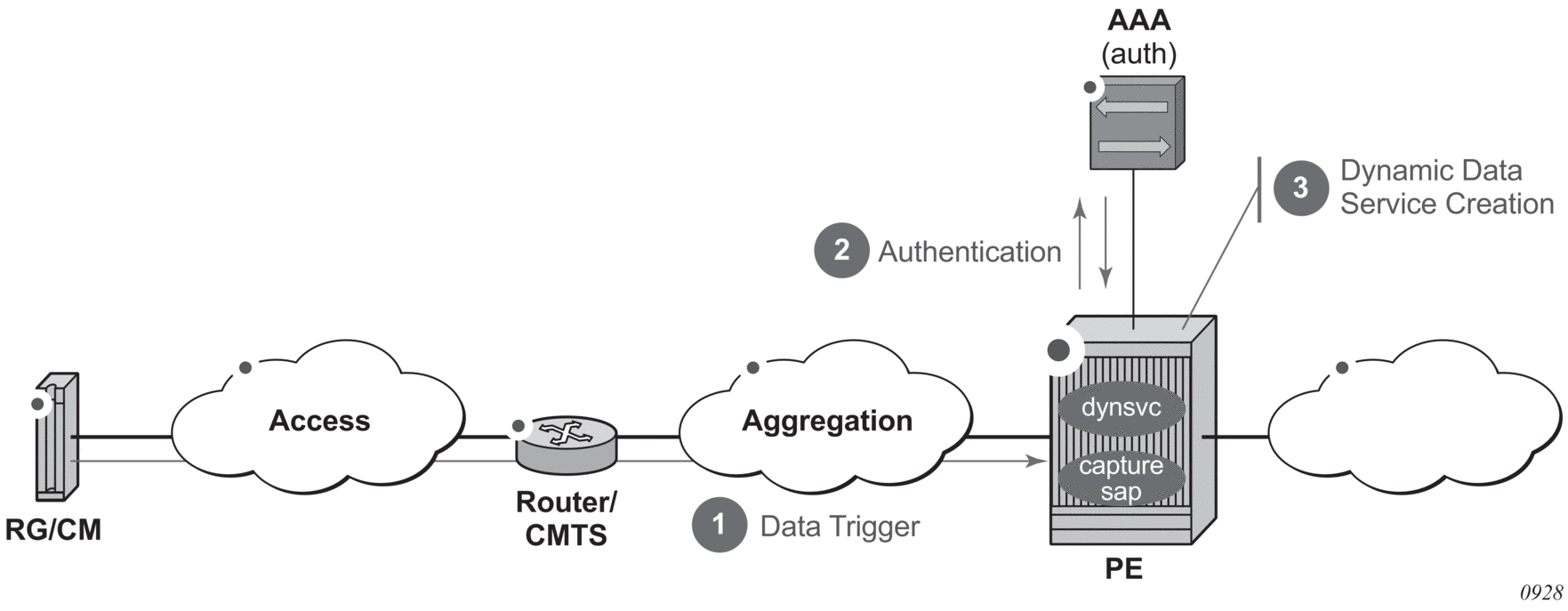
16.3.1. Data Trigger
A dynamic services data trigger is an object that is created when a frame received on a dynamic services capture SAP is sent to the control plane for authentication. A dynamic services data trigger is uniquely identified with its SAP ID. If the dynamic services data trigger was received on capture SAP x / y / z:*.* with outer-tag = a and inner-tag = b, then the dynamic service data trigger SAP ID is “x / y / z:a.b”. For each dynamic services data trigger, the following information is stored.
