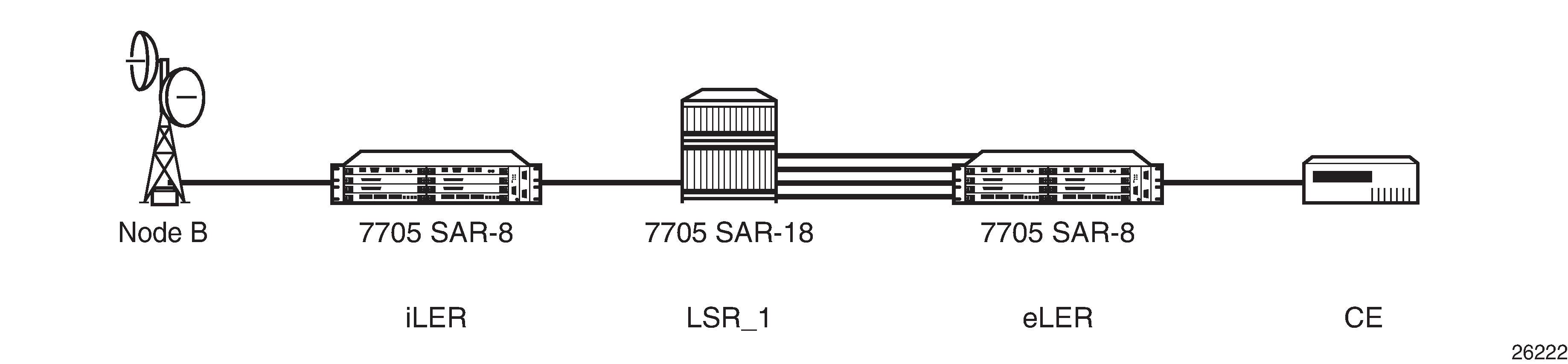
Figure: Entropy Label and Load Balancing illustrates the use of entropy labels at the service level.
The iLER has entropy label enabled under an applicable service context and the eLER has entropy label capability enabled. The iLER inserts the ELI and the EL into the label stack. The entropy label value is based on the service ID for point-to-point Layer 2 services.
At the LSR, if hashing is enabled, the LSR recognizes the ELI and uses the entropy label value as the hash result. If the entropy-label command had been disabled at the iLER, the LSR would not find the ELI and would default to hashing based on the label stack, if applicable.
At the ingress LER:
config>service>cpipe>spoke-sdp>entropy-label
config>service>epipe>spoke-sdp>entropy-label
config>service>ipipe>spoke-sdp>entropy-label
config>service>vpls>spoke-sdp>entropy-label
config>service>vpls>mesh-sdp>entropy-label
config>service>vprn>entropy-label
config>service>vprn>interface>spoke-sdp>entropy-label
config>router>isis>segment-routing>entropy-label
config>router>ospf>segment-routing>entropy-label
At the egress LER:
config>router>entropy-label
config>router>rsvp>entropy-label-capability
config>router>mpls>lsp>entropy-label
config>router>isis>entropy-label>override-tunnel-elc
config>router>ospf>entropy-label>override-tunnel-elc
The per-service-hashing command and the l4-load-balancing, teid-load-balancing, and spi-load-balancing commands are mutually exclusive.
For IP traffic, use the l4-load-balancing command. For IP traffic with mobile payload, use the teid-load-balancing and/or the spi-load-balancing command.