EVPN-VPWS is often used as an aggregation technology to connect access devices to the residential or business PE in the service provider network. The PE receives tagged traffic inside EVPN-VPWS circuits and maps each tag to a different service in the core, such as ESM services, Epipe services, or VPRN services.
SR OS implements this PW headend functionality by using PW ports that use multihomed Ethernet Segments (ESs) for redundancy. ESs can be associated with PW ports in two different modes of operation.
- PW port-based ESes with multihoming procedures on PW SAPs
- PW port-based ESes with multihoming procedures on stitching Epipe
PW port-based ESes with multihoming procedures on PW SAPs
PW ports in ESs and virtual ESs (vESs) are supported for EVPN-VPWS MPLS services. In addition to LAG, port, and SDP objects, PW port ID can be configured in an Ethernet Segment. In this mode of operation, PW port-based ESs only support all-active configuration mode, and not single-active configuration mode.
The following requirements apply:
- Port-based or FPE-based PW ports can be used in ESs
- PW port scenarios supported along with ESs are as follows:
- port-based PW port
- FPE-based PW port, where the stitching service uses a spoke SDP to the access CE
- FPE-based PW port, where the stitching service uses EVPN-VPWS (MPLS) to the access CE
For all the preceding scenarios, fault-propagation to the access CE only works in the case of physical failures. Administrative shutdown of individual Epipes, PW SAPs, ESs or BGP-EVPN may result in traffic black holes.
The following figure shows the use of PW ports in ESs. In this example, an FPE-based PW port is associated with the ES, where the stitching service itself also uses EVPN-VPWS.
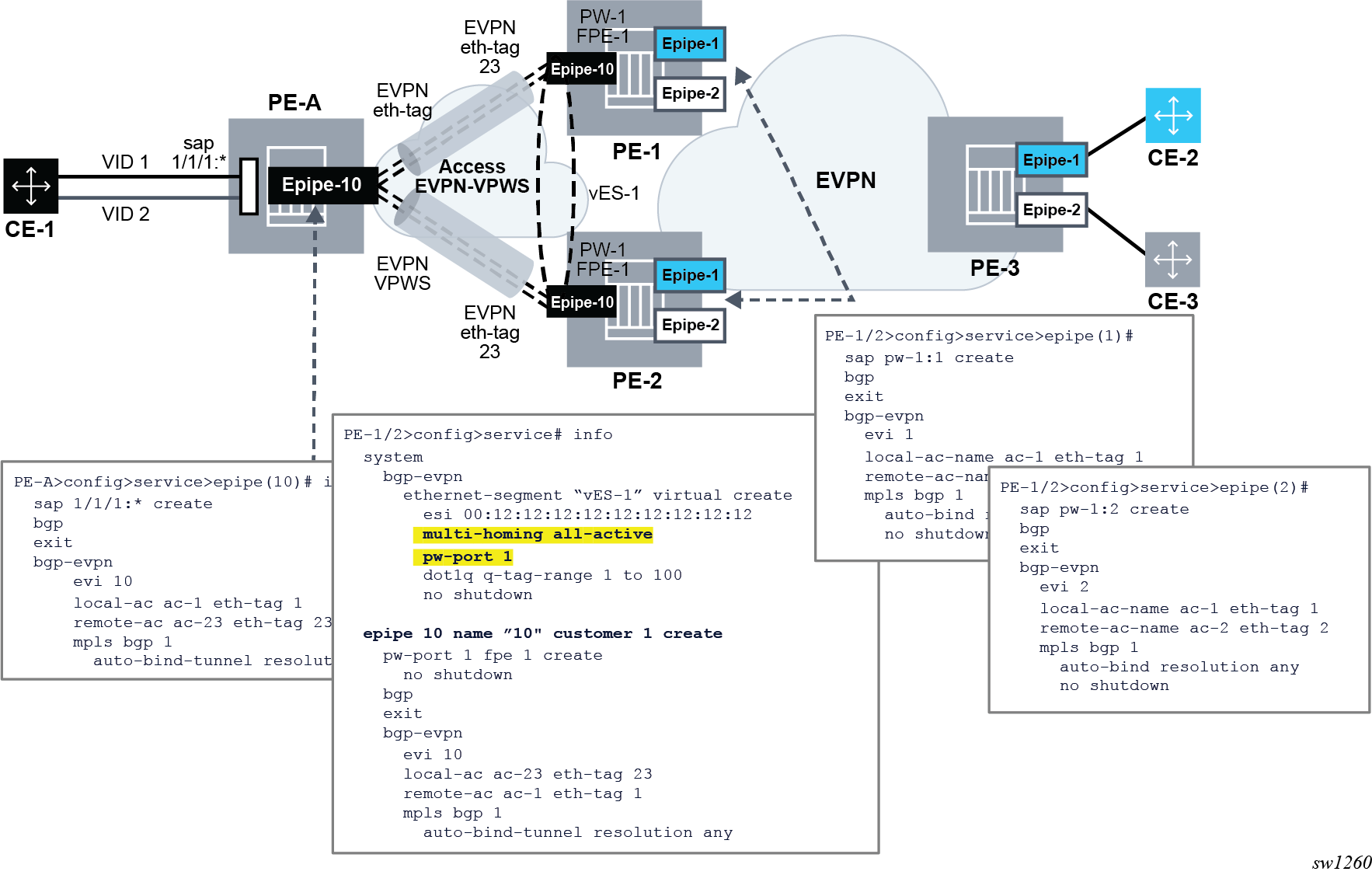
In this example, the following conditions apply:
- Redundancy is driven by EVPN all-active multihoming. ES-1 is a virtual ES configured on the FPE-based PW port on PE-1 and PE-2.