Table 54: Data Trigger Information
Data Trigger Information | Description |
Acct-Session-ID | The RADIUS accounting session ID for this dynamic services data trigger. This accounting session ID is used as accounting multi-session ID in RADIUS accounting for associated dynamic services. It can also be used as a key in CoA or Disconnect Messages to set up or terminate associated dynamic services. |
MAC | The MAC address learned to set up this dynamic service data trigger. The MAC address is included in the Access-Request message for RADIUS authentication. |
IP | The IPv4 or IPv6 address learned to set up this dynamic service data trigger. If the data trigger packet was not an IP packet, then this field is empty. When available, the IP address is included in the RADIUS authentication and accounting messages. |
State | The current state of the dynamic service data trigger: Pending: (initial state) data trigger received and authentication started Accepted: (transient state) authentication succeeded; dynsvc script started but not yet completed sapCreated: (final state) corresponding dynamic services SAP created |
The dynamic services data trigger information can be displayed as follows:
For a data-triggered dynamic data service to be successfully set up, a dynamic services SAP equal to the data trigger SAP ID must be created.
In the same way as the control channel model, multiple dynamic data services can be associated with a single dynamic services data trigger: up to 32 dynamic services during data trigger authentication or up to 4000 in total through CoA. When the dynamic services SAP that corresponds to a data trigger is deleted (teardown action), then all dynamic services associated with that dynamic services data trigger are deleted (teardown action).
16.3.2. Dynamic Services Data Trigger Capture SAP
In the same way as an Enhanced Subscriber Management (ESM) capture SAP is configured, a dynamic services data trigger capture SAP is configured in a VPLS service and captures frames for authentication. A dynamic service data trigger capture SAP does not forward traffic within the VPLS service, and no MAC learning occurs.
A VPLS capture SAP becomes a dynamic services data trigger capture SAP when a dynamic services policy is configured and the dynamic-services context is enabled (no shutdown). The dynamic services policy specifies the authentication mechanism to be used as detailed in the authentication sections below.
For example:
The trigger-packet type needs to be configured. A dynamic services data trigger capture-sap captures any valid Ethernet frames, including non-IP frames.
Valid dynamic services data trigger capture SAPs are:
- dot1q-encapsulated Ethernet, anchoring, satellite ports or LAGs
- sap x/y/z:*
- lag-x:*
- pxc-x.a:*
- esat-x/y/z:*
- qinq-encapsulated Ethernet, anchoring, satellite ports or LAGs:
- sap x/y/z:*.*
- sap lag-x:*.*
- sap x/y/z:tag.*
- sap x/y/z:*.tag
- sap lag-x:tag.*
- sap lag-x:*.tag
- pxc-x.a:*.*
- pxc-x.a:tag.*
- esat-x/y/z:*.*
- esat-x/y/z:tag.*
Enhanced Subscriber Management (ESM) and dynamic services data trigger cannot be enabled simultaneously on a single capture SAP: a no shutdown command of the dynamic-services CLI context is mutually exclusive when configuring an ESM trigger-packet type.
Use the following CLI commands to display capture SAP statistics:
- To display the number of data trigger packets forwarded to the CPM and dropped on the IOM:# show service id <service-id> sap <sap-id> sap-stats===============================================================================Service Access Points(SAP)===============================================================================--- snip ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------Sap Statistics-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Last Cleared Time : N/APackets OctetsCPM Ingress : 108 6696Forwarding Engine StatsDropped : 6144 405504
Table 55: Data Trigger Packets Forwarded/Dropped Counters
Counter
Description
CPM Ingress
Number of dynamic service data triggers received on the capture SAP that are forwarded to CPM
Forwarding Engine Stats Dropped
Number of dynamic service data triggers is received on the capture SAP that are dropped on IOM
- To display the dynamic services capture SAP control plane statistics (data triggers received and data trigger drop reason counters):# show service id 10 dynamic-services capture-sap 1/1/4:1214.* statistics===============================================================================Dynamic Services Capture SAP 1/1/4:1214.* Statistics===============================================================================Data packets received by SAP : 3-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Drop Reason Counters-------------------------------------------------------------------------------No policy configured at capture SAP level : 0No authentication configured in policy : 0Data-trigger already exists : 0Lockout is active : 0Reached data-trigger system limit : 0No memory available : 0Unsuccessful authentication : 1No data-trigger SAP-id in authentication : 0Corresponding dynamic SAP is not created : 0===============================================================================
Table 56: Data Triggers Received/Dropped Reason Counters
Counter
Description
Data packets received by SAP
Number of dynamic service data triggers received on the capture-sap that reached the CPM
No policy configured at capture SAP level
No dynamic services policy configured at the capture-sap; required to determine the authentication destination.
