Table 1 lists all the EVPN routes supported in 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS SR OS and their usage in EVPN-VXLAN, EVPN-MPLS, and PBB-EVPN.
| EVPN route | Usage | EVPN-VXLAN | EVPN-MPLS | PBB-EVPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Type 1 - Ethernet Auto-Discovery route (A-D) |
Mass-withdraw, ESI labels, Aliasing |
Y |
Y |
— |
|
Type 2 - MAC/IP Advertisement route |
MAC/IP advertisement, IP advertisement for ARP resolution |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Type 3 - Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag route |
Flooding tree setup (BUM flooding) |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Type 4 - ES route |
ES discovery and DF election |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Type 5 - IP Prefix advertisement route |
IP Routing |
Y |
Y |
— |
|
Type 6 - Selective Multicast Ethernet Tag route |
Signal interest on a multicast group |
Y |
Y |
— |
| Type 7 - Multicast Join Synch route |
Join a multicast group on a multihomed ES |
Y |
Y |
— |
| Type 8 - Multicast Leave Synch route |
Leave a multicast group on a multihomed ES |
Y |
Y |
— |
RFC 7432 describes the BGP-EVPN control plane for MPLS tunnels. If EVPN multihoming is not required, two route types are needed to set up a basic EVI (EVPN Instance): MAC/IP Advertisement and the Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag routes. If multihoming is required, the ES and the Auto-Discovery routes are also needed.
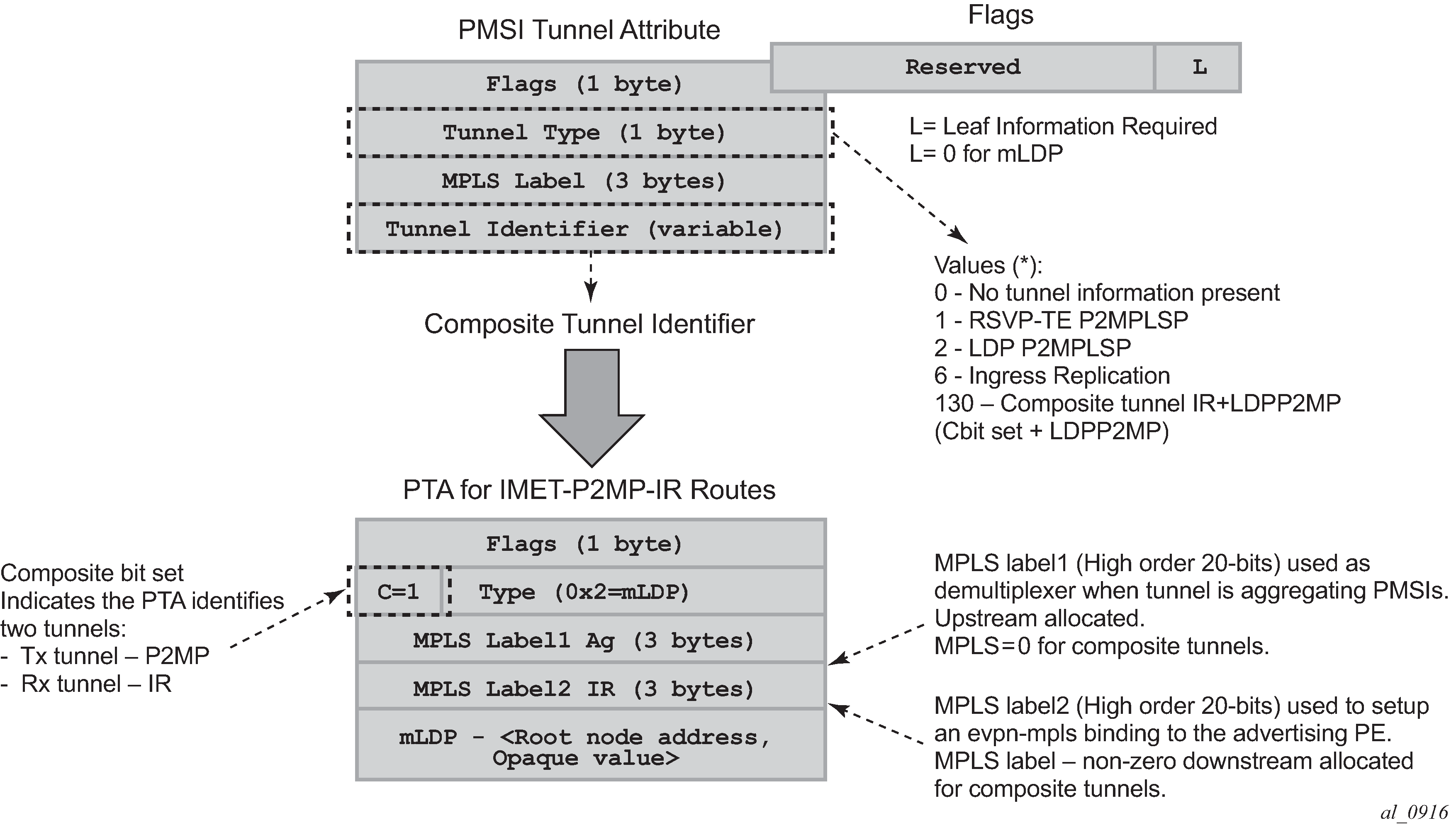
The route fields and extended communities for route types 2 and 3 are shown in Figure 1. BGP-EVPN control plane for VXLAN overlay tunnels The changes compared to their use in EVPN-VXLAN are described below.