- The access network between the access PE (PE-A) and the network PEs (PE-1 and
PE-2), uses EVPN-VPWS to backhaul the traffic. Therefore, PE-1 and PE-2 use
EVPN-VPWS in the PW port stitching service, where:
- PE-1 and PE-2 apply the same Ethernet tag configuration on the stitching service (Epipe 10)
- Optionally PE-1 and PE-2 can use the same RD on the stitching service
- AD per-EVI routes for the stitching service Ethernet tags are advertised with ESI=0
- Forwarding in the CE-1 to CE-2 or CE-3 direction, works as follows:
- PE-A forwards traffic based on the selection of the best AD per-EVI route advertised by PE-1 and PE-2 for the stitching Epipe 10. This selection can be either BGP-based if PE-2 and PE-3 use the same RD in the stitching service, or EVPN-based if different RD is used.
- When the PE-1 route is selected, PE-1 receives the traffic on the local PW-SAP for Epipe 1 or Epipe 2, and forwards it based on the customer EVPN-VPWS rules in the core.
- Forwarding in the CE-2 or CE-3 to CE-1 direction, works as follows:
- PE-3 forwards the traffic based on the configuration of ECMP and aliasing rules for Epipe 1 and Epipe 2.
- PE-3 can send the traffic to PE-2 and PE-2 to PE-A, following different directions.
- If the user needs the traffic to follow a symmetric path in both directions, then the AD per-EVI route selection on PE-A and PE-3 can be handled so that the same PE (PE-1 or PE-2) is selected for both directions.
- For this example, the solution provides redundancy in case of node failures in
PE-1 or PE-2. However, the administrative shutdowns, configured in some objects,
are not propagated to PE-A, leading to traffic blackholing. As a result, black
holes may be caused by the following events in PE-1 or PE-2:
- Epipe 1 or Epipe 2 service shutdown
- Epipe 1 or Epipe 2 BGP-EVPN MPLS shutdown
- vES-1 shutdown
- BGP shutdown
PW port-based ESes with multihoming on stitching Epipe
The solution described in PW port-based ESes with multihoming procedures on PW SAPs provides PW-headend redundancy where the access PE selects one of the PW-headend PE devices based on BGP best path selection, and the traffic from the core to the access may follow an asymmetric path. This is because the multihoming procedures are actually run on the PW SAPs of the core services, and the AD per-EVI routes advertised in the context of the stitching Epipe use an ESI=0.
SR OS also supports a different mode of operation called pw-port headend which allows running the multihoming procedures in the stitching Epipe and, therefore, use regular EVPN-VPWS primary or backup signaling to the access PE. The mode of operation is supported in a single-active mode shown in the following figure.
