The following terminology is used in this section:
TNC is an acronym for Technically Non-Conformant.
QoS is an acronym for Quality of Service.
POA is an acronym for Program Off Air.
TNC event (also known as impaired event) refers to a trap/alarm that detects an impairment event and is therefore termed TNC.
An impaired event is said to have occurred if:
A PAT/PMT syntax error occurs in that second.
Continuity counter errors were detected.
PAT /PMT/PCR PIDs were not present in the video stream for a time period equal to or greater than the configured TNC value in the respective alarm.
The default value of the impaired threshold in terms of milliseconds is:
PAT (100 ms)
PCR (100 ms)
PMT (400 ms)
An unreferenced PID is seen in the video stream which has not been referred in the PMT.
TNC seconds (also known as impaired seconds) refer to the number of seconds elapsed before an impaired event was detected and a TNC SNMP trap was sent. Although multiple TNC events may have occurred within a second, counters in the show>video>channel>analyzer command only increment once per second.
QoS event (also known as degraded event) refers to a trap/alarm that detects a degraded event and is therefore termed QoS. A QoS event is said to have occurred if PAT/PMT/PCR PIDs are absent in the video stream for a time period equal to or greater than the configured QoS value in their respective alarms.
The default value of the degraded threshold in terms of milliseconds is:
-
PAT (200 ms)
-
PCR (200 ms)
-
PMT (800 ms)
-
QoS seconds (also known as degraded seconds) refer to the number of seconds elapsed before a degraded event was detected and a QoS SNMP trap was sent. Although multiple QoS events may have occurred within a second, counters in the show>video>channel>analyzer command only increment once per second.
POA event (also known as error event) refers to a trap/alarm that detects an error event and is therefore termed POA.
A POA event has occurred if:
-
A synchronization loss error has occurred for that particular second. A synchronization loss is said to have occurred if more than 1 consecutive synchronization byte error is seen in the stream.
-
PAT/PMT/PCR PIDs are absent from the video stream for a time period equal to or greater than the configured POA value.
The default value of the degraded threshold in terms of milliseconds is:
-
PAT (500 ms)
-
PCR (500 ms)
-
PMT (2000 ms)
-
-
Traffic loss has occurred for that particular second.
-
A transport error indicator or TEI indicator is set in the transport stream packet header for that particular second in the video stream.
-
POA seconds (also known as error seconds) refer to the number of seconds elapsed before an errored event was detected and a POA SNMP trap was sent. Although multiple POA events may have occurred within a second, counters in the show>video>channel>analyzer command only increment once per second.
Good seconds refer to the number of seconds where there are no impaired, degraded, or error events.
PID stats are described in Table: PID stats — description of fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
PID |
Displays the value of the PID. |
|
Is PCR PID |
Can be set to Yes or No. If set to Yes, then it indicates that the PID is the PCR PID. |
|
TEI Err Sec |
Counts the number of seconds TEI was set for that particular PID. |
|
Absent Err Secs |
The number of seconds for which the PID was not seen for a particular interval of time which is decided by the alarms set for the Non-Vid PID Absent and Video PID Absent. |
|
PID bitrate |
Calculated by counting the number of times the PID occurred in the last second x 188 x 8.
|
|
CC Err Secs |
Number of seconds Continuity Counter errors were seen for that particular PID in the stream. |
|
PID Type |
Specifies that the PID is either video, audio, PAT, PMT, or PCR. |
|
MPEG Stream Type |
If the PID is video or audio, this field indicates how the video or
audio is encoded. For example:
|
To address interval statistics, except for the PID statistics all other statistics described above have interval statistics. Information can be obtained about stream status for the last 1 minute, 5 minute, and 15 minute interval.
MDI - Media Delivery Index (RFC 4445, A Proposed Media Delivery Index (MDI))
Delay Factor (RFC 4445)
The delay factor is a value which indicates the minimum amount of time a STB buffers to resolve network jitter (that is, it is the minimum STB buffer depth in ms). RTP timestamp is used as the definitive time indicator (the notional drain rate).
