PW port based traffic is subject to a number of MTU checks, some of which depend on the tunnel type and signaling method. Downstream traffic (toward the remote end of the tunnel) is forced through several MTU checks in the data plane, and an MTU size violation can cause fragmentation or a packet drop. Other MTU checks are performed only in the control plane.
In TLDP tunnels, the service MTU is negotiated through signaling in the control plane where values on both sides of the tunnel must match, otherwise, the tunnel fails to transition into an operational state.
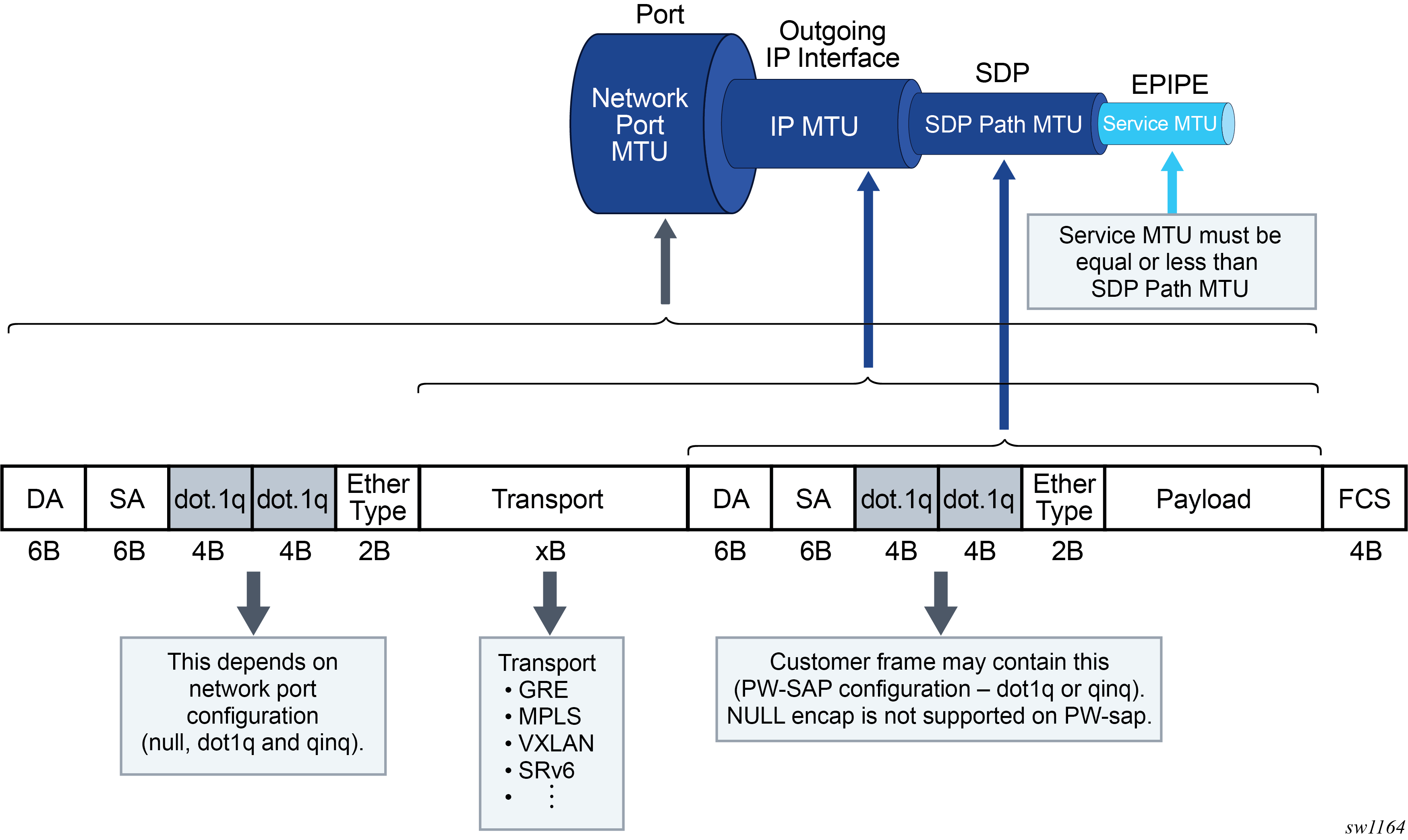
A generic SDP-based tunnel (such as a L2oGRE or TLDP GRE/MPLS tunnel) under an Epipe service has the following configurable MTUs:
- Port MTU represents the maximum frame size on the outgoing physical port. This is configured under the physical port and is enforced in the data plane.
- IP MTU is the maximum IP packet size on the outgoing IP interface. This is configurable under an IP interface and is enforced in the data plane.
- SDP path MTU represents the maximum size of the frame that is encapsulated within the tunnel (excluding the transport header). Its value is determined based on the smallest MTU size on the path between the endpoints of the tunnel. In SR OS, this SDP path MTU is calculated automatically by subtracting the size of the transport header from the configured IP MTU of the outgoing interface. This is configurable under the SDP and is enforced in the data plane.
- Service MTU indicates the maximum frame size of the customer payload that can be
transmitted over the service. Its value is determined by the MTU size within the
customer’s network. The service MTU is significant because it can customize the size
of the customer’s payload independently of the MTUs in the transport network. The
service MTU is negotiated using signaling and must match on both sides of the
tunnel. This MTU is not enforced in the data plane.
The service MTU is configured under the Epipe service, which is also the basic configuration construct used for FPE-based PW ports. Hence, the service MTU configured under the Epipe service also applies to FPE-based PW ports.
However, fixed PW ports (bound to a fixed port) are not configured under an Epipe service and therefore the service MTU configuration under the Epipe is inaccessible. Fixed PW ports are stitched to the tunnel within the SDP context with the configure service sdp binding command. This requires a separate configuration for the service MTU. Considering that fixed PW ports support only TLDP-signaled MPLS and GRE pseudowires in which the service MTU is advertised from each endpoint of the pseudowire, the adv-service-mtu command signals the service MTU for fixed PW ports.
Classic CLI
>config>service# info
----------------------------------------------
sdp 1 mpls create
far-end 10.20.1.3
ldp
binding
port lag-1
pw-port 1 vc-id 10 create
[no] adv-service-mtu <1..9782>
no shutdown
exit
MD-CLI
[gl:configure pw-port 1]
sdp 1 {
admin-state enable
vc-id 10
adv-service-mtu 1514
}