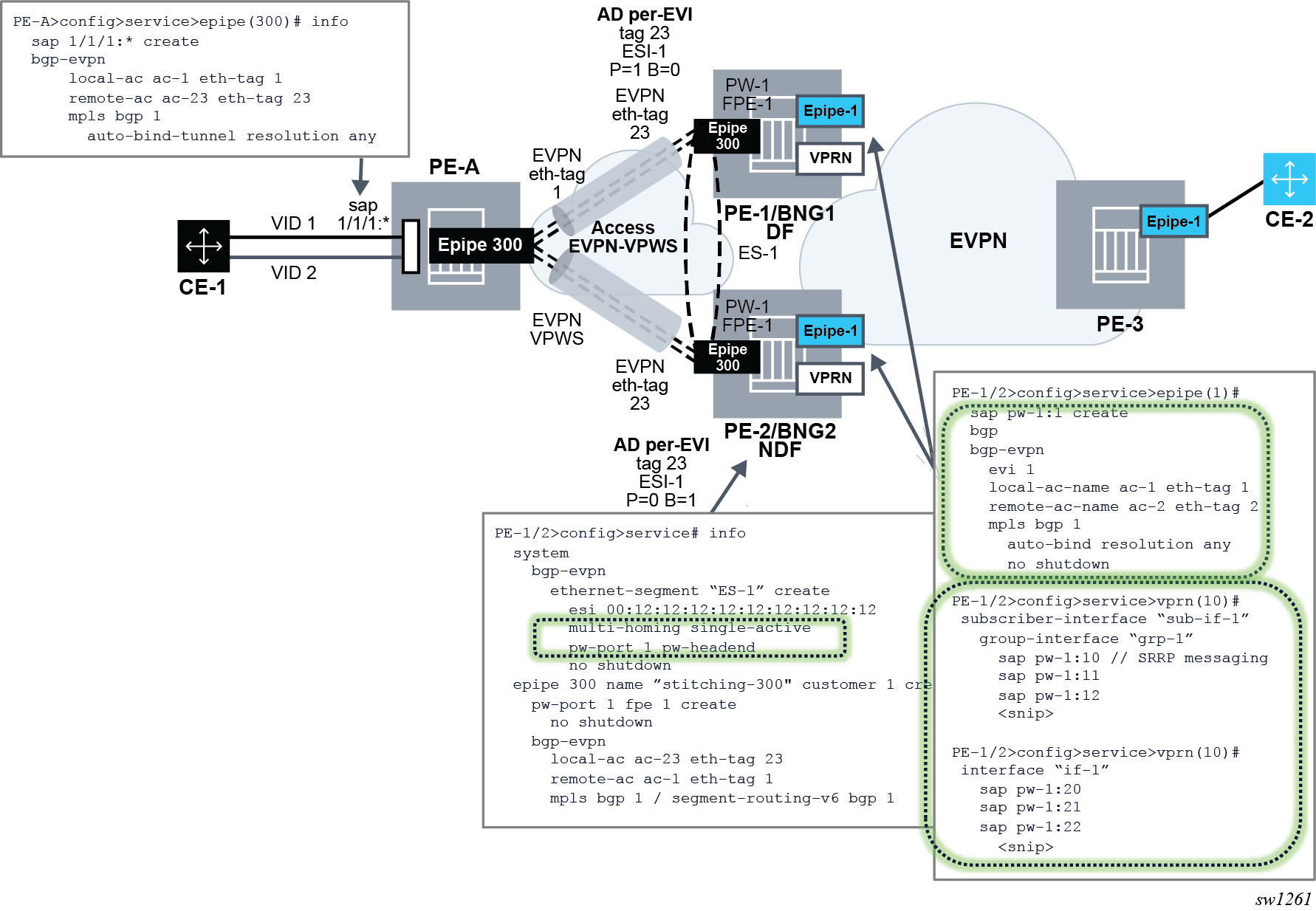
The following configuration triggers the needed behavior:
// ES and stitching Epipe config
PE-1/2>config>service# info
system
bgp-evpn
ethernet-segment “ES-1” create
esi 00:12:12:12:12:12:12:12:12:12
multi-homing single-active
pw-port 1 pw-headend
no shutdown
epipe 300 name ”stitching-300" customer 1 create
pw-port 1 fpe 1 create
no shutdown
bgp-evpn
local-attachment-circuit ac-23 eth-tag 23
remote-attachment-circuit ac-1 eth-tag 1
mpls bgp 1
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
// Services config
epipe 10
sap pw-1:10 create
bgp-evpn
mpls bgp 1
epipe 11
sap pw-1:10 create
bgp-evpn
mpls bgp 1
The configuration and functionality are divided in four aspects.
Configuration of single-active multihoming on ESs associated with PW ports of type pw-headend
In this mode, PW Ports are associated with single-active non-virtual Ethernet Segments. The pw-headend keyword is needed when associating the PW port.
PE-1/2>config>service# info
system
bgp-evpn
ethernet-segment “ES-1” create
esi 00:12:12:12:12:12:12:12:12:12
multi-homing single-active
pw-port 1 pw-headend
no shutdown
The pw-port id pw-headend command indicates to the system that the multihoming procedures are run in the PW port stitching Epipe and the routes advertised in the context of the stitching Epipe contains the ESI of the ES.
