Synchronization Status Messaging (SSM) provides a mechanism for downstream network elements to determine the quality level of the source.
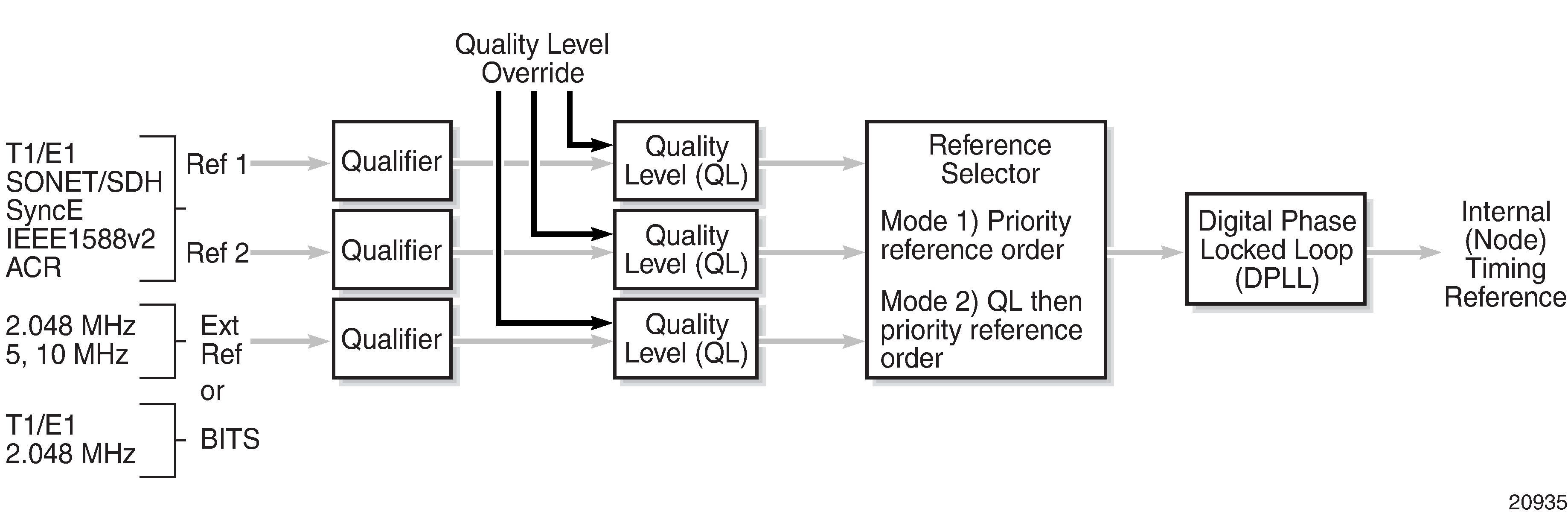
The quality level values are processed by the 7705 SAR system timing module (SSU) to track the network timing flow and select the highest-quality source. The selection process is described in Timing Reference Selection Based on Quality Level. Also see Figure: Timing Reference Selection Based on Quality Level. SSM also allows the network elements to autonomously reconfigure the timing path to select the best possible source for timing and to avoid timing loops. This function is especially useful in a ring topology where network timing may be passed in both directions around the ring.
Synchronization status messages containing the quality level values are placed in prescribed overhead bytes for SONET and SDH signals and in bit-oriented messages within the data link for DS1 (ESF) and E1 physical ports.
For synchronous Ethernet interfaces, there is no equivalent fixed location to convey synchronization status messages; therefore, the quality level values are transported using Ethernet frames over a message channel. This channel, called the Ethernet Synchronization Message Channel (ESMC), uses an Ethernet protocol based on an IEEE Organization Specific Slow Protocol (OSSP). The 4-bit quality level value is carried within a Type-Length-Value (TLV) byte of an Ethernet OAM Protocol Data Unit (PDU) that uses the OSSP subtype.
The clock source quality levels identified for the purpose of tracking network timing flow are listed below. They make up all of the defined network deployment options given in Recommendations G.803 and G.781 (option I pertains to the SDH model and Option II pertains to the SONET model).
The received quality level values for the two network options based on the specific interfaces within these options are provided in the first two columns of Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (SDH, SONET, SyncE) (for SONET, SDH, and Synchronous Ethernet interfaces) and Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (E1 and T1) (for E1 and T1 interfaces). The transmitted quality level values are shown in the last two columns of Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (SDH, SONET, SyncE) and Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (E1 and T1).
prs — SONET Primary Reference Source Traceable
stu — SONET Synchronous Traceability Unknown
st2 — SONET Stratum 2 Traceable
tnc — SONET Transit Node Clock Traceable
st3e — SONET Stratum 3E Traceable
st3 — SONET Stratum 3 Traceable
smc — SONET Minimum Clock Traceable
eec1 — SDH Ethernet Equipment Clock Option 1 Traceable
eec2 — SONET Ethernet Equipment Clock Option 2 Traceable
prc — SDH Primary Reference Clock Traceable
ssu-a — SDH Primary Level Synchronization Supply Unit Traceable
ssu-b — SDH Second Level Synchronization Supply Unit Traceable
sec — SDH Synchronous Equipment Clock Traceable
The user may override the received quality level value of the system synchronization reference input by using the ql-override command to configure one of the above values as a static value. This in turn may affect the transmitted quality level value on each SSM-capable port. Also, the user may use the tx-dus command to force the quality level value that is transmitted on the SSM channel to be set to dnu (do not use) or dus (do not use for synchronization). This capability is provided to block the interface from being a timing source for the 7705 SAR. The dus/dnu quality level value cannot be overridden.
