The 7705 SAR does not support CSPF path computation for an SR-TE LSP and uses hop-to-label translation to compute the path. The ingress LER does not monitor network events that affect the reachability of the adjacency SID or node SID used in the label stack of the LSP; therefore, the label stack is not updated to reflect changes in the path except when seamless BFD is used to detect path failures. As a result, it is recommended that this type of SR-TE LSP be used in the following configurations only:
empty path
path with a single node SID loose hop
path of an LSP to a directly connected router (single-hop LSP) with an adjacency SID or a node SID loose or strict hop
strict path with hops of adjacencies explicitly configured in the path and seamless BFD used to monitor the LSP
In addition, the user can configure an SR-TE LSP with a single loose hop, using the anycast SID concept to provide LSR node protection within a particular plane of the network TE topology. This is illustrated in Figure: Multi-plane TE with Node Protection. The user configures all LSRs in a plane with the same loopback interface address, which must be different from that of the system interface and the router ID of the router, and assigns them the same node SID index value. All routers must use the same SRGB.
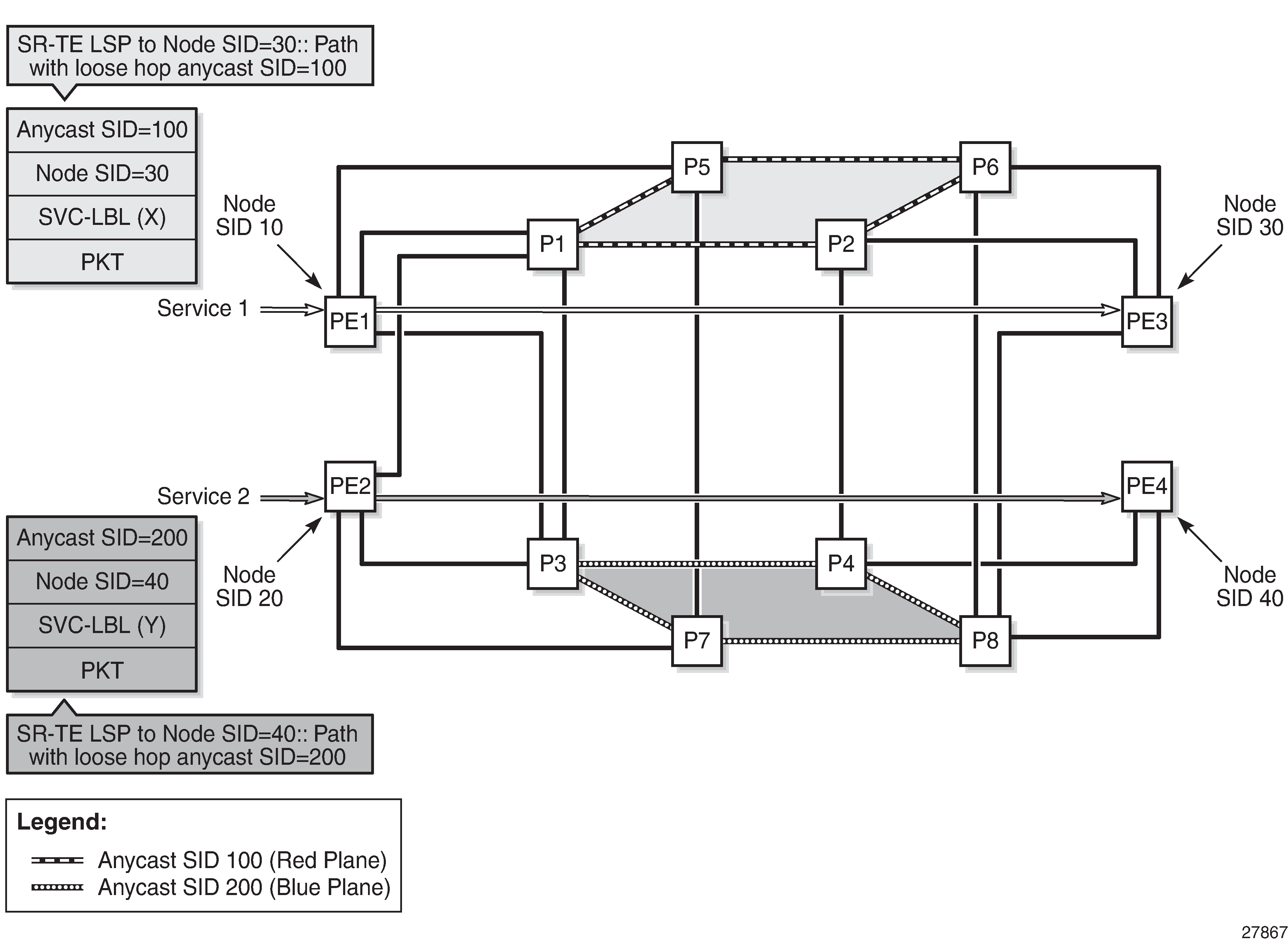
The user then configures an SR-TE LSP on an LER to a destination and adds to its path a loose hop matching the anycast loopback address. The SR-TE LSP to any destination will hop over the closest of the LSRs owning the anycast SID because the resolution of the node SID for that anycast loopback address uses the closest router. If that router fails, the resolution is updated to the next closest router owning the anycast SID without changing the label stack of the SR-TE LSP.