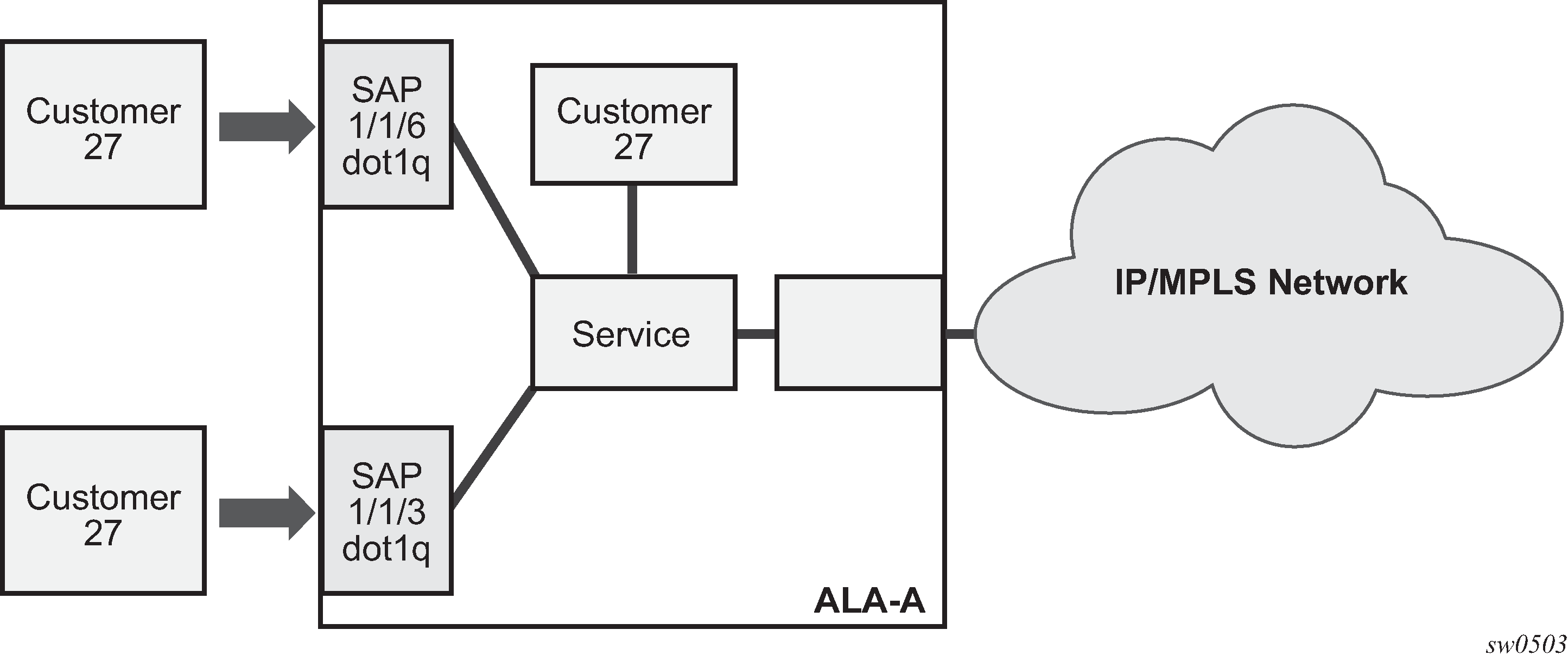
Each subscriber service type is configured with at least one SAP. A SAP identifies the customer interface point for a service on a 7210 SAS router (Figure: SAPs for 7210 SAS configured in network mode). The SAP configuration requires that slot, MDA, and port information be specified. The slot, MDA, and port parameters must be configured before provisioning a service (see the Cards, MDAs, and Ports sections of the 7210 SAS-Mxp, R6, R12, S, Sx, T Interface Configuration Guide).
A SAP is a local entity to the router and is uniquely identified by:
physical Ethernet port
encapsulation type
encapsulation identifier (ID)
Depending on the encapsulation, a physical port can have more than one SAP associated with it. SAPs can only be created on ports designated as ‟access” in the physical port configuration.