No authentication configured in policy
The authentication section in the specified dynamic services policy is missing or incomplete.
Data-trigger already exists
A new data trigger frame is received for an existing data trigger that is authenticated, but the corresponding dynamic SAP is not yet created. The new data trigger packet is dropped.
Lockout is active
The data trigger for this managed SAP is currently in a lockout state due to previous authentication failures.
Reached data-trigger system limit
The maximum number of dynamic service data triggers supported on the system is reached. Additional data triggers are dropped.
No memory available
There is not enough system memory available to process the data trigger.
Unsuccessful authentication
The authentication for a data trigger on this capture SAP failed or timed out.
No data-trigger SAP-id in authentication
The dynamic services data trigger SAP ID is not provided in authentication. This is a mandatory parameter.
Corresponding dynamic SAP is not created
The data trigger successfully authenticated but the corresponding dynamic SAP was not created. This is typically caused by a dynamic services script error.
- to clear the dynamic services capture SAP control plane statistics:# clear service id <service-id> dynamic-services capture-sap <sap-id> statistics
16.3.3. RADIUS Authentication
When a valid Ethernet frame is received on a dynamic services data trigger capture SAP, it is sent to the control plane for authentication. The dynamic services policy configured at the capture SAP specifies the RADIUS authentication parameters, as shown in the following example:
Local authentication and RADIUS authentication are mutually exclusive and cannot be configured simultaneously in a config>service>dynsvc>plcy>authentication context.
The server-policy CLI command references the config>aaa>radius-server-policy policy-name to be used for authentication.
The password CLI command specifies the password that is used in all RADIUS Access-Request messages.
RADIUS Access-Request Message Attributes specifies the attributes that are included in the RADIUS Access-Request message for dynamic services data triggers.
Table 57: RADIUS Access-Request Message Attributes
RADIUS Attribute | Description |
[1] User-Name | The username format for dynamic services data trigger authentication is fixed to nas-port-id (SAP). |
[2] Password | The password as configured in the authentication section of the dynamic-services-policy. |
[4] NAS-IP-Address | The outband management interface or system interface IPv4 address. Only included if the RADIUS server is reachable via an IPv4 address. |
[95] NAS-IPv6-Address | The outband management interface or system interface IPv6 address. Only included if the RADIUS server is reachable via an IPv6 address. |
[44] Acct-Session-Id | A unique accounting session ID (number format) per dynamic service data trigger. Included as [50] Acct-Multi-Session-Id in radius accounting for all dynamic services that are associated with this data trigger. |
[87] NAS-Port-Id | The dynamic service data trigger sap-id |
[32] NAS-Identifier | The system name of the router |
[26-6527-27] Alc-Client-Hardware-Addr | The MAC address of the data trigger frame that resulted in the authentication. Fixed format (xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) |
[8] Framed-IP-Address | The IPv4 source address of the IPv4 data trigger frame that resulted in the authentication. Not included if the data trigger frame is not an IPv4 packet. |
[26-6527-99] Alc-Ipv6-Address | The IPv6 source address of the IPv6 data trigger frame that resulted in the authentication. Not included if the data trigger frame is not an IPv6 packet. |
The attributes that must be returned in the Access-Accept message are the same as for RADIUS-triggered Dynamic Data Services associated with an IPoE or PPPoE session as a control channel.
16.3.4. Local Authentication
Local authentication is available for data-triggered dynamic services deployments where RADIUS is used for accounting and dynamic changes (CoA) but cannot provide the actual service provisioning parameters.
When a valid Ethernet frame is received on a dynamic services data trigger capture SAP, it is sent to the control plane for authentication. The dynamic services policy configured at the capture SAP specifies the local authentication parameters, as shown in the following example:
Local authentication and RADIUS authentication are mutually exclusive and cannot be configured simultaneously in a config>service>dynsvc>plcy>authentication context.