Loss Rate (RFC 4445)
The Media Loss Rate is the number of media (Transport Stream) packets lost over a specific time interval. This is reported in TS/sec. Each RTP packet lost is assumed to have 7 TS packets lost.
In many instances IPTV operators are unable to identify the cause of visual impairments which are present in almost every video distribution network because the IPTV network has so many moving parts While head end transport-stream monitoring; full reference video analysis (comparing the source content to the encoded output), and; STB probes allow an operator to establish whether the contribution source, the encoder, or the network is the problem the network is a very complex thing.
Operators can use another measurement point in the network, just before the last mile such that network faults can be characterized as being between the head end and last mile (transport) or in the last-mile itself.
The multicast video quality monitoring solution provides an inspection point for the multicast video stream that is combined with other analysis methods to create a full view of video issues and help troubleshoot the part of the network causing the issue.
Video quality monitoring is one part of a video assurance program and is combined with:
TS analysis on the encoder output (to detect encoder errors)
Full-reference PSNR and PQR on the encoder output (to detect over-encoding, noise and other contribution or encoding artifacts)
STB reporting (such as packet-loss, RET events, packet errors) from the entire STB population
STB probes performing full-reference monitoring (against test streams)
STB probes performing channel-change times, estimated PSNR, and so on
Multicast video monitoring within the network can be positioned as complementary to STB reporting and head end analysis, and but should not attempt to perform either of these functions. Because the network node is not capable of decrypting a MPEG transport stream is primarily used to identify correctable and uncorrectable network errors, correlate them with network events (such as routing re-convergence, interface failure, and so on) and provide summary reports and alarms.
For operators who do not have existing STB probes or reporting, a network-based VQM solution can provide insight into quality issues the network may be contributing to, possibly reducing the amount of STB probe investment that is needed. (that is, both probes and the 7750 SR VQM reports many of the same issues in terms of picture quality, fewer probes are needed to test channel change delay, and so on).
The metrics which VQM can report are based on the use of RTP streams which provide per-packet sequencing and an indication of picture type. These two parameters along with measured bitrate allow VQM to produce estimated MOSv scores for both stream ingress (uncorrected) and stream egress (corrected) outputs.
Reportable metrics include:
Relevant SCTE-143 error counters
PAT
PMT
PCR
transport errors, and so on
ETSI TR 101 290
PID
SI repetition
degraded blocks/intervals, and so on
MDI (RFC 4445)
forwarded and impaired I-/B-/P-frame counts
GOP length
video/audio/stream bitrate
These metrics are collected for each multicast group and have relevant parameters. Use the command show video channel analyzer address group-address detail to generate a numeric metrics summary report for a specific multicast group. Other information that is also captured by VQM but can only be expressed on a per-PID basis uses the command show video channel pid address group-address. The per-PID information captured by VQM includes:
- CC Err secs
- TEI Err secs
- Absent Err secs
The following is example output generated by the show video channel analyzer address group-address detail command:
*A:vmq-11# show video channel analyzer address 239.0.1.1 detail
===============================================================================
Video channel analyzer detail
===============================================================================
Channel number : 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
MDI Delay Factor : 4 MDI Loss Rate : 0
Good Secs : 0
===============================================================================
GOP Stats
===============================================================================
Min Max Avg
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GOP Length 10 31 24
Frames/Sec 21 28 25
===============================================================================
Frame Stats
===============================================================================
I-Frame P-Frame B-Frame
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Good 42 957 0
Bad 0 0 0
===============================================================================
Error Stats
===============================================================================
POA Events QoS Events TNC Events
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PAT Rep 0 1215 0
PMT Rep 0 0 0
PCR Rep 0 0 1
PAT Syntax Err - 0 -
PMT Syntax Err - 0 -
Sync Byte Err - 0 -
Sync Loss 0 - -
Unref PID - - 34600
Traffic Loss 0 - -
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Overall 30285 77 4238
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reoccurring events only increment counter once every second