The G.803 and G.781 standards also define additional codes for internal use.
QL-INVx is generated internally by the system when an unallocated synchronization status message value is received; x represents the binary value of this synchronization status message. Within the 7705 SAR, all these independent values are assigned a single value of QL-INVALID.
QL-FAILED is generated internally by the system when the terminated network synchronization distribution trail is in the signal fail state.
QL-UNKNOWN is generated internally by the system to differentiate from a received QL-STU code. It is equivalent to QL-STU for the purposes of quality level selection.
If the node clock is in a holdover state, a holdover message is generated internally by the system and the transmitted SSM quality level value on an SSM-capable port is st3, eec1, eec2, or ssu-b, depending on the type of interface (as shown in Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (SDH, SONET, SyncE) and Table: Quality Level (QL) Values by Interface Type (E1 and T1)).
SSM Quality Level Value Received on Port |
Internal Relative Quality Level |
SSM Quality Level Value to be Transmitted |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
SDH interface SyncE interface in SDH mode |
SONET interface SyncE interface in SONET mode |
|
SDH interface SyncE interface in SDH mode |
SONET interface SyncE interface in SONET mode |
0010 (prc) |
0001 (prs) |
Best quality 1 |
0010 (prc) |
0001 (prs) |
— |
0000 (stu) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
0000 (stu) |
— |
0111 (st2) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
0111 (st2) |
0100 (ssu-a) |
0100 (tnc) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
0100 (tnc) |
— |
1101 (st3e) |
|
1000 (ssu-b) |
1101 (st3e) |
1000 (ssu-b) |
— |
|
1000 (ssu-b) |
1010 (st3/eec2) |
— |
1010 (st3/eec2) |
|
1011 (sec/eec1) |
1010 (st3/eec2) |
1011 (sec/eec1) |
— |
Lowest quality qualified in QL-enabled mode |
1011 (sec/eec1) |
1100 (smc) |
— |
1100 (smc) |
See note 2 |
1111 (dnu) |
1100 (smc) |
1111 (dnu) |
1111 (dus) |
See note 2 |
1111 (dnu) |
1111 (dus) |
Any other |
Any other |
QL-INVALID |
1111 (dnu) |
1111 (dus) |
— |
— |
QL-FAILED |
1111 (dnu) |
1111 (dus) |
— |
— |
QL-UNC |
1011 (sec/eec1) |
1010 (st3/eec2) |
SSM Quality Level Value Received on Port |
Internal Relative Quality Level |
SSM Quality Level Value to be Transmitted |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
E1 interface |
T1 interface (ESF) |
|
E1 interface |
T1 interface (ESF) |
0010 (prc) |
00000100 11111111 (prs) |
Best quality3 |
0010 (prc) |
00000100 11111111 (prs) |
— |
00001000 11111111 (stu) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
00001000 11111111 (stu) |
— |
00001100 11111111 (st2) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
00001100 11111111 (st2) |
0100 (ssu-a) |
01111000 11111111 (tnc) |
|
0100 (ssu-a) |
01111000 11111111 (tnc) |
— |
01111100 11111111 (st3e) |
|
1000 (ssu-b) |
01111100 11111111 (st3e) |
1000 (ssu-b) |
— |
|
1000 (ssu-b) |
00010000 11111111 (st3) |
— |
00010000 11111111 (st3) |
|
1011 (sec) |
00010000 11111111 (st3) |
1011 (sec) |
— |
Lowest quality qualified in QL-enabled mode |
1011 (sec) |
00100010 11111111 (smc) |
— |
00100010 11111111 (smc) |
See note 4 |
1111 (dnu) |
00100010 11111111 (smc) |
1111 (dnu) |
00110000 11111111 (dus) |
See note 4 |
1111 (dnu) |
00110000 11111111 (dus) |
Any other |
N/A |
QL-INVALID |
1111 (dnu) |
00110000 11111111 (dus) |
— |
— |
QL-FAILED |
1111 (dnu) |
00110000 11111111 (dus) |
— |
— |
QL-UNC |
1011 (sec) |
00010000 11111111 (st3) |
Notes:
As the received QL on the port drops from prc/prs to sec/eec1 (row 1 to row 8), the quality level of the internal SSU drops from ‟Best quality” to ‟Lowest quality”.
These quality level indications are considered to be lower than the internal clock of the system. They are relayed to the line interfaces when ql-selection is disabled. When ql-selection is enabled, these inputs are never selected. If there is no valid reference available for the internal clock, then the clock enters holdover mode and the quality level is QL-UNC.