The local-auth-db CLI command references the local authentication database to be used for authentication, as shown in the following example:
A username is used as a key for a lookup in the local authentication database. The username format for dynamic service data triggers is fixed to the SAP ID of the data trigger. For each username entry (data trigger sap-id), multiple dynamic service SAPs can be specified (indexes). The index enables multiple dynamic service SAPs to be associated with a single dynamic service data trigger.
The following data can be specified for each index (dynamic service SAP) in a user-name entry:
- dynamic service sap-id (mandatory)The dynamic service SAP ID that is created. The SAP ID of one of the indexes must match the dynamic service data trigger sap-id.
- dynamic-services-policy dynsrv-policy-name (optional)Specifies the policy to use for setting up the dynamic service. If not specified, the policy provisioned at the dynamic service data trigger capture-sap is used.
- script-parameters (mandatory)Script parameters are used as input to the dynamic data service Python script. They are specified as four strings of up to 250 characters each. The concatenation of all four script parameter strings are passed to the Python script and must be formatted as function-key dictionary. The function-key specifies which Python functions is called, and dictionary contains the actual parameters in a Python dictionary structure format. The format should match the format of the [26-6527-165] Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params attribute when RADIUS authentication is used.
- accounting overrides (optional)For each of the two RADIUS accounting destinations, the stats-type and update-interval can be specified. These parameters override the configured value in the dynamic services policy:
- stats-type: specifies if dynamic service RADIUS accounting should be enabled or disabled. RADIUS accounting is enabled by specifying the statistics type: volume and time or time only. RADIUS accounting is disabled when no stats-type is specified.
- update-interval: specifies the time between each dynamic data service accounting interim update. The generation of interim accounting updates is disabled when no update-interval is specified.
A local authentication database can only be used to authenticate a dynamic service data trigger and provide parameters to set up associated dynamic services. The script action cannot be specified and is always set to “setup”.
The setup timeout for Access=Accept (CLI command: configure service dynamic-services timers setup-timeout access-accept timeout) also applies for local authenticated dynamic services.
16.3.5. Data-Triggered Dynamic Service Provisioning
Once authenticated, the mechanism to set up, modify, and tear down a data triggered dynamic service is the same as for RADIUS-triggered Dynamic Data Services associated with an IPoE or PPPoE session as a control channel.
The auto-provisioning of a data-triggered dynamic service is initiated by the RADIUS messages or local authentication as listed in Table 58.
Notes:
- Using the Nas-Port-Id as a key in a CoA or Disconnect-Message targets the corresponding dynamic services SAP; this also occurs when the Nas-Port-Id corresponds with the SAP ID of a data trigger.
- Using the Acct-Session-Id as a key in a CoA or Disconnect-Message targets:
- the corresponding dynamic services SAP if the Acct-Session-Id belongs to a dynamic services SAP that is not a dynamic services data trigger SAP
- the data trigger SAP if the Acct-Session-Id belongs to the dynamic services data trigger SAP
- In the event of a tear down, if the dynamic services SAP ID is a dynamic service data trigger SAP ID, all dynamic services associated with that dynamic services data trigger are also removed.
