Figure: 7705 SAR Ethernet OAM Endpoints illustrates the complementary use of dot3ah and dot1ag to locate points of failure along a route from BTS to BSC. Because dot1ag and Y.1731 have similar functions, only dot1ag is discussed in order to simplify the explanation.
In Figure: 7705 SAR Ethernet OAM Endpoints, from the IP/MPLS (network) layer perspective, the 7705 SAR looks as though it is connected directly to the 7750 SR. From the Ethernet (transport) layer perspective, the route passes through many ports and nodes, where each port or node is a potential point of failure. These failure points cannot be detected using IP/MPLS OAM capabilities (that is, using ETH-CFM (dot1ag)). However, they can be detected using EFM OAM (dot3ah) capabilities.
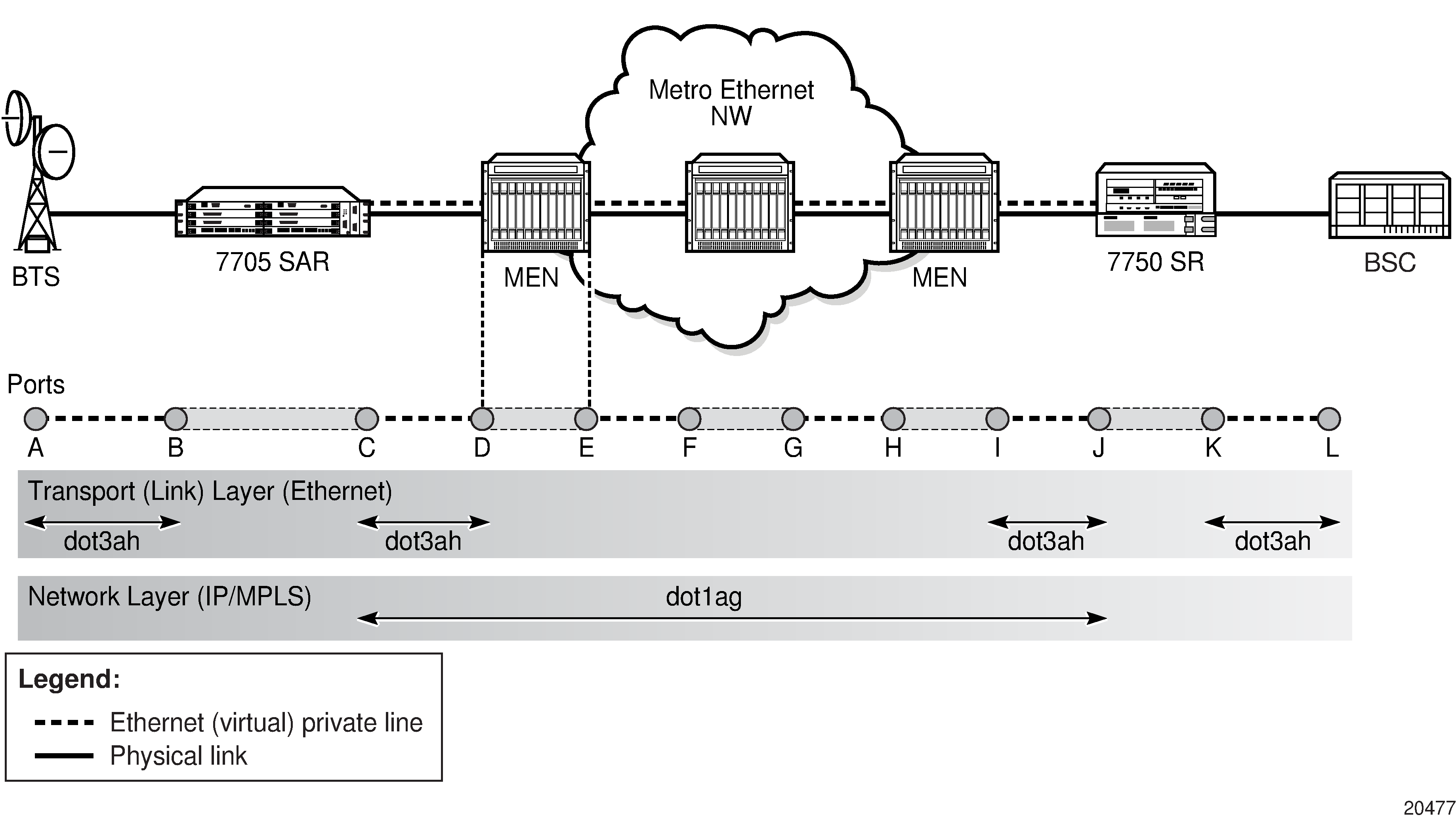
Dot3ah uses port-level loopbacks to check and verify last-mile Ethernet frame integrity, connectivity verification between ports and nodes, and so on. As shown in Figure: 7705 SAR Ethernet OAM Endpoints, dot3ah provides transport (link) layer OAM between the BTS and the 7705 SAR access port facing the BTS (ports A and B), or between the 7705 SAR network port and the MEN switch (ports C and D). Ethernet first mile (EFM) OAM allows users to test frame integrity and detect Ethernet layer failures faster than using associated heartbeat messages.
