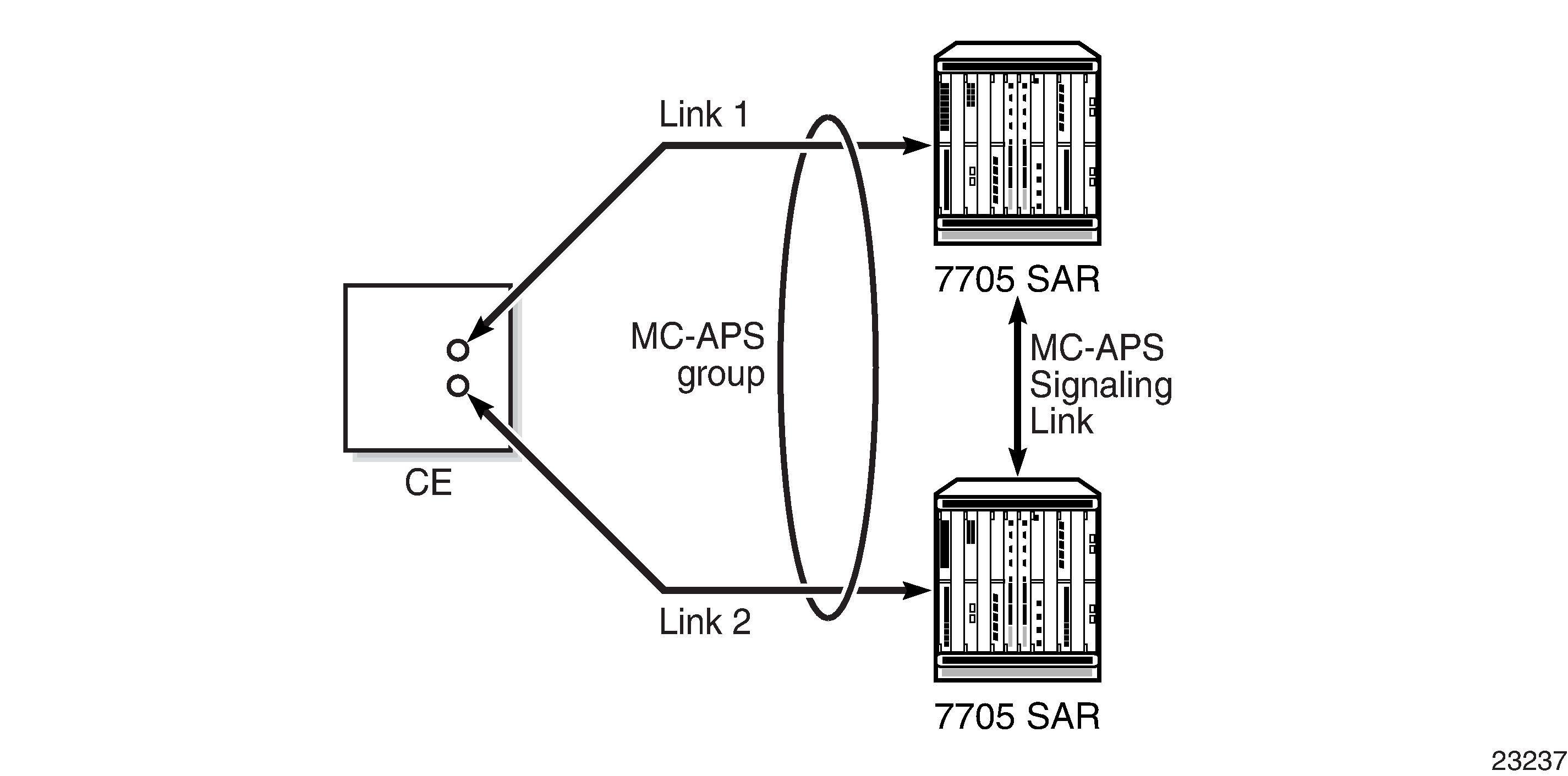
MC-APS extends the functionality offered by SC-APS to include protection against 7705 SAR node failure. MC-APS is supported in bidirectional mode on:
2-port OC3/STM1 Channelized Adapter cards for TDM CES (Cpipes) and TDM CESoETH with MEF 8 with DS3/DS1/E1/DS0 channels
4-port OC3/STM1 / 1-port OC12/STM4 Adapter cards for MLPPP access ports or CES (Cpipes) and TDM CESoETH (MEF 8) access ports with DS1/E1 channels
MC-APS with TDM access is supported on DS3, DS1, E1, and DS0 (64 kb/s) channels. TDM SAP-to-SAP with MC-APS is not supported.
With MC-APS, the working circuit of an APS group can be configured on one 7705 SAR node while the protection circuit of the same APS group is configured on a different 7705 SAR node. The working and protection nodes are connected by an IP link that establishes an MC-APS signaling path between the nodes.
The working and protection circuits must have compatible configurations, such as the same speed, framing, and port type. The circuits in an APS group on both the working and protection nodes must also have the same group ID, but they can have different port descriptions. In order for MC-APS to function correctly, pseudowire redundancy must be configured on both the working and protection circuits. For more information, refer to 7705 SAR Services Guide. MC-APS with pseudowire redundancy also supports Inter-Chassis Backup (ICB); see MC-APS and Inter-Chassis Backup for more information.
The working and protection nodes can be different platforms, such as a 7705 SAR-8 Shelf V2 and a 7705 SAR-18. However, to prevent possible switchover performance issues, avoid mixing different platform types in the same MC-APS group. The 7705 SAR does not enforce configuration consistency between the working circuit and the protection circuit. Additionally, no service or network-specific configuration data is signaled or synchronized between the two routers.
An MC-APS signaling path is established using the IP link between the two routers by matching APS group IDs. A heartbeat protocol can also be used to add robustness. The signaling path verifies that one router is configured as the working circuit and the other is configured as the protection circuit. In case of a mismatch, an incompatible neighbor trap is generated. The protection router uses K1/K2 byte data, member circuit status, and the settings configured for the APS Tools Commands to select the working circuit. Changes in working circuit status are sent across the MC-APS signaling link from the working router to keep the protection router synchronized. External requests such as lockout, force, and manual switches are allowed only on the node with the protection circuit.
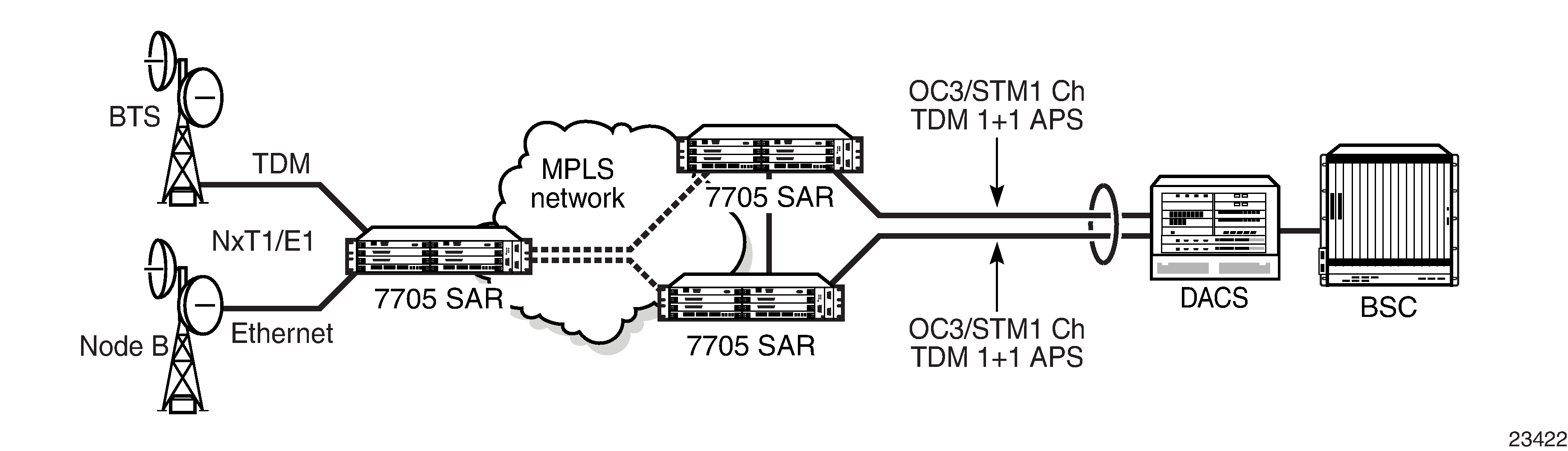
Figure: MC-APS with Physical Port, Adapter Card and Node Protection shows an MC-APS group with physical port, adapter card, and node protection. Figure: MC-APS Application shows a packet network using MC-APS.