The NISH manager is an optional Linux service that provides the NISH client with a dynamic inventory of the SR OS nodes that can be managed. It correlates information about the nodes that are available. The following figure shows the inventory communication flow for the NISH client when used in conjunction with a NISH manager in a BNG CUPS deployment with two CPF nodes and three UPF nodes.
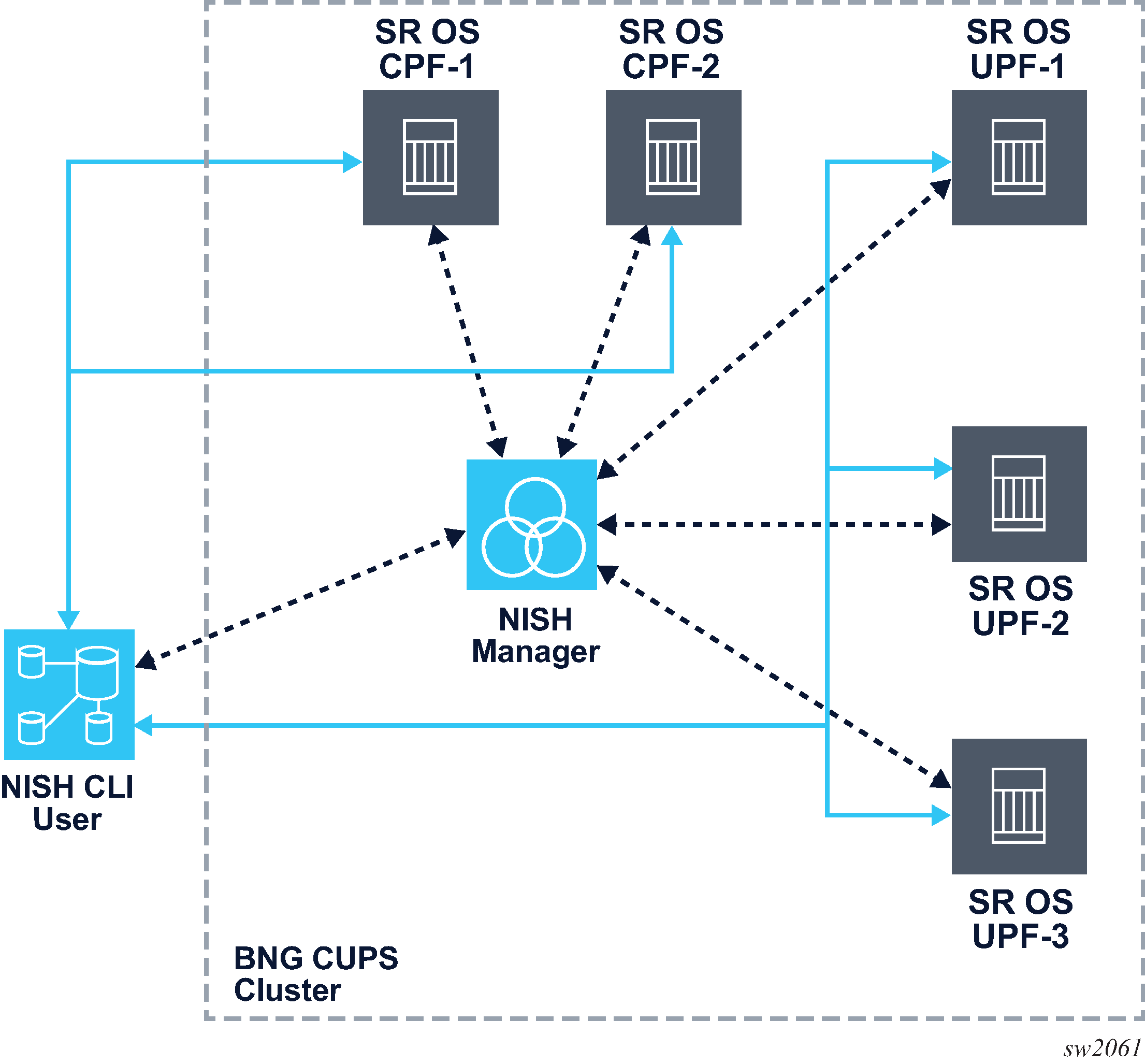
Communication with the NISH manager