Dot1ag checks end-to-end connectivity across an Ethernet PW (across a network). Because end-to-end connectivity differs depending on the service provided and the span of the network, dot1ag can operate at several MD levels (as defined in the IEEE 802.1ag standard). For example, in Figure: 7705 SAR Ethernet OAM Endpoints, ETH-CFM (dot1ag) could be used by a MEN provider at one MD level to ensure connectivity between ports D and I (or possibly all the way to their customer's Ethernet ports, C and J). Similarly, a mobile backhaul service provider (MBSP) can use dot1ag at another MD level to ensure connectivity between ports B and K (and possibly between ports A and L).
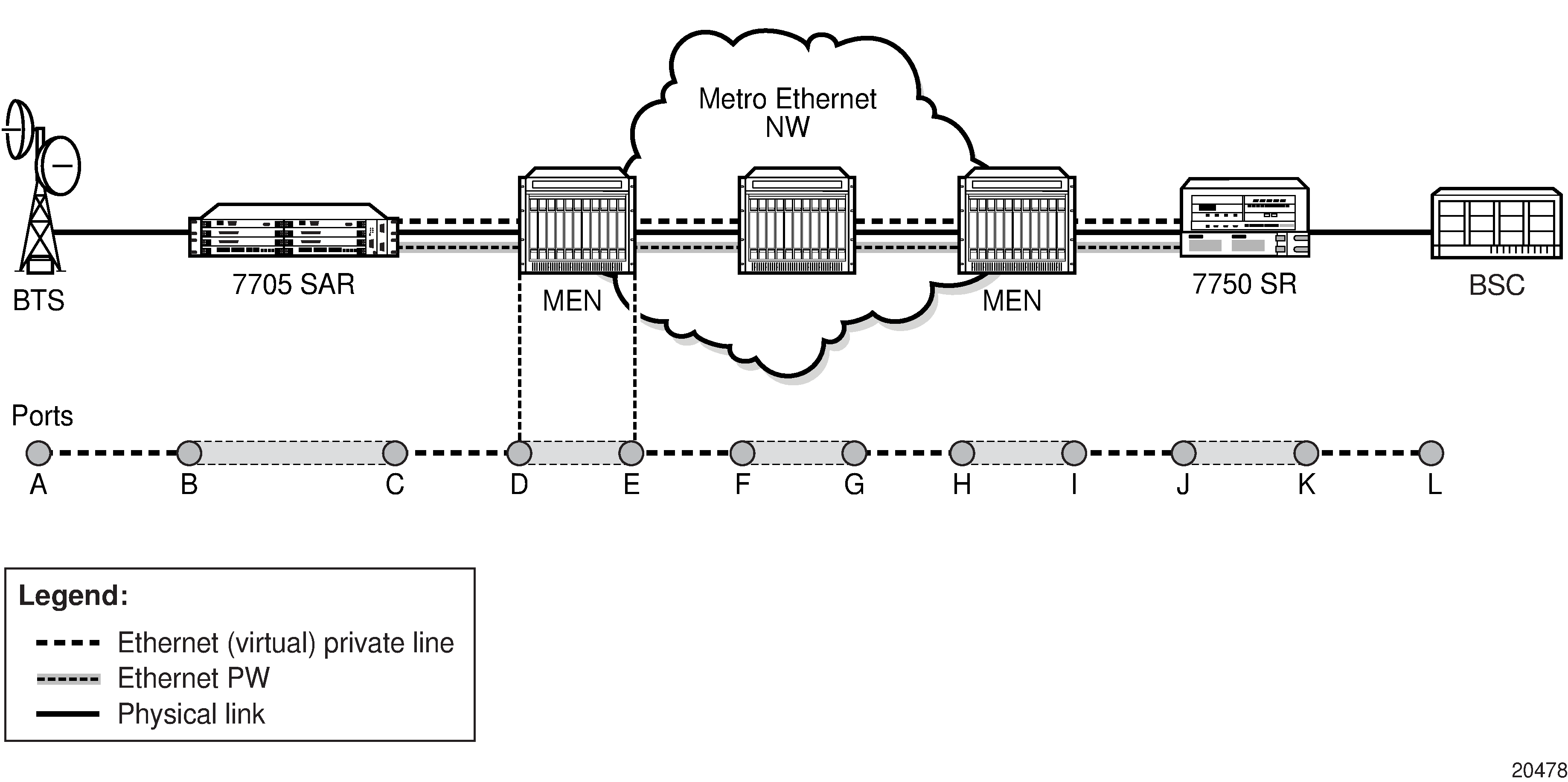
Figure: ETH-CFM (Dot1ag) Capabilities on the 7705 SAR and Figure: EFM OAM (Dot3ah) Capabilities on the 7705 SAR illustrate the use of ETH-CFM to verify connectivity across an Ethernet PW and EFM OAM to verify transport layer connectivity between two directly connected nodes.
