In global SID index range mode of operation, the resulting ILM label value is the same across the IGP instances. The router programs ILM/NHLFE for the prefix of the winning IGP instance based on the RTM route-type preference. The router logs a trap and generates a syslog error message, and does not program the other prefix SIDs in the datapath.
In the per-instance SID index range mode of operation, the resulting ILM label has different values across the IGP instances. The router programs ILM/NHLFE for each prefix as expected.
The following figure shows an IS-IS example of handling in case of a global SID index range.
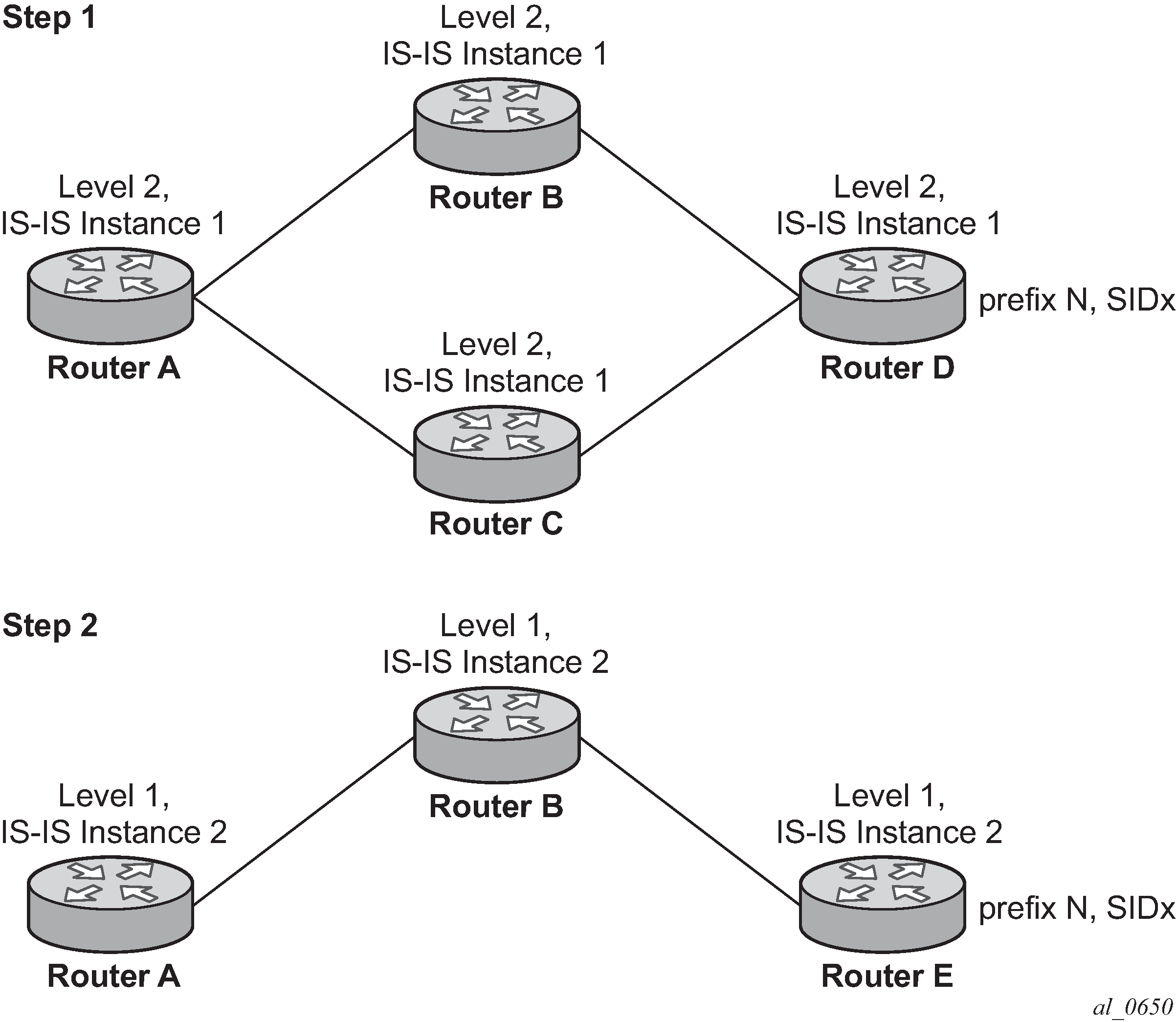
Assume the following route-type preference in RTM and tunnel-type preference in TTM are configured:
-
ROUTE_PREF_ISIS_L1_INTER (RTM) 15
-
ROUTE_PREF_ISIS_L2_INTER (RTM) 18
-
ROUTE_PREF_ISIS_TTM 10
- Router A performs the following resolution within the single level 2, IS-IS instance 1. All
metrics are the same and ECMP = 2.
-
For prefix N, the RTM entry is:
-
prefix N
-
nhop1 = B
-
nhop2 = C
-
preference 18
-
-
For prefix N, the SR tunnel TTM entry is:
-
tunnel-id 1: prefix N-SIDx
-
nhop1 = B
-
nhop2 = C
-
tunl-pref 10
-
-
- Add Level 1, IS-IS instance 2 in the same configuration, but in routers A, B, and E only.
-
For prefix N, the RTM entry is:
-
prefix N
-
nhop1 = B
-
preference 15
The RTM prefers L1 route over L2 route.
-
-
For prefix N, there is one SR tunnel entry for L2 in TTM:
-
tunnel-id 1: prefix N-SIDx
-
nhop1 = B
-
nhop2 = C
-
tunl-pref 10
-
-