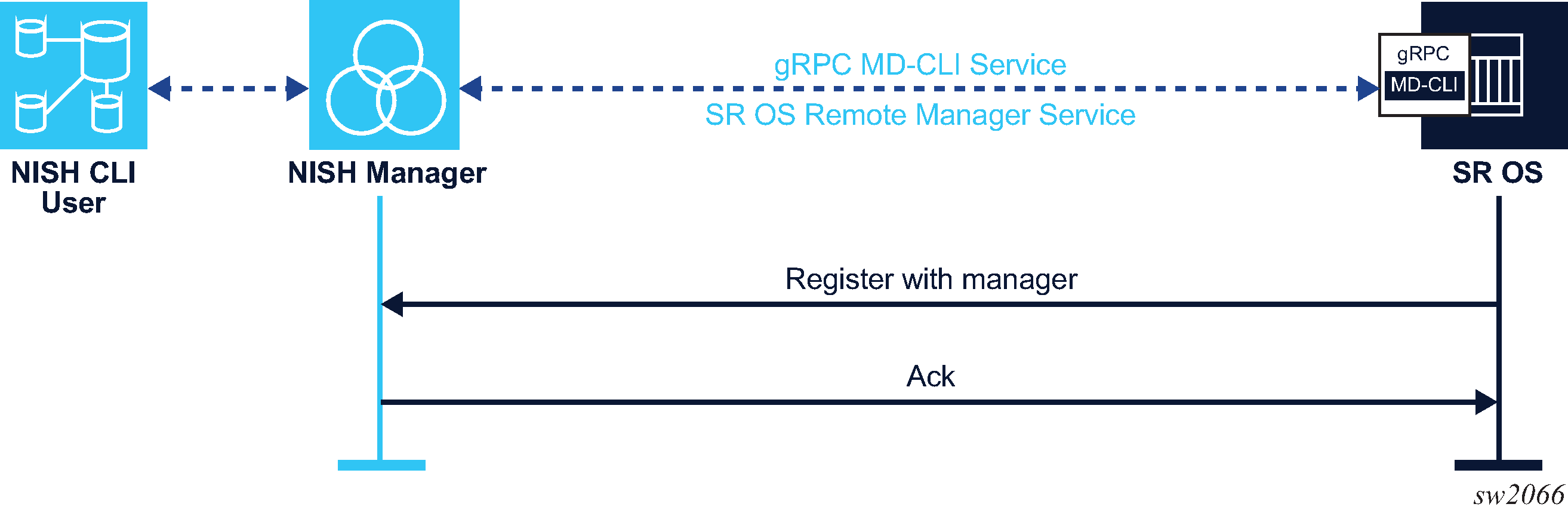
SR OS nodes register with the NISH manager when configured to do so through the SR OS remote management feature. The following figure shows the SR OS remote management communication with the NISH manager.
See the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide, section ‟Remote Management Using a Remote Network Interface Shell Manager” for more information about the SR OS remote management feature.