For example, in Figure: ETH-CFM (Dot1ag) Capabilities on the 7705 SAR, an MBSP can use dot1ag between the two Ethernet spoke SDP endpoints (ports C and J, which define the Ethernet PW) to ensure connectivity. Similarly, a MEP can use dot1ag between ports D and I to ensure the health status of the Ethernet (virtual) private line.
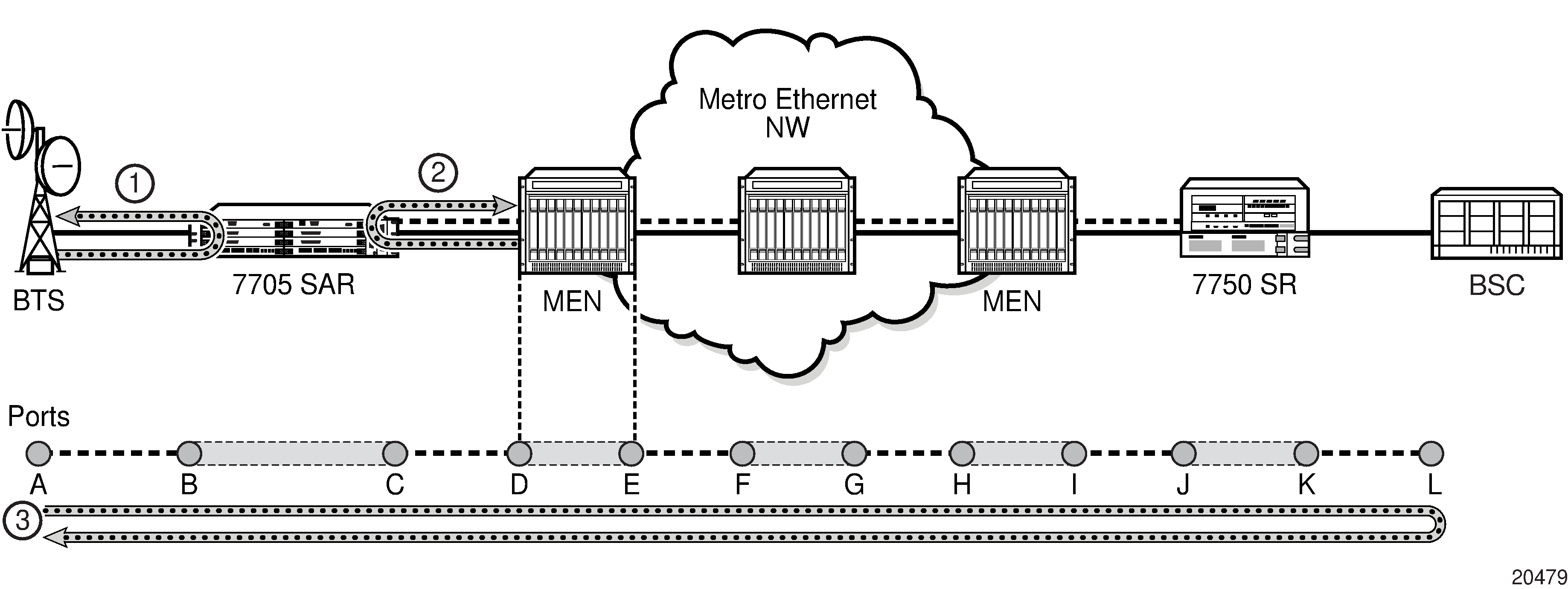
In Figure: EFM OAM (Dot3ah) Capabilities on the 7705 SAR, EFM OAM ensures transport layer connectivity between two directly connected nodes. Figure: EFM OAM (Dot3ah) Capabilities on the 7705 SAR illustrates three scenarios in which EFM can be used by the MEN provider to ensure error-free connectivity to the 7705 SAR (the cell site) via loopback tests, including:
scenario 1: EFM termination at the Ethernet access port, which includes loopback tests, heartbeat messages at the Ethernet layer with dying gasp, and termination of customer device-initiated EFM packets at the access port
scenario 2: EFM termination at the Ethernet network port, which includes network-side loopbacks
scenario 3: EFM tunneling through an Epipe service