Table 58: Dynamic Service Script Actions
Action | Dynamic Service Script Action | Comments | |
Rx Access-Accept or local authentication (dynamic services data trigger authentication) | Setup | Up to 32 dynamic data services SAPs in a single message The dynamic services SAP that corresponds with the data trigger (also referred to as the dynamic services data trigger sap-id) must be part of this list. The Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action VSA is optional for RADIUS authentication. | |
Modify / Teardown | Not supported | ||
Rx CoA (Nas-Port-Id or Acct-Session-Id of a dynamic service SAP different from the data trigger) | Setup | Not supported | |
Modify | Only a single dynamic data service per message Mandatory VSAs: Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params | ||
Teardown | Tear down the dynamic service of the dynamic services SAP identified by the Acct-Session-Id or Nas-Port-Id. Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action VSA is mandatory | ||
Rx CoA (Nas-Port-Id of a data trigger) | Setup | Not supported. Nas-Port-Id always targets the dynamic services SAP and not the data trigger. | |
Modify | Only a single dynamic data service per message Mandatory VSAs: Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params | ||
Teardown | Tear down the dynamic service of the dynamic services SAP identified by the Nas-Port-Id. Because this is the data trigger SAP that is deleted, all dynamic services SAPs associated with the data trigger are also deleted. Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action VSA is mandatory | ||
Rx CoA (Acct-Session-Id of a data trigger) | Setup | Only a single dynamic service SAP per message When successful, the dynamic services SAP is associated with the data trigger identified by the specified Acct-Session-Id. Mandatory VSAs: Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params Alc-Dyn-Serv-Policy (if no “default” policy configured) | |
Modify | Only a single dynamic service per message Modify the dynamic service of the dynamic services SAP identified by the Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id. The dynamic services SAP must be associated with the data trigger identified with the specified Acct-Session-Id. Mandatory VSAs: Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params | ||
Teardown | Tear down the dynamic service of the dynamic services SAP identified by the Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id. The dynamic services SAP must be associated with the data trigger identified with the specified Acct-Session-Id. If the dynamic services SAP identified by the Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id is a data trigger sap, then teardown the dynamic services of all dynamic services saps associated with that data trigger Mandatory VSAs: Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action Alc-Dyn-Serv-SAP-Id | ||
Rx Disconnect Message (Nas-Port-Id or Acct-Session-Id of a dynamic service SAP different from a data trigger) | N/A | Tear down the dynamic service of the dynamic services SAP identified by the Acct-Session-Id or Nas-Port-Id | |
Rx Disconnect Message (Nas-Port-Id or Acct-Session-Id of a data trigger) | N/A | Tear down the dynamic services of all dynamic services SAPs associated with the data trigger identified by the Acct-Session-Id or Nas-Port-Id | |
A data-triggered dynamic service must be explicitly removed by one of the following:
- with a RADIUS Disconnect message containing the Acct-Session-Id or NAS-Port-Id as key
- with a RADIUS CoA message containing the Acct-Session-Id or NAS-Port-Id as key and Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Action VSA with value 3 (teardown)
- with a CLI clear command: clear>service>dynamic-services>data-trigger sap sap-idAll dynamic service SAPs associated with the dynamic services data trigger is removed.
- with a CLI tools command: tools>perform>service>dynamic-services> evaluate-script sap sap-id control-session acct-session-id action teardownThe control session accounting session ID corresponds to the dynamic services data trigger accounting session ID.
The removal of a dynamic service SAP that is a data trigger SAP results in the removal (teardown) of all dynamic service SAPs associated with that dynamic services data trigger.
To prevent a data-triggered dynamic service from being immediately set up again after it was removed (because traffic is still being received), the following procedures can be used:
- Authentication failure
- Update the configuration of the RADIUS server or local authentication such that the authentication for the dynamic service data trigger fails
- Tear down the dynamic service
- The dynamic service is not set up again because the data trigger authentication fails, resulting in a host-lockout when provisioned.
- VID filter on the capture-sap
- Add the data trigger encapsulation to a VID filter (ingress MAC filter of type vid) that is applied on the data trigger capture-sap
- Tear down the dynamic service
- The dynamic service is not set up again because the data trigger is now dropped by the VID filter applied on the capture-sap
16.3.6. Control Plane Protection
As a dynamic services data trigger capture-saps potentially forward all valid Ethernet frames for authentication to the control plane, control plane protection mechanisms are required to prevent overload conditions.
- capture-sap data trigger packet throttling (frames dropped at IOM)The number of data trigger packets sent to the control plane via the ingress forwarding complex is rate-limited based on a hash using the sap ID, outer tag, and inner tag as the key. The per-hash result is that a maximum of 1 frame is forwarded to the control plane.This throttling mechanism is always enabled and has no configuration options. It guarantees fairness between different encapsulation while limiting the frame rate sent to the control plane.
