Service ingress QoS policies define ingress service forwarding class queues and map flows to those queues. When a service ingress QoS policy is created, it always has a default ingress traffic queue defined that cannot be deleted. These queues exist within the definition of the policy. The queues only get created when the policy is applied to a SAP.
In the simplest service ingress QoS policy, all traffic is treated as a single flow and mapped to a single queue. The required elements to define a service ingress QoS policy are:
a unique service ingress QoS policy ID
a QoS policy scope of template or exclusive
at least one default ingress forwarding class queue. The parameters that can be configured for a queue are discussed in Network and Service QoS Queue Parameters.
Optional service ingress QoS policy elements include:
additional ingress queues up to a total of eight
QoS policy match criteria to map packets to a forwarding class
Each queue can have unique queue parameters to allow individual policing and rate shaping of the flow mapped to the forwarding class. Figure: Traffic Queuing Model for Three Queues and Three Classes depicts service traffic being classified into three different forwarding class queues.
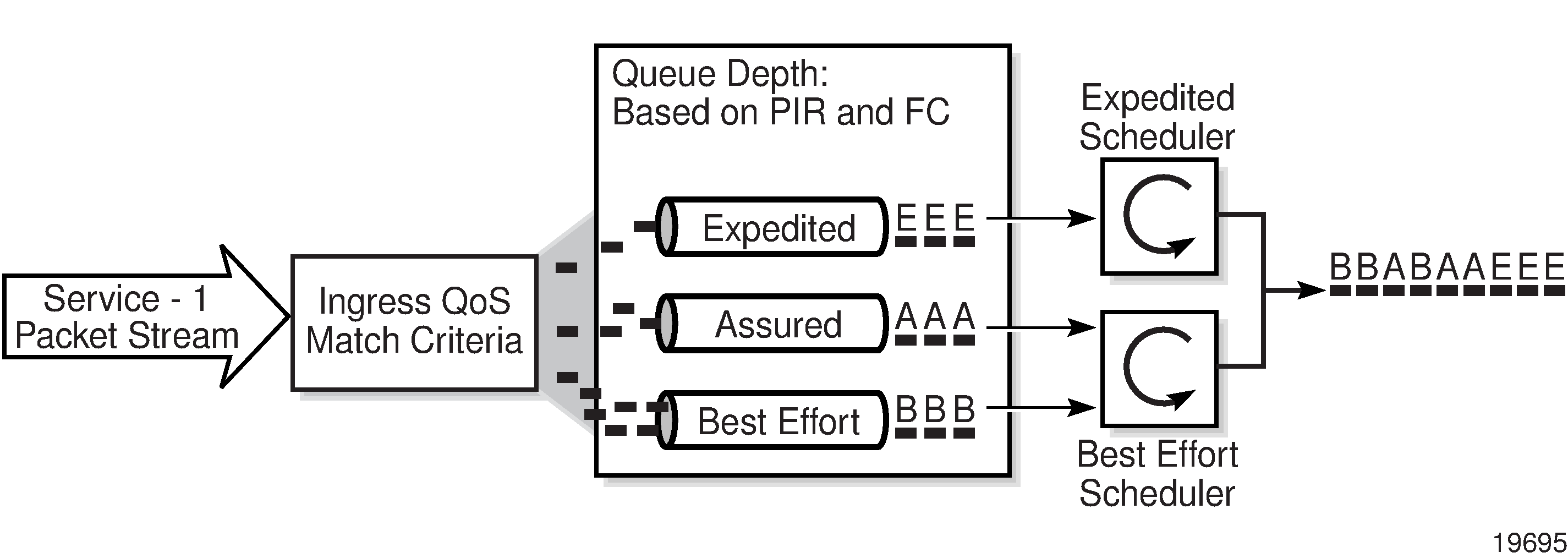
Mapping flows to forwarding classes is controlled by comparing each packet to the match criteria in the QoS policy. The ingress packet classification to forwarding class and enqueuing priority is subject to a classification hierarchy. Each type of classification rule is interpreted with a specific priority in the hierarchy.
Table: Forwarding Class and Enqueuing Priority Classification Hierarchy Based on Rule Type is given as an example for an Ethernet SAP (that is, a SAP defined over a whole Ethernet port, over a single VLAN, or over QinQ VLANs). It lists the classification rules in the order in which they are evaluated.
Rule |
Forwarding Class |
Enqueuing Priority |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
default-fc |
Set to the policy’s default FC. |
Set to the policy default |
All packets match the default rule |
dot1p dot1p-value |
Set when an fc-name exists in the policy. Otherwise, preserve from the previous match. |
Set when the priority parameter is high or low. Otherwise, preserve from the previous match. |
Each dot1p-value must be explicitly defined. Each packet can only match a single dot1p rule. For QinQ applications, the dot1p-value used (top or bottom) is specified by the match-qinq-dot1p command. |
dscp dscp-name |
Set when an fc-name exists in the policy. Otherwise, preserve from the previous match. |
Set when the priority parameter is high or low in the entry. Otherwise, preserve from the previous match. |
Each dscp-name that defines the DSCP value must be explicitly defined. Each packet can only match a single DSCP rule. |
The enqueuing priority is specified as part of the classification rule and is set to high or low. The enqueuing priority relates to the forwarding class queue’s high-priority-only allocation, where only packets with a high enqueuing priority are accepted into the queue once the queue’s depth reaches the defined threshold. See High-Priority-Only Buffers.
The mapping of ingress traffic to a forwarding class based on dot1p or DSCP bits is optional. The default service ingress policy is implicitly applied to all SAPs that do not explicitly have another service ingress policy assigned. The characteristics of the default policy are listed in Table: Default Service Ingress Policy ID 1 Definition .
Characteristic |
Item |
Definition |
|---|---|---|
Queues |
Queue 1 |
One queue for all ingress traffic:
|
Flows |
Default FC |
One flow defined for all traffic:
|