RSVP-based signaling for P2MP LSPs is only supported on the 7210 SAS-Mxp, 7210 SAS-R6, 7210 SAS-R12, 7210 SAS-Sx/S 1/10GE (standalone and standalone-VC mode), and 7210 SAS-T.
P2MP LSP is only supported on the 7210 SAS-Mxp, 7210 SAS-R6, 7210 SAS-R12, 7210 SAS-Sx/S 1/10GE (standalone and standalone-VC mode), and 7210 SAS-T.
Generate an LSP trace by entering the following OAM command:
oam p2mp-lsp-trace lsp-name p2mp-instance instance-name s2l-dest-addr ip-address [fc fc-name] [size octets] [max-fail no-response-count] [probe-count probes-per-hop] [min-ttl min-label-ttl]] [max-ttl max-label-ttl] [timeout timeout] [interval interval] [detail]
The LSP trace capability allows the user to trace the path of a single S2L path of a P2MP LSP. Its operation is similar to that of the p2mp-lsp-ping command but the sender of the echo reply request message includes the downstream mapping TLV to request the downstream branch information from a branch LSR or bud LSR. The branch LSR or bud LSR will then also include the downstream mapping TLV to report the information about the downstream branches of the P2MP LSP. An egress LER does not include this TLV in the echo response message.
The operation of the probe-count parameter is modeled after the LSP trace on a P2P LSP. It represents the maximum number of probes sent per TTL value before the device gives up on receiving the echo reply message. If a response is received from the traced node before reaching the maximum number of probes, no additional probes are sent for that TTL. The sender of the echo request increments the TTL and uses the information received in the downstream mapping TLV to send probes to the node downstream of the last node that replied. This continues until the egress LER for the traced S2L path replies.
Because the command traces a single S2L path, the timeout and interval parameters keep the same value range as the LSP trace for a P2P LSP.
The following supported options in lsp-trace for P2P LSP are not applicable: path, prefix, path-destination, and [interface | next-hop].
The P2MP LSP trace uses the Downstream Detailed Mapping (DDMAP) TLV defined in RFC 6424. The following figure shows the format of the new DDMAP TLV entered in the path-destination that belongs to one of the possible outgoing interfaces of the FEC.
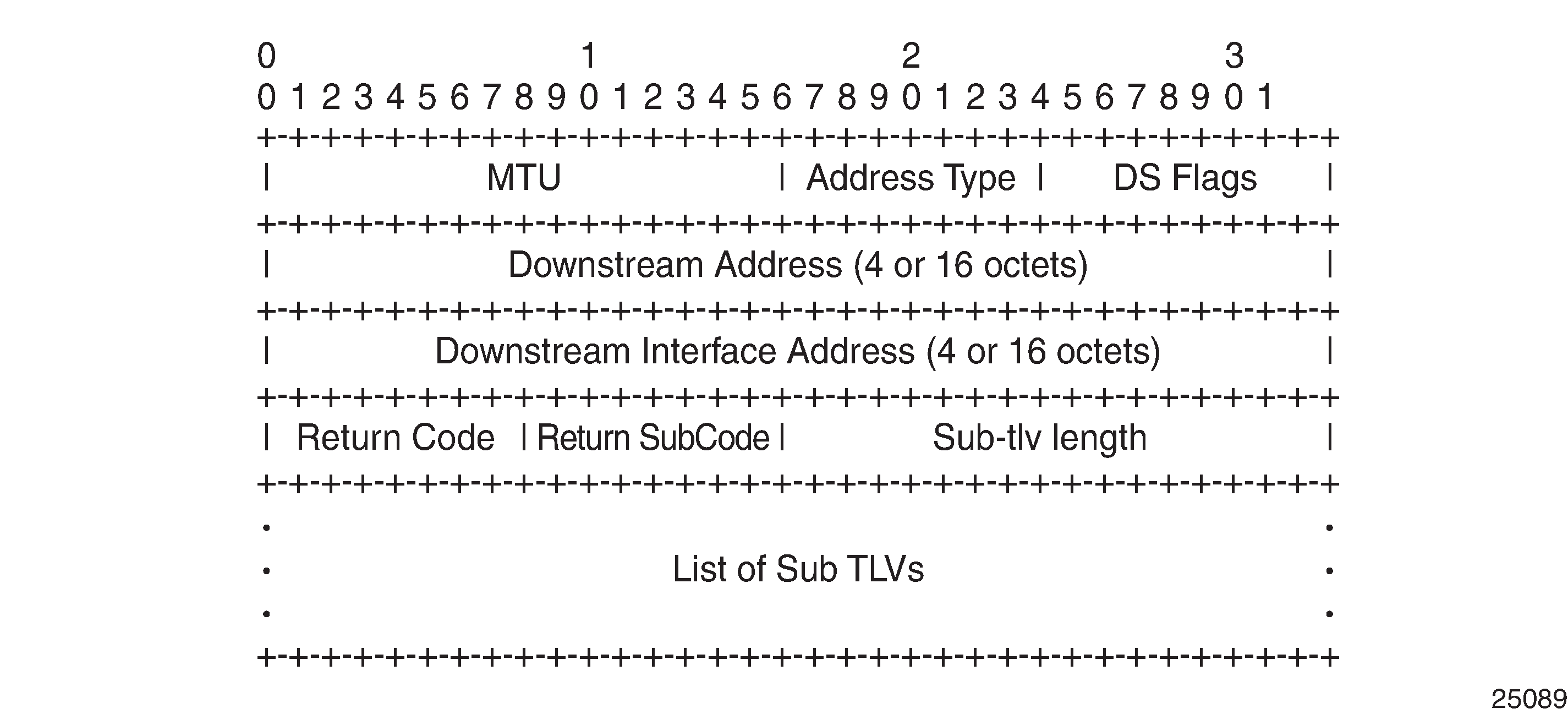
The DDMAP TLV format is derived from the Downstream Mapping (DSMAP) TLV format. The key change is that in the DDMAP TLV, the variable length and optional fields are converted into sub-TLVs. The fields have the same use and meaning as in RFC 4379.
Similar to P2MP LSP ping, an LSP trace probe results on all egress LER nodes that eventually receive the echo request message, but only the traced egress LER node replies to the last probe.
Any branch LSR node or bud LSR node in the P2MP LSP tree may receive a copy of the echo request message with the TTL in the outer label expiring at this node. However, only a branch LSR or bud LSR that has a downstream branch over which the traced egress LER is reachable must respond.
When a branch LSR or BUD LSR node responds to the sender of the echo request message, it sets the global return code in the echo response message to RC=14, ‟See DDMAP TLV for Return Code and Return Sub-Code” and the return code in the DDMAP TLV corresponding to the outgoing interface of the branch used by the traced S2L path to RC=8, ‟Label switched at stack-depth <RSC>”.
Because a single egress LER address, for example an S2L path, can be traced, the branch LSR or bud LSR node sets the multipath type to zero in the downstream mapping TLV in the echo response message because including an egress LER address is not required.