The following figure shows SAPs used for customer service delivery, with SDP used for service transport on 7210 SAS devices that support MPLS uplinks (also known as network mode platforms).
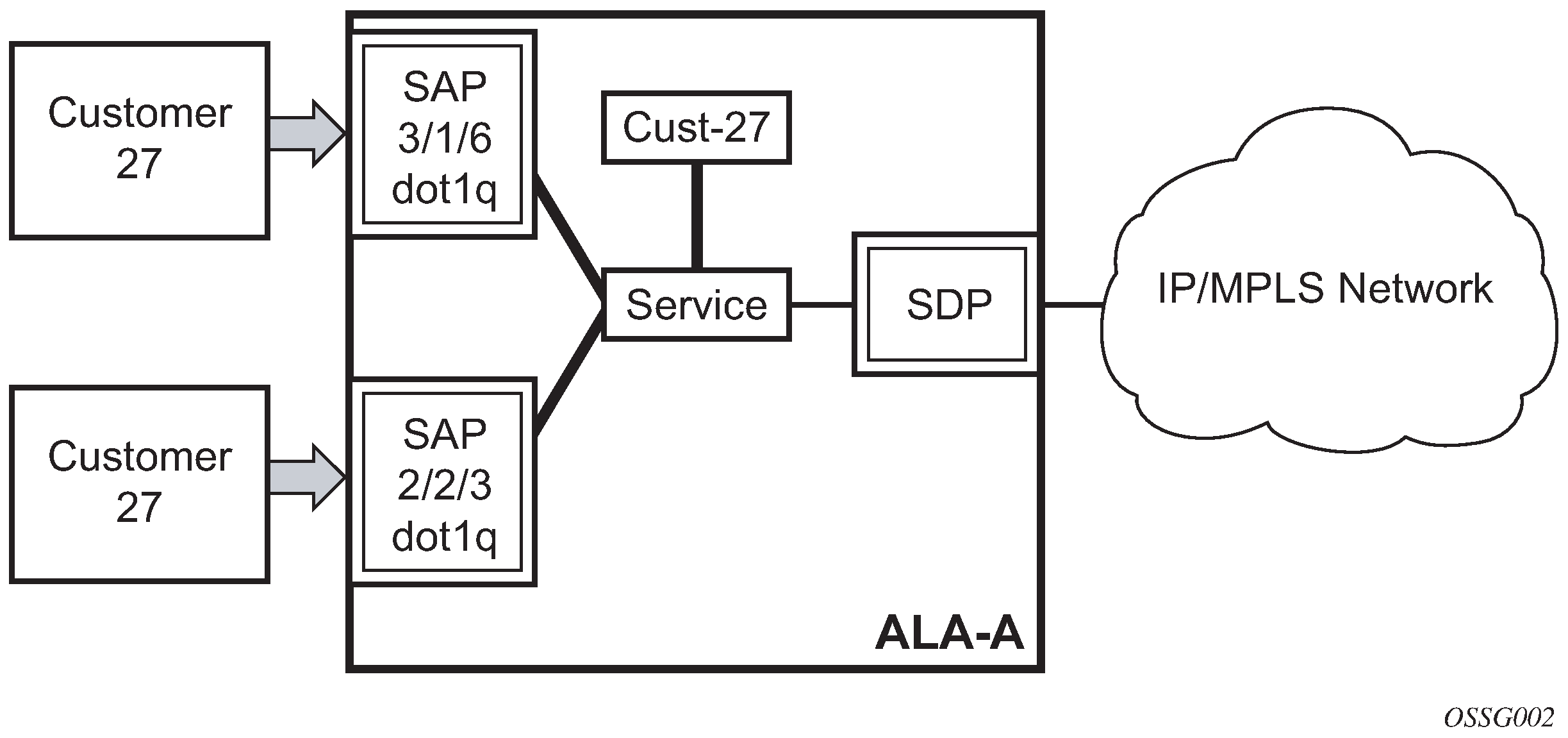
The following figure shows multiple SAPs used for customer service delivery, with access-uplink SAPs (also known as QinQ SAPs) used for service transport on 7210 SAS devices that support only Layer 2 uplinks (also known as access-uplink mode platforms).