RFC2547bis is an extension to the original RFC 2547, which details a method of distributing routing information and forwarding data to provide a Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to end customers.
Each Virtual Private Routed Network (VPRN) consists of a set of customer sites connected to one or more PE routers. Each associated PE router maintains a separate IP forwarding table for each VPRN. Additionally, the PE routers exchange the routing information configured or learned from all customer sites via MP-BGP peering. Each route exchanged via the MP-BGP protocol includes a Route Distinguisher (RD), which identifies the VPRN association.
The service provider uses BGP to exchange the routes of a VPN among the PE routers that are attached to that VPN. This is done in a way which ensures that routes from different VPNs remain distinct and separate, even if two VPNs have an overlapping address space. The PE routers distribute routes from other CE routers in that VPN to the CE routers in a VPN. Since the CE routers do not peer with each other there is no overlay visible to the VPN's routing algorithm.
When BGP distributes a VPN route, it also distributes an MPLS label for that route. The label distributed with a VPN route depends on the configured label-mode of the VPRN that is originating the route. On 7210 SAS routers, only one method of label allocation mode is supported: label per VRF. That is, when 7210 allocates a label for a VPN route, it allocates a single label for all the VPN routes belonging to a single VRF. This does not restrict the label distribution method on the remote PE. The label distribution method configured on the remote PE must consider the scale of the PEs participating in the VPRN service.
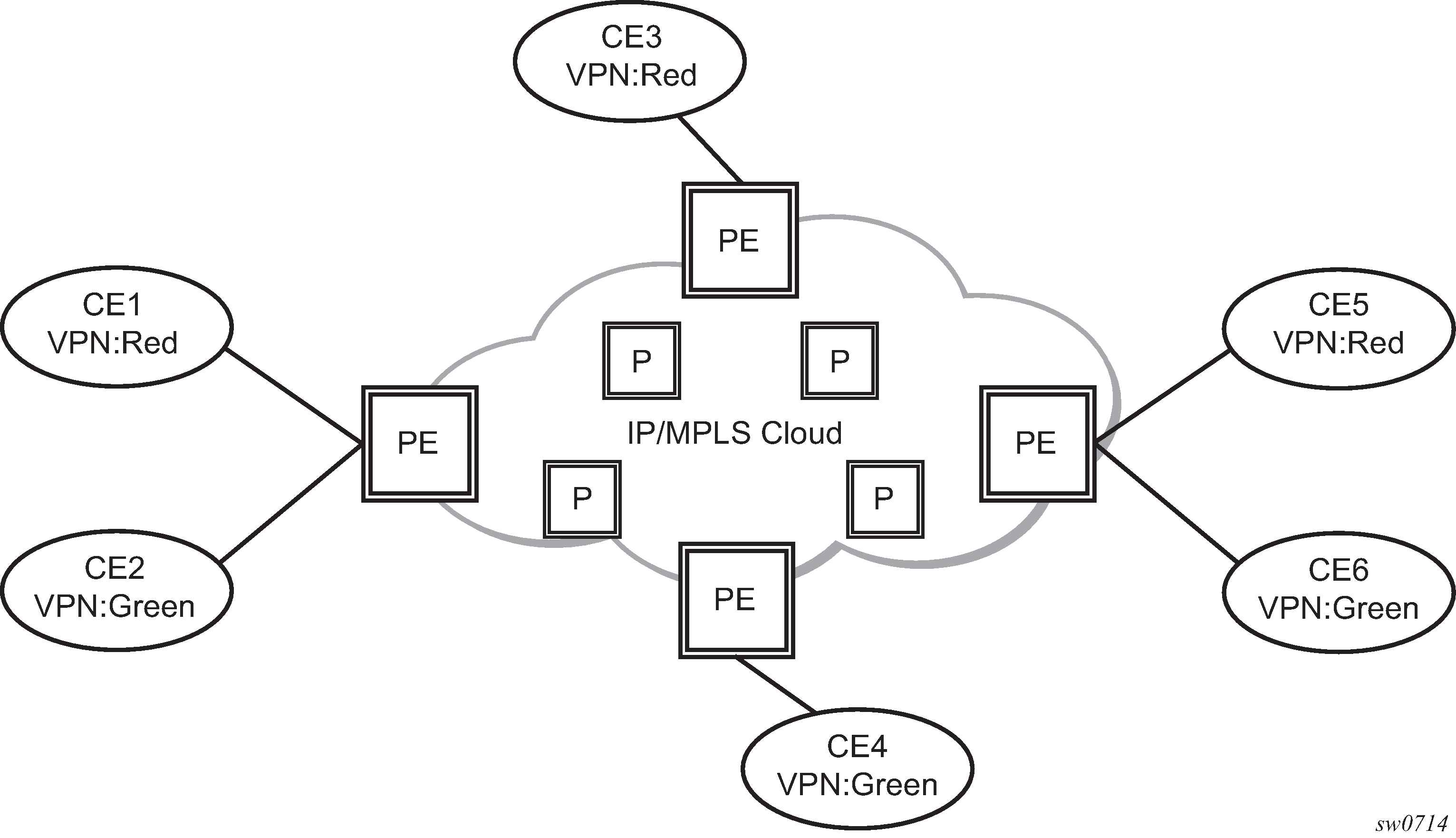
Before a customer data packet travels across the service provider's backbone, it is encapsulated with the MPLS label that corresponds, in the customer's VPN, to the route which best matches the packet's destination address. The MPLS packet is further encapsulated with either another MPLS label header, so that it gets tunneled across the backbone to the correct PE router. Each route exchanged by the MP-BGP protocol includes a route distinguisher (RD), which identifies the VPRN association. Therefore, the backbone core routers do not need to know the VPN routes. Figure: Virtual Private Routed Network shows a VPRN network diagram example.