- Blocking certain VLANs from authenticating (frames dropped at the IOM)This can be achieved by applying ingress MAC filters of type VID with the capture-sap command. In the example below, frames with encap 1/1/4:1214.20 is dropped by the VID filter.configureservicevpls <service-id> customer <customer-id>sap 1/1/4:1214.* capture-sapdynamic-servicesdynamic-services-policy <dynsvc-policy-name>no shutdownexitingressfilter mac 10exitexitexitexitfiltermac-filter 10 createdefault-action forwardtype videntry 10 creatematch frame-type ethernet_IIouter-tag 20 4095exitactiondropexitexitexitexit
- Dynamic service data trigger rate limiting in the control plane (frames dropped at the CPM)An overall rate limit of dynamic service data triggers limits the number of frames that come from the different IOMs to an acceptable rate for the control plane to handle.Control plane rate-limiting for dynamic service data triggers is always enabled and has no configuration options.
- Using a lockout mechanism to protect the RADIUS infrastructure from overload because of permanent failing authentications of Python script errors.The existing Enhanced Subscriber Management (ESM) host lockout mechanism can be enabled on a dynamic services data trigger capture-sap.The dynamic services data trigger sap-id is used as a key for the host-lockout context. A host-lockout context is created whenever a data trigger is deleted:
- Authentication failures: RADIUS Access Reject, RADIUS Access-Accept with a wrong or missing data trigger SAP ID, timeout, local authentication lookup failure, local authentication returns a wrong or no data-trigger sap-id.
- No data trigger SAP created within the configured dynamic services access-accept setup timeout (30 seconds by default):configure service dynamic-services timers setup-timeout access-accept <timeout>
- A dynamic services Python script failure
- A clear command on a data trigger:clear service dynamic-services data-trigger sap <sap-id>
- A tear down of a data trigger initiated via a CoA or Disconnect Message
The last two bullets are tear down operations that occur infrequently and should not result in an actual lockout; only the host lockout context is created and should disappear again when the lockout-reset-time expires. This is configured in the host-lockout-policy:configure subscriber-mgmt host-lockout-policy <policy-name> lockout-reset-time<seconds> (default 60 seconds).To enable host lockout for dynamic services data trigger, configure a host-lockout-policy at the dynamic services data trigger capture-sap:configure servicevpls <service-id> customer <customer-id>sap <sap-id> capture-sapdynamic-servicesdynamic-services-policy <dynsvc-policy-name>no shutdownexithost-lockout-policy <policy-name>exitexitThe host-lockout-policy is configured in the config>subscr-mgmt CLI context. For data-triggered dynamic services, the host-key in the policy must be set to all which is achieved with the no host-key CLI command (default). Configuring the host key to mac in a host lockout policy associated with a dynamic service data trigger capture-sap is a configuration error and results in a faulty host lockout behavior.Use the following show command to display active dynamic services data trigger capture SAP lockouts (the capture SAP must be used as the sap-id):# show subscriber-mgmt host-lockout-policy "host-lockout-1" all sap 1/1/4:1214.*===============================================================================Host Lockout Policy "host-lockout-1"===============================================================================Description Host lockout policyLast Mgmt Change 01/25/2016 16:37:47Lockout time min 10Lockout time max 3600Lockout reset time 60Max lockout hosts 100Host key all-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Active Lockouts for SAP: 1/1/4:1214.*===============================================================================circuit-id/ elapsed current elapsed next nrmac/ reset lock lock lock ofremote-id time (s) time (s) time (s) time (s) lockouts-------------------------------------------------------------------------------:1214.101 0 10 1 20 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Nr of active lockouts 1Nr of lockouts in grace period 0Nr of total lockouts: 1-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Totals for Host Lockout Policy "host-lockout-1"-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Nr of active lockouts 1Nr of lockouts in grace period 0Nr of total lockouts: 1===============================================================================Use the following command to clear active dynamic services data trigger capture SAP lockouts (the capture SAP must be used as the sap-id):# clear subscriber-mgmt host-lockout-policy [policy <host-lockout-policy-name>] <lockout-state># clear subscriber-mgmt host-lockout-policy sap <sap-id> [lockout-state] - Use the cpu-protection and dist-cpu-protection commands on the platforms that support it.When using the cpu-protection command, a cpu-protection policy-id is needed to apply on the capture SAP.configuresystemsecuritycpu-protectionpolicy 200 createoverall-rate 100out-profile-rate 50exitexitexitexitservicevpls <service-id> customer <customer-id>sap 1/1/1:*.