The standby-signaling-master command is supported on all 7210 SAS platforms as described in this document, except for those operating in access-uplink mode. The standby-signaling-slave command is not supported. In the following section, references to the standby-signaling-slave command are only used to describe the complete solution. The 7210 SAS platforms can only be used where the standby-signaling-master command is used in the example.
This section describes a mechanism in which one end on a pseudowire (the ‟master”) dictates the active PW selection, which is followed by the other end of the PW (the ‟slave”). This mechanism and associated terminology is specified in RFC 6870.
This section describes master-slave pseudowire redundancy. This redundancy adds the ability for the remote peer to react to the pseudowire standby status notification, even if only one spoke-SDP terminates on the VLL endpoint on the remote peer, by blocking the transmit (Tx) direction of a VLL spoke-SDP when the far-end PE signals standby. This solution enables the blocking of the Tx direction of a VLL spoke-SDP at both master and slave endpoints when standby is signalled by the master endpoint. This satisfies a majority of deployments where bidirectional blocking of the forwarding on a standby spoke-SDP is required.
The following figure shows the operation of master-slave pseudowire redundancy. In this scenario, an Epipe service is provided between CE1 and CE2. CE2 is dual-homed to PE2 and PE3, and therefore PE1 is dual-homed to PE2 and PE3 using Epipe spoke-SDPs. The objective of this feature is to ensure that only one pseudowire is used for forwarding in both directions by PE1, PE2, and PE3, in the absence of a native dual homing protocol between CE2 and PE2/PE3, such as MC-LAG. In normal operating conditions (the SAPs on PE2 and PE3 toward CE2 are both up and there are no defects on the ACs to CE2), PE2 and PE3 cannot choose which spoke-SDP to forward on based on the status of the AC redundancy protocol.
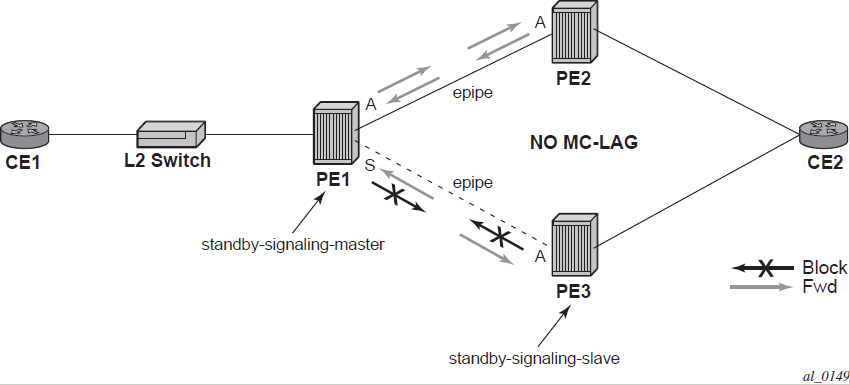
Master-slave pseudowire redundancy adds the ability for the remote peer to react to the pseudowire standby status notification, even if only one spoke-SDP terminates on the VLL endpoint on the remote peer. When the CLI command standby-signaling-slave is enabled at the spoke-SDP or explicit endpoint level in PE2 and PE3, any spoke-SDP for which the remote peer signals PW FWD standby will be blocked in the transmit direction.
This is achieved as follows. The standby-signaling-master state is activated on the VLL endpoint in PE1. In this case, a spoke-SDP is blocked in the transmit direction at this master endpoint if it is either in operDown state, or it has lower precedence than the highest precedence spoke-SDP, or the specific peer PE signals one of the following pseudowire status bits:
pseudowire not forwarding (0x01)
SAP (ingress) receive fault (0x02)
SAP (egress) transmit fault (0x04)
SDP binding (ingress) receive fault (0x08)
SDP binding (egress) transmit fault (0x10)
That the specific spoke-SDP has been blocked will be signaled to the LDP peer through the pseudowire status bit (PW FWD standby (0x20)). This will prevent traffic being sent over this spoke-SDP by the remote peer, but only in case that remote peer supports and reacts to pseudowire status notification. Previously, this applied only if the spoke-SDP terminated on an IES, VPRN, or VPLS.
Note that although master-slave operation provides bidirectional blocking of a standby spoke-SDP during steady-state conditions, it is possible that the Tx directions of more than one slave endpoint can be active for transient periods during a fail-over operation. This is due to slave endpoints transitioning a spoke-SDP from standby to active receiving and/or processing a pseudowire preferential forwarding status message before those transitioning a spoke-SDP to standby.
This transient condition is most likely when a forced switch-over is performed, or the relative preferences of the spoke-SDPs are changed, or the active spoke-SDP is shutdown at the master endpoint. During this period, loops of unknown traffic may be observed. Fail-overs due to common network faults that can occur during normal operation, or a failure of connectivity on the path of the spoke-SDP or the SAP, would not result in such loops in the datapath.