The Two-way active measurement protocol (TWAMP) provides a standards-based method to measure the round-trip performance (including the packet loss, delay, and jitter) of IP packets that are transmitted between two devices. TWAMP, which is described in RFC 5357, uses the methodology and architecture of the One-way active measurement protocol (OWAMP) to assess the two-way transmission of IP packets.
TWAMP offers advantages for performance monitoring at Layer 3/IP because it provides functions that other performance monitoring methods, such as ICMP, lack:
timestamping for delay and jitter measurements
high-accuracy timestamping at Tx and Rx on 7705 SAR nodes for error-free results
intelligent control plane
There are four logical entities in TWAMP:
control client—initiates the TWAMP control session and negotiates the security protocols to be used and the tests to be performed with the server
server—negotiates with the control client request to establish the control session
session sender—transmits test packets to the session reflector
session reflector—transmits a packet to the session sender in response to each packet it receives
The TWAMP control and data (test) protocol operate on separate planes, as shown in Figure: TWAMP Logical Entities (RFC 5357). The TWAMP control protocol initiates test sessions and starts and stops the tests. The TWAMP test protocol exchanges test packets between TWAMP entities.
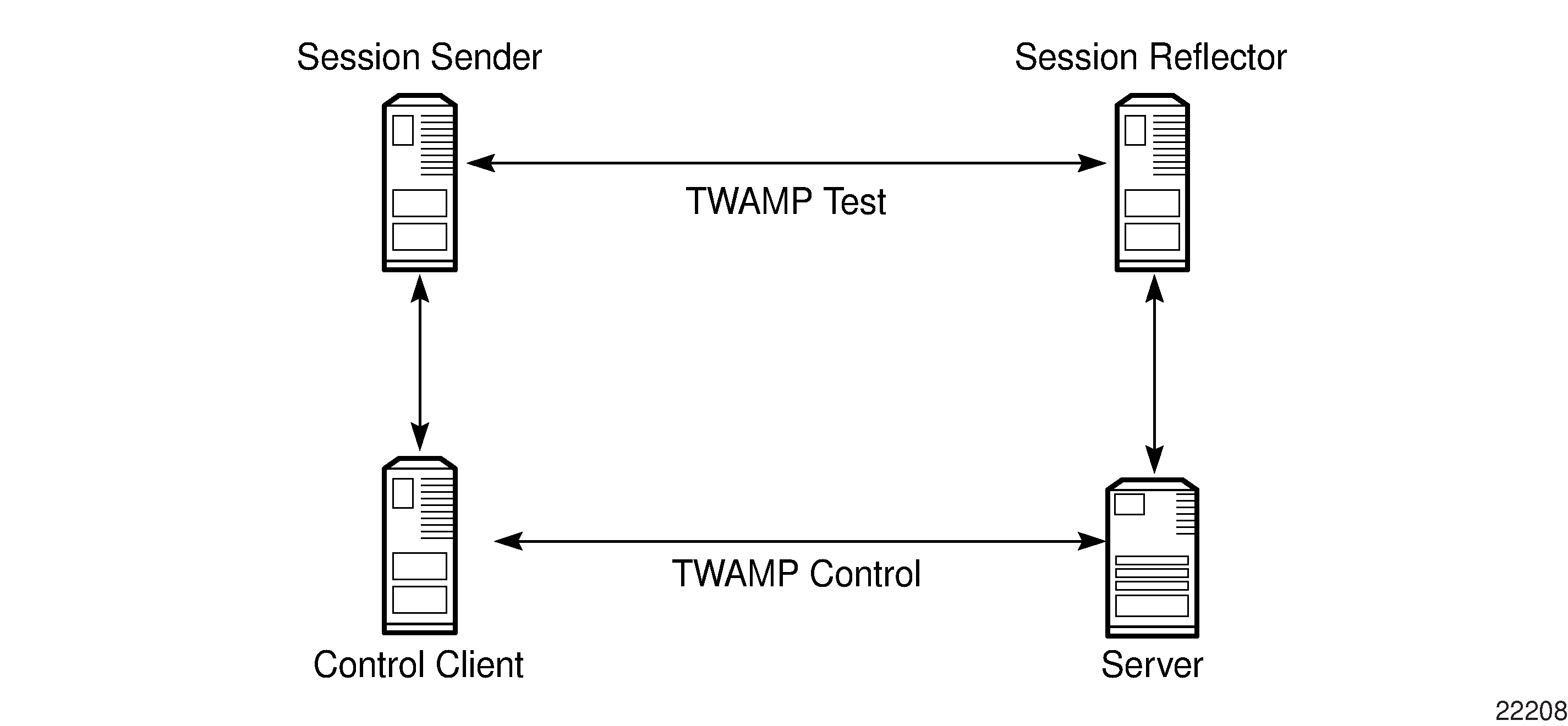
The control client and session sender are typically implemented in one physical device (also known as the client device) and the server and session reflector are typically implemented in a second physical device (also known as the server device), as shown in Figure: Typical TWAMP Implementation.

The control client and server establish a TCP connection and exchange TWAMP control messages over the connection. To start the test, the client communicates the test parameters to the server. If the server agrees to conduct the test, the test begins as soon as the client sends a start-sessions message. As part of a test, the session sender sends a stream of UDP-based test packets to the session reflector. The session reflector responds to each received packet with a UDP-based packet response. When the session sender receives the response packets from the session reflector, the information is used to calculate two-way delay, packet loss, and packet delay variation between the two devices.
The following ports are assigned for the TWAMP control protocol, as defined in RFC 5357:
862/tcp
862/udp