The SR-TE on-demand LSP simplifies provisioning for networks that may or may not be managed by a network service manager, such as the Nokia NSP. Instead of using a full mesh, LSPs can be automatically created on-demand when a suitable tunnel does not exist for a specific BGP prefix next hop. The prefix could be for VPRN, EVPN, BGP-LU, or BGP shortcut routes. Both intradomain and inter-domain use cases are supported.
- VPRN auto-bind-tunnel
- EVPN VPWS auto-bind-tunnel
- EVPN VPLS auto-bind-tunnel
- BGP-LU, both as an LER and LSR at an ABR or ASBR
- BGP shortcuts
The following figure shows an application of SR-TE on-demand LSPs.
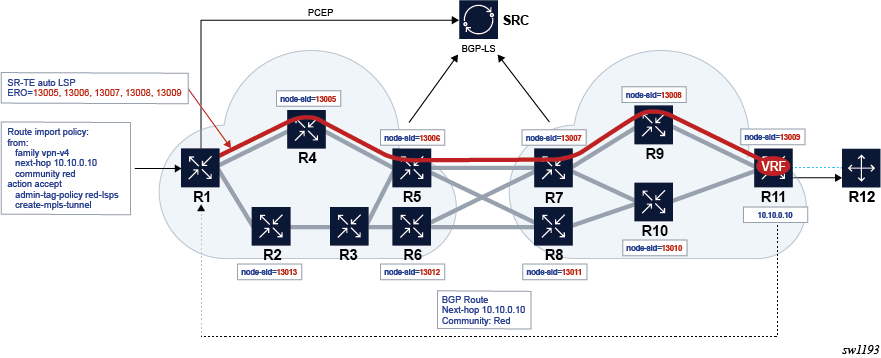
This example combines route transport coloring and auto LSPs to simplify provisioning for intent-based networking for specific services. In this use case, intent means the ability to meet traffic engineering requirements for a service. This could be, for example, a delay or loss, or the ability to steer the service traffic to avoid LSPs that transit specific geographies or prefer those that take another route.
In this example, a BGP route is advertised for a VRF in a PE for a VPRN service. An extended color community is assigned to the route. This color implies an intent associated with the transport requirements.
- The route is matched in a route-import policy.
- An admin-tag policy called red-lsps is applied.
- A trigger action occurs to create an MPLS tunnel to the BGP next-hop for the route.
This causes the head-end router to create an SR-TE auto-LSP that matches the red-lsps admin-tag policy and steers the traffic associated with "red" routes to the far-end PE, into the red LSP. This SR-TE auto-LSP is created based on the configuration in the matching LSP template.
SR OS also offers the ability to use the local CSPF, hop-to-label-translation, or a PCE to provide a path for the red LSP. This is determined by a configuration in the matching LSP template.