Configuration of the PW port stitching Epipe
A configuration example of the stitching Epipe follows.
epipe 300 name ”stitching-300" customer 1 create
pw-port 1 fpe 1 create
no shutdown
bgp-evpn
local-attachment-circuit ac-23 eth-tag 23
remote-attachment-circuit ac-1 eth-tag 1
mpls bgp 1
auto-bind-tunnel resolution any
The preceding example shows the configuration of a stitching EVPN VPWS Epipe with MPLS transport, however SRv6 transport is also supported.
When the ES is configured with a PW port in pw-headend mode, the stitching Epipe associated with the PW port is now running the ES and DF election procedures. Therefore, the following actions apply:
- an AD per-ES route is advertised with:
- the RD or RT of the stitching Epipe
- the configured ESI of the ES associated with the PW port
- the ESI-label extended community with the multihomed mode indication and ESI label
- an AD per EVI route is advertised with:
- the RD or RT of the stitching Epipe
- the configured ESI where the PW port resides
- the P/B bits according to the DF election procedures
- the non-DF drives the PW port operationally down with a flag MHStandby. As a result, all the PW SAPs contained in the PW port are brought operationally down. Optionally, the config>service>epipe>pw-port>oper-up-on-mhstandby command can be configured so that the PW port stays operationally up even if it is in MHStandby state (that is, the PE is non-DF). This command may speed up convergence in case a significant number of PW SAPs are configured in the same PW port.
Configuration of the PW port-contained PW SAPs and edge services
The edge services that contain the PW SAPs of the pw-headend pw-port command are configured without any other additional commands. These PW SAPs can be configured on Epipes, VPRN interfaces, or subscriber interfaces, VPLS (capture SAPs). As an example, if the PW SAP is configured on an Epipe EVPN-VPWS service:
epipe 10
sap pw-1:10 create
bgp-evpn
mpls bgp 1
- The PW SAP is brought operationally down if the PW port is down. The PW port goes down with the reason MHStandby if the PE is a non-DF, or with reason stitching-svc-down if the EVPN destination is removed from the stitching Epipe.
- If the PW SAP is configured in an EVPN-VPWS edge service as in the preceding
example, the following actions are performed:
- An AD per ES route is advertised for the EVPN-VPWS service with the RD or RT of the service Epipe, the configured ESI of the ES associated with the PW port, and the ESI-label extended community with the multihomed mode indication of the ES and ESI label (label is the same value as in the AD per ES for the stitching Epipe). If the PW port is only down because of the MHStandby flag, the AD per ES route for the Epipe service is still advertised.
- In addition, an AD per EVI route is advertised with the RD or RT of
the service Epipe, the configured ESI of the ES associated with the
PW port, and the P/B flags of the ES:
- P=1/B=0 on the DF
- P=0/B=1 on backup
- P=0/B=0 on non-DFs and non-backup
- If the PW port is down only because of MHStandby, the AD per EVI route for the service Epipe is still advertised.
Some considerations and dependencies between the PW port and the service Epipe PW SAPs
- If all the PW SAPs associated with the FPE PW port are brought down, the
following rules apply:
- state of the PW port does not change
- does not trigger any AD per-ES/EVI or ES route withdraw toward the CE from the stitching Epipe
- Any event that brings down the PW port (except for MHStandby) triggers:
- an AD per-EVI/ES route withdrawal within the context of the stitching Epipe
- an ES route withdrawal
- an AD per-EVI/ES routes withdrawal within the context of the service Epipes
- the pw-port>monitoring-oper-group command can also modify the state of the PW port driven by the state of the operational group
- An individual PW SAP going administrative or operationally down while the PW
port is still operationally up, the following actions may be performed:
- may create black holes for that particular service
- triggers the withdrawal of the AD per-EVI routes for the service Epipe (not the AD per-ES route, which is kept advertised if the PW port is up)
- if the PW SAP is administratively not shutdown, the service Epipe AD per-ES/EVI routes mirror the AD per-ES/EVI routes of the stitching service and they are advertised if the routes for the stitching Epipe are advertised
The PW SAP can also be configured on VPRN services (under regular interfaces or subscriber interfaces) and works without any special consideration, other than that a PW port in non-DF state brings down the PW SAP and, therefore, the interface. Similarly, VPLS services with capture PW SAPs support this mode of operation too.