LSPs are unidirectional tunnels. When an LSP ping is sent, the echo request is transmitted via the tunnel and the echo response is transmitted as an IP packet to the source. Similarly, for a p2mp-lsp-ping, on the root, the echo request is transmitted via the mLDP point-to-multipoint tunnel to all leafs and the leafs use the IP packet to respond to the root.
The echo request for mLDP is generated carrying a root Target FEC Stack TLV (see Figure: ECHO Request Target FEC Stack TLV), which is used to identify the multicast point-to-multipoint LSP under test at the leaf. The Target FEC Stack TLV must carry an mLDP point-to-multipoint FEC Stack Sub-TLV from RFC 6388 or RFC 6512.
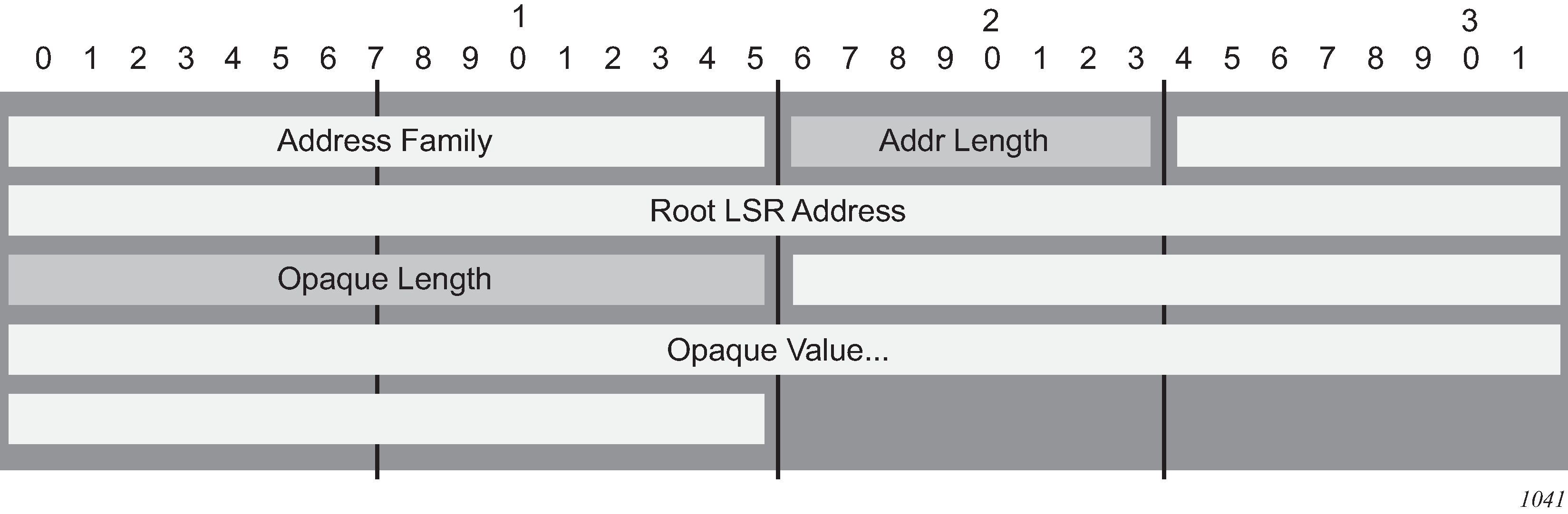
The same concept applies to inter-AS and non-segmented mLDP. The leafs in the remote AS should be able to resolve the root via GRT routing. This is possible for inter-AS Option C where the root is usually in the leaf RTM, which is a next-hop ASBR.
OAM functionality for Option C is summarized in Table: OAM Functionality for Option C.
|
OAM Command (for mLDP) |
Leaf and Root in Same AS |
Leaf and Root in Different AS (Option C) |
|---|---|---|
|
p2mp-lsp-ping ldp |
✓ |
✓ |