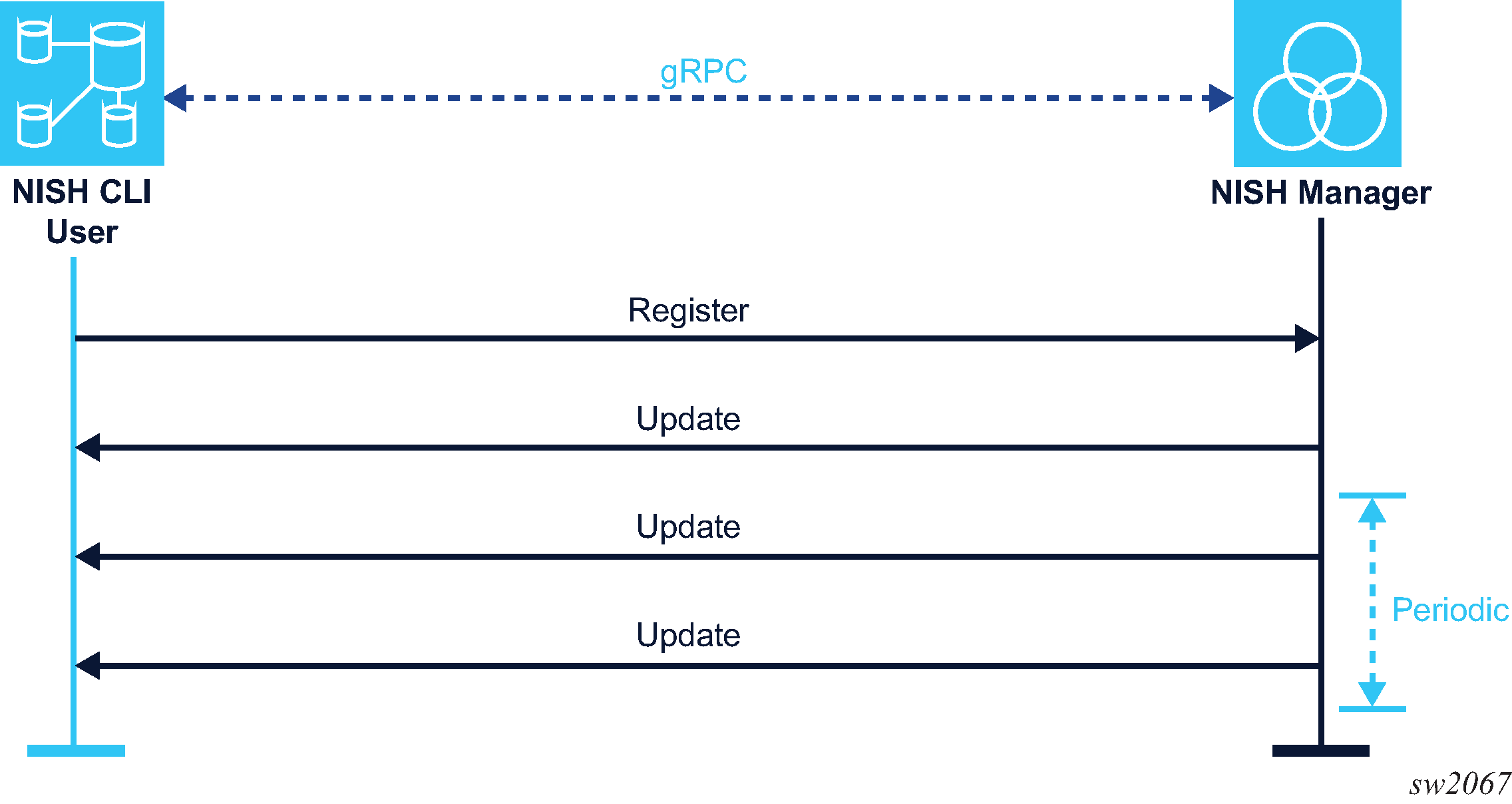
When a NISH client is started in manager mode, it registers with the NISH manager. The NISH manager provides the details of the available SR OS nodes to the NISH client, including names, device labels, and IP address and port information.
The following figure shows the NISH client communication with the NISH manager.
The NISH manager runs as a standalone application in the foreground or background of the Linux shell or as a systemd service on the CentOS 7 Linux distribution. Using user-specified IP address and port combinations, the NISH manager listens for connections from the NISH client and the SR OS nodes that are configured with the SR OS remote management feature. By default, the NISH manager listens on all available IP interfaces and on the default gRPC port (57400).
The NISH manager does not make any outbound connections to the SR OS nodes or to the NISH client, although it does respond to both.
SR OS node state transitions in the NISH manager
When an SR OS node registers with the NISH manager, its state in the database of the NISH manager is up.
If the NISH manager misses the specified number of consecutive hello messages from the SR OS node, the state of the node transitions to stale in the database. Stale nodes appear in the NISH client but are not usable.
When the specified retention interval has passed, an SR OS node in the stale state transitions to the down state in the NISH manager database. The NISH manager removes SR OS nodes in the down state from its database immediately. Nodes in the down state are not shown.
If the number of hello messages is not configured, is set to 0, or the SR OS node does not support the state transition functionality, nodes transition from the up to the down (deleted) state when the specified retention interval has passed. They do not transition through the stale state.
To set the number of hello messages and the retention interval, see Command options and NISH manager configuration files.