* capture-sap createcpu-protection 200dynamic-servicesdynamic-services-policy "dynServPolicy"no shutdownexitno shutdownexitexitexitWhen using the dist-cpu-protection command, a dist-cpu-protection policy-id is needed to apply on the capture SAP.configuresystemsecuritydist-cpu-protectionpolicy "distCpuProt" createstatic-policer "dcpuStatPol" createrate packets 50 within 1exceed-action discarddetection-time 5exitprotocol all-unspecified createenforcement static "dcpuStatPol"exitexitexitexitexitservicevpls <service-id> customer <customer-id>sap 1/1/1:*.* capture-sap createdynamic-servicesdynamic-services-policy "dynServPolicy"no shutdownexitdist-cpu-protection "distCpuProt"no shutdownexitexitexit
16.3.7. Debugging
To enable dynamic services data trigger debugging, use the following debug commands:
During debugging, the system logs data trigger events such as:
- data trigger received
- data trigger authentication events
- data trigger SAP created
- dynamic service SAP created
- dropped data trigger with drop reason such as data trigger already exists or lockout active
The encap-val command limits the debug output to data trigger events for specific encapsulation values.
The mode specifies which data trigger events are logged: all events or dropped data trigger events only.
16.4. Dynamic Data Services Python API
Table 59 describes the functions available in the SR OS alc.dyn Python module to create dynamic data services.
Table 59: Dynamic Data Services Functions in the alc.dyn Module
alc.dyn functions | Description |
dyn.action (dictionary) | Executes the setup, modify or teardown function that is found with a lookup in the specified dictionary using the function-key present in the script parameters. The script-parameters can be obtained from RADIUS in the Alc-Dyn-Serv-Script-Params VSA or can be configured in the local authentication database. The action (setup, modify or teardown) is determined from the Alc-Dyn-Script-Action VSA. Returns: None (no value) dictionary - Python dictionary with format: dictionary = {function-key-1 : (setup-function-1, modify-function-1|None, revert-function-1|None, teardown-function-1), …, function-key-n : (setup-function-n, modify-function-n|None, revert-function-n|None, teardown-function-n) } where:
|
dyn.add_cli (string) | Executes the specified CLI commands to create the dynamic data service Returns: None (no value) string - CLI commands. The string can span multiple lines in the script when enclosed in three double quotes ("""). |
dyn.get_circuit-id() | Returns a string containing the control channel circuit-id (DHCP relay agent option 82 or PPP tags) |
dyn.get_remote-id() | Returns a string containing the control channel remote-id (DHCP relay agent option 82 or PPP tags) |
dyn.get_sap() | Returns a string containing the dynamic data service sap id: the value of the Alc-DynServ-SAP-Id VSA. A wildcard hash (#) in the VSA value is replaced with the corresponding control channel or data trigger port or vlan id field. |
dyn.reference (function-key, reference-id, dictionary) | Create a dynamic reference to another function in the script. Typically used to create n:1 relations between dynamic data services, such as multiple SAPs in a VPLS service or multiple services for the same customer. Dynamic referencing is only allowed in setup functions. Corresponding teardown functions will automatically dereference. Returns a dictionary provided by the setup script matching the function-key: function-key - key in the action dictionary (see dyn.action) to find the corresponding setup or teardown functions. reference-id - unique reference ID string that identifies the dynamic reference (for example, all SAPs from a VPLS service would have the same reference id). dictionary - a Python dictionary containing parameters for use in the setup or teardown function, such as to generate CLI output. |
dyn.select_free_id (type) | Returns a string representing a free identifier of the specified type. type - identifier type that will be returned:
The corresponding filters will be shown in the system as “_tmnx_dyn_<number>” |