EVPN route type 3 - inclusive multicast Ethernet tag route
As in EVPN-VXLAN, route type 3 is used for setting up the flooding tree (BUM flooding) for a specified VPLS service. The received inclusive multicast routes add entries to the VPLS flood list in the 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, and 7950 XRS. Ingress replication, p2mp mLDP, and composite tunnels are supported as tunnel types in route type 3 when BGP-EVPN MPLS is enabled
The following route values are used for EVPN-MPLS services:
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the RD of the VPLS service within the BGP context. The RD can be configured or derived from the bgp-evpn evi value.
-
Ethernet Tag ID: 0.
-
IP address length: always 32.
-
Originating router's IP address: carries an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
-
PMSI attribute: the PMSI attribute can have different formats depending on the tunnel type enabled in the service.
-
Tunnel type = Ingress replication (6)
The route is referred to as an Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag IR (IMET-IR) route and the PMSI Tunnel Attribute (PTA) fields are populated as follows:
-
Flags—Leaf not required.
-
MPLS label—Carries the MPLS label allocated for the service in the high-order 20 bits of the label field.
Unless bgp-evpn mpls ingress-replication-bum-label is configured in the service, the MPLS label used is the same as that used in the MAC/IP routes for the service.
-
Tunnel endpoint—Equal to the originating IP address.
-
-
Tunnel type=p2mp mLDP (2)
The route is referred to as an IMET-P2MP route and its PTA fields are populated as follows.
-
Flags—Leaf not required.
-
MPLS label—0.
-
Tunnel endpoint—Includes the route node address and an opaque number. This is the tunnel identifier that the leaf-nodes use to join the mLDP P2MP tree.
-
-
Tunnel type=Composite tunnel (130)
The route is referred to as an IMET-P2MP-IR route and its PTA fields are populated as follows.
-
Flags—Leaf not required.
-
MPLS label 1— 0.
-
Tunnel endpoint identifier includes the following:
MPLS label2—Non-zero, downstream allocated label (like any other IR label). The leaf-nodes use the label to set up an EVPN-MPLS destination to the root and add it to the default-multicast list.
mLDP tunnel identifier—The route node address and an opaque number. This is the tunnel identifier that the leaf-nodes use to join the mLDP P2MP tree.
-
-
IMET-P2MP-IR routes are used in EVIs with a few root nodes and a significant number of leaf-only PEs. In this scenario, a combination of P2MP and IR tunnels can be used in the network, such that the root nodes use P2MP tunnels to send broadcast, Unknown unicast, and Multicast traffic but the leaf-PE nodes use IR to send traffic to the roots. This use case is documented in IETF RFC 8317 and the main advantage it offers is the significant savings in P2MP tunnels that the PE/P routers in the EVI need to handle (as opposed to a full mesh of P2MP tunnels among all the PEs in an EVI).
In this case, the root PEs signals a special tunnel type in the PTA, indicating that they intend to transmit BUM traffic using an mLDP P2MP tunnel but they can also receive traffic over an IR evpn-mpls binding. An IMET route with this special ‟composite” tunnel type in the PTA is called an IMET-P2MP-IR route and the encoding of its PTA is shown in Figure 1.
EVPN route type 2 - MAC/IP advertisement route
The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS router generates this route type for advertising MAC addresses (and IP addresses if proxy-ARP/proxy-ND is enabled). The router generates MAC advertisement routes for the following:
-
Learned MACs on SAPs or SDP bindings—if mac-advertisement is enabled.
-
Conditional static MACs—if mac-advertisement is enabled.
Note: The unknown-mac-route is not supported for EVPN-MPLS services.
The route type 2 generated by a router uses the following fields and values:
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the RD of the VPLS service within the BGP context. The RD can be configured or derived from the bgp-evpn evi value.
-
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): zero for MACs learned from single-homed CEs and different from zero for MACs learned from multihomed CEs.
