The WLAN interface AP can connect directly to the WLAN Gateway (WLAN-GW) over a Layer 2 Epipe service. For information about the WLAN-GW, see "WiFi aggregation and offload" in the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, and VSR Triple Play Service Delivery Architecture Guide.
Figure: Using an Epipe to connect a WLAN AP to a WLAN-GW illustrates the use of an Epipe service to connect the WLAN AP on a 7705 SAR-Hm to the WLAN-GW.
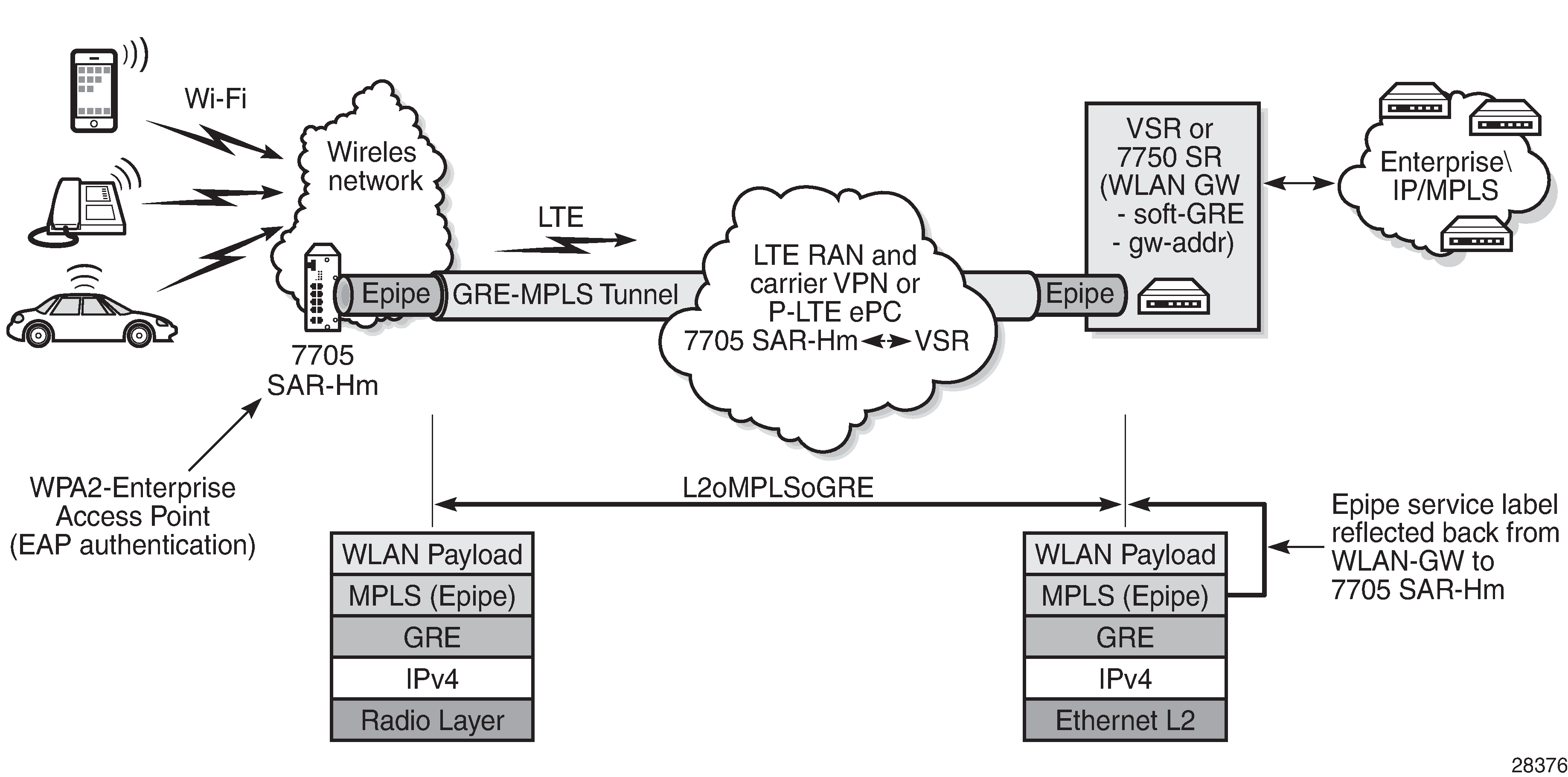
In Figure: Using an Epipe to connect a WLAN AP to a WLAN-GW , to connect to the WLAN-GW, the WLAN interface AP port ID must be configured as the L2 SAP of an Epipe service. The Epipe service is configured with a spoke SDP where the far-end address of the SDP (GRE) is configured to reach the gateway address of the WLAN-GW.
There is no signaling required to establish the Epipe service because a static ingress and egress VC label must be configured with the same value. The VC label received by the WLAN-GW from the WLAN AP node (the egress VC label) is reflected back from the WLAN-GW for traffic destined for the WLAN AP node. The 7705 SAR-Hm uses the received VC label (the ingress VC label) to determine that the received traffic is for the Epipe service associated with the WLAN AP SAP.
If the same SSID is used for multiple WLAN APs in the network (for example, an enterprise SSID for a campus-wide WLAN network), the same VC label should be used for each WLAN AP Epipe participating in the same SSID network WLAN service. Using a unique VC label per SSID allows WLAN clients connecting to the SSID to roam between WLAN APs that are broadcasting the same SSID.
The output below shows a configuration example of the SDP and Epipe SAP.
A:ALA-1>config>service# info
----------------------------------------------
...
epipe 5500 customer 5 vpn 5500 create
description "WLAN AP mySSIDname to WLAN GW"
sap 1/4/1 create
no shutdown
exit
spoke-sdp 1:123 create
description "SDP 1 binding to WLAN GW gw-address"
ingress
vc-label 5500
exit
egress
vc-label 5500
exit
exit
no shutdown
exit
The WLAN AP authenticates users before forwarding their traffic over the Epipe. For information about security parameters and supported authentication protocols, see the 7705 SAR-Hm and SAR-Hmc Interface Configuration Guide.
DHCP snooping and DHCP relay must be enabled on the WLAN AP so that attached clients can successfully acquire an IP address from the WLAN GW when they issue DHCP requests. The WLAN AP snoops for DHCP requests and modifies them to include DHCP option 82, specifically the circuit ID sub-option that includes the MAC address of the AP, the SSID of the AP, and the SSID type of either open or secured. The DHCP request is then relayed to the WLAN GW over the Epipe service. To enable DHCP snooping and DHCP relay on the WLAN port, the command config>port>wlan>access-point>dhcp>no shutdown must be executed in the CLI. For more information, see the 7705 SAR-Hm and SAR-Hmc Interface Configuration Guide.