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of channels : 1
===============================================================================
*A:vmq-11# show video channel pid address 239.0.1.1
===============================================================================
Video Channel PID
===============================================================================
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 0 PID Type : pat
MPEG Stream Type : 0 Is PCR PID : No
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 0 PID Bitrate : 0
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 100 PID Type : pmt
MPEG Stream Type : 0 Is PCR PID : No
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 0 PID Bitrate : 0
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 101 PID Type : video
MPEG Stream Type : 27 Is PCR PID : Yes
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 0 PID Bitrate : 5564800
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 201 PID Type : audio
MPEG Stream Type : 3 Is PCR PID : No
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 0 PID Bitrate : 204544
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 202 PID Type : audio
MPEG Stream Type : 3 Is PCR PID : No
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 0 PID Bitrate : 132352
Service Id : 31905555 Interface Name : vi-1
Group Address : 239.0.1.1 Source Address : 10.10.10.10
PID : 401 PID Type : other
MPEG Stream Type : 6 Is PCR PID : No
Cc Err Secs : 0 TEI Err Secs : 0
Absent Err Secs : 30310 PID Bitrate : 0
Number of pids for this channel: 6
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of channels : 1
===============================================================================
Event alarms are reported by log, syslog, or SNMP. The following is an example of a trap:
1 2017/02/11 18:11:20.42 UTC WARNING: VIDEO #2009 Base Video[1/video-300]
Service Id - 300, Video interface - video-300, Group address - 192.0.2.6, Source address - 10.20.13.2 Last 10 seconds of analyzer state is good good good good good good good good good poa
A trap is only raised when a POA, QoS, or TNC event occurs within the last 10 seconds. The trap captures events within the last 10 seconds. In the example above, the first nine seconds were ‟good”, which indicates that no events occurred and that every single RTP packet was received. At the 10-second mark, a POA event occurred, which triggered the SNMP trap. This sampling continues every 10 seconds. If an event (POA, QoS, or TNC) continues to be detected, an SNMP trap is raised every 10 seconds.
When the analyzer detects 10 seconds of a ‟good” condition, another trap is raised to clear the alarm for the multicast (S,G). Subsequent alarms are raised and SNMP traps are triggered only when the analyzer detects another event (POA, QoS, or TNC).
61 2016/10/18 15:40:56.83 UTC WARNING: VIDEO #2010 Base Video[1/video-300]
Analyzer state is cleared for - Service Id - 300, Video interface - video-300, Group address - 192.0.2.6, Source address - 10.20.13.2
VQM is an optional module available on the input side, or output side of the video ISA. On input, it is applied before perfect stream protection. Conversely when on the output side it is applied only to multicast streams after perfect stream protection.
Because of the large number of channels and the nature of measuring input and output sides, VQM is highly reliant on the use of RTP extensions to provide relevant transmission metrics to the VQM analysis module. In a typical head end, a multicast stream is scrambled to encrypt its video or audio. When this encryption occurs, it is typical for the entire payload of the transport stream (for the nominated PID) to be completely scrambled. The consequence of such is that the video and audio PES headers, which reveal much about the picture and timing information, are unavailable to the VQM program.
VQM uses intelligent RTP re-wrapping. RTP re-wrapping is a prerequisite for ad insertion and Fast Channel Change (FCC) and involves marking packets before encryption based on the picture type (most importantly, the start of the I frame of IDR frame in H.264.
The VSA as currently defined, re-multiplexes each transport stream into a new RTP packet. By doing so it allows the separation of different picture types into their own respective RTP packets, and the separation of audio packets from video packets to allow different synchronization in events of FCC. In effect, it pulls the elementary streams back into their component forms while retaining the syntax and structure of the MPTS.
For information about VSAs, see the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR System Management Guide.
Meanwhile, additional information can be made available, before scrambling, of the picture information for quality analysis. The quality analysis performed by the VQM module emphasizes impairments caused by network issues and transport stream syntax given the relative proximity of the router to the customer.
When the video ISA is deployed alongside the ALU VSA re-wrapper, a custom RTP header extension is sent with each RTP packet. The RTP header is shown in Figure: RTP header.