-
Ethernet Tag ID: 0.
-
MAC address length: always 48.
-
MAC Address learned or statically configured.
-
IP address and IP address length:
-
It is the IP address associated with the MAC being advertised with a length of 32 (or 128 for IPv6).
-
In general, any MAC route without IP has IPL=0 (IP length) and the IP is omitted.
-
When received, any IPL value not equal to zero, 32, or 128 discards the route.
-
MPLS Label 1: carries the MPLS label allocated by the system to the VPLS service. The label value is encoded in the high-order 20 bits of the field and is the same label used in the routes type 3 for the same service unless bgp-evpn mpls ingress-replication-bum-label is configured in the service.
-
-
MPLS Label 2: 0.
-
The MAC mobility extended community: used for signaling the sequence number in case of MAC moves and the sticky bit in case of advertising conditional static MACs. If a MAC route is received with a MAC mobility ext-community, the sequence number and the 'sticky' bit are considered for the route selection.
When EVPN multihoming is enabled in the system, two more routes are required. Figure 2 shows the fields in routes type 1 and 4 and their associated extended communities.
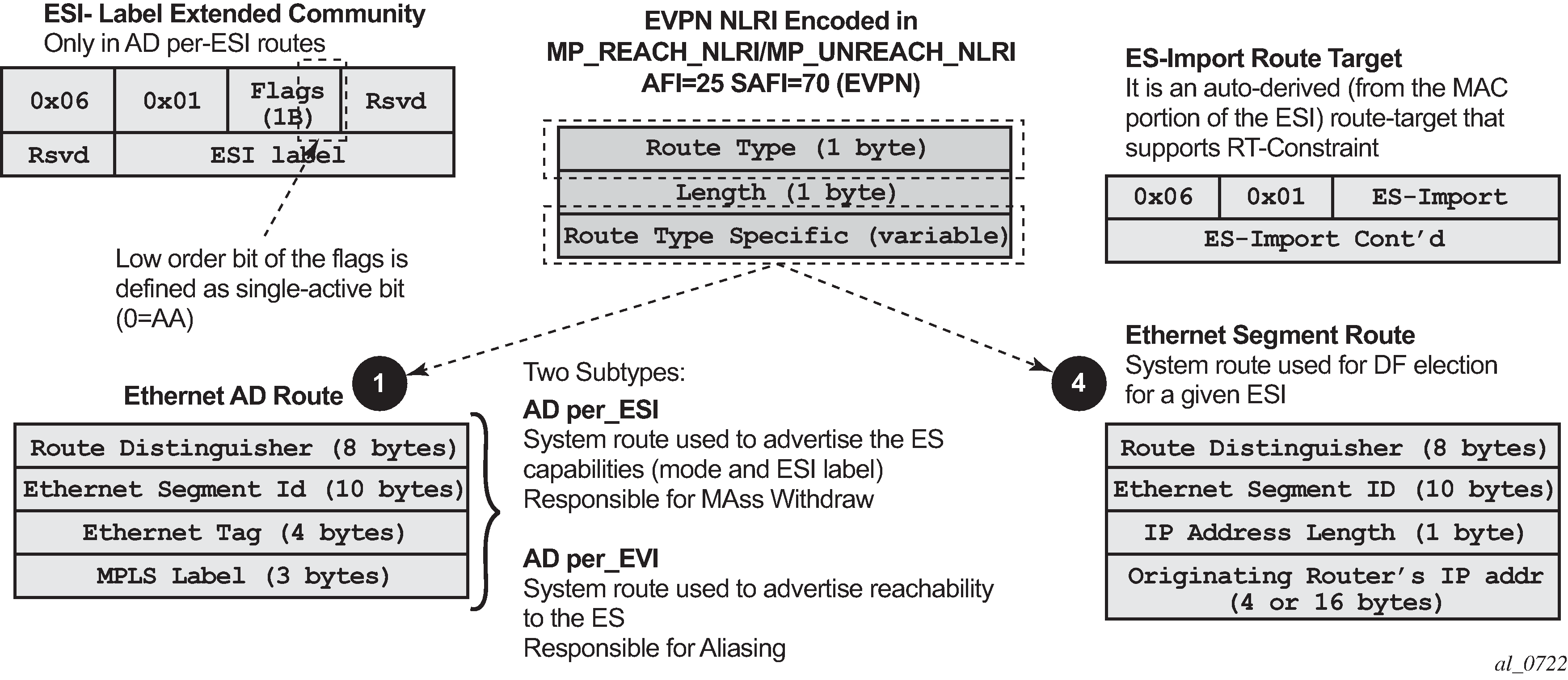
EVPN route type 1 - Ethernet auto-discovery route (AD route)
The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS router generates this route type for advertising for multihoming functions. The system can generate two types of AD routes:
-
Ethernet AD route per-ESI (Ethernet Segment ID)
-
Ethernet AD route per-EVI (EVPN Instance)
The Ethernet AD per-ESI route generated by a router uses the following fields and values:
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the system level RD or service level RD.
-
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): contains a 10-byte identifier as configured in the system for a specified ethernet-segment.
-
Ethernet Tag ID: MAX-ET (0xFFFFFFFF). This value is reserved and used only for AD routes per ESI.
-
MPLS label: 0.
-
ESI Label Extended community: includes the single-active bit (0 for all-active and 1 for single-active) and ESI label for all-active multihoming split-horizon.
-
Route target extended community: taken from the service level RT or an RT-set for the services defined on the Ethernet segment.
The system can either send a separate Ethernet AD per-ESI route per service, or a few Ethernet AD per-ESI routes aggregating the route-targets for multiple services. While both alternatives inter-operate, RFC 7432 states that the EVPN Auto-Discovery per-ES route must be sent with a set of route-targets corresponding to all the EVIs defined on the Ethernet Segment (ES). Either option can be enabled using the command: config>service>system>bgp-evpn#ad-per-es-route-target <[evi-rt ] | [evi-rt-set]> route-distinguisher ip-address [extended-evi-range]
The default option ad-per-es-route-target evi-rt configures the system to send a separate AD per-ES route per service. When enabled, the evi-rt-set option supports route aggregation: a single AD per-ES route with the associated RD (ip-address:1) and a set of EVI route targets are advertised (up to a maximum of 128). When the number of EVIs defined in the Ethernet Segment is significant (therefore the number of route-targets), the system sends more than one route. For example:
-
AD per-ES route for evi-rt-set 1 is sent with RD ip-address:1
-
AD per-ES route for evi-rt-set 2 is sent with RD ip-address:2
-
up to an AD per-ES route is sent with RD ip-address:512
The extended-evi-range option is needed for the use of evi-rt-set with a comm-val extended range of 1 through 65535. This option is recommended when EVIs greater than 65535 are configured in some services. In this case, there are more EVIs for which the route-targets must be packed in the AD per-ES routes. This command option extends the maximum number of AD per-ES routes that can be sent (since the RD now supports up to ip-address:65535) and allows many more route-targets to be included in each set.
The Ethernet AD per-EVI route generated by a router uses the following fields and values:
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the service level RD.
-
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): contains a 10-byte identifier as configured in the system for a specified Ethernet Segment.
-
Ethernet Tag ID: 0.
-
MPLS label: encodes the unicast label allocated for the service (high-order 20 bits).
-
Route-target extended community: taken from the service level RT.
EVPN route type 4 - ES route
The router generates this route type for multihoming ES discovery and DF (Designated Forwarder) election.
-
Route Distinguisher: taken from the service level RD.
-
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): contain a 10-byte identifier as configured in the system for a specified ethernet-segment.
-
ES-import route-target community: the value is automatically derived from the MAC address portion of the ESI. This extended community is treated as a route-target and is supported by RT-constraint (route-target BGP family).
EVPN route type 5 - IP prefix route
IP Prefix Routes are also supported for MPLS tunnels. The route fields for route type 5 are shown in Figure 3. The 7750 SR, 7450 ESS, or 7950 XRS router generateS this route type for advertising IP prefixes in EVPN using the same fields that are described in section BGP-EVPN control plane for VXLAN overlay tunnels, with the following exceptions:
-
MPLS Label—Carries the MPLS label allocated for the service
-
This route IS sent with the RFC 5512 tunnel encapsulation extended community with the tunnel type value set to MPLS
RFC 5512 - BGP tunnel encapsulation extended community
The following routes are sent with the RFC 5512 BGP Encapsulation Extended Community: MAC/IP, Inclusive Multicast Ethernet Tag, and AD per-EVI routes. ES and AD per-ESI routes are not sent with this Extended Community.
The router processes the following BGP Tunnel Encapsulation tunnel values registered by IANA for RFC 5512:
-
VXLAN encapsulation: 8.
-
MPLS encapsulation: 10.
Any other tunnel value makes the route 'treat-as-withdraw'.
If the encapsulation value is MPLS, the BGP validates the high-order 20-bits of the label field, ignoring the low-order 4 bits. If the encapsulation is VXLAN, the BGP takes the entire 24-bit value encoded in the MPLS label field as the VNI.
If the encapsulation extended community (as defined in RFC 5512) is not present in a received route, BGP treats the route as an MPLS or VXLAN-based configuration of the config>router>bgp>neighbor# def-recv-evpn-encap [mpls | vxlan] command. The command is also available at the bgp and group levels.