Multilink point-to-point protocol (MLPPP) is a method of splitting, recombining, and sequencing packets across multiple logical data links. MLPPP is defined in the IETF RFC 1990, The PPP Multilink Protocol (MP).
MLPPP allows multiple PPP links to be bundled together, providing a single logical connection between two routers. Data can be distributed across the multiple links within a bundle to achieve high bandwidth. As well, MLPPP allows for a single frame to be fragmented and transmitted across multiple links. This capability allows for lower latency and also for a higher maximum receive unit (MRU).
Multilink protocol is negotiated during the initial LCP option negotiations of a standard PPP session. A system indicates to its peer that it is willing to perform MLPPP by sending the MP option as part of the initial LCP option negotiation.
The system indicates the following capabilities.
The system offering the option is capable of combining multiple physical links into one logical link.
The system is capable of receiving upper layer protocol data units (PDUs) that are fragmented using the MP header and then reassembling the fragments back into the original PDU for processing.
The system is capable of receiving PDUs of size N octets, where N is specified as part of the option, even if N is larger than the maximum receive unit (MRU) for a single physical link.
Once MLPPP has been successfully negotiated, the sending system is free to send PDUs encapsulated and/or fragmented with the MP header.
MP introduces a new protocol type with a protocol ID (PID) of 0x003d. Figure: MLPPP 24-bit Fragment Format and Figure: MLPPP 12-bit Fragment Format show the MLPPP fragment frame structure. Framing to indicate the beginning and end of the encapsulation is the same as that used by PPP and described in RFC 1662, PPP in HDLC-like Framing.
MP frames use the same HDLC address and control pair value as PPP: Address – 0xFF and Control – 0x03. The 2-octet protocol field is also structured the same way as in PPP encapsulation.
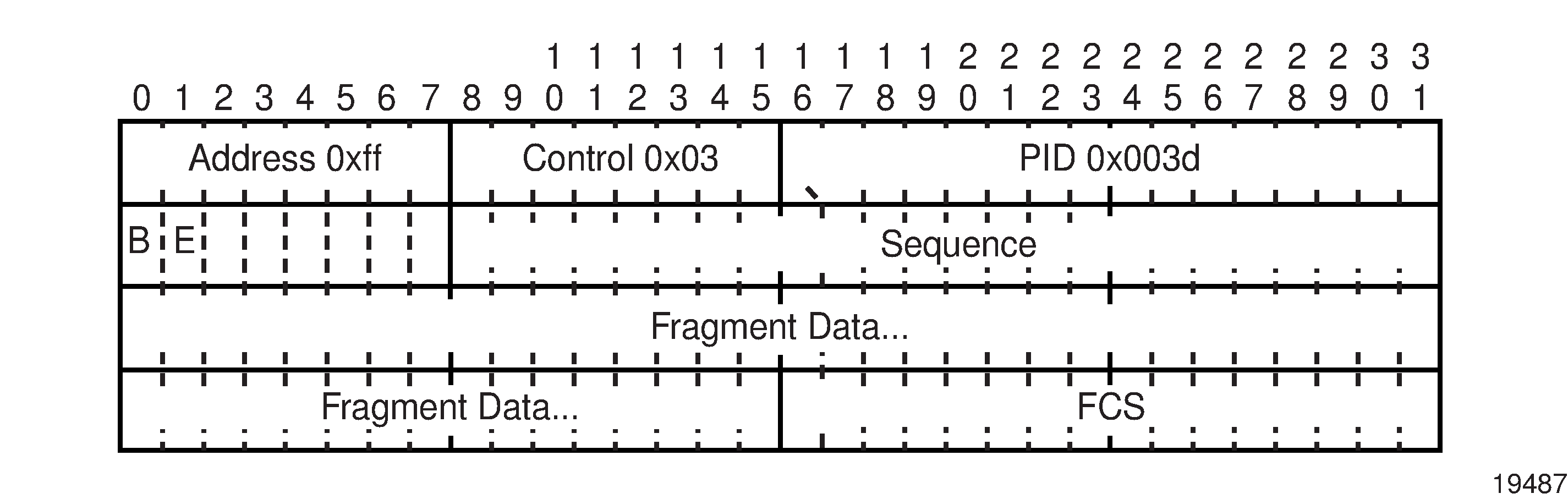
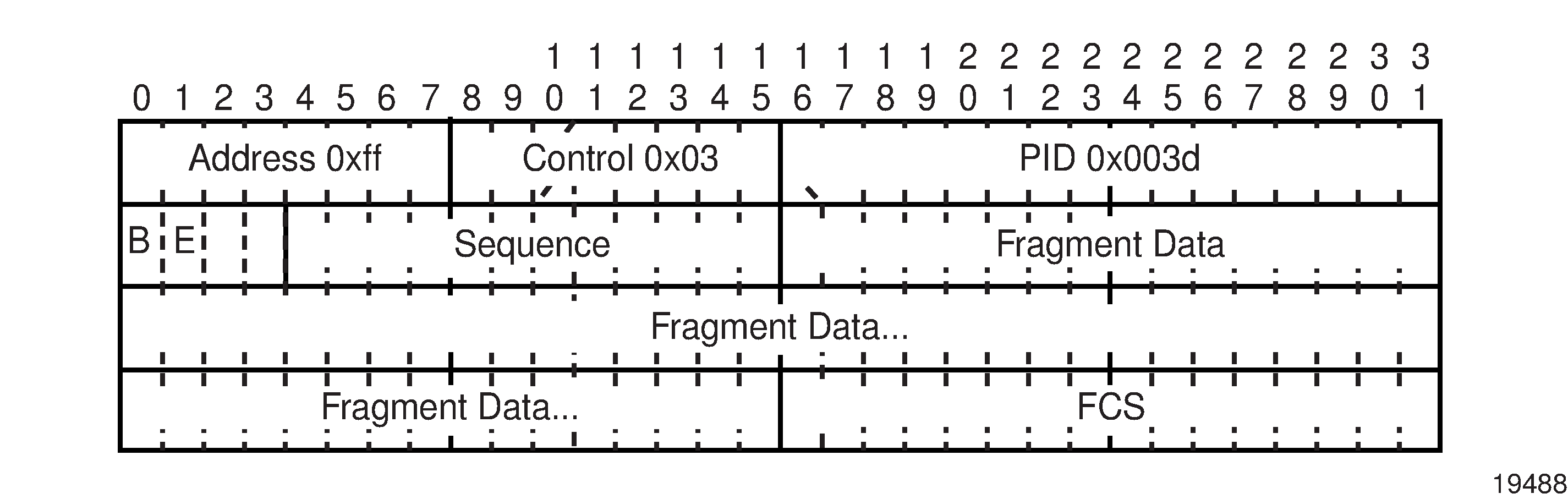
The required and default format for MP is the 24-bit format. During the LCP state, the 12-bit format can be negotiated. The 7705 SAR is capable of supporting and negotiating the alternate 12-bit frame format.
The maximum differential delay supported for MLPPP is 25 ms.