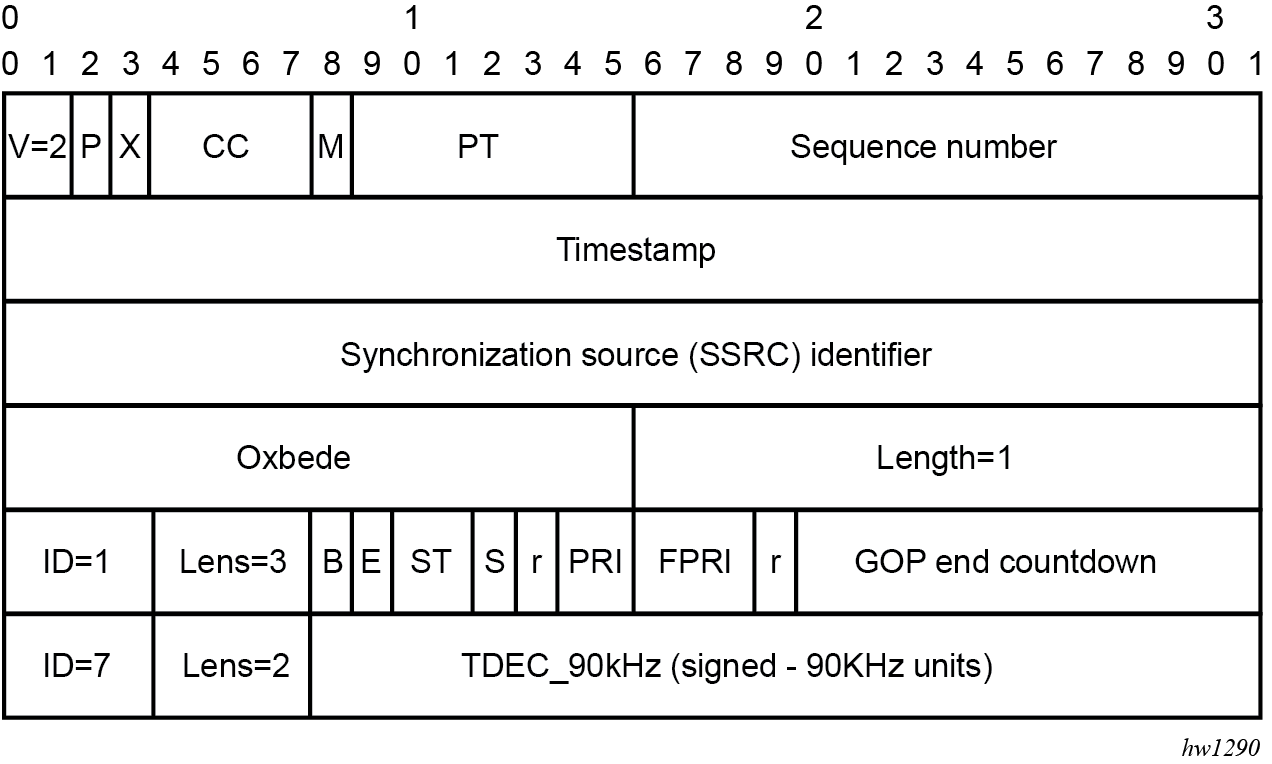
Where:
B (Frame Begin Flag): set if a frame starts in this packet
E (Frame End Flag): set if a frame finishes in this packet
ST (Stream Type)
00 video
01 audio
10 data/padd/other
11 Reserved
S (Switch bit): set to 1 in all RTP packets from the moment
the client should do the IGMP join (rewrap does not fill it)
r: reserved (set to 1)
PRI: Packet Priority (coarse)
FPRI: Fine-grained priority
PRI FPRI dec DSCP
--- ---- --- ----
3 7 31 AF41 Video IDR frame
3 0 24 AF41 Audio
2 0 16 AF41 Reference frame (P in MPEG2, I or P or some Bs in AVC)
1 7 15 AF42 Non-reference frame (most Bs in MPEG2, some Bs in AVC)
1 5 13 AF42 Trans-GOP frames, undecodable in some circumstances (some Bs in MPEG2)
0 4 4 AF43 Rest of cases (data, secondary videos, etc)
0 1 1 AF43 Padding packets
where AF41=100010, AF42=100100, AF43=100110 (DSCP bits in the IP header)