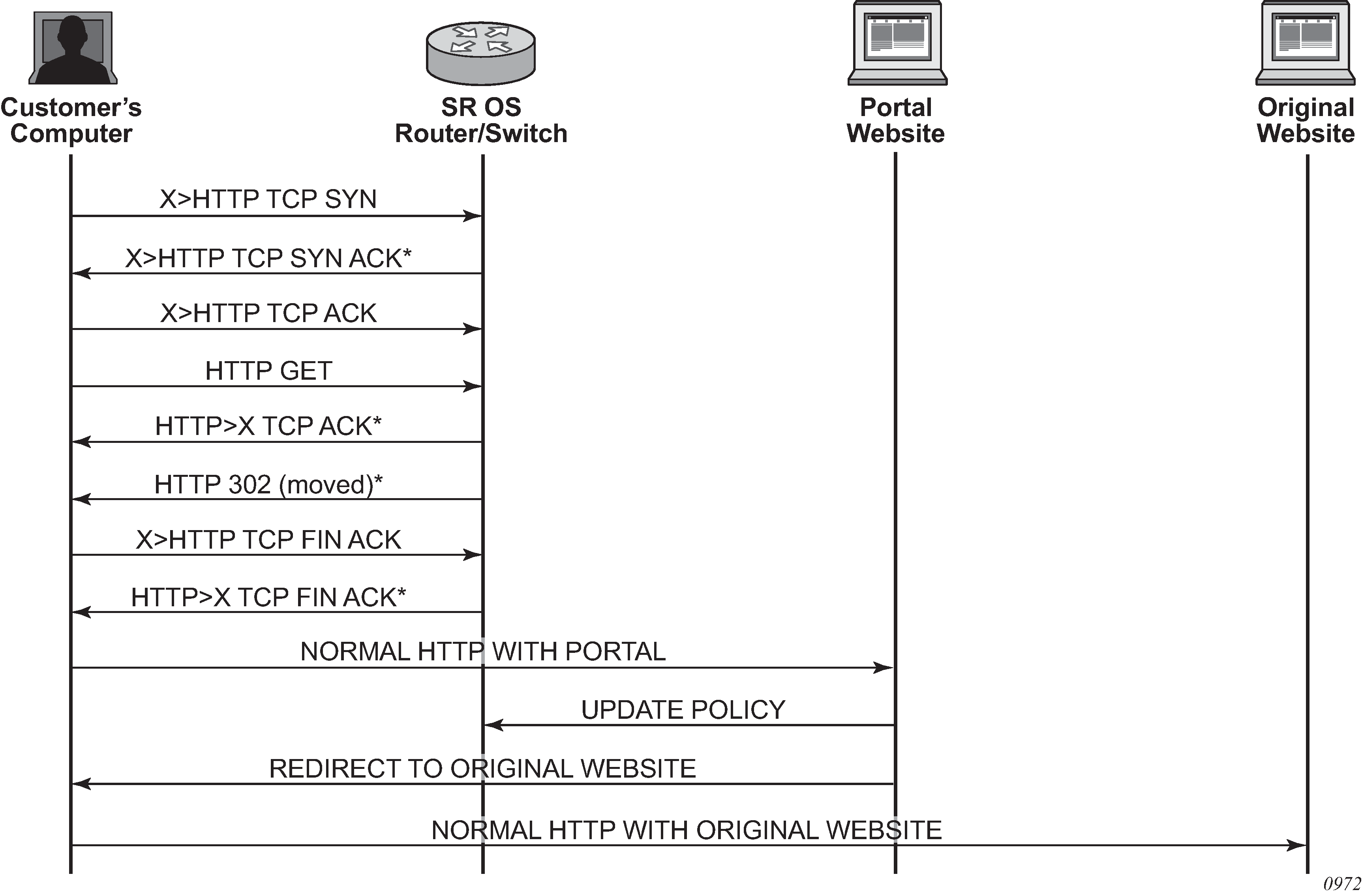
The following example provides a brief scenario of a subscriber connecting to a new network, where it is required to authenticate or accept the network terms of use, before getting access to Internet:
The subscriber typically receives an IP address upon connecting to the network using DHCP, and is assigned a filter policy to redirect HTTP traffic to a web portal.
The subscriber HTTP session TCP traffic is intercepted by the router. The CPM completes the TCP three-way handshake on behalf of the destination HTTP server, and responds to the HTTP request with an HTTP 302 ‟Moved Temporarily” response. This response contains the URL of the web portal configured in the filter policy.
Upon receiving this redirect message, the subscriber web browser closes the original TCP session, and opens a new TCP session to the redirection portal.
The subscriber can now authenticate or accept the terms of use. After, the subscriber filter policy is dynamically modified.
The subscriber